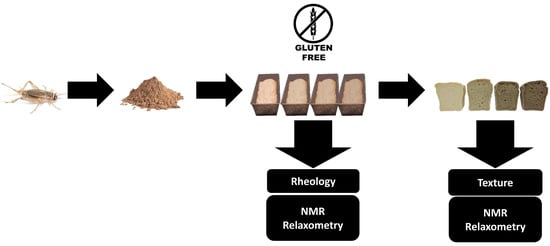
Gluten-Free Bread with Cricket Powder—Mechanical Properties and Molecular Water Dynamics in Dough and Ready Product
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Production of Bread
2.3. Rheological Properties of Dough
2.4. Texture Analysis
2.5. NMR Relaxometry
2.6. Measurements of Water Activity
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Dough Rheology
3.2. Water Behavior of Dough and Crumb
3.3. Crumb Texture
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Green, P.H.R.; Cellier, C. Celiac Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 1731–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Heel, D.A. Recent advances in coeliac disease. Gut 2006, 55, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, M.J.; Robins, G.G.; Howdle, P.D. Recent advances in coeliac disease. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2009, 25, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niewinski, M.M. Advances in Celiac Disease and Gluten-Free Diet. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2008, 108, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, P.H.R. The many faces of celiac disease: Clinical presentation of celiac disease in the adult population. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, S74–S78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lebwohl, B.; Sanders, D.S.; Green, P.H.R. Coeliac disease. Lancet 2018, 391, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindfors, K.; Ciacci, C.; Kurppa, K.; Lundin, K.E.A.; Makharia, G.K.; Mearin, M.L.; Murray, J.A.; Verdu, E.F.; Kaukinen, K. Coeliac disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2019, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zannini, E.; Arendt, E.K. Low FODMAPs and gluten-free foods for irritable bowel syndrome treatment: Lights and shadows. Food Res. Int. 2018, 110, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torbica, A.; Hadnadev, M.; Dapčević, T. Rheological, textural and sensory properties of gluten-free bread formulations based on rice and buckwheat flour. Food Hydrocoll. 2010, 24, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujral, H.S.; Rosell, C.M. Improvement of the breadmaking quality of rice flour by glucose oxidase. Food Res. Int. 2004, 37, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaridou, A.; Duta, D.; Papageorgiou, M.; Belc, N.; Biliaderis, C.G. Effects of hydrocolloids on dough rheology and bread quality parameters in gluten-free formulations. J. Food Eng. 2007, 79, 1033–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacyński, M.; Wojtasiak, R.Z.; Mildner-Szkudlarz, S. Improving the aroma of gluten-free bread. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybicka, I.; Doba, K.; Bińczak, O. Improving the sensory and nutritional value of gluten-free bread. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybicka, I.; Gliszczyńska-Świgło, A. Minerals in grain gluten-free products. The content of calcium, potassium, magnesium, sodium, copper, iron, manganese, and zinc. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2017, 59, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raheem, D.; Carrascosa, C.; Oluwole, O.B.; Nieuwland, M.; Saraiva, A.; Millán, R.; Raposo, A. Traditional consumption of and rearing edible insects in Africa, Asia and Europe. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Jung, C.; Meyer-Rochow, V.B. What Governs Selection and Acceptance of Edible Insect Species. In Edible Insects in Sustainable Food Systems; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 331–351. [Google Scholar]
- Van Huis, A. Potential of Insects as Food and Feed in Assuring Food Security. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 563–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montowska, M.; Kowalczewski, P.Ł.; Rybicka, I.; Fornal, E. Nutritional value, protein and peptide composition of edible cricket powders. Food Chem. 2019, 289, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielińska, E.; Baraniak, B.; Karaś, M.; Rybczyńska, K.; Jakubczyk, A. Selected species of edible insects as a source of nutrient composition. Food Res. Int. 2015, 77, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulma, M.; Kouřimská, L.; Plachý, V.; Božik, M.; Adámková, A.; Vrabec, V. Effect of sex on the nutritional value of house cricket, Acheta domestica L. Food Chem. 2019, 272, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska, E.; Baraniak, B.; Karaś, M. Identification of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory peptides obtained by simulated gastrointestinal digestion of three edible insects species (Gryllodes sigillatus, Tenebrio molitor, Schistocerca gragaria). Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 2542–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska, E.; Baraniak, B.; Karaś, M. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Hydrolysates and Peptide Fractions Obtained by Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Selected Heat-Treated Edible Insects. Nutrients 2017, 9, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauter, P.; Różańska, M.; Wiza, P.; Dworczak, S.; Grobelna, N.; Sarbak, P.; Kowalczewski, P.Ł. Effects of the replacement of wheat flour with cricket powder on the characteristics of muffins. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2018, 17, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smarzyński, K.; Sarbak, P.; Musiał, S.; Jeżowski, P.; Piątek, M.; Kowalczewski, P.Ł. Nutritional analysis and evaluation of the consumer acceptance of pork pâté enriched with cricket powder-preliminary study. Open Agric. 2019, 4, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda, A.; Adamczak, J.; Chełmińska, P.; Juszkiewicz, J.; Kowalczewski, P. Quality and Nutritional/Textural Properties of Durum Wheat Pasta Enriched with Cricket Powder. Foods 2019, 8, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korus, J.; Juszczak, L.; Ziobro, R.; Witczak, M.; Grzelak, K.; Sójka, M. Defatted strawberry and blackcurrant seeds as functional ingredients of gluten-free bread. J. Texture Stud. 2012, 43, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczewski, P.; Różańska, M.; Makowska, A.; Jeżowski, P.; Kubiak, P. Production of wheat bread with spray-dried potato juice: Influence on dough and bread characteristics. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2019, 25, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranowska, H.M.; Masewicz, Ł.; Kowalczewski, P.Ł.; Lewandowicz, G.; Piątek, M.; Kubiak, P. Water properties in pâtés enriched with potato juice. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2018, 244, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosio, E.; Gianferri, R.R. An analytical tool in foods characterization and traceability. In Basic NMR in Foods Characterization; Research Signpost: Kerala, India, 2009; pp. 9–37. [Google Scholar]
- Baranowska, H.M. Water Molecular Properties in Forcemeats and Finely Ground Sausages Containing Plant Fat. Food Biophys. 2011, 6, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Płowaś-Korus, I.; Masewicz, Ł.; Szwengiel, A.; Rachocki, A.; Baranowska, H.M.; Medycki, W. A novel method of recognizing liquefied honey. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 885–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masewicz, L.; Lewandowicz, J.; Le Thanh-Blicharz, J.; Kempka, M.; Baranowska, H.M. Diffusion of water in potato starch pastes. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Polysaccharides-Glycoscience, Prague, Czech Republic, 19–21 October 2016; pp. 193–195. [Google Scholar]
- Abang Zaid, D.N.; Chin, N.L.; Yusof, Y.A. A Review on Rheological Properties and Measurements of Dough and Gluten. J. Appl. Sci. 2010, 10, 2478–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, H.; Yayuan, Z.; Ling, Z.; Zhengbiao, G. Study on physicochemical characteristics of waxy potato starch in comparison with other waxy starches. Starch-Stärke 2011, 63, 754–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowicz, J.; Baranowska, H.M.; Szwengiel, A.; Le Thanh-Blicharz, J. Molecular structure vs. Functional properties of waxy and normal corn starch. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Polysaccharides-Glycoscience, Prague, Czech Republic, 19–21 October 2016; pp. 53–57. [Google Scholar]
- Makowska, A.; Baranowska, H.M.; Michniewicz, J.; Chudy, S.; Kowalczewski, P.Ł. Triticale extrudates—Changes of macrostructure, mechanical properties and molecular water dynamics during hydration. J. Cereal Sci. 2017, 74, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piątek, M.; Baranowska, H.M.; Krzywdzińska-Bartkowiak, M. Microstructure and water molecular dynamics in meat after thawing. Fleischwirtschaft 2013, 93, 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- van Nieuwenhuijzen, N.H.; Tromp, R.H.; Mitchell, J.R.; Primo-Martín, C.; Hamer, R.J.; van Vliet, T. Relations between sensorial crispness and molecular mobility of model bread crust and its main components as measured by PTA, DSC and NMR. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curti, E.; Bubici, S.; Carini, E.; Baroni, S.; Vittadini, E. Water molecular dynamics during bread staling by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 854–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassett, F. Comparison of Functional, Nutritional, and Sensory Properties of Spray-Dried and Oven-Dried Cricket (Acheta Domesticus) Powder. Master’s Thesis, Brigham Young University, Provo, UT, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Giannou, V.; Tzia, C. Frozen dough bread: Quality and textural behavior during prolonged storage—Prediction of final product characteristics. J. Food Eng. 2007, 79, 929–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.A.; Bemiller, J.N. Bread Staling: Molecular Basis and Control. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2003, 2, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, P.; Del Caro, A.; Balestra, F.; Piga, A.; Fadda, C. Bee pollen as a functional ingredient in gluten-free bread: A physical-chemical, technological and sensory approach. LWT 2018, 90, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Jubete, L.; Auty, M.; Arendt, E.K.; Gallagher, E. Baking properties and microstructure of pseudocereal flours in gluten-free bread formulations. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2010, 230, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirkesen, I.; Mert, B.; Sumnu, G.; Sahin, S. Rheological properties of gluten-free bread formulations. J. Food Eng. 2010, 96, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyango, C.; Mutungi, C.; Unbehend, G.; Lindhauer, M.G. Modification of gluten-free sorghum batter and bread using maize, potato, cassava or rice starch. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample | K * | n * | R2 | K’ | n’ | R2 | K’’ | n’’ | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RD | 51,550 | 0.347 | 0.994 | 55,460 | 0.135 | 0.965 | 12,750 | 0.121 | 0.984 |
| DCP2 | 45,830 | 0.353 | 0.994 | 38,780 | 0.146 | 0.974 | 8877 | 0.125 | 0.989 |
| DCP6 | 46,780 | 0.356 | 0.994 | 39,240 | 0.146 | 0.975 | 9570 | 0.123 | 0.983 |
| DCP10 | 41,730 | 0.401 | 0.990 | 34,780 | 0.175 | 0.982 | 9054 | 0.146 | 0.979 |
| Sample | T1 (ms) | T21 (ms) | T22 (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD | 279.9 ± 3.1 A | 5.24 ± 0.88 A | 45.46 ± 0.76 A |
| DCP2 | 251.9 ± 2.3 B | 3.16 ± 0.31 B | 43.65 ± 0.56 B |
| DCP6 | 246.6 ± 0.9 C | 2.25 ± 0.22 C | 38.66 ± 0.30 C |
| DCP10 | 223.1 ± 0.9 D | 2.17 ± 0.35 C | 32.10 ± 0.19 D |
| RB | 235.7 ± 1.5 a | 1.39 ± 0.22 c | 16.07 ± 0.41 b |
| BCP2 | 213.4 ± 0.6 b | 2.43 ± 0.15 a | 16.39 ± 0.31 b |
| BCP6 | 198.1 ± 0.8 c | 2.52 ± 0.27 a | 15.84 ± 0.32 b |
| BCP10 | 179.3 ± 0.6 d | 2.83 ± 0.25 a | 17.05 ± 0.84 a |
| Sample | aw (-) | ap (-) | VD (s−1) | Vp (s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RB | 0.925 ± 0.002 a | 0.487 ± 0.013 a | 0.024 ± 0.002 a | 0.0030 ± 0.0001 a |
| BCP2 | 0.926 ± 0.003 a | 0.503 ± 0.015 a | 0.022 ± 0.002 ab | 0.0026 ± 0.0001 b |
| BCP6 | 0.929 ± 0.006 a | 0.641 ± 0.037 a | 0.019 ± 0.004 b | 0.0025 ± 0.0006 b |
| BCP10 | 0.910 ± 0.007 a | 0.591 ± 0.016 a | 0.019 ± 0.002 b | 0.0018 ± 0.0002 c |
| Sample | Hardness (N) | Springiness (%) | Cohesiveness (-) | Chewiness (-) | Resilience (-) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RB | 37.21 ± 4.28 a | 99.3 ± 1.5 a | 0.556 ± 0.022 b | 2238 ± 286 a | 0.341 ± 0.028 b |
| BCP2 | 35.73 ± 1.53 a | 99.3 ± 0.5 a | 0.612 ± 0.068 ab | 2096 ± 277 ab | 0.400 ± 0.079 a |
| BCP6 | 25.08 ± 2.19 b | 99.5 ± 2.2 a | 0.645 ± 0.052 a | 1726 ± 293 b | 0.431 ± 0.035 a |
| BCP10 | 24.53 ± 1.79 b | 99.9 ± 1.8 a | 0.691 ± 0.062 a | 1710 ± 77 b | 0.443 ± 0.049 a |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kowalczewski, P.Ł.; Walkowiak, K.; Masewicz, Ł.; Bartczak, O.; Lewandowicz, J.; Kubiak, P.; Baranowska, H.M. Gluten-Free Bread with Cricket Powder—Mechanical Properties and Molecular Water Dynamics in Dough and Ready Product. Foods 2019, 8, 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8070240
Kowalczewski PŁ, Walkowiak K, Masewicz Ł, Bartczak O, Lewandowicz J, Kubiak P, Baranowska HM. Gluten-Free Bread with Cricket Powder—Mechanical Properties and Molecular Water Dynamics in Dough and Ready Product. Foods. 2019; 8(7):240. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8070240
Chicago/Turabian StyleKowalczewski, Przemysław Łukasz, Katarzyna Walkowiak, Łukasz Masewicz, Olga Bartczak, Jacek Lewandowicz, Piotr Kubiak, and Hanna Maria Baranowska. 2019. "Gluten-Free Bread with Cricket Powder—Mechanical Properties and Molecular Water Dynamics in Dough and Ready Product" Foods 8, no. 7: 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8070240
APA StyleKowalczewski, P. Ł., Walkowiak, K., Masewicz, Ł., Bartczak, O., Lewandowicz, J., Kubiak, P., & Baranowska, H. M. (2019). Gluten-Free Bread with Cricket Powder—Mechanical Properties and Molecular Water Dynamics in Dough and Ready Product. Foods, 8(7), 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8070240