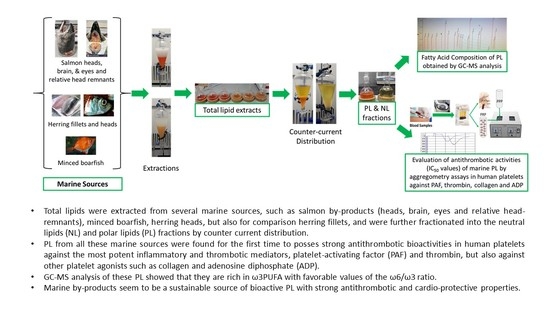
Bioprospecting for Antithrombotic Polar Lipids from Salmon, Herring, and Boarfish By-Products
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Total, Neutral, and Polar Lipid Content of Salmon, Herring, Boarfish and Their By-Products
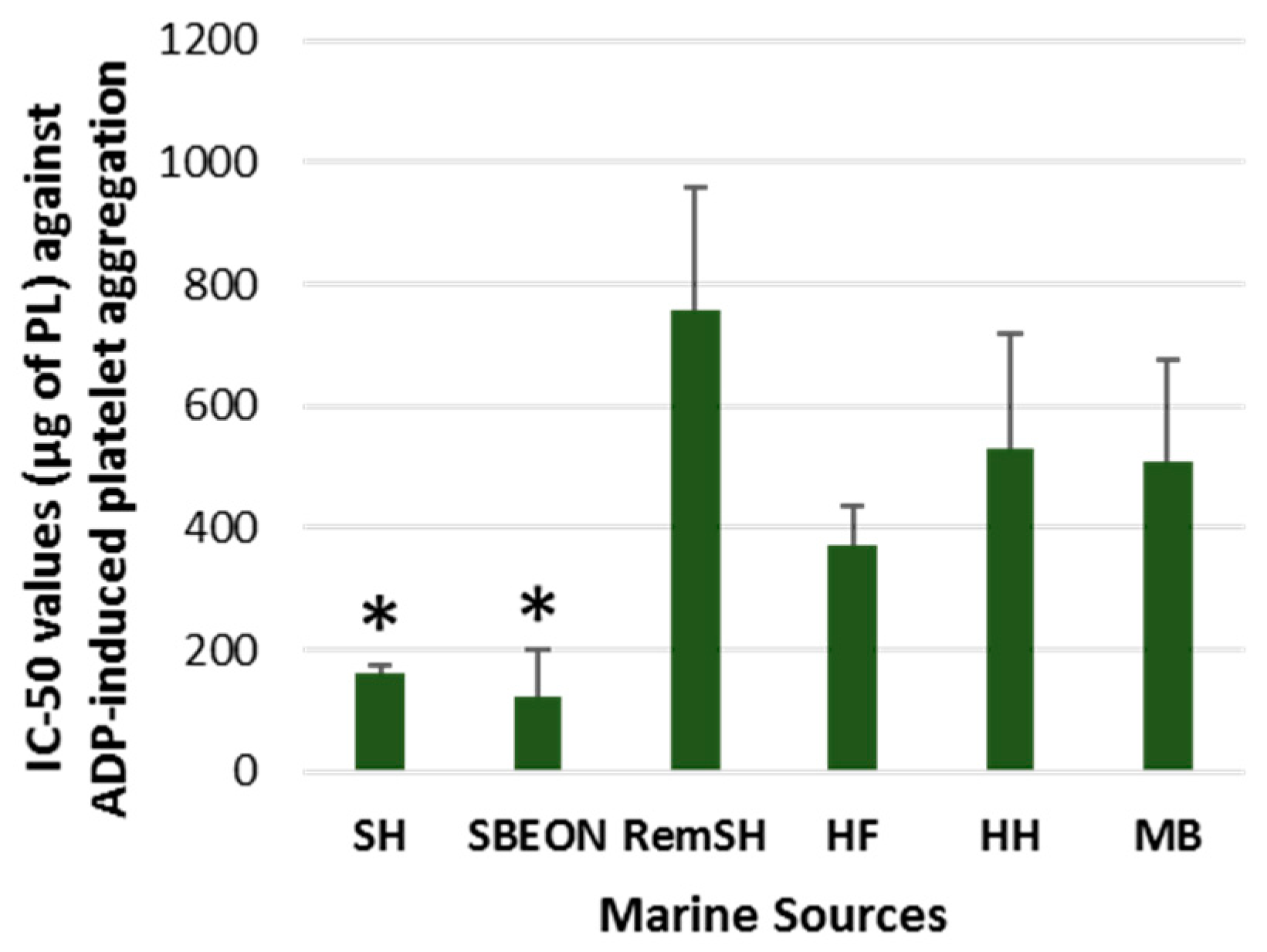
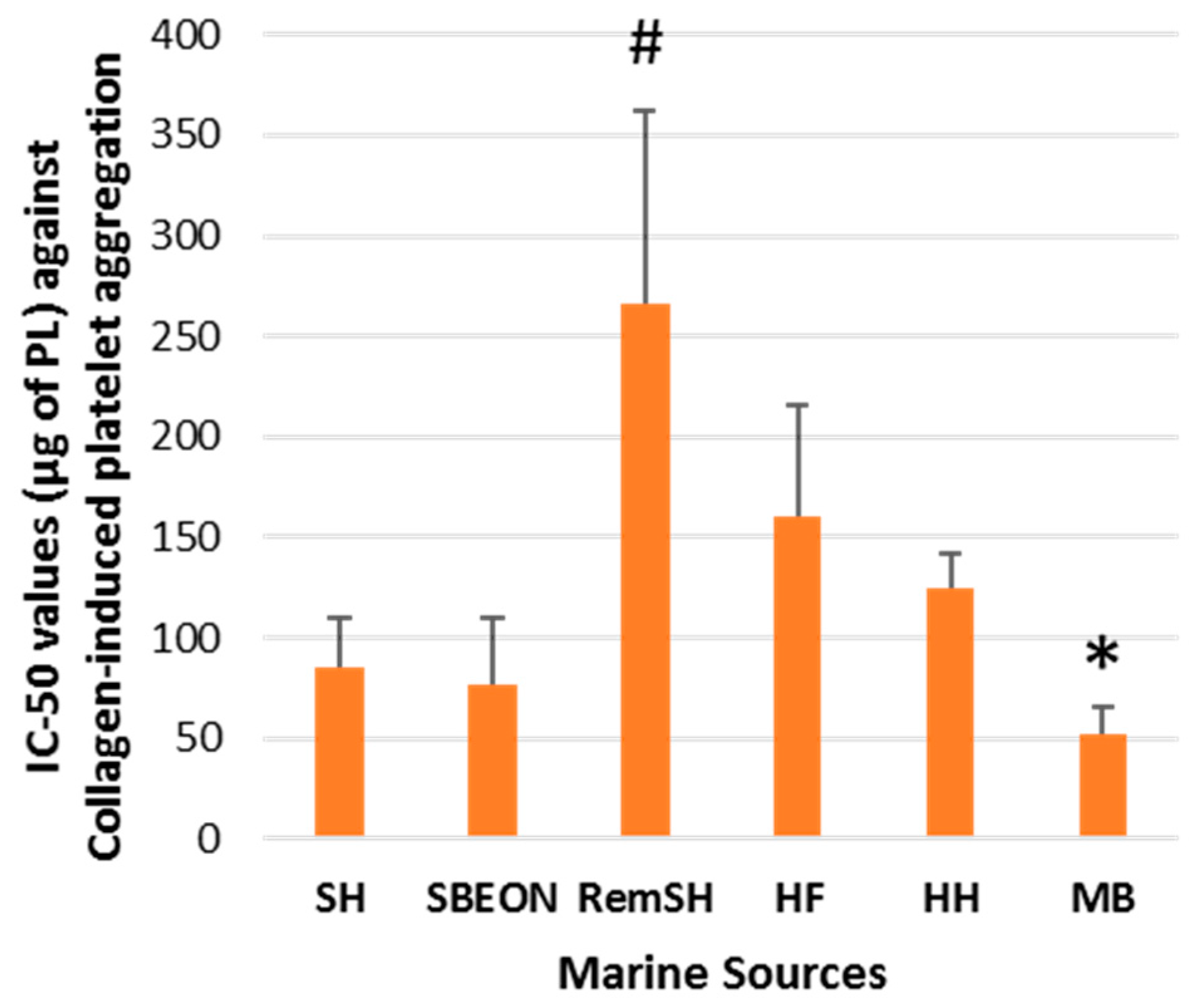
2.2. Antithrombotic Bioactivities of PLs from Salmon, Herring, Boarfish, and Their By-Products in Human Platelets
2.3. Fatty Acid Composition of PLs from Salmon, Herring, Boarfish, and Their By-Products
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Instrumentation
4.2. Samples of Salmon, Herring, Boarfish, and Their By-Products Assessed
4.3. Extraction and Isolation of Total Lipid, Neutral Lipid, and Polar Lipid Extracts from Salmon, Herring, Boarfish, and Their By-Products
4.4. Human Platelet Aggregation Studies of PL Extracts from Salmon, Herring, Boarfish, and Their By-Products against PAF, Thrombin, Collagen, and ADP
4.5. Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry of PL Extracts from Salmon, Herring, Boarfish, and Their By-Products
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsoupras, A.; Lordan, R.; Zabetakis, I. Inflammation, not cholesterol, is a cause of chronic disease. Nutrients 2018, 10, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lordan, R.; Tsoupras, A.; Zabetakis, I. Inflammation. In The Impact of Nutrition and Statins on Cardiovascular Diseases; Zabetakis, I., Lordan, R., Tsoupras, A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; Volume 2, pp. 23–51. [Google Scholar]
- Tsoupras, A.; Lordan, R.; Zabetakis, I. Inflammation and Cardiovascular Diseases. In The Impact of Nutrition and Statins on Cardiovascular Diseases; Zabetakis, I., Lordan, R., Tsoupras, A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; Volume 3, pp. 53–117. [Google Scholar]
- Santos-Gallego, C.G.; Picatoste, B.; Badimón, J.J. Pathophysiology of acute coronary syndrome. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2014, 16, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos-Gallego, C.G.; Bayón, J.; Badimón, J.J. Thrombi of different pathologies: Implications for diagnosis and treatment. Curr. Treat. Options Cardiovasc. Med. 2010, 12, 274–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokes, K.Y.; Granger, D.N. Platelets: A critical link between inflammation and microvascular dysfunction. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Delaney, M.K.; O’Brien, K.A.; Du, X. Signaling during platelet adhesion and activation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 2341–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tierney, A.; Ronan, L.; Tsoupras, A.; Zabetakis, I. Diet and Cardiovascular Disease: The Mediterranean Diet. In The Impact of Nutrition and Statins on Cardiovascular Diseases; Zabetakis, I., Ronan, L., Tsoupras, A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; Volume 8, pp. 267–288. [Google Scholar]
- Lordan, R.; Nasopoulou, C.; Tsoupras, A.; Zabetakis, I. The anti-inflammatory properties of food polar lipids. In Bioactive Molecules in Food; Mérillon, J.M., Ramawat, K.G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, T.A.; Beilin, L.J.; Burke, V.; Morris, J.; Ritchie, J. Interactions between dietary fat, fish, and fish oils and their effects on platelet function in men at risk of cardiovascular disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1997, 17, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, A.; Pothineni, N.V.; Singhal, M.; Paydak, H.; Saldeen, T.; Mehta, J.L. Fish, Fish Oils and Cardioprotection: Promise or Fish Tale? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorngren, M.; Gustafson, A. Effects of 11-week increase in dietary eicosapentaenoic acid on bleeding time, lipids, and platelet aggregation. Lancet 1981, 318, 1190–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, V.; Carvalho, A.P.; Piccirillo, C.; Santos, M.M.; Castro, P.M.; Pintado, M.E. Extraction of high added value biological compounds from sardine, sardine-type fish and mackerel canning residues—A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 3111–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, D.L.; Steg, P.G.; Miller, M.; Brinton, E.A.; Jacobson, T.A.; Ketchum, S.B.; Doyle, R.T.; Juliano, R.A.; Jiao, L.; Granowitz, C.; et al. Cardiovascular risk reduction with icosapent ethyl for hypertriglyceridemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, D.L.; Steg, P.G.; Miller, M.; Brinton, E.A.; Jacobson, T.A.; Jiao, L.; Tardif, J.-C.; Gregson, J.; Pocock, S.J.; Ballantyne, C.M. Reduction in first and total ischemic events with icosapent ethyl across baseline triglyceride tertiles. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 1159–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manson, J.E.; Cook, N.R.; Lee, I.-M.; Christen, W.; Bassuk, S.S.; Mora, S.; Gibson, H.; Albert, C.M.; Gordon, D.; Copeland, T.; et al. Marine n−3 fatty acids and prevention of cardiovascular disease and cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizos, E.C.; Ntzani, E.E.; Bika, E.; Kostapanos, M.S.; Elisaf, M.S. Association between omega-3 fatty acid supplementation and risk of major cardiovascular disease events: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2012, 308, 1024–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enns, J.E.; Yeganeh, A.; Zarychanski, R.; Abou-Setta, A.M.; Friesen, C.; Zahradka, P.; Taylor, C.G. The impact of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation on the incidence of cardiovascular events and complications in peripheral arterial disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2014, 14, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walz, C.P.; Barry, A.R.; Koshman, S.L. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation in the prevention of cardiovascular disease. Can. Pharm. J. 2016, 149, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kwak, S.; Myung, S.; Lee, Y.; Seo, H.; Korean Meta-Analysis Study Group. Efficacy of omega-3 fatty acid supplements (eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid) in the secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease: A meta-analysis of randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. Arch. Intern. Med. 2012, 172, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, R.; Stevens, S.; Gorman, D.; Pan, A.; Warnakula, S.; Chowdhury, S.; Ward, H.; Johnson, L.; Crowe, F.; Hu, F.B. Association between fish consumption, long chain omega 3 fatty acids, and risk of cerebrovascular disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2012, 345, e6698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lordan, R.; Tsoupras, A.; Zabetakis, I. Phospholipids of animal and marine origin: Structure, function, and anti-inflammatory properties. Molecules 2017, 22, 1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoupras, A.; Lordan, R.; Shiels, K.; Saha, S.K.; Nasopoulou, C.; Zabetakis, I. In Vitro Antithrombotic Properties of Salmon (Salmo salar) Phospholipids in a Novel Food-Grade Extract. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoupras, A.; Lordan, R.; Demuru, M.; Shiels, K.; Saha, S.K.; Nasopoulou, C.; Zabetakis, I. Structural Elucidation of Irish Organic Farmed Salmon (Salmo salar) Polar Lipids with Antithrombotic Activities. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burri, L.; Hoem, N.; Banni, S.; Berge, K. Marine omega-3 phospholipids: Metabolism and biological activities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 15401–15419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, M.H.; Johnson, J.; Rooney, M.W.; Kyle, M.L.; Kling, D.F. A novel omega-3 free fatty acid formulation has dramatically improved bioavailability during a low-fat diet compared with omega-3-acid ethyl esters: The ECLIPSE (Epanova((R)) compared to Lovaza((R)) in a pharmacokinetic single-dose evaluation) study. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2012, 6, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørndal, B.; Strand, E.; Gjerde, J.; Bohov, P.; Svardal, A.; Diehl, B.W.; Innis, S.M.; Berger, A.; Berge, R.K. Phospholipids from herring roe improve plasma lipids and glucose tolerance in healthy, young adults. Lipids Health Dis. 2014, 13, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasopoulou, C.; Tsoupras, A.B.; Karantonis, H.C.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Zabetakis, I. Fish polar lipids retard atherosclerosis in rabbits by down-regulating PAF biosynthesis and up-regulating paf catabolism. Lipids Health Dis. 2011, 10, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogeropoulos, N.; Nomikos, T.; Chiou, A.; Fragopoulou, E.; Antonopoulou, S. Chemical composition of greek avgotaracho prepared from mullet (Mugil cephalus): Nutritional and health benefits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 5916–5925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulou, S.; Karantonis, H.C.; Nomikos, T.; Oikonomou, A.; Fragopoulou, E.; Pantazidou, A. Bioactive polar lipids from Chroococcidiopsis sp.(cyanobacteria). Comp. Biochem. Phys. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2005, 142, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruthu Murthy, P.S.; Rai, A.K.; Bhaskar, N. Fermentative recovery of lipids and proteins from freshwater fish head waste with reference to antimicrobial and antioxidant properties of protein hydrolysate. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 1884–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.K.; Nagao, T.; Kurihara, H.; Takahashi, K. Production of a Health-Beneficial Food Emulsifier by Enzymatic Partial Hydrolysis of Phospholipids Obtained from the Head of Autumn Chum Salmon. J. Oleo Sci. 2017, 66, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shavandi, A.; Hou, Y.; Carne, A.; McConnell, M.; Bekhit, A.E.A. Marine Waste Utilization as a Source of Functional and Health Compounds. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2019, 87, 187–254. [Google Scholar]
- Lordan, S.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C. Marine bioactives as functional food ingredients: Potential to reduce the incidence of chronic diseases. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1056–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Inoue, Y. Marine by-product phospholipids as booster of medicinal compounds. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2012, 65, 31–46. [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez, J.A.; Meduíña, A.; Durán, A.I.; Nogueira, M.; Fernández-Compás, A.; Pérez-Martín, R.I.; Rodríguez-Amado, I. Production of Valuable Compounds and Bioactive Metabolites from By-Products of Fish Discards Using Chemical Processing, Enzymatic Hydrolysis, and Bacterial Fermentation. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aidos, I.; van der Padt, A.; Luten, J.B.; Boom, R.M. Seasonal changes in crude and lipid composition of herring fillets, byproducts, and respective produced oils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 4589–4599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoknes, I.S.; Økland, H.M.; Falch, E.; Synnes, M. Fatty acid and lipid class composition in eyes and brain from teleosts and elasmobranchs. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2004, 138, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bower, C.K.; Hietala, K.A.; Oliveira, A.C.; Wu, T.H. Stabilizing oils from smoked pink salmon (Oncorhynchus gorbuscha). J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, C248–C257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanos, D.S.; Kapoulas, V.M. Isolation of polar lipids from triglyceride mixtures. J. Lipid Res. 1962, 3, 134–136. [Google Scholar]
- Simopoulos, A.P. The importance of the omega-6/omega-3 fatty acid ratio in cardiovascular disease and other chronic diseases. Exp. Biol. Med. 2008, 233, 674–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasopoulou, C.; Psani, E.; Sioriki, E.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Zabetakis, I. Evaluation of sensory and in vitro cardio protective properties of sardine (Sardina pilchardus): The effect of grilling and brining. Food Nutr. Sci. 2013, 4, 940. [Google Scholar]
- Nasopoulou, C.; Nomikos, T.; Demopoulos, C.; Zabetakis, I. Comparison of antiatherogenic properties of lipids obtained from wild and cultured sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) and gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Food Chem. 2007, 100, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panayiotou, A.; Samartzis, D.; Nomikos, T.; Fragopoulou, E.; Karantonis, H.C.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Zabetakis, I. Lipid fractions with aggregatory and antiaggregatory activity toward platelets in fresh and fried cod (Gadus morhua): Correlation with platelet-activating factor and atherogenesis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 6372–6379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Lopez, N.; Stubhaug, I.; Ipharraguerre, I.; Rimbach, G.; Menoyo, D. Positional distribution of fatty acids in triacylglycerols and phospholipids from fillets of atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) fed vegetable and fish oil blends. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4255–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beppu, F.; Yasuda, K.; Okada, A.; Hirosaki, Y.; Okazaki, M.; Gotoh, N. Comparison of the distribution of unsaturated fatty acids at the sn-2 position of phospholipids and triacylglycerols in marine fishes and mammals. J. Oleo Sci. 2017, 66, 1217–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Larondelle, Y.; Pham, D.; Ackman, R.G.; Rollin, X. Polyunsaturated fatty acid profiles of whole body phospholipids and triacylglycerols in anadromous and landlocked atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) fry. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 134, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aidos, I.; Van Der Padt, A.; Boom, R.M.; Luten, J.B. Upgrading of maatjes herring byproducts: Production of crude fish oil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 8, 3697–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aidos, I.; Masbernat-Martinez, S.; Luten, J.B.; Boom, R.M.; Van Der Padt, A. Composition and stability of herring oil recovered from sorted byproducts as compared to oil from mixed byproducts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 2818–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemova, N.N.; Murzina, S.A.; Nefedova, Z.A.; Pekkoeva, S.N.; Ripatti, P.O. Lipid status of larvae and adults of the White Sea herring Clupea pallasii marisalbi Berg (Clupeiformes, Clupeidae). Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 460, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, M.U.; Santos-Gallego, C.G.; Badimon, L.; Badimon, J.J. Badimon perfusion chamber: An ex vivo model of thrombosis. In Experimental Models of Cardiovascular Diseases: Methods and Protocols; Ishikawa, K., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 161–171. [Google Scholar]
- Tsoupras, A.; Zabetakis, I.; Lordan, R. Platelet aggregometry assay for evaluating the effects of platelet agonists and antiplatelet compounds on platelet function in vitro. MethodsX 2018, 6, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Marine Source | TLs * | NLs * | PLs * |
|---|---|---|---|
| SH | 15.3 ± 5.3 # | 14.2 ± 4.4 | 1.1 ± 0.1 |
| SBEON | 1.2 ± 0.4 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 |
| RemSH | 13.9 ± 2.3 | 13 ± 2.1 | 0.9 ± 0.2 |
| HF | 1.2 ± 0.3 | 0.7 ± 0.2 | 0.4 ± 0.1 |
| HH | 8.6 ± 0.7# | 6.2 ± 0.4 | 0.9 ± 0.1 |
| MB | 7.3 ± 0.2 | 5.9 ± 0.2 | 1.2 ± 0.2 |
| Fatty Acid | HF | HH | SH | MB |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10:0 | ND | ND | ND | 0.015 ± 0.002 a |
| 12:0 | ND | ND | 0.001 ± 0.000 a | 0.062 ± 0.003 b |
| 14:0 | 0.477 ± 0.015 a | 3.101 ± 0.364 b | 1.401 ± 0.110 a | 12.76 ± 0.798 c |
| 13-me-14:0 | 0.024 ± 0.008 a | 0.013 ± 0.001 a | ND | ND |
| 14:1 | ND | 0.015 ± 0.002 a | 0.019 ± 0.001 a | 0.177 ± 0.020 b |
| 15:0 | 0.079 ± 0.017 ab | 0.544 ± 0.096 c | 0.019 ± 0.000 a | 0.160 ± 0.018 b |
| 16:0 | 48.74 ± 2.352 a | 19.89 ± 0.314 b | 1.367 ± 0.071 a | 32.17 ± 1.565 c |
| 15-me-16:0 | 0.012 ± 0.003 a | 0.035 ± 0.022 a | 0.022 ± 0.002 a | 0.015 ± 0.005 b |
| 16:1 c9 | 0.330 ± 0.044 a | 5.686 ± 0.531 e | 1.854 ± 0.045 c | 1.340 ± 0.085 bc |
| 16:1 c6 | ND | 0.992 ± 0.052 | ND | ND |
| 17:0 | 0.151 ± 0.006 ab | 0.325 ± 0.022 b | 0.078 ± 0.007 ab | 0.054 ± 0.008 ab |
| 17:1 | 0.016 ± 0.005 a | 0.044 ± 0.004 c | ND | 0.089 ± 0.012 d |
| 18:0 | 8.621 ± 0.144 c | 5.088 ± 0.063 a | 5.732 ± 0.170 b | 15.39 ± 0.281 e |
| 18:1 c9 | 8.969 ± 0.576 a | 13.30 ± 0.381 b | 14.16 ± 1.341 bc | 13.63 ± 0.337 b |
| 18:1 c11 | ND | 0.410 ± 0.040 a | 2.388 ± 0.229 b | ND |
| 18:1 t13 | 0.267 ± 0.012 c | 0.045 ± 0.002 ab | 0.029 ± 0.006 a | 0.253 ± 0.007 c |
| 18:2 c9, c12 | 0.242 ± 0.012 a | 1.205 ± 0.063 b | 8.822 ± 0.639 c | 0.088 ± 0.007 a |
| 18:2 c9, t11 | 0.064 ± 0.017 a | 0.707 ± 0.114 b | 0.039 ± 0.004 a | ND |
| 18:3 c9, c12, c15 | 0.269 ± 0.028 ab | 0.538 ± 0.031 b | 1.496 ± 0.289 c | 0.026 ± 0.005 a |
| 20:0 | ND | ND | 0.028 ± 0.007 | ND |
| 20:1 c11 or c13 | 0.217 ± 0.036 a | 0.0296 ± 0.001 a | 3.370 ± 0.471 b | 11.61 ± 0.760 c |
| 20:4 c5, c8, c11, c14 | 0.343 ± 0.051 | 1.796 ± 0.206 b | 2.404 ± 0.147 c | 0.160 ± 0.008 a |
| 20:5 c5, c8, c11, c14, c17 | 10.12 ± 0.642 d | 8.776 ± 0.505 c | 10.89 ± 0.494 d | 12.26 ± 0.761 e |
| 22:0 | ND | ND | 0.708 ± 0.564 | ND |
| 22:1 | 4.962 ± 0.830 c | 2.994 ± 0.277 c | 2.681 ± 0.663 b | 0.159 ± 0.008 a |
| 22:5 | 0.063 ± 0.007 a | 1.751 ± 0.480 b | 4.010 ± 0.289 c | ND |
| 22:6 | 16.79 ± 0.911 c | 25.62 ± 0.142 d | 36.87 ± 0.464 e | 0.501 ± 0.058 a |
| ω3 | 27.25 ± 1.308 | 36.39 ± 0.768 | 53.27 ± 1.441 | 12.79 ± 0.447 |
| ω6 | 0.650 ± 0.034 | 3.707 ± 0.198 | 11.26 ± 0.651 | 0.248 ± 0.098 |
| ω6/ω3 | 0.024 ± 0.002 | 0.101 ± 0.007 | 0.211 ± 0.018 | 0.019 ± 0.008 |
| SFA | 58.07 ± 2.491 de | 28.95 ± 0.756 b | 9.588 ± 0.577 a | 60.60 ± 2.105 e |
| MUFA | 14.76 ± 0.428 a | 29.52 ± 0.601 de | 24.51 ± 2.370 bc | 27.10 ± 0.990 cd |
| PUFA | 27.90 ± 1.303 b | 40.40 ± 0.958 c | 60.53 ± 1.866 d | 12.78 ± 0.451 a |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsoupras, A.; O’Keeffe, E.; Lordan, R.; Redfern, S.; Zabetakis, I. Bioprospecting for Antithrombotic Polar Lipids from Salmon, Herring, and Boarfish By-Products. Foods 2019, 8, 416. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8090416
Tsoupras A, O’Keeffe E, Lordan R, Redfern S, Zabetakis I. Bioprospecting for Antithrombotic Polar Lipids from Salmon, Herring, and Boarfish By-Products. Foods. 2019; 8(9):416. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8090416
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsoupras, Alexandros, Eoin O’Keeffe, Ronan Lordan, Shane Redfern, and Ioannis Zabetakis. 2019. "Bioprospecting for Antithrombotic Polar Lipids from Salmon, Herring, and Boarfish By-Products" Foods 8, no. 9: 416. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8090416
APA StyleTsoupras, A., O’Keeffe, E., Lordan, R., Redfern, S., & Zabetakis, I. (2019). Bioprospecting for Antithrombotic Polar Lipids from Salmon, Herring, and Boarfish By-Products. Foods, 8(9), 416. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8090416