Effect of Sweet Corn Residue on Micronutrient Fortification in Baked Cakes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. SCR Preparation
2.2. Cake Formulation and Preparation
2.3. Sensory Evaluation
2.4. Texture Profile Analysis of Cakes
2.5. Determination of Total Sugar
2.6. Determination of Dietary Fiber
2.7. In Vitro Digestion
2.8. Extraction and Determination of Vitamin E
2.9. Extraction and Determination of Carotenoids
2.10. Extraction and Determination of Folate
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of SCR on Sensory Quality of Cake
3.2. Effect of SCR on Texture Characteristics of Cake
3.3. Dietary Fiber in Cakes
3.4. In Vitro Digestion of Cakes
3.5. Composition and Content of Vitamin E in Cakes
3.6. Composition and Content of Carotenoids in Cakes
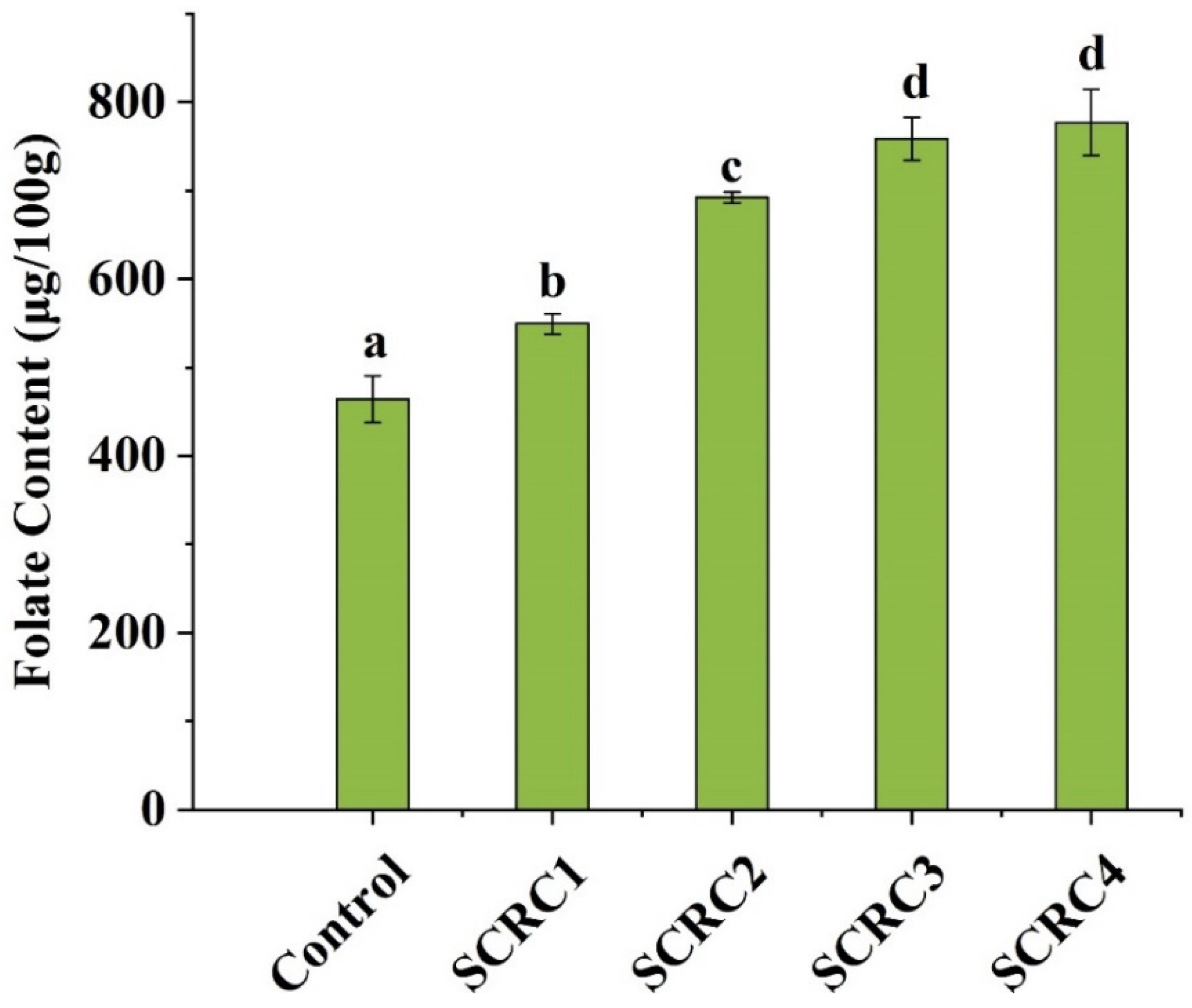
3.7. Folate Content in Cakes
3.8. Correlation between SCR Addition and Detection Indicators
4. Discussion
4.1. The Relationship between Sensory and Textural Characteristics
4.2. Interaction between Dietary Fiber and Digestion In Vitro
4.3. Micronutrient Fortification Effects in Cakes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beilharz, J.; Maniam, J.; Morris, M. Diet-induced cognitive deficits: The role of fat and sugar, potential mechanisms and nutritional interventions. Nutrients 2015, 7, 6719–6738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okarter, N.; Liu, R.H. Health benefits of whole grain phytochemicals. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2010, 50, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borneo, R.; León, A.E. Whole grain cereals: Functional components and health benefits. Food Funct. 2012, 3, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, M.; Manchón, L.; Oliete, B.; Ruiz, E.; Caballero, P.A. Adequacy of wholegrain non-wheat flours for layer cake elaboration. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žilić, S.; Kocadağlı, T.; Vančetović, J.; Gökmen, V. Effects of baking conditions and dough formulations on phenolic compound stability, antioxidant capacity and color of cookies made from anthocyanin-rich corn flour. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 65, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoba, O.S.; Taylor, J.R.N.; de Kock, H.L. Sensory and nutritive profiles of biscuits from whole grain sorghum and pearl millet plus soya flour with and without sourdough fermentation. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 2554–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aal el, S.M.; Young, J.C.; Akhtar, H.; Rabalski, I. Stability of lutein in wholegrain bakery products naturally high in lutein or fortified with free lutein. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 10109–10117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattimer, J.M.; Haub, M.D. Effects of dietary fiber and its components on metabolic health. Nutrients 2010, 2, 1266–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, F.; Azzi, A.; Birringer, M.; Cook-Mills, J.M.; Eggersdorfer, M.; Frank, J.; Cruciani, G.; Lorkowski, S.; Ozer, N.K. Vitamin E: Emerging aspects and new directions. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 102, 16–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, A.; Basirnejad, M.; Shahbazi, S.; Bolhassani, A. Carotenoids: Biochemistry, pharmacology and treatment. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 1290–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.V.; Rao, L.G. Carotenoids and human health. Pharmacol. Res. 2007, 55, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNulty, H.; Pentieva, K.; Hoey, L.; Strain, J.; Ward, M. Nutrition throughout life: Folate. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2012, 82, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamm, R.; Houghton, L. Nutrient intake values for folate during pregnancy and lactation vary widely around the world. Nutrients 2013, 5, 3920–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, X.; Guohua, H. Effects of xanthan gum and corn flour on the quality of sponge cake using response surface methodology. Czech J. Food Sci. 2018, 36, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 8587:2006. Sensory Analysis–Methodology–Ranking; Iso International Standard: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 5495:2005. Sensory Analysis. Methodology. Paired Comparison Test; Iso International Standard: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Brites, C.; Trigo, M.J.; Santos, C.; Collar, C.; Rosell, C.M. Maize-Based Gluten-Free Bread: Influence of Processing Parameters on Sensory and Instrumental Quality. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2008, 3, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldar, D.; Sen, D.; Gayen, K. Development of spectrophotometric method for the analysis of multi-component carbohydrate mixture of different moieties. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 181, 1416–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamotho, S.; Kyallo, F.; Sila, D. Biofortification of maize flour with grain amaranth for improved nutrition. Afr. J. Food Agric. Nutr. Dev. 2017, 17, 12574–12588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Brennan, M.A.; Mason, S.L.; Brennan, C.S. Effect of sugar replacement with stevianna and inulin on the texture and predictive glycaemic response of muffins. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 1979–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goñi, I.; Garcia-Alonso, A.; Saura-Calixto, F. A starch hydrolysis procedure to estimate glycemic index. Nutr. Res. 1997, 17, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Yu, Y.; Mao, J.; Liu, H.; Hu, J.G.; Li, T.; Guo, X.; Liu, R.H. Evaluation of Biosynthesis, Accumulation and Antioxidant Activityof Vitamin E in Sweet Corn (Zea mays L.) during Kernel Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Xiang, N.; Hu, J.G.; Shijuan, Y.; Xie, L.; Brennan, C.S.; Huang, W.; Guo, X. The manipulation of gene expression and the biosynthesis of Vitamin C, E and folate in light-and dark-germination of sweet corn seeds. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Mao, J.; Yan, S.; Yu, Y.; Xie, L.; Hu, J.G.; Li, T.; Abbasi, A.M.; Guo, X.; Liu, R.H. Evaluation of carotenoid biosynthesis, accumulation and antioxidant activities in sweetcorn (Zea mays L.) during kernel development. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Q.-J.; Liu, J.-H.; Li, W.; Wang, H.; Hu, X.-D.; Li, T.; Hu, J.-G.; Guo, X.-B.; Liu, R.H. Comprehensive evaluation of biosynthesis, accumulation, regulation of folate and vitamin C in waxy maize (Zea mays L. var. ceratina) with kernel development. J. Cereal Sci. 2019, 87, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Liu, S.X.; Vaughn, S.F. Effect of corn bran as dietary fiber addition on baking and sensory quality. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2012, 1, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebesi, D.M.; Tzia, C. Effect of the Addition of Different Dietary Fiber and Edible Cereal Bran Sources on the Baking and Sensory Characteristics of Cupcakes. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2009, 4, 710–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foschia, M.; Peressini, D.; Sensidoni, A.; Brennan, C.S. The effects of dietary fibre addition on the quality of common cereal products. J. Cereal Sci. 2013, 58, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foschia, M.; Peressini, D.; Sensidoni, A.; Brennan, M.A.; Brennan, C.S. Synergistic effect of different dietary fibres in pasta on in vitro starch digestion? Food Chem. 2015, 172, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavin, J.L.; Lloyd, B. Health benefits of fruits and vegetables. Adv. Nutr. 2012, 3, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewanto, V.; Wu, X.; Liu, R.H. Processed sweet corn has higher antioxidant activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 4959–4964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwandi, J. Carotenoids: Sources, medicinal properties and their application in food and nutraceutical industry. J. Med. Plants Res. 2011, 5, 7119–7131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aal el, S.M.; Akhtar, H.; Zaheer, K.; Ali, R. Dietary sources of lutein and zeaxanthin carotenoids and their role in eye health. Nutrients 2013, 5, 1169–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, R.; Pike, O.A.; Eggett, D.L.; Dunn, M.L. Folate Stability in Folic Acid Enriched Corn Masa Flour, Tortillas, and Tortilla Chips over the Expected Shelf Life. Cereal Chem. 2017, 94, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, K.; Steele, F.M.; Jefferies, L.; Pike, O.A.; Dunn, M.L. Effect of micronutrient fortification on nutritional and other properties of nixtamal tortillas. Cereal Chem. 2008, 85, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichholzer, M.; Tönz, O.; Zimmermann, R. Folic acid: A public-health challenge. Lancet 2006, 367, 1352–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ingredients (g) | Control | SCRC1 | SCRC2 | SCRC3 | SCRC4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCR | 0 | 15 | 30 | 45 | 50 |
| Low-gluten flour | 40 | 28 | 16 | 4 | 0 |
| High-gluten flour | 10 | 7 | 4 | 1 | 0 |
| Egg | 95 | 95 | 95 | 95 | 95 |
| Sugar | 36 | 36 | 36 | 36 | 36 |
| Salt | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Soybean lecithin | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Baking powder | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| Corn oil | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| Milk | 60 | 65 | 65 | 70 | 70 |
| Products | Color | Texture | Shape | Taste | Flavor | Total Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 14.18 ± 2.36 | 17.55 ± 2.11 | 16.64 ± 1.96 | 18.00 ± 1.61 | 14.64 ± 3.53 | 81.00 ± 7.81 |
| SCRC1 | 15.82 ± 1.72 | 16.00 ± 2.00 | 16.00 ± 2.28 | 16.00 ± 3.29 | 16.27 ±2.65 | 80.09 ± 8.61 |
| SCRC2 | 15.36 ± 2.94 | 15.73 ± 2.69 | 15.82 ± 2.56 | 15.36 ± 2.94 | 17.18 ± 2.14 | 79.45 ± 10.93 |
| SCRC3 | 14.55 ± 3.50 | 14.09 ± 2.91 | 13.82 ± 3.34 | 12.55 ± 4.27 | 15.27 ± 2.971 | 70.27 ± 14.46 |
| SCRC4 | 14.45 ± 5.16 | 13.82 ± 3.37 | 14.09 ± 4.30 | 12.09 ± 3.51 | 15.00 ± 3.46 | 69.45 ± 15.45 |
| Products | Hardness (g) | Resilience (%) | Cohesion | Springiness (%) | Gumminess (g) | Chewiness (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 269.6 ± 14.2b | 28.00 ± 1.17c | 0.7245 ± 0.016bc | 78.86 ± 3.76ab | 195.8 ± 8.3bc | 153.0 ± 6.6bc |
| SCRC1 | 195.1 ± 7.1a | 30.93 ± 0.45d | 0.7497 ± 0.0178c | 84.76 ± 6.70b | 144.8 ± 5.3a | 123.3 ± 11.5a |
| SCRC2 | 259.9 ± 12.2b | 27.50 ± 0.93c | 0.7122 ± 0.0154b | 75.41 ± 1.98a | 183.4 ± 8.0b | 135.5 ± 10.4ab |
| SCRC3 | 310.8 ± 26.1c | 24.54 ± 0.44b | 0.6741 ± 0.0053a | 76.08 ± 0.40a | 201.0 ± 16.7c | 159.6 ± 11.9c |
| SCRC4 | 388.8 ± 20.0d | 22.01 ± 0.80a | 0.6598 ± 0.0083a | 73.81 ± 0.52a | 256.9 ± 9.4d | 188.2 ± 9.0d |
| Products | Total Sugar (mg/g) | AUC (Area under the Curve) |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 158.9 ± 9.1c | 4133 ± 54e |
| SCRC1 | 169.2 ± 1.9d | 2895 ± 50d |
| SCRC2 | 135.6 ± 3.6b | 2115 ± 10c |
| SCRC3 | 165.0 ± 5.5cd | 454.9 ± 16.5b |
| SCRC4 | 168.2 ± 1.9d | 359.5 ± 17.5a |
| Blank | 112.5 ± 0.4a | 5212 ± 35f |
| Compositions | Control | SCRC1 | SCRC2 | SCRC3 | SCRC4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-T | 615.4 ± 13.8a | 1022 ± 1b | 937.0 ± 33.7b | 946.4 ± 53.9b | 989.1 ± 52.3b |
| α-T3 | 73.34 ± 3.61a | 146.2 ± 0.2b | 193.3 ± 3.4c | 221.0 ± 10.5d | 232.0 ± 12.4d |
| β-T | 39.56 ± 0.04a | 48.24 ± 0.63b | 42.21 ± 2.30a | 39.31 ± 1.91a | 42.12 ± 1.57a |
| γ-T | 1056 ± 12a | 1367 ± 1d | 1142 ± 26b | 1168 ± 36b | 1251 ± 39c |
| γ-T3 | 127.0 ± 8.5a | 245.8 ± 1.1b | 318.4 ± 0.9c | 381.8 ± 16.6d | 393.8 ± 17.9d |
| δ-T | 47.27 ± 0.84c | 51.05 ± 0.62d | 39.96 ± 0.35a | 42.02 ± 1.34b | 48.67 ± 1.49c |
| δ-T3 | 14.66 ± 1.02a | 17.29 ± 0.48b | 18.48 ± 0.59bc | 20.44 ± 1.19d | 19.28 ± 0.23cd |
| Total | 1973 ± 41a | 2878 ± 2cd | 2692 ± 63b | 2820 ± 115bc | 2976 ± 119d |
| Compositions | Control | SCRC1 | SCRC2 | SCRC3 | SCRC4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lut | 12.68 ± 0.55a | 31.37 ± 1.29b | 51.54 ± 2.64c | 69.31 ± 4.04e | 64.32 ± 2.73c |
| Zea | 14.05 ± 0.77a | 20.14 ± 0.24b | 26.14 ± 1.03c | 31.73 ± 1.81d | 31.16 ± 3.08d |
| α-Cry | 3.28 ± 0.10a | 10.33 ± 0.05b | 15.69 ± 0.28c | 20.68 ± 1.02d | 19.63 ± 0.56c |
| β-Cry | 13.38 ± 1.38d | 7.74 ± 0.36a | 9.67 ± 0.11b | 11.58 ± 0.18c | 10.44 ± 0.71bc |
| ε-Car | ND | 6.67 ± 0.09a | 8.00 ± 0.24b | 8.89 ± 0.37c | 8.37 ± 0.18b |
| α-Car | ND | 3.45 ± 0.23a | 4.65 ± 0.24b | 5.72 ± 0.67c | 5.34 ± 0.34bc |
| β-Car | 2.35 ± 0.02d | 3.14 ± 0.02a | 3.95 ± 0.20b | 4.91 ± 0.20c | 4.59 ± 0.10bc |
| (6R)-δ-Car | ND | 3.66 ± 0.01a | 5.38 ± 0.05b | 6.35 ± 0.15c | 6.14 ± 0.23c |
| Total μg/100 g | 45.74 ± 2.11a | 86.50 ± 1.24b | 125.0 ± 4.6c | 159.2 ± 8.1e | 145.0 ± 7.9d |
| Addition | Hardness | Resilience | Cohesion | Springiness | Gumminess | Chewiness | Sensory Scores | Total Sugar | Fiber | AUC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Addition | 1.000 | ||||||||||
| Hardness | 0.719 | 1.000 | |||||||||
| Resilience | −0.807 | −0.986 ** | 1.000 | ||||||||
| Cohesion | −0.856 | −0.950 * | 0.989 ** | 1.000 | |||||||
| Springiness | −0.676 | −0.847 | 0.871 | 0.867 | 1.000 | ||||||
| Gumminess | 0.655 | 0.996 ** | −0.970 ** | −0.925 * | −0.845 | 1.000 | |||||
| Chewiness | 0.599 | 0.978 ** | −0.940 * | −0.890 * | −0.741 | 0.984 ** | 1.000 | ||||
| Sensory score | −0.879 * | −0.856 | 0.909 * | 0.936 * | 0.639 | −0.814 | −0.826 | 1.000 | |||
| Total sugar | 0.122 | 0.222 | −0.190 | −0.172 | 0.309 | 0.207 | 0.368 | −0.456 | 1.000 | ||
| Fiber | 1.000 ** | 0.717 | −0.805 | −0.854 | −0.681 | 0.652 | 0.594 | −0.872 | 0.106 | 1.000 | |
| AUC | −0.993 ** | −0.707 | 0.800 | 0.855 | 0.626 | −0.641 | −0.602 | 0.911 * | −0.213 | −0.991 ** | 1.000 |
| Addition | α-T | α-T3 | βT | γT | γT3 | δT | δT3 | Total VE | Lut | Zea | α-Cry | β-Cry | ε-Car | α-Car | β-Car | (6R)-δ-Car | Total Car | Folate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Addition | 1.000 | ||||||||||||||||||
| α-T | 0.709 | 1.000 | |||||||||||||||||
| α-T3 | 0.981 ** | 0.813 | 1.000 | ||||||||||||||||
| βT | −0.185 | 0.532 | −0.045 | 1.000 | |||||||||||||||
| γT | 0.238 | 0.780 | 0.333 | 0.871 | 1.000 | ||||||||||||||
| γT3 | 0.987 ** | 0.800 | 0.998 ** | −0.070 | 0.326 | 1.000 | |||||||||||||
| δT | −0.316 | −0.006 | −0.347 | 0.575 | 0.579 | −0.336 | 1.000 | ||||||||||||
| δT3 | 0.944 * | 0.794 | 0.968 ** | −0.083 | 0.311 | 0.973 ** | −0.414 | 1.000 | |||||||||||
| Total VE | 0.782 | 0.988 ** | 0.859 | 0.457 | 0.764 | 0.851 | 0.034 | 0.831 | 1.000 | ||||||||||
| Lut | 0.983 ** | 0.724 | 0.983 ** | −0.197 | 0.206 | 0.989 ** | −0.439 | 0.982 ** | 0.778 | 1.000 | |||||||||
| Zea | 0.990 ** | 0.748 | 0.990 ** | −0.158 | 0.248 | 0.995 ** | −0.393 | 0.979 ** | 0.804 | 0.998 ** | 1.000 | ||||||||
| α-Cry | 0.983 ** | 0.767 | 0.991 ** | −0.133 | 0.266 | 0.995 ** | −0.403 | 0.987 ** | 0.817 | 0.998 ** | 0.999 ** | 1.000 | |||||||
| β-Cry | −0.184 | −0.814 | −0.348 | −0.898 * | −0.870 | −0.317 | −0.237 | −0.313 | −0.736 | −0.204 | −0.235 | −0.266 | 1.000 | ||||||
| ε-Car | 0.912 | −0.629 | 0.936 | −0.989 * | −0.797 | 0.940 | −0.622 | 0.967 * | −0.056 | 0.988 * | 0.971 * | 0.981 * | 0.994 ** | 1.000 | |||||
| α-Car | 0.952 * | −0.523 | 0.962 * | −0.962 * | −0.716 | 0.972 * | −0.515 | 0.972 * | 0.073 | 0.999 ** | 0.992 ** | 0.997 ** | 0.991 ** | 0.992 ** | 1.000 | ||||
| β-Car | 0.981 ** | 0.697 | 0.971 ** | −0.231 | 0.187 | 0.980 ** | −0.432 | 0.981 ** | 0.757 | 0.998 ** | 0.994 ** | 0.993 ** | −0.161 | 0.982 * | 0.997 ** | 1.000 | |||
| (6R)-δ-Car | 0.958 * | −0.546 | 0.979 * | −0.962 * | −0.754 | 0.977 * | −0.543 | 0.936 | 0.042 | 0.993 ** | 0.990 * | 0.992 ** | 0.972 * | 0.987 * | 0.992 ** | 0.981 * | 1.000 | ||
| Total Car | 0.980 ** | 0.736 | 0.983 ** | −0.181 | 0.223 | 0.988 ** | −0.435 | 0.987 ** | 0.788 | 1.000 ** | 0.998 ** | 0.998 ** | −0.220 | 0.989 * | 1.000 ** | 0.998 ** | 0.989 * | 1.000 | |
| Folate | 0.991 ** | 0.692 | 0.983 ** | −0.224 | 0.165 | 0.985 ** | −0.432 | 0.948 * | 0.752 | 0.990 ** | 0.991 ** | 0.986 ** | −0.176 | 0.955 * | 0.970 * | 0.982 ** | 0.990 * | 0.985 ** | 1.000 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lao, Y.-X.; Yu, Y.-Y.; Li, G.-K.; Chen, S.-Y.; Li, W.; Xing, X.-P.; Wang, X.-M.; Hu, J.-G.; Guo, X.-B. Effect of Sweet Corn Residue on Micronutrient Fortification in Baked Cakes. Foods 2019, 8, 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8070260
Lao Y-X, Yu Y-Y, Li G-K, Chen S-Y, Li W, Xing X-P, Wang X-M, Hu J-G, Guo X-B. Effect of Sweet Corn Residue on Micronutrient Fortification in Baked Cakes. Foods. 2019; 8(7):260. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8070260
Chicago/Turabian StyleLao, Yu-Xia, Yu-Ying Yu, Gao-Ke Li, Shao-Yun Chen, Wu Li, Xu-Pu Xing, Xue-Min Wang, Jian-Guang Hu, and Xin-Bo Guo. 2019. "Effect of Sweet Corn Residue on Micronutrient Fortification in Baked Cakes" Foods 8, no. 7: 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8070260
APA StyleLao, Y.-X., Yu, Y.-Y., Li, G.-K., Chen, S.-Y., Li, W., Xing, X.-P., Wang, X.-M., Hu, J.-G., & Guo, X.-B. (2019). Effect of Sweet Corn Residue on Micronutrient Fortification in Baked Cakes. Foods, 8(7), 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8070260





