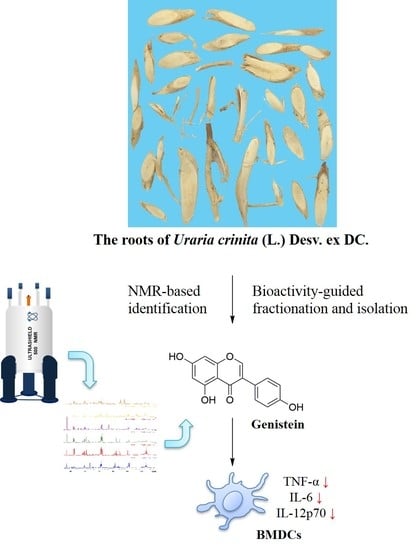
Bioactivity-Guided Fractionation and NMR-Based Identification of the Immunomodulatory Isoflavone from the Roots of Uraria crinita (L.) Desv. ex DC
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. The EtOAc-Soluble Fraction from UCME Inhibited LPS-Stimulated DC Activation
2.2. Bioactivity-Guided Fractionation and NMR-Based Identification of the EtOAc-Soluble Fraction of UCME
2.3. The Role of Genistein in Modulating LPS-Stimulated DC Activation of UCME
2.4. LPS-Stimulated DC Maturation was Impaired by Genistein at Non-Cytotoxic Concentrations
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Sample Preparation and Isolation
3.3. HPLC Conditions Used for the D-4 and D-5 Subfractions
3.4. NMR Analysis
3.5. Preparation of BMDC
3.6. Measurement of Cytokine Production
3.7. Cytotoxicity Assessment
3.8. Analysis of DC Maturation
3.9. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CCK-8 | Cell-Counting Kit-8 |
| CD | co-stimulatory molecules |
| ERK | extracellular-regulated protein kinases |
| GM-CSF | granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor |
| HSQC | heteronuclear single-quantum correlation |
| HMBC | heteronuclear multiple-bond correlation |
| IL | interleukin |
| MHC | major histocompatibility complex molecules |
| MS | mass spectrometry |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| NMR | nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| TLRs | Toll-like receptors |
References
- Liu, S.Y.; Liou, P.C.; Wang, J.Y.; Shyu, Y.T.; Hu, M.F.; Chang, Y.M.; Shieh, J.I. Production and electrophoretic analysis of medical plants in Taiwan. In Proceeding of a Symposium on Development and Utilization of Resources of Medicinal Plants in Taiwan; Tu, C.C., Lu, H.S., Liu, S.Y., Eds.; Taiwan Agricultural Research Institute: Taichung, Taiwan, 1995; pp. 149–188. [Google Scholar]
- Yen, G.C.; Lai, H.H.; Chou, H.Y. Nitric oxide-scavenging and antioxidant effects of Uraria crinita root. Food Chem. 2001, 74, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.P.; Cao, Y.; Kong, H.Y.; Zhu, W.F.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J.J.; Qiu, Y.C.; Pang, J.X. Antihyperglycemic and antihyperlipidemic effect of Uraria crinita water extract in diabetic mice induced by STZ and food. J. Med. Plants Res. 2010, 4, 370–374. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Y.W.; Lin, R.D.; Hung, H.C.; Lee, M.H. Stimulation of osteogenic activity in human osteoblast cells by edible Uraria crinita. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 5581–5588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okawa, M.; Akahoshi, R.; Kawasaki, K.; Nakano, D.; Tsuchihashi, R.; Kinjo, J.; Nohara, T. Two new triterpene glycosides in the roots of Uraria crinita. Chem Pharm Bull. 2019, 67, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.Q.; Gong, L.M.; Ruan, H.L.; Pi, H.F.; Zhang, Y.H. Studies on chemical constituents in roots of Uraria crinita. Chin. Pharm. J. 2009, 44, 1217–1220. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, M.; Young, J.W. Human dendritic cells: Potent antigen-presenting cells at the crossroads of innate and adaptive immunity. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, P.; Palucka, A.K.; Pascual, V.; Banchereau, J. Dendritic cells and cytokines in human inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2008, 19, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.K.; Yun, C.H.; Han, S.H. Induction of dendritic cell maturation and activation by a potential adjuvant, 2-hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyman, H.M.; Meyer, J.J.M. NMR-based metabolomics as a quality control tool for herbal products. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2012, 82, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van der Kooy, F.; Maltese, F.; Choi, Y.H.; Kim, H.K.; Verpoorte, R. Quality control of herbal material and phytopharmaceuticals with MS and NMR based metabolic fingerprinting. Planta Med. 2009, 75, 763–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Bharti, S.; Roy, R. Metabolite identification in NMR-based metabolomics. Curr. Metabol. 2014, 2, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussin, M.; Abdul Hamid, A.; Abas, F.; Ramli, N.S.; Jaafar, A.H.; Roowi, S.; Majid, N.A.; Pak Dek, M.S. NMR-based metabolomics profiling for radical scavenging and anti-aging properties of selected herbs. Molecules 2019, 24, 3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mediani, A.; Abas, F.; Maulidiani, M.; Khatib, A.; Tan, C.P.; Ismail, I.S.; Shaari, K.; Ismail, A. Characterization of metabolite profile in Phyllanthus niruri and correlation with bioactivity elucidated by nuclear magnetic resonance based metabolomics. Molecules 2017, 22, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontes, J.G.M.; Brasil, A.J.M.; Cruz, G.C.F.; de Souza, R.N.; Tasic, L. NMR-based metabolomics strategies: Plants, animals and humans. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 1078–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hatzakis, E.; Patterson, A.D. NMR-based metabolomics and its application in drug metabolism and cancer research. Curr. Pharmacol. Rep. 2016, 2, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhan, R.; Chen, Y. A new isoflavanone from the trunk of Horsfieldia pandurifolia. Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 30, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukayama, M.; Oda, A.; Kawamura, Y.; Nishiuchi, M.; Yamashita, K. Facile synthesis of polyhydroxycoumaronochromones with quinones: Synthesis of alkylpolyhydroxy- and alkoxycoumaronochromones from 2′-hydroxyisoflavones. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 6163–6166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.C.; Shi, J.T.; Tan, Q.W.; Chen, Q.J. Phenylpropionamides, piperidine, and phenolic derivatives from the fruit of Ailanthus altissima. Molecules 2017, 22, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Yu, J.Q. Pd(II)-catalyzed hydroxylation of arenes with 1 atm of O2 or air. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 14654–14655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.W.; Liang, Q.L.; Zhang, X.L.; Jiang, Z.; Fan, X.H.; Yue, W.; Wu, Q.N. New isocoumarin and stilbenoid derivatives from the tubers of Sparganium stoloniferum (Buch.-Ham.). Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 31, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schievano, E.; Morelato, E.; Facchin, C.; Mammi, S. Characterization of markers of botanical origin and other compounds extracted from unifloral honeys. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 1747–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Yin, C.; Cao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wu, T.; Cheng, Z. Chemical constituents from Gueldenstaedtia verna and their anti-inflammatory activity. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masilamani, M.; Wei, J.; Bhatt, S.; Paul, M.; Yakir, S.; Sampson, H.A. Soybean isoflavones regulate dendritic cell function and suppress allergic sensitization to peanut. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, 1242–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, M.; Han, H.; Zhong, C.; Geng, Q. Effects of genistein and daidzein on hippocampus neuronal cell proliferation and BDNF expression in H19-7 neural cell line. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2012, 16, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Z.; Xing, K.; Li, G.; Liu, D.; Guo, Y. Dietary genistein alleviates lipid metabolism disorder and inflammatory response in laying hens with fatty liver syndrome. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Jung, W.S.; Kim, M.E.; Lee, H.W.; Youn, H.Y.; Seon, J.K.; Lee, H.N.; Lee, J.S. Genistein inhibits proinflammatory cytokines in human mast cell activation through the inhibition of the ERK pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 34, 1669–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijsselbloem, N.; Goriely, S.; Albarani, V.; Gerlo, S.; Francoz, S.; Marine, J.C.; Goldman, M.; Haegeman, G.; Vanden Berghe, W. A critical role for p53 in the control of NF-ΚB-dependent gene expression in TLR4-stimulated dendritic cells exposed to genistein. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 5048–5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziani, V.; Scognamiglio, M.; Belli, V.; Esposito, A.; D’Abrosca, B.; Chambery, A.; Russo, R.; Panella, M.; Russo, A.; Ciardiello, F.; et al. Metabolomic approach for a rapid identification of natural products with cytotoxic activity against human colorectal cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, R.T.; Bero, J.; Beaufay, C.; Selegato, D.M.; Coqueiro, A.; Choi, Y.H.; Quetin-Leclercq, J. Identification of antiplasmodial triterpenes from Keetia species using NMR-based metabolic profiling. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.K.; Yu, Y.L.; Chen, K.C.; Chang, W.T.; Lee, M.S.; Yang, M.J.; Cheng, H.C.; Liu, C.H.; Chen Dz, C.; Chu, C.L. Kaempferol from Semen cuscutae attenuates the immune function of dendritic cells. Immunobiology 2011, 216, 1103–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.H.; Lin, S.H.; Lin, C.C.; Liu, Y.C.; Chen, C.J.; Chu, C.L.; Huang, H.C.; Lin, M.K. Inhibitory effect of clove methanolic extract and eugenol on dendritic cell functions. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 27, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Compounds | δH (mult, J in Hz) |
|---|---|
| Genistein | 13.01 (s), 8.13 (s), 7.44 (d, 8.7), 6.88–6.94 1, 6.40 (d, 2.2), 6.28 (d, 2.2) |
| p-Hydroxybenzoic acid 2 | 7.90 (d, 8.9), 6.88–6.94 1 |
| Salicylic acid | 7.88 (dd, 7.6, 1.7), 7.55 (ddd, 8.9, 7.6. 1.8), 6.88–6.94 1 |
| Vanillic acid | 7.58 (dd, 8.2, 2.0), 6.88–6.94 1, 3.89 (s) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tu, P.-C.; Chan, C.-J.; Liu, Y.-C.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Lin, M.-K.; Lee, M.-S. Bioactivity-Guided Fractionation and NMR-Based Identification of the Immunomodulatory Isoflavone from the Roots of Uraria crinita (L.) Desv. ex DC. Foods 2019, 8, 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8110543
Tu P-C, Chan C-J, Liu Y-C, Kuo Y-H, Lin M-K, Lee M-S. Bioactivity-Guided Fractionation and NMR-Based Identification of the Immunomodulatory Isoflavone from the Roots of Uraria crinita (L.) Desv. ex DC. Foods. 2019; 8(11):543. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8110543
Chicago/Turabian StyleTu, Ping-Chen, Chih-Ju Chan, Yi-Chen Liu, Yueh-Hsiung Kuo, Ming-Kuem Lin, and Meng-Shiou Lee. 2019. "Bioactivity-Guided Fractionation and NMR-Based Identification of the Immunomodulatory Isoflavone from the Roots of Uraria crinita (L.) Desv. ex DC" Foods 8, no. 11: 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8110543
APA StyleTu, P.-C., Chan, C.-J., Liu, Y.-C., Kuo, Y.-H., Lin, M.-K., & Lee, M.-S. (2019). Bioactivity-Guided Fractionation and NMR-Based Identification of the Immunomodulatory Isoflavone from the Roots of Uraria crinita (L.) Desv. ex DC. Foods, 8(11), 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8110543