Bioprocessed Production of Resveratrol-Enriched Rice Wine: Simultaneous Rice Wine Fermentation, Extraction, and Transformation of Piceid to Resveratrol from Polygonum cuspidatum Roots
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Rice Wine Production
2.3. Clarification and Sterilization by Ultrafiltration
2.4. Antioxidative Properties of Resveratrol-Enriched Rice Wine
2.5. Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
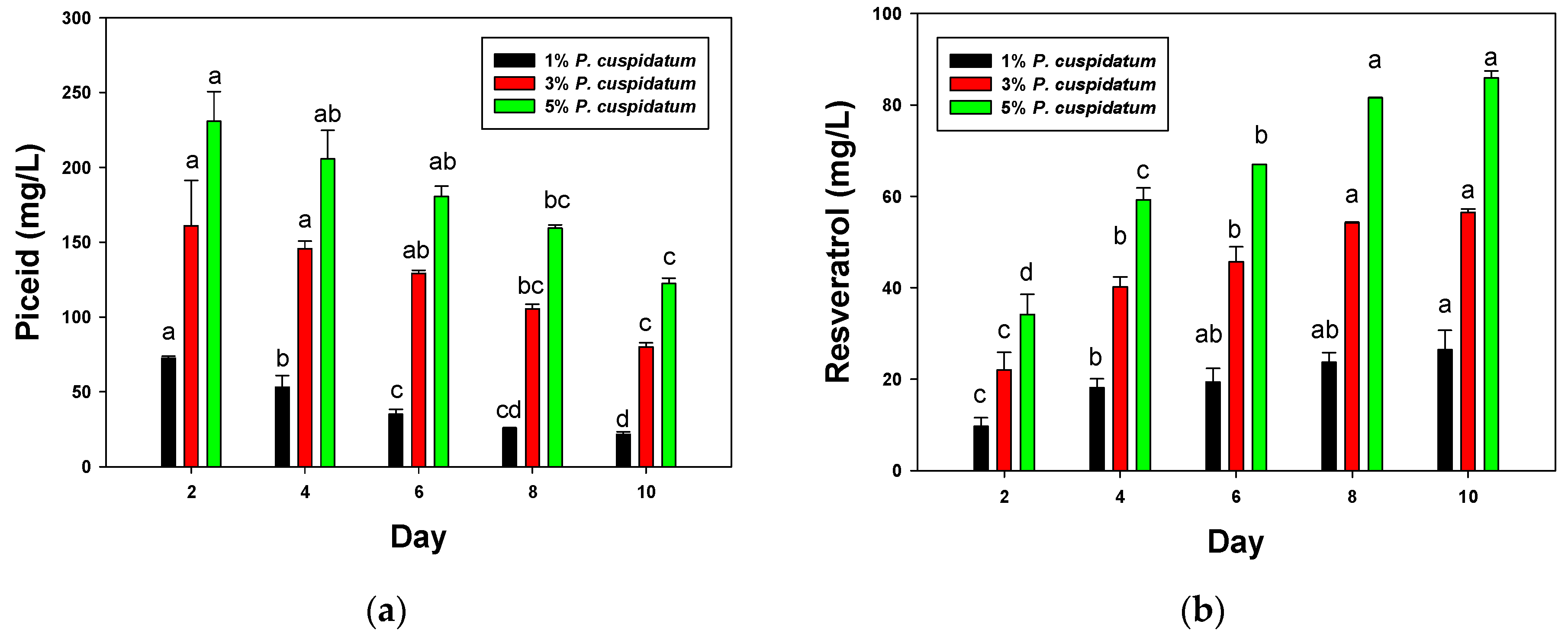
3.1. Rice Wine Fermented with P. cuspidatum
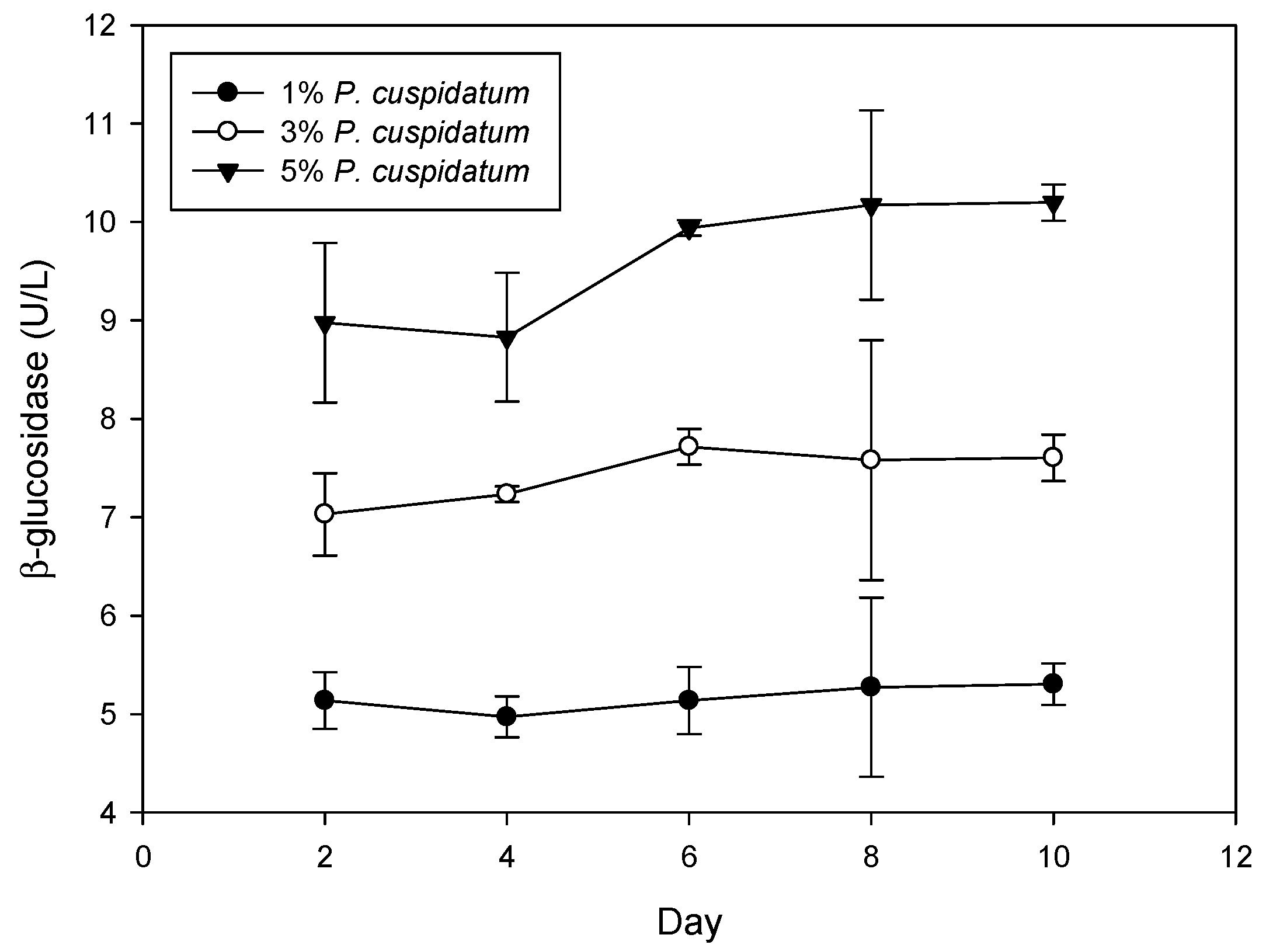
3.2. Biotransformation of Piceid to Resveratrol during Rice Wine Fermentation
3.3. Antioxidant Capacity of Resveratrol-Enriched Rice Wine
3.4. Clarification and Sterilization of Resveratrol-Enriched Rice Wine
3.5. Storage Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hasan, M.; Bae, H. An overview of stress-induced resveratrol synthesis in grapes: Perspectives for resveratrol-enriched grape products. Molecules 2017, 22, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neto, C.C. Cranberry and blueberry: Evidence for protective effects against cancer and vascular diseases. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 652–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.-S.; Wu, P.-L.; Chiou, R.Y.-Y. Peanut roots as a source of resveratrol. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 1665–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zhou, Q.-M.; Lu, Y.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Q.-L.; Zhao, M.; Su, S.-B. Resveratrol inhibits the migration and metastasis of MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer by reversing TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Molecules 2019, 24, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-C.; Chen, Y.-T.; Chiu, C.-C.; Liao, W.-T.; Liu, Y.-C.; Wang, H.-M.D. Polygonum cuspidatum extracts as bioactive antioxidaion, anti-tyrosinase, immune stimulation and anticancer agents. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2015, 119, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio-Ruiz, M.E.; Guarner-Lans, V.; Cano-Martínez, A.; Díaz-Díaz, E.; Manzano-Pech, L.; Gamas-Magaña, A.; Castrejón-Tellez, V.; Tapia-Cortina, C.; Pérez-Torres, I. Resveratrol and quercetin administration improves antioxidant defenses and reduces fatty liver in metabolic syndrome rats. Molecules 2019, 24, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Pérez, C.; Segura-Carretero, A.; del Mar Contreras, M. Phenolic compounds as natural and multifunctional anti-obesity agents: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci Nutr. 2019, 59, 1212–1229. [Google Scholar]
- Chimento, A.; De Amicis, F.; Sirianni, R.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Puoci, F.; Casaburi, I.; Saturnino, C.; Pezzi, V. Progress to improve oral bioavailability and beneficial effects of resveratrol. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.M.; Yun, H.-K.; Kwak, E.-J.; Baek, K.-H. Preparation of resveratrol-enriched grape juice from ultrasonication treated grape fruits. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2014, 21, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, M.; Kido, H.; Ohyama, K.; Ichibangase, T.; Kishikawa, N.; Ohba, Y.; Nakashima, M.; Kuroda, N.; Nakashima, K. Chemiluminescent screening of quenching effects of natural colorants against reactive oxygen species: Evaluation of grape seed, monascus, gardenia and red radish extracts as multi-functional food additives. Food Chem. 2007, 101, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katalinić, V.; Možina, S.S.; Skroza, D.; Generalić, I.; Abramovič, H.; Miloš, M.; Ljubenkov, I.; Piskernik, S.; Pezo, I.; Terpinc, P. Polyphenolic profile, antioxidant properties and antimicrobial activity of grape skin extracts of 14 Vitis vinifera varieties grown in Dalmatia (Croatia). Food Chem. 2010, 119, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavaresco, L.; Lucini, L.; Busconi, M.; Flamini, R.; De Rosso, M. Wine resveratrol: From the ground up. Nutrients 2016, 8, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arranz, S.; Chiva-Blanch, G.; Valderas-Martínez, P.; Medina-Remón, A.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M.; Estruch, R. Wine, beer, alcohol and polyphenols on cardiovascular disease and cancer. Nutrients 2012, 4, 759–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragusa, A.; Centonze, C.; Grasso, M.E.; Latronico, M.F.; Mastrangelo, P.F.; Sparascio, F.; Maffia, M. HPLC analysis of phenols in negroamaro and primitivo red wines from Salento. Foods 2019, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallithraka, S.; Arvanitoyannis, I.; El-Zajouli, A.; Kefalas, P. The application of an improved method for trans-resveratrol to determine the origin of Greek red wines. Food Chem. 2001, 75, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragusa, A.; Centonze, C.; Grasso, M.; Latronico, M.; Mastrangelo, P.; Sparascio, F.; Fanizzi, F.; Maffia, M. A comparative study of phenols in Apulian Italian Wines. Foods 2017, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosun, I.; Inkaya, A.N. Resveratrol as a health and disease benefit agent. Food Rev. Int. 2009, 26, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, C.; Kwok, S.-T.; Zhang, Q.-W.; Chan, S.-W. A review of the pharmacological effects of the dried root of Polygonum cuspidatum (Hu Zhang) and its constituents. Evid. Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 208349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.-Y.; Kuo, C.-H.; Liu, Y.-C.; Ye, L.-Y.; Chen, J.-H.; Shieh, C.-J. Ultrasonic-assisted extraction of the botanical dietary supplement resveratrol and other constituents of Polygonum cuspidatum. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1810–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wei, F.; Chen, L.-J.; Xiong, H.-R.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Luo, F.; Hou, W.; Xiao, H.; Yang, Z.-Q. In vitro and in vivo studies of the inhibitory effects of emodin isolated from Polygonum cuspidatum on Coxsakievirus B4. Molecules 2013, 18, 11842–11858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, M.-X.; Xu, Z.; Su, H.-W.; Hu, J.; Yan, Y.-J. Emodin-8-O-β-d-glucoside from Polygonum Amplexicaule D. Don var. Sinense Forb. promotes proliferation and differentiation of osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 Cells. Molecules 2011, 16, 728–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.-L.; Chen, H.-L.; Li, H.; Zhang, K.-L.; Chen, X.-Y.; Wang, X.-W.; Kong, Q.-Y.; Liu, J. Regulatory effects of emodin on NF-κB activation and inflammatory cytokine expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2005, 16, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froldi, G.; Baronchelli, F.; Marin, E.; Grison, M. Antiglycation activity and HT-29 cellular uptake of aloe-Emodin, aloin, and aloe arborescens leaf extracts. Molecules 2019, 24, 2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.-H.; Chen, B.-Y.; Liu, Y.-C.; Chang, C.-M.; Deng, T.-S.; Chen, J.-H.; Shieh, C.-J. Optimized ultrasound-assisted extraction of phenolic compounds from Polygonum cuspidatum. Molecules 2014, 19, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.-A.; Kuo, C.-H.; Chen, B.-Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.-C.; Chen, J.-H.; Shieh, C.-J. A novel enzyme-assisted ultrasonic approach for highly efficient extraction of resveratrol from Polygonum cuspidatum. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 32, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Li, D.; Yu, H.; Zhang, B.; Jin, F. Purification and characterization of piceid-β-D-glucosidase from Aspergillus oryzae. Process Biochem. 2007, 42, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.-H.; Chen, B.-Y.; Liu, Y.-C.; Chen, J.-H.; Shieh, C.-J. Production of resveratrol by piceid deglycosylation using cellulase. Catalysts 2016, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-J.; Lee, S.; Song, S.; Kim, Y.-S. Characterization of volatile components in Makgeolli, a traditional Korean rice wine, with or without pasteurization, during storage. Molecules 2013, 18, 5317–5325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, X.; Xu, Y.; Fan, W. Characterization of aroma compounds in Chinese rice wine Qu by solvent-assisted flavor evaporation and headspace solid-phase microextraction. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 2462–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.F.; Li, W.J.; Lu, J.; Cao, Y.; Fang, H.; Zou, H.J.; Hu, Z.M. Isolation and identification of representative fungi from Shaoxing rice wine wheat Qu using a polyphasic approach of culture-based and molecular-based methods. J. Inst. Brew 2007, 113, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.-H.; Shieh, C.-J.; Huang, S.-M.; Wang, H.-M.D.; Huang, C.-Y. The effect of extrusion puffing on the physicochemical properties of brown rice used for saccharification and Chinese rice wine fermentation. Food Hydrocolloids 2019, 94, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Deen, A.M.N.; Shata, H.M.A.H.; Farid, M.A.F. Improvement of β-glucosidase production by co-culture of Aspergillus niger and A. oryzae under solid state fermentation through feeding process. Ann. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, M.; Ray, R.R. A statistical approach for optimization of simultaneous production of β-glucosidase and endoglucanase by Rhizopus oryzae from solid-state fermentation of water hyacinth using central composite design. Biotechnol. Res. Int. 2011, 2011, 574983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tazawako Beer. Available online: https://www.warabi.or.jp/beer/dragon.html (accessed on 24 June 2019).
- Kuo, C.H.; Chen, C.C.; Chiang, B.H. Process characteristics of hydrolysis of chitosan in a continuous enzymatic membrane reactor. J. Food Sci. 2004, 69, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.T.; Chiang, B.H. Bioactive peptide production by hydrolysis of porcine blood proteins in a continuous enzymatic membrane reactor. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2009, 89, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conidi, C.; Destani, F.; Cassano, A. Performance of hollow fiber ultrafiltration membranes in the clarification of blood orange juice. Beverages 2015, 1, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, A.; Xu, X.; Jin, Z. Research progress on the brewing techniques of new-type rice wine. Food Chem. 2017, 215, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharjee, C.; Saxena, V.K.; Dutta, S. Analysis of fouling and juice quality in crossflow ultrafiltration of watermelon juice. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 38, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Debien, I.C.D.N.; Gomes, M.T.D.M.S.; Ongaratto, R.S.; Viotto, L.A. Ultrafiltration performance of PVDF, PES, and cellulose membranes for the treatment of coconut water (Cocos nucifera L.). Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 33, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Kuo, C.-H.; Chen, P.-W. Compressional-puffing pretreatment enhances neuroprotective effects of fucoidans from the brown seaweed Sargassum hemiphyllum on 6-hydroxydopamine-induced apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells. Molecules 2018, 23, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde, E.; Cara, C.; Moure, A.; Ruiz, E.; Castro, E.; Domínguez, H. Antioxidant activity of the phenolic compounds released by hydrothermal treatments of olive tree pruning. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.-C.; Pan, B.S.; Chang, C.-L.; Shiau, C.-Y. Low-molecular-weight peptides as related to antioxidant properties of chicken essence. J. Food Drug Anal. 2005, 13, 176–183. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, C.-H.; Lin, P.-J.; Wu, Y.-Q.; Ye, L.-Y.; Yang, D.-J.; Shieh, C.-J.; Lee, C.-K. Simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of waste textiles for ethanol production. BioResources 2014, 9, 2866–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, F.C.; Swaisgood, H.E.; Porter, D.H.; Catignani, G.L. Spectrophotometric assay using o-phthaldialdehyde for determination of proteolysis in milk and isolated milk proteins. J. Dairy Sci. 1983, 66, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, L.; Guo, Y.-X.; Dong, Y.-S.; Zhang, D.-J.; Xiu, Z.-L. Biotransformation of piceid in Polygonum cuspidatum to resveratrol by Aspergillus oryzae. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 75, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orozco, H.; Matallana, E.; Aranda, A. Two-carbon metabolites, polyphenols and vitamins influence yeast chronological life span in winemaking conditions. Microb. Cell Fact. 2012, 11, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, H.; You, H.; Park, M.; Johnston, T.; Ku, S.; Ji, G. Biocatalysis of platycoside E and platycodin D3 using fungal extracellular B-glucosidase responsible for rapid platycodin D production. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Torre, G.L.; Laganà, G.; Bellocco, E.; Vilasi, F.; Salvo, F.; Dugo, G. Improvement on enzymatic hydrolysis of resveratrol glucosides in wine. Food Chem. 2004, 85, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todaro, A.; Palmeri, R.; Barbagallo, R.N.; Pifferi, P.G.; Spagna, G. Increase of trans-resveratrol in typical Sicilian wine using β-glucosidase from various sources. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 1570–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Kuo, C.-H.; Lee, C.-H. Antibacterial and antioxidant capacities and attenuation of lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes by low-molecular-weight fucoidans prepared from compressional-puffing-pretreated sargassum crassifolium. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Sae-Lee, N.; Kerdchoechuen, O.; Laohakunjit, N. Enhancement of phenolics, resveratrol and antioxidant activity by nitrogen enrichment in cell suspension culture of Vitis vinifera. Molecules 2014, 19, 7901–7912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Liang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Q. Antioxidant potential of ethanolic extract of Polygonum cuspidatum and application in peanut oil. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 1518–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loizzo, M.R.; Sicari, V.; Tundis, R.; Leporini, M.; Falco, T.; Calabrò, V. The influence of ultrafiltration of Citrus limon L. Burm. cv Femminello comune juice on its chemical composition and antioxidant and hypoglycemic properties. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abadi, S.; Mahdi, M.; Kashani Nejad, M.; Mahunak, S.; Reza, A. Effect of ultrafiltration process on quality characteristics of sour orange juice. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 13, 119–129. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Ge, Y.; Sun, Q.; Hu, X. Clarification and sterilization of raw depectinized apple juice by ceramic ultrafiltration membranes. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006, 86, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Muñoz, R.; Barragán-Huerta, B.E.; Yáñez-Fernández, J. The use of nixtamalization waste waters clarified by ultrafiltration for production of a fraction rich in phenolic compounds. Waste Biomass Valorization 2016, 7, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar]
- Štajner, D.; Milošević, M.; Popović, B. Irradiation effects on phenolic content, lipid and protein oxidation and scavenger ability of soybean seeds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2007, 8, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRae, J.M.; Kennedy, J.A. Wine and grape tannin interactions with salivary proteins and their impact on astringency: A review of current research. Molecules 2011, 16, 2348–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorrain, B.; Ky, I.; Pechamat, L.; Teissedre, P.-L. Evolution of analysis of polyhenols from grapes, wines, and extracts. Molecules 2013, 18, 1076–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Group | DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity (%) | Reducing Power (Vitamin C Equivalent ppm) | Ferrous-Ion Chelating Activity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 5.12 ± 2.70 c | 6.93 ± 0.20 d | 69.36 ± 0.83 c |
| 1% P. cuspidatum | 29.70 ± 0.11 b | 107.29 ± 6.43 c | 73.05 ± 1.36 b |
| 3% P. cuspidatum | 30.42 ± 1.60 b | 189.63 ± 6.94 b | 79.14 ± 0.61 a |
| 5% P. cuspidatum | 37.18 ± 6.05 a | 293.92 ± 3.47 a | 80.91 ± 1.28 a |
| Item | Boiling | Ultrafiltration | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 KD | 3 KD | ||
| Ethanol (%; v/v) | 14.22 ± 0.66 | 14.40 ± 0.24 | 14.50 ± 0.92 |
| Piceid (mg/L) | 120.10 ± 6.07 | 120.67 ± 3.05 | 104.75 ± 2.51 |
| Resveratrol (mg/L) | 82.50 ± 2.52 | 84.93 ± 0.47 | 80.58 ± 0.43 |
| Clarity (%T) | 91.4 ± 0.00 | 99.35 ± 0.05 | 99.60 ± 0.05 |
| Aerobic plate count (CFU/mL) | N.D. 1 | N.D. | N.D. |
| Total acidity (g/L) | 3.83 ± 0.23 | 4.05 ± 0.00 | 4.05 ± 0.00 |
| pH | 3.66 | 3.65 | 3.65 |
| Reducing sugars (mg/mL) | 3.59 ± 0.08 | 4.09 ± 0.19 | 3.55 ± 0.21 |
| Amino acids (mg/mL) | 1.11 ± 0.03 | 1.04 ± 0.00 | 1.05 ± 0.02 |
| Treat | No. of Weeks | Ethanol (%) | Piceid (mg/L) | Resveratrol (mg/L) | Clarity (%T) | APC (CFU/mL) | Total Acidity (g/L) | pH | Reducing Sugars (mg/mL) | Amino Acids (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boiling | 1 | 14.8 ± 1.9 a | 120.9 ± 0.9 a | 84.1 ± 2.6 a | 89.8 ± 0.1 b | N.D.1 | 3.38 ± 0.2 a | 3.60 | 3.7 ± 0.2 b | 1.55 ± 0.02 d |
| 2 | 14.8 ± 0.5 a | 117.9 ± 8.2 a | 85.8 ± 4.1 a | 91.0 ± 0.0 a | N.D. | 4.05 ± 0.0 a | 3.69 | 4.1 ± 0.1 a | 1.97 ± 0.01 a | |
| 3 | 14.6 ± 0.0 a | 113.2 ± 9.3 a | 79.1 ± 1.3 a | 88.6 ± 0.1 c | N.D. | 4.05 ± 0.0 a | 3.60 | 4.0 ± 0.1 a | 1.75 ± 0.01 b | |
| 4 | 14.2 ± 0.3 a | 113.4 ± 1.0 a | 80.0 ± 2.1 a | 90.0 ± 0.0 b | N.D. | 4.73 ± 0.7 a | 3.60 | 4.0 ± 0.1 ab | 1.67 ± 0.01 c | |
| UF-10K | 1 | 14.1 ± 0.7 a | 120.4 ± 8.0 a | 83.9 ± 0.8 a | 99.3 ± 0.0 a | N.D. | 3.60 ± 0.0 c | 3.60 | 4.3 ± 0.2 a | 1.48 ± 0.02 d |
| 2 | 14.2 ± 0.7 a | 122.8 ± 6.5 a | 85.2 ± 3.7 a | 98.7 ± 0.1 c | N.D. | 4.05 ± 0.0 b | 3.62 | 4.4 ± 0.1 a | 1.95 ± 0.02 a | |
| 3 | 14.6 ± 0.3 a | 120.9 ± 8.2 a | 81.7 ± 2.4 a | 99.0 ± 0.1 b | N.D. | 4.05 ± 0.0 b | 3.61 | 4.4 ± 0.1 a | 1.74 ± 0.02 b | |
| 4 | 14.2 ± 0.9 a | 116.9 ± 2.1 a | 82.6 ± 0.6 a | 98.6 ± 0.0 c | N.D. | 4.95 ± 0.0 a | 3.59 | 4.1 ± 0.2 a | 1.66 ± 0.03 c | |
| UF-3K | 1 | 14.1 ± 2.3 a | 107.9 ± 4.2 a | 80.9 ± 1.1 a | 99.6 ± 0.1 a | N.D. | 3.60 ± 0.0 b | 3.61 | 3.9 ± 0.1 a | 1.47 ± 0.02 d |
| 2 | 14.2 ± 1.6 a | 101.0 ± 5.6 a | 78.0 ± 0.4 a | 98.5 ± 0.1 b | N.D. | 4.05 ± 0.0 a | 3.63 | 4.0 ± 0.1 a | 1.94 ± 0.00 a | |
| 3 | 14.8 ± 1.7 a | 109.8 ± 12 a | 73.9 ± 0.2 a | 98.7 ± 0.1 b | N.D. | 4.05 ± 0.0 a | 3.61 | 4.1 ± 0.1 a | 1.74 ± 0.02 b | |
| 4 | 14.1 ± 0.6 a | 97.2 ± 0.0 a | 75.1 ± 3.4 a | 97.8 ± 0.1 c | N.D. | 4.28 ± 0.2 a | 3.57 | 4.0 ± 0.2 a | 1.62 ± 0.04 c |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, K.-R.; Yu, H.-C.; Huang, C.-Y.; Kuo, J.-M.; Chang, C.; Shieh, C.-J.; Kuo, C.-H. Bioprocessed Production of Resveratrol-Enriched Rice Wine: Simultaneous Rice Wine Fermentation, Extraction, and Transformation of Piceid to Resveratrol from Polygonum cuspidatum Roots. Foods 2019, 8, 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8070258
Yang K-R, Yu H-C, Huang C-Y, Kuo J-M, Chang C, Shieh C-J, Kuo C-H. Bioprocessed Production of Resveratrol-Enriched Rice Wine: Simultaneous Rice Wine Fermentation, Extraction, and Transformation of Piceid to Resveratrol from Polygonum cuspidatum Roots. Foods. 2019; 8(7):258. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8070258
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Kai-Ruei, Hui-Chuan Yu, Chun-Yung Huang, Jen-Min Kuo, Cheng Chang, Chwen-Jen Shieh, and Chia-Hung Kuo. 2019. "Bioprocessed Production of Resveratrol-Enriched Rice Wine: Simultaneous Rice Wine Fermentation, Extraction, and Transformation of Piceid to Resveratrol from Polygonum cuspidatum Roots" Foods 8, no. 7: 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8070258
APA StyleYang, K.-R., Yu, H.-C., Huang, C.-Y., Kuo, J.-M., Chang, C., Shieh, C.-J., & Kuo, C.-H. (2019). Bioprocessed Production of Resveratrol-Enriched Rice Wine: Simultaneous Rice Wine Fermentation, Extraction, and Transformation of Piceid to Resveratrol from Polygonum cuspidatum Roots. Foods, 8(7), 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8070258








