Liking Product Landscape: Going Deeper into Understanding Consumers’ Hedonic Evaluations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Results of Experiment 1
3.2. Results of Experiment 2
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lipan, L.; Cano-Lamadrid, M.; Corell, M.; Sendra, E.; Hérnandez, F.; Stan, L.; Vodnar, D.C.; Vázquez-Araújo, L.; Carbonell-Barrachina, Á.A. Sensory profile and acceptability of HydroSOStainable almonds. Foods 2019, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjos, O.; Frazáo, D.; Caldeira, I. Physicochemical and Sensorial Characterization of Honey Spirits. Foods 2017, 6, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hough, G.; Sánchez, R. Descriptive analysis and external preference mapping of powdered chocolate milk. Food Qual. Prefer. 1998, 9, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, C.; Guinard, J.X. Internal and external quality mapping as a new approach to the evaluation of sensory quality-A case study with olive oil. J. Sens. Stud. 2012, 27, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, E. Analysis of Sensory Properties in Foods: A Special Issue. Foods 2019, 8, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worch, T.; Lệ, S.; Punter, P. How reliable are the consumers? Comparison of sensory profiles from consumers and experts. Food Qual. Prefer. 2010, 21, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothman, L.; Parker, M.J. Structure and Use of Just-About-Right Scales; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Popper, R. Use of just-about-right scales in consumer research. In Novel Techniques in Sensory Characterization and Consumer Profiling; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 150–169. [Google Scholar]
- Gacula, M., Jr.; Rutenbeck, S.; Pollack, L.; Resurreccion, A.V.; Moskowitz, H.R. The Just-About-Right intensity scale: Functional analyses and relation to hedonics. J. Sens. Stud. 2007, 22, 194–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Hayes, J.E.; Ziegler, G.R. Just-about-right and ideal scaling provide similar insights into the influence of sensory attributes on liking. Food Qual. Prefer. 2014, 37, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gere, A.; Sipos, L.; Héberger, K. Generalized Pairwise Correlation and method comparison: Impact assessment for JAR attributes on overall liking. Food Qual. Prefer. 2015, 43, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conley, C. Appendix A: Graphical Data Display; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Delwiche, J. Appendix K: Thurstonian Ideal Point Modeling; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Scharaidt, M. Appendix L: Penalty Analysis or Mean Drop Analysis; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Templeton, L. Appendix R: Chi-Squere; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Takkunen, A. Appendix T: Correlation; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Herskovic, J.E. Appendix U: Regression; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, R.; Meullenet, J.F. Appendix W: Application of JAR Data to Preference Mapping Using Dummy Variables; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Horn, E.; Ford, C. Appendix S: Biplots, Correspondence Analysis and Principal Components Analysis; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Helgesen, H.; Solheim, R.; Næs, T. Consumer preference mapping of dry fermented lamb sausages. Food Qual. Prefer. 1997, 8, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Næs, T.; Lengard, V.; Johansen, S.B.; Hersleth, M. Alternative methods for combining design variables and consumer preferences with information about attitudes and demographics in conjoint analysis. Food Qual. Prefer. 2010, 21, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helgesen, H.; Næs, T. Selection of dry fermented lamb sausages for consumer testing. Food Qual. Prefer. 1995, 6, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ares, G.; Giménez, A.; Barreiro, C.; Gámbaro, A. Use of an open-ended question to identify drivers of liking milk desserts. Comparison with preference mapping techniques. Food Qual. Prefer. 2010, 21, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhoff, K.; MacFie, H. Preference mapping in practice. In Measurement of Food Preferences; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1994; pp. 137–166. [Google Scholar]
- Costell, E.; Pastor, M.V.; Izquierdo, L.; Durán, L. Relationships between acceptatiblity and sensory attributes of peach nectars using internal preference mapping. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2000, 211, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meullenet, J.F.; Xiong, R.; Findlay, C.J. Multivariate and Probabilistic Analyses of Sensory Science Problems; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; Volume 25. [Google Scholar]
- Meullenet, J.F.; Lovely, C.; Threlfall, R.; Morris, J.; Striegler, R. An ideal point density plot method for determining and optimal sensory profile for Muscadine grape juice. Food Qual. Prefer. 2008, 19, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, J.D. Individual differences and multidimensional scaling. Multidimens. Scaling Theory Appl. Behav. Sci. Theory 1972, 1, 105–155. [Google Scholar]
- Alves, L.R.; Battochio, J.R.; Cardoso, J.M.P.; De Melo, L.L.M.M.; Da Silva, V.S.; Siqueira, A.C.P.; Bolini, H.M.A. Time-intensity profile and internal preference mapping of strawberry jam. J. Sens. Stud. 2008, 23, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ares, G.; Barrios, S.; Lareo, C.; Lema, P. Development of a sensory quality index for strawberries based on correlation between sensory data and consumer perception. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2009, 52, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rødbotten, M.; Martinsen, B.K.; Borge, G.I.; Mortvedt, H.S.; Knutsen, S.H.; Lea, P.; Næs, T. A cross-cultural study of preference for apple juice with different sugar and acid contents. Food Qual. Prefer. 2009, 20, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yackinous, C.; Wee, C.; Guinard, J.X. Internal preference mapping of hedonic ratings for Ranch salad dressings varying in fat and garlic flavor. Food Qual. Prefer. 1999, 10, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danzart, M. Quadratic model in preference mapping. In Proceedings of the 4th Sensometric Meeting, Copenhagen, Denmark, 6–8 August 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Danzart, M.; Sieffermann, J.; Delarue, J. New developments in preference mapping techniques: Finding out a consumer optimal product, its sensory profile and the key sensory attributes. In Proceedings of the 7th Sensometrics Conference, Davis, CA, USA, 28–30 July 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Faber, N.K.M.; Mojet, J.; Poelman, A.A. Simple improvement of consumer fit in external preference mapping. Food Qual. Prefer. 2003, 14, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delarue, J.; Danzart, M.; Sieffermann, J.M. Revisting the definition of preference in preference mapping studies. In Proceedings of the Kansei Engineering and Emotion Research international conference KEER 2010, Paris, France, 2–4 March 2010; pp. 1875–1881. [Google Scholar]
- Lệ, S.; Husson, F.; Pagés, J. Another Look at Sensory Data: How to “Have Your Salmon and Eat It, Too!”. Food Qual. Prefer. 2006, 17, 3–5. [Google Scholar]
- Faye, P.; Brémaud, D.; Teillet, E.; Courcoux, P.; Giboreau, A.; Nicod, H. An alternative to external preference mapping based on consumers perceptive mapping. Food Qual. Prefer. 2006, 17, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worch, T. PrefMFA, a solution taking the best of both internal and external preference mapping techniques. Food Qual. Prefer. 2013, 30, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennis, D.M. Analytic approaches to accounting for individual ideal points. IFPress 2005, 8, 2–3. [Google Scholar]
- Ennis, D.M.; Ennis, J.M. Mapping hedonic data: A process perspective. J. Sens. Stud. 2013, 28, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, B.; Ennis, D.M.; Rossi, F. Internal preference mapping and the issue of satiety. Food Qual. Prefer. 2012, 24, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worch, T.; Ennis, J.M. Investigating the single ideal assumption using Ideal Profile Method. Food Qual. Prefer. 2013, 29, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worch, T.; Lệ, S.; Punter, P.; Pagés, J. Ideal profile method (IPM): The ins and outs. Food Qual. Prefer. 2013, 28, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worch, T.; Lệ, S.; Punter, P.; Pagés, J. Assessment of the consistency of ideal profiles according to non-ideal data for IPM. Food Qual. Prefer. 2012, 24, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovely, C.; Meullenet, J.F. Comparison of preference mapping techniques for the optimization of strawberry yogurt. J. Sens. Stud. 2009, 24, 457–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, C.N.; Dominguez-Soberanes, J.; Escalona-Buendía, H.B.; Graff, M. Available online: http://github.com/ClaudiaSanchez/LikingProductLandscape (accessed on 6 October 2019).
- Schaefer, E.; Wax, J. Manual on Consumer Sensory Evaluation; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Oliphant, T.E. Python for scientific computing. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2007, 9, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thririon, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Anaconda Distribution. Available online: https://www.anaconda.com/distribution/ (accessed on 6 October 2019).
- Bishop, C.M. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hotelling, H. Analysis of a complex of statistical variables into principal components. J. Educ. Psychol. 1933, 24, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castada, H.Z.; Hanas, K.; Barringer, S.A. Swiss Cheese Flavor Variability Based on Correlations of Volatile Flavor Compounds, Descriptive Sensory Attributes and Consumer Preference. Foods 2019, 8, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraggerud, H.; Solem, S.; Abrahamsen, R.K. Quality scoring-A tool for sensory evaluation of cheese? Food Qual. Prefer. 2012, 26, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos Navarro, R.d.C.; Minim, V.P.R.; Simiqueli, A.A.; da Silva Moraes, L.E.; Gomide, A.I.; Minim, L.A. Optimized Descriptive Profile: A rapid methodology for sensory description. Food Qual. Prefer. 2012, 24, 190–200. [Google Scholar]
- Dolnicar, S. Using Cluster Analysis for Market Segmentation-Typical Misconceptions, Established Methodological Weaknesses and Some Recommendations for Improvement. Australas. J. Mark. Res. 2003, 11, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Carbonell, L.; Izquierdo, L.; Carbonell, I. Sensory analysis of Spanish mandarin juices. Selection of attributes and panel performance. Food Qual. Prefer. 2007, 18, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torri, L.; Salini, S. An itinerant sensory approach to investigate consumers’ perception and acceptability at a food exhibition. Food Res. Int. 2016, 90, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teillet, E.; Schlich, P.; Urbano, C.; Cordelle, S.; Guichard, E. Sensory methodologies and the taste of water. Food Qual. Prefer. 2010, 21, 967–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, S.; Soglia, F.; Palagano, R.; Tesini, F.; Bendini, A.; Petracci, M.; Cavani, C.; Toschi, T.G. Sensory and rapid instrumental methods as a combined tool for quality control of cooked ham. Heliyon 2016, 2, e00202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kruskal, J.B. Multidimensional scaling by optimizing goodness of fit to a nonmetric hypothesis. Psychometrika 1964, 29, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartier, R.; Rytz, A.; Lecomte, A.; Poblete, F.; Krystlik, J.; Belin, E.; Martin, N. Sorting procedure as an alternative to quantitative descriptive analysis to obtain a product sensory map. Food Qual. Prefer. 2006, 17, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblatt, M. Remarks on some nonparametric estimates of a density function. Ann. Math. Stat. 1956, 27, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacoullos, T. Estimation of a multivariate density. Ann. Inst. Stat. Math. 1966, 18, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.W. Multivariate Density Estimation: Theory, Practice and Visualization; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Smola, A.; Scholkopf, B. A tutorial on support vector regression. Statist. Comput. 2004, 14, 199–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




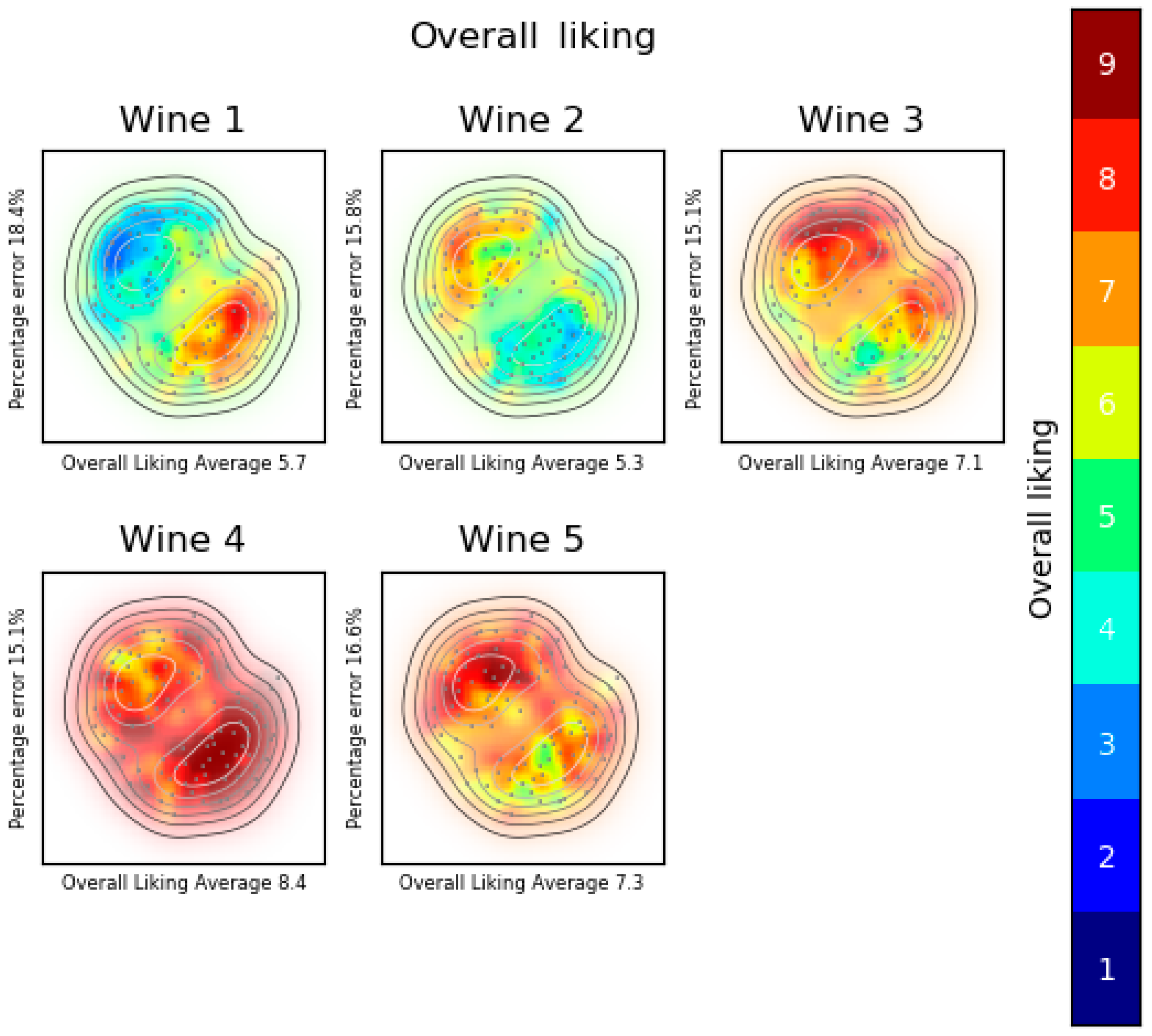



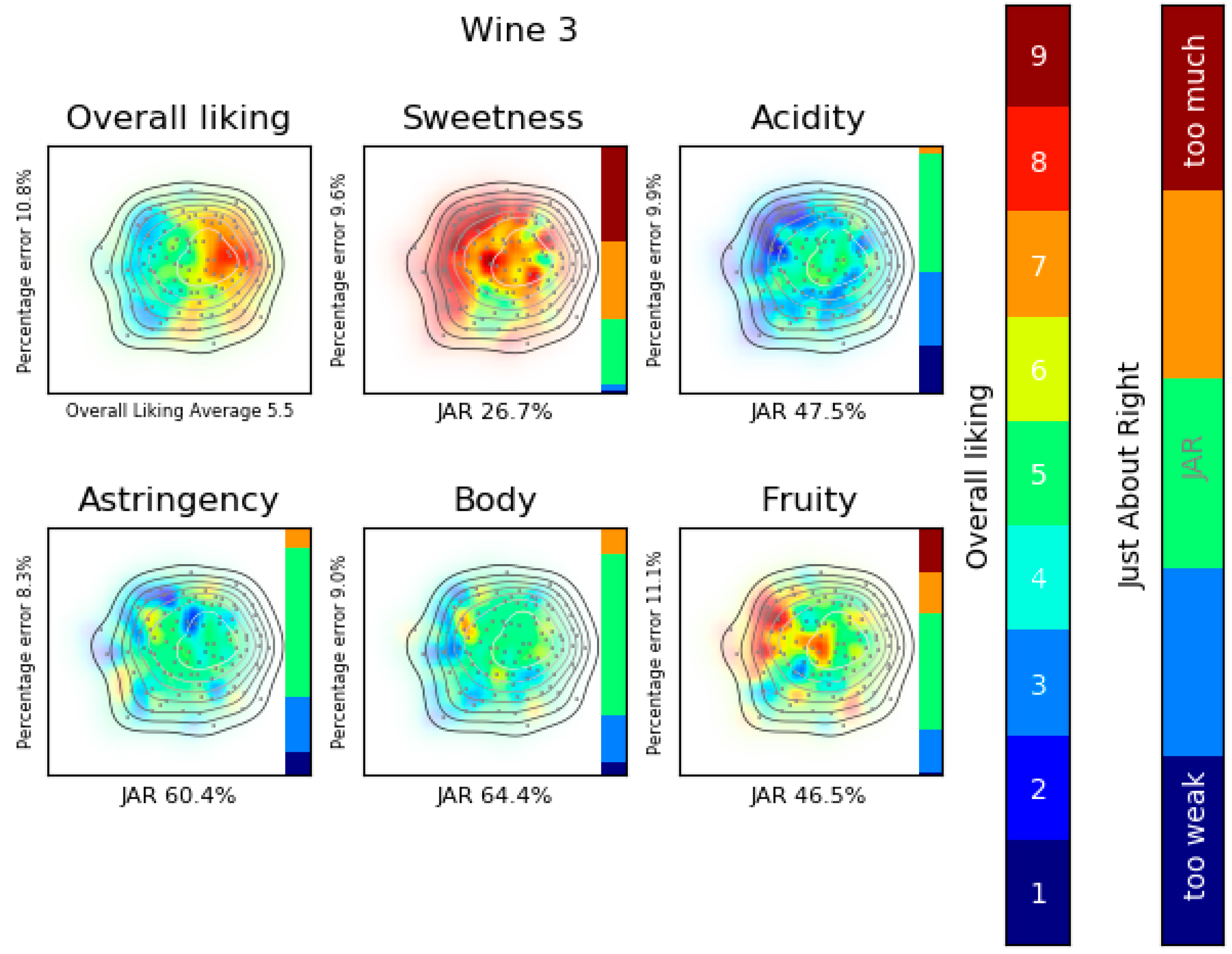
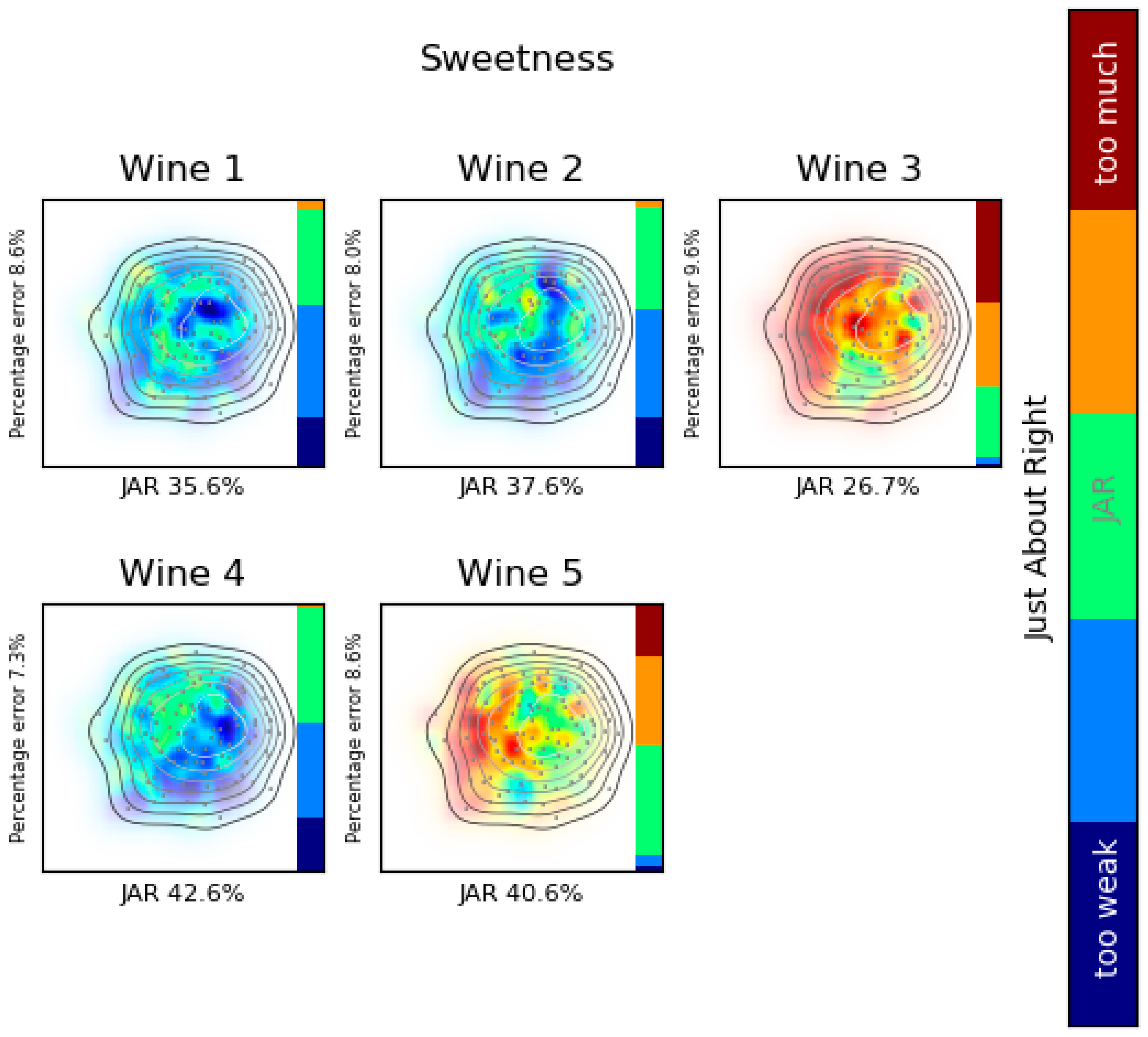
| Experiment Number | Products | Description | Number of Products | Number of Consumers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Red wines | A simulated experiment designed to have two consumers’ segments, women and men, that evaluate the products differently. | 5 | 100 |
| 2 | Red wines | A real experiment where consumers tested and evaluated different wines. | 5 | 100 |
| Wine 1 | Wine 2 | Wine 3 | Wine 4 | Wine 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Women | |||||
| Overall liking | 3 | 7 | 8 | 7 | 9 |
| Sweetness | −2 | +1 | 0 | −1 | +1 |
| Acidity | −1 | +1 | 0 | +1 | 0 |
| Astringency | +2 | 0 | +1 | −1 | 0 |
| Body | +1 | 0 | +2 | −2 | +1 |
| Fruity | −1 | +1 | −1 | 0 | +1 |
| Men | |||||
| Overall liking | 8 | 4 | 6 | 9 | 6 |
| Sweetness | 0 | +2 | +2 | 0 | +1 |
| Acidity | 0 | 0 | 0 | +1 | −1 |
| Astringency | +1 | −1 | −1 | −2 | −1 |
| Body | 0 | −1 | −1 | −2 | 0 |
| Fruity | 0 | +2 | +2 | −1 | 0 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sánchez, C.N.; Domínguez-Soberanes, J.; Escalona-Buendía, H.B.; Graff, M.; Gutiérrez, S.; Sánchez, G. Liking Product Landscape: Going Deeper into Understanding Consumers’ Hedonic Evaluations. Foods 2019, 8, 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8100461
Sánchez CN, Domínguez-Soberanes J, Escalona-Buendía HB, Graff M, Gutiérrez S, Sánchez G. Liking Product Landscape: Going Deeper into Understanding Consumers’ Hedonic Evaluations. Foods. 2019; 8(10):461. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8100461
Chicago/Turabian StyleSánchez, Claudia N., Julieta Domínguez-Soberanes, Héctor B. Escalona-Buendía, Mario Graff, Sebastián Gutiérrez, and Gabriela Sánchez. 2019. "Liking Product Landscape: Going Deeper into Understanding Consumers’ Hedonic Evaluations" Foods 8, no. 10: 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8100461
APA StyleSánchez, C. N., Domínguez-Soberanes, J., Escalona-Buendía, H. B., Graff, M., Gutiérrez, S., & Sánchez, G. (2019). Liking Product Landscape: Going Deeper into Understanding Consumers’ Hedonic Evaluations. Foods, 8(10), 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8100461








