Cyclospora Cayetanensis—Major Outbreaks from Ready to Eat Fresh Fruits and Vegetables
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Historic Taxonomy and Molecular Characteristics
3. Infection
4. Cyclosporiasis Outbreaks
4.1. Raspberries
- United States and Canada, 1996
- United States and Canada, 1997
- Canada, 1998
- United States (Pennsylvania), 2000
4.2. Basil
- United States, 1997
- United States, 1999
- United States, 2019
4.3. Snow Peas
- United States (Pennsylvania), 2004
4.4. Cilantro
- United States (Iowa, Nebraska/Texas), 2013
4.5. Green Onions
- United States (Texas), 2017
4.6. Salads
- Germany, 2000
- United States, 2020
5. Travel Associated Cases
- Australia 2010
- UK and Canada, 2015
6. Control and Prevention
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global Burden of Diseases (GBD). Estimates of the global, regional, and national morbidity, mortality, and aetiologies of diarrhoea in 195 countries: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 1211–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Diarrhoeal Disease. Available online: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diarrhoeal-disease (accessed on 2 February 2020).
- Di Genova, B.M.; Tonelli, R.R. Infection strategies of intestinal parasite pathogens and host cell responses. Front. Microbiol 2016, 7, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, Y.R.; Sanchez, R. Update on Cyclospora cayetanensis, a food-borne and waterborne parasite. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 218–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lainson, R. The genus Cyclospora: (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae), with a description of Cyclospora schneideri n.sp. in the snake Anilius scytale (Anilüdae) from Amazonian Brazil—A review. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2005, 100, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chacín-Bonilla, L. Cyclospora cayetanensis. In Global Water Pathogens Project; Rose, J.B., Jimenez-Cisneros, B., Eds.; Michigan State University: East Lansing, MI, USA, 2017; pp. 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Beuchat, L.R.; World Health Organization (WHO). Surface Decontamination of Fruits and Vegetables Eaten Raw: A Review; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Levine, N.D. Taxonomy and life cycles of coccidia. In The Biology of the Coccidia; Long, P.L., Ed.; Edward Arnold: London, UK, 1982; pp. 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, H.A.; Molyneux, D.H. Developmental stages of Cyclospora talpae in the liver and bile duct of the mole (Talpa europa). Parasitology 1990, 101, 345–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashford, R.W. Occurrence of an undescribed coccidian in man in Papua New Guinea. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1979, 73, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soave, R.; Dubey, J.P.; Ramos, L.J.; Tummings, M. A new intestinal pathogen? Clin. Res. 1986, 34, 533. [Google Scholar]
- Naranjo, J.; Sterling, C.R.; Gilman, R. Cryptosporidium muris-like objects from fecal samples of Peruvians. In Proceedings of the 38th Annual Meeting of the American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, Honolulu, HI, USA, 10–14 December 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Long, E.G.; Ebrahimzadeh, A.; White, E.H.; Swisher, B.; Callaway, C.S. Alga associated with diarrhea in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and in travelers. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1990, 28, 1101–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, E.G.; White, E.H.; Carmichael, W.W.; Quinlisk, P.M.; Raja, R.; Swisher, B.L.; Daugharty, H.; Cohen, M.T. Morphologic and staining characteristics of a cyanobacterium-like organism associated with diarrhea. J. Infect. Dis. 1991, 164, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendall, R.P.; Lucas, S.; Moody, A.; Tovey, G.; Chiodini, P.L. Diarrhea associated with cyanobacterium-like bodies: A new coccidian enteritis of man. Lancet 1993, 341, 590–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, B.A.; Shlim, D.R.; Scholes, J.V.; Rayburn, J.L.; Reidy, J.; Rajah, R. Pathologic changes in the small bowel in nine patients with diarrhea associated with a coccidia-like body. Ann. Intern. Med. 1993, 119, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, Y.R.; Sterling, C.R.; Gilman, R.H.; Cama, V.A.; Diaz, F. Cyclospora species—A new protozoan pathogen of humans. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 328, 1308–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, Y.R.; Gilman, R.H.; Sterling, C.R. A new coccidian parasite (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae) from humans. J. Parasitol. 1994, 80, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Chang, Y.; Shi, K.E.; Wang, R.; Fu, K.; Li, S.; Xu, J.; Jia, L.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, L. Multilocus sequence typing and clonal population genetic structure of Cyclospota cayetanensis in humans. Parasitology 2017, 144, 1890–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinar, H.N.; Gopinath, G.K.; Jarvis, K.; Murphy, H.R. The complete mitochondrial genome of the foodborne parasitic pathogen Cyclospora cayetanensis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.H.; Cong, M.M.; Bian, Q.Q.; Cheng, W.Y.; Wang, R.J.; Qi, M.; Zhang, L.X.; Lin, Q.; Zhu, X.Q. Molecular characterization of Cyclospora-like organisms from golden snub-nosed monkeys in Qinling Mountain in Shaanxi province, northwestern China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinar, H.N.; Qvarnstrom, Y.; Wei-Pridgeon, Y.; Li, W.; Nascimento, F.S.; Arrowood, M.J.; Murphy, H.R.; Jang, A.Y.; Kim, E.; Kim, R.Y.; et al. Comparative sequence analysis of Cyclospora cayetanensis apicoplast genomes originating from diverse geographical regions. Parasit. Vectors 2016, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, I.M.; Torres, P.; Simpson, S.; Kerdahi, K.; Ortega, Y. Sequence characterization of heat shock protein gene of Cyclospora cayetanensis isolates from Nepal, Mexico, and Peru. J. Parasitol. 2013, 99, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, I.M.; Ortega, Y.; Simpson, S.; Kerdahi, K. Genetic characterization of human-pathogenic Cyclospora cayetanensis parasites from three endemic regions at the 18S ribosomal RNA locus. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 22, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhard, M.L.; Da Silva, A.J.; Lilley, B.G.; Pieniazek, N.J. Morphologic and molecular characterization of new Cyclospora species from Ethiopian monkeys: C. cercopitheci sp.n., C. colobi sp.n., and C. papionis sp.n. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1999, 5, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhard, M.L.; Njenga, M.N.; DaSilva, A.J.; Owino, D.; Nace, E.K.; Won, K.Y.; Mwenda, J.M. A survey for Cyclospora spp. in Kenyan primates, with some notes on its biology. J. Parasitol. 2001, 87, 1394–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiman, D.A.; Schmidt, T.M.; Gajadhar, A.; Sogin, M.; Cross, J.; Yoder, K.; Sethabutr, O.; Echeverria, P. Molecular phylogenetic analysis of Cyclospora, the human intestinal pathogen, suggests that it is closely related to Eimeria species. J. Infect. Dis. 1996, 173, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, B.R.; Bussey, J.M.; Parrington, L.J.; Parenteau, M. Cyclospora cayetanensis oocysts in human fecal specimens by flow cytometry. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 2375–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers of Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Epidemiology & Risk Factors Parasites—Cyclosporiasis (Cyclospora Infection). 2018. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/cyclosporiasis/epi.html. (accessed on 10 May 2019).
- Herwaldt, B.L. Cyclospora cayetanensis: A review, focusing on the outbreaks of cyclosporiasis in the 1990s. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 31, 1040–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Braiken, F.A.; Amin, A.; Beeching, N.J.; Hommel, M.; Hart, C.A. Detection of Cryptoporidium amongst diarrhoeic and asymptomatic children in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 2003, 97, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shlim, D.R.; Cohen, M.T.; Eaton, M.; Rajah, R.; Long, E.G.; Ungar, B.L. An alga-like organism associated with an outbreak of prolonged diarrhea among foreigners in Nepal. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1991, 45, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sifuentes-Osornio, J.; Porras-Cortes, G.; Bendall, R.P.; Morales-Villarreal, F.; Reyes-Teran, G.; Ruiz-Palacios, G.M. Cyclospora cayetanensis infection in patients with and without AIDS: Biliary disease as another clinical manifestation. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1995, 21, 1092–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, J.M.; Olson, B.H. Cyclospora cayetanensis: A review of an emerging parasitic coccidian. Int. J. Parasitol. 2003, 33, 371–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalonde, L.F.; Gajadhar, A.A. Detection and differentiation of coccidian oocysts by real-time PCR and melting curve analysis. J. Parasitol. 2011, 97, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Roellig, D.M.; Li, N.; Tang, K.; Frace, M.; Ortega, Y.; Arrowood, M.J.; Feng, Y.; Qvarnstrom, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. Multilocus sequence typing tool for Cyclospora cayetanensis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1464–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, F.S.; Barta, J.R.; Whale, J.; Hofstetter, J.N.; Casillas, S.; Barratt, J.; Talundzic, E.; Arrowood, M.J.; Qvarnstrom, Y. Mitochondrial junction region as genotyping marker for Cyclospora cayetanensis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 1314–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, R.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, L. Cyclospora cayetanensis infection in humans: Biological characteristics, clinical features, epidemiology, detection method and treatment. Parasitology 2019, 147, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herwaldt, B.L.; Ackers, M.L. An outbreak in 1996 of cyclosporiasis associated with imported raspberries. The Cyclospora Working Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 336, 1548–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers of Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Update: Outbreaks of Cyclospora cayetanensis Infection --United States and Canada, 1996. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 1996, 45, 611–612. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/00043133.htm (accessed on 2 May 2019).
- Centers of Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Update: Outbreaks of Cyclosporiasis—United States and Canada, 1997. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 1997, 46, 521–523. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/00047875.html (accessed on 20 April 2019).
- Centers of Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Outbreak of Cyclosporiasis—Ontario, Canada, May 1998. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 1998, 47, 806–809. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/00055016.htm (accessed on 21 April 2019).
- Ho, A.Y.; Lopez, A.S.; Eberhart, M.G.; Levenson, R.; Finkel, B.S.; Da Silva, A.J.; Roberts, J.M.; Orlandi, P.A.; Johnson, C.C.; Herwaldt, B.L. Outbreak of Cyclosporiasis Associated with Imported Raspberries, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, 2000. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 783–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers of Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Outbreak of Cyclosporiasis—Northern Virginia-Washington, D.C.-Baltimore, Maryland, Metropolitan Area, 1997. MMWR 1997, 46, 689–691. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/00048551.htm (accessed on 20 April 2019).
- Lopez, A.S.; Dodson, D.R.; Arrowood, M.J.; Orlandi, P.A., Jr.; Da Silva, A.J.; Bier, J.W.; Hanauer, S.D.; Kuster, R.L.; Oltman, S.; Baldwin, M.S.; et al. Outbreak of cyclosporiasis associated with basil in Missouri in 1999. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 32, 1010–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers of Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Outbreak of Cyclospora Infections Linked to Fresh Basil from Siga Logistics de RL de CV of Morelos, Mexico. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/cyclosporiasis/outbreaks/2019/weekly/index.html (accessed on 10 June 2019).
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Outbreak Investigation of Cyclospora Illnesses Linked to Imported Fresh Basil, July 2019. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/outbreaks-foodborne-illness/outbreak-investigation-cyclospora-illnesses-linked-imported-fresh-basil-july-2019?fbclid=IwAR2w11S3abe1uRmUtn9nRR_M9W8AsQnyx1yPJL_i2Nm2se4nsHbwL_8R_Z8 (accessed on 10 June 2019).
- Centers of Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Outbreak of Cyclosporiasis Associated with Snow Peas—Pennsylvania, 2004. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2004, 53, 876–878. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm5337a6.htm (accessed on 20 May 2019).
- Buss, B.F.; Joshi, M.V.; O’Keefe, A.L.; Allensworth, C.D.; Garvey, A.; Obbink, K.; Mandernach, S.; Safranek, T.J. Regional investigation of a cyclosporiasis outbreak linked to imported romaine lettuce - Nebraska and Iowa, June-August 2013. Epidemiol. Infect. 2016, 144, 1807–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers of Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Notes from the Field: Outbreaks of Cyclosporiasis—United States, June–August 2013. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2013, 62, 862. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4585602/ (accessed on 22 May 2019).
- Keaton, A.A.; Hall, N.B.; Chancey, R.J.; Heines, V.; Cantu, V.; Vakil, V.; Long, S.; Short, K.; Franciscus, E.; Wahab, N.; et al. Notes from the Field: Cyclosporiasis cases associated with dining at a Mediterranean-style restaurant chain—Texas, 2017. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2018, 67, 609–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doller, P.C.; Dietrich, K.; Filipp, N.; Brockmann, S.; Dreweck, C.; Vonthein, R.; Wagner-Wiening, C.; Wiedenmann, A. Cyclosporiasis outbreak in Germany associated with the consumption of salad. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 992–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers of Disease Control and Prevention. Parasites (CDC) Cyclosporiasis (Cyclospora Infection). Outbreak of Cyclospora Infections Linked to Bagged Salad Mix. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/cyclosporiasis/outbreaks/2020/ (accessed on 7 September 2020).
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Outbreak Investigation of Cyclospora: Bagged Salads (June 2020). Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/outbreaks-foodborne-illness/outbreak-investigation-cyclospora-bagged-salads-june-2020 (accessed on 7 September 2020).
- Gibbs, R.A.; Nanyonjo, R.; Pingault, N.M.; Combs, B.G.; Mazzucchelli, T.; Armstrong, P.; Tarling, G.; Dowse, G.K. An outbreak of Cyclospora infection on a cruise ship. Epidemiol. Infect. 2013, 141, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, G.L.; Freedman, J.; Pollock, K.G.; Rumble, C.; Chalmers, R.M.; Chiodini, P.; Hawkins, G.; Alexander, C.L.; Godbole, G.; Williams, C.; et al. Cyclospora infection linked to travel to Mexico, June to September 2015. Euro Surveill. 2015, 20, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herwaldt, B.L.; Beach, M.J. The return of Cyclospora in 1997: Another outbreak of cyclosporiasis in North America associated with imported raspberries. Ann. Intern. Med. 1999, 130, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). U.S. Foodborne Outbreaks of Cyclosporiasis—2000–2017. Cyclosporiasis. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/parasites/cyclosporiasis/outbreaks/foodborneoutbreaks.html (accessed on 11 February 2020).
- Hoang, L.M.N.; Fyfe, M.; Ong, C.; Harb, J.; Champagne, S.; Dixon, B.; Isaac-Renton, J. Outbreak of cyclosporiasis in British Columbia associated to imported Thai basil. Epidemiol. Infect. 2005, 133, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala-Gaytan, J.J.; Diaz-Olachea, C.; Riojas-Montalvo, P.; Palacios-Martinez, C. Cyclosporidiosis: Clinical and diagnostic characteristics of an epidemic outbreak. Rev. Gastroenterol. Mex. 2004, 69, 226–229. [Google Scholar]
- Botero-Garces, J.; Montoya-Palacio, M.N.; Barguil, J.I.; Castaño-González, A. Brote epidémico por Cyclospora cayetanensis en Medellín, Colombia. Rev. Salud Pública 2006, 8, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, G.K.; MacDonald, D.; Landry, L.; Farber, J.M. Foodborne outbreaks in Canada linked to produce: 2001 through 2009. J. Food Prot. 2013, 76, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puente, S.; Morente, A.; Garcia-Benayas, T.; Subirats, M.; Gascon, J.; Gonzalez-Lahoz, J.M. Cyclosporiasis: A point source outbreak acquired in Guatemala. J. Travel Med. 2006, 13, 334–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, R. Cyclospora outbreak in Florida, 2005. In Addressing Foodborne Threats to Health: Policies, Practices, and Global Coordination: Workshop Summary; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, L.; MacDougall, L.; Ellis, A.; Ong, C.; Shyng, S.; LeBlanc, L.; British Columbia Cyclospora Investigation Team. Challenges of investigating community outbreaks of cyclosporiasis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1286–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Insulander, M.; Svenungsson, B.; Lebbad, M.; Karlsson, L.; De Jong, B. A foodborne outbreak of Cyclospora infection in Stockholm, Sweden. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2010, 7, 1585–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foodborne Illness Outbreak Database. Available online: http://www.outbreakdatabase.com/ (accessed on 3 June 2019).
- Abanyie, F.; Harvey, R.R.; Harris, J.R.; Wiegand, R.E.; Gaul, L.; Desvignes-Kendrick, M.; Irvin, K.; Williams, I.; Hall, R.L.; Herwaldt, B.; et al. Multistate outbreaks of Cyclospora cayetanensis infections associated with fresh produce: Focus on the Texas investigations. Epidemiol. Infect. 2015, 143, 3451–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buss, B.F.; Joshi, M.V.; Dement, J.L.; Cantu, V.; Safranek, T.J. Multistate porduct traceforward investigation to link imported romaine lettuce to a US cyclosporoiasis outbreak—Nebraska, Texas, and Florida, June–August 2013. Epidemiol. Infect. 2016, 144, 2709–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers of Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Cyclosporiasis Outbreak Investigations—United States, 2014 Parasites—Cyclosporiasis (Cyclospora infection). 2014. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/cyclosporiasis/outbreaks/2014/index.html (accessed on 22 May 2019).
- Centers of Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Cyclosporiasis Outbreak Investigations—United States, 2015 Parasites—Cyclosporiasis (Cyclospora infection). 2015. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/cyclosporiasis/outbreaks/2015/index.html (accessed on 23 May 2019).
- Public Health Agency of Canada (PHCA). Public Health Notice—Outbreak of Cyclospora appears to be over. 2016. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/public-health-notices/2016/public-health-notice-outbreak-cyclospora.html (accessed on 3 June 2019).
- Centers of Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Multistate Outbreak of Cyclosporiasis Linked to Del Monte Fresh Produce Vegetable Trays—United States, 2018: Final Update. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/cyclosporiasis/outbreaks/2018/a-062018/index.html (accessed on 3 June 2019).
- Centers of Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Multistate Outbreak of Cyclosporiasis Linked to Fresh Express Salad Mix Sold at McDonald’s Restaurants—United States, 2018: Final Update. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/cyclosporiasis/outbreaks/2018/b-071318/index.html (accessed on 11 February 2020).
- Centers of Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Domestically Acquired Cases of Cyclosproriasis—United States, May–August 2018. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/parasites/cyclosporiasis/outbreaks/2018/c-082318/index.html (accessed on 11 February 2019).
- Centers of Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Domestically Acquired Cases of Cyclosporiasis—United States, May–July 2019. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/cyclosporiasis/outbreaks/2019/a-050119/index.html (accessed on 10 June 2019).
- Almeira, S.; Cinar, H.N.; Dubey, J.P. Cyclospora cayetanensis and Cyclosporiasis: An Update. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathyanarayanan, L.; Ortega, Y. Effects of temperature and different food matrices on Cyclospora cayetanensis oocyst sporulation. J. Parasitol. 2006, 92, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, E.M.; Ahmed, S.A.; Mokhtar, A.B.; Elzagawy, S.M.; Yahi, S.H.; Hussein, A.M.; El-Tantawey, F. Antiprotozoal activity of magnesium oxide (MgO) nanoparticles against Cyclospora cayetanensis oocysts. Parasitol. Int. 2018, 67, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Zawawy, L.A.; El-Said, D.; Ali, S.M.; Fathy, F.M. Disinfection efficacy of sodium dichloroisocyanurate(NADCC) against common food-borne intestinal protozoa. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 2010, 40, 165–185. [Google Scholar]
- Gérard, C.; Franssen, F.; La Carbona, S.; Monteiro, S.; Cozma-Petruţ, A.; Utaaker, K.S.; Jambrakg, A.R.; Rowanh, N.; Rodríguez-Lazaroi, D.; Nasserj, A.; et al. Inactivation of parasite transmission stages: Efficacy of treatments on foods of non-animal origin. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 91, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.B.; Lee, E.H. Coccidial contamination of raspberries: Mock contamination with Eimeria acervulina as a model for decontamination treatment studies. J. Food Protect. 2001, 64, 1854–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kniel, K.E.; Shearer, A.E.H.; Cascarino, J.L.; Wilkins, G.C.; Jenkins, M.C. High hydrostatic pressure and UV light treatment of produce contaminated with Eimeria acervulina as a Cyclospora cayetanensis surrogate. J. Food Protect. 2007, 70, 2837–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrant, R.L.; DeBoer, M.D.; Scharf, R.J.; Lima, A.A. The impoverished gut-a triple burden of diarrhoea, stunting and chronic disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, D.F.P.; Alexander, C.L.; Chalmers, R.M.; Elson, R.; Freedman, J.; Hawkins, G.; Lo, J.; Robinson, G.; Russell, K.; Smith-Palmer, A.; et al. Cyclosporiasis in travelers returning to the United Kingdom from Mexico in summer 2017: Lessons from the recent past to inform the future. Euro Surveill. 2017, 22, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Casillas, S.M.; Bennett, C.; Straily, A. Notes from the Field: Multiple Cyclosporiasis Outbreaks—United States. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2018, 67, 1101–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoge, C.W.; Shlim, D.R.; Ghimire, M.; Rabold, J.G.; Pandey, P.; Walch, A.; Rajah, R.; Gaudio, P.; Echeverria, P. Placebo-controlled trial of co-trimoxazole for Cyclospora infections among travelers and foreign residents in Nepal. Lancet 1995, 345, 691–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
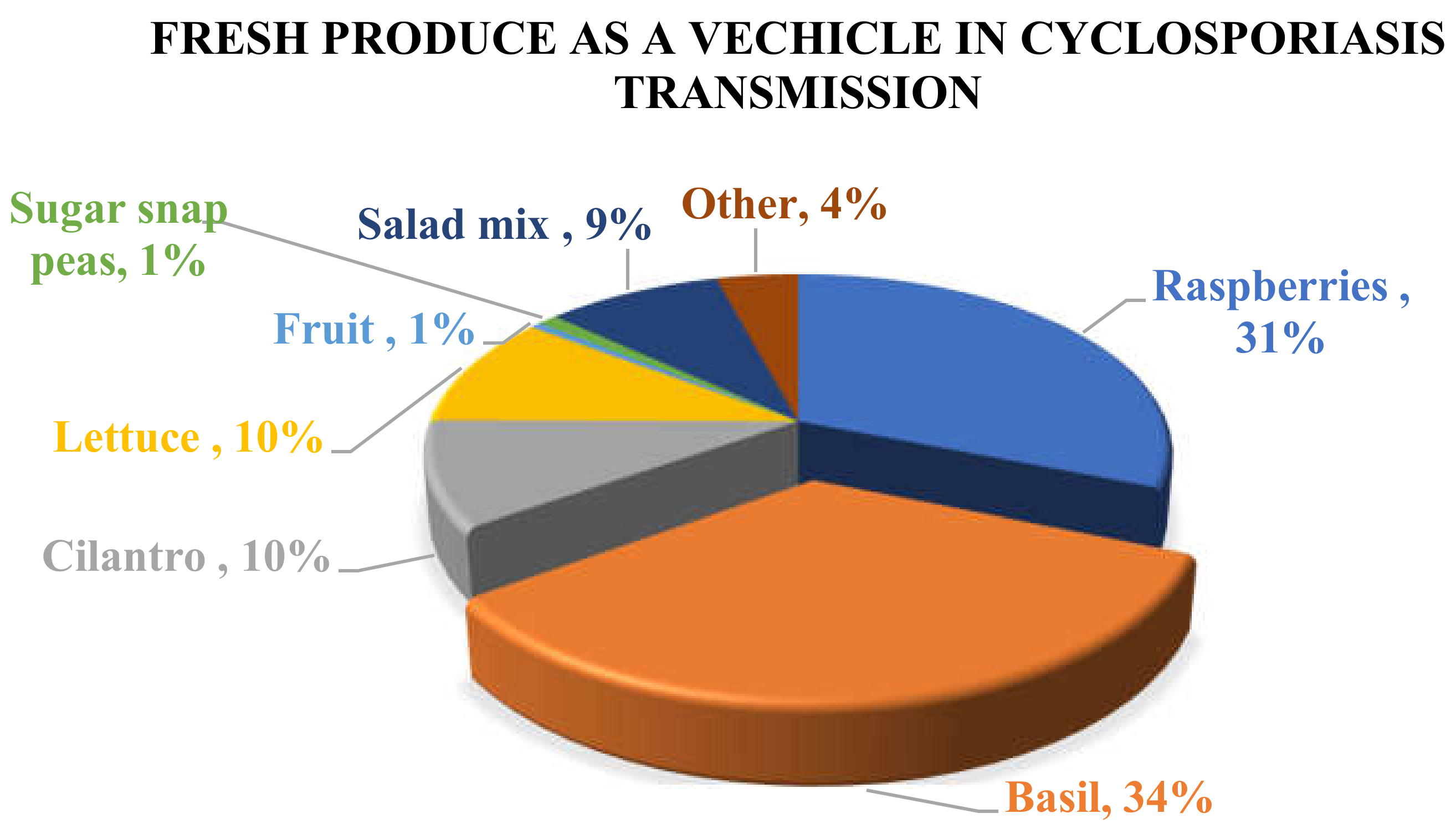
| Date | Area | Number of Cases | Vehicle | Origin | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1995 May | USA (Florida) | 38 | Raspberries a | Guatemala a | [30] |
| 1995 May–June | USA (New York) | 32 | Fruit a | UD b | [30] |
| 1997 May–June | USA (Florida) | 305 a | Mesclun a | Peru or US a | [30] |
| 1997 September | USA (Virginia) | 21 | Fruit plate | UD | [30] |
| 1997 April–June | USA Canada | 1021 | Raspberries | Guatemala | [57] |
| 1998 May | USA (Georgia) | 17 | Fruit salad a | UD | [30] |
| 1999 May | USA (Florida) | 94 | Fruit/raspberries a | UD | [30] |
| 1999 | Canada | 104 | Blackberries a | Guatemala | [39] |
| 2000 May | USA (Georgia) | 19 | Raspberries and/or Blackberries a | Guatemala a | [58] |
| 2001 January–June | Canada (British Columbia) | 30 | Thai basil | UD | [59] |
| 2001 April | Mexico (Monterrey) | 97 | Watercress | UD | [60] |
| 2001 May | Canada (British Columbia) | 17 | Thai basil | Vietnam | [59] |
| 2002 April | Colombia (Medellin) | 56 | Salads, juice | UD | [61] |
| 2003 July | Canada (British Columbia) | 11 | Cilantro a | UD | [62] |
| 2003 May | Spain (Madrid) | 13 | Raspberry juice c | Guatemala | [63] |
| 2004 May–June | Canada (British Columbia) | 8 | Cilantro a | UD | [62] |
| 2004 | Canada (British Columbia) | 17 | Mango or basil a | UD | [62] |
| 2005 April | Canada (Ontario) | 44 | Basil a | Peru, Costa Rica | [62] |
| 2005 April | United States (Florida) | 592 | Fresh basil a | Peru | [64] |
| 2005 June | Canada (Quebec) | 250 | Basil a | Mexico | [62] |
| 2005 June | USA (Connecticut) | 30 | Basil a | UD | [58] |
| 2006 June–July | Canada (British Columbia) | 28 | Basil or garlic | UD | [62] |
| 2007 June | Canada (British Columbia) | 23 | Organic basil a | Mexico | [65] |
| 2008 March | USA (Wisconsin) | 4 | Sugar snap peas a | Guatemala a | [58] |
| 2008 | USA (California) | 45 | Raspberries and/or Blackberries a | UD | [58] |
| 2009 May–June | Sweden (Stockholm) | 18 | Sugar snap peas | Guatemala | [66] |
| 2010 May | Canada (Ontario) | 210 | Fresh basil a | UD | [67] |
| 2013 June–August | USA (Texas) | 270 | Cilantro | Mexico | [68] |
| 2013 July | USA (Wisconsin) | 8 | Berry salad a | UD | [58] |
| 2014 June–August | USA (25 states) | 631 | Romaine Lettuce | Mexico | [69] |
| 2014 August | USA (19 states) | 304 | Fresh cilantro | Mexico (Puebla) | [70] |
| 2015 May | USA (31 states) | 546 | Fresh cilantro | Mexico (Puebla) | [71] |
| 2016 May–August | Canada (British Columbia, Alberta, Ontario, Quebec) | 87 | Fresh produce a | UD | [72] |
| 2018 May–June | USA (Minnesota, Wisconsin, Michigan, Iowa) | 250 | Vegetable trays d | UD | [73] |
| 2018 (May–July) | USA (16 states) | 511 | Salad mix | Illinois | [74] |
| 2018 June | USA (2 states) | 8 | Basil | UD | [75] |
| 2018 May–August | USA | 53 | Cilantro | Mexican-style restaurants | [75] |
| 2019 May–August | USA (37 states, District of Columbia, and New York City) | 2408 | Basil | Mexico | [76] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hadjilouka, A.; Tsaltas, D. Cyclospora Cayetanensis—Major Outbreaks from Ready to Eat Fresh Fruits and Vegetables. Foods 2020, 9, 1703. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9111703
Hadjilouka A, Tsaltas D. Cyclospora Cayetanensis—Major Outbreaks from Ready to Eat Fresh Fruits and Vegetables. Foods. 2020; 9(11):1703. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9111703
Chicago/Turabian StyleHadjilouka, Agni, and Dimitris Tsaltas. 2020. "Cyclospora Cayetanensis—Major Outbreaks from Ready to Eat Fresh Fruits and Vegetables" Foods 9, no. 11: 1703. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9111703
APA StyleHadjilouka, A., & Tsaltas, D. (2020). Cyclospora Cayetanensis—Major Outbreaks from Ready to Eat Fresh Fruits and Vegetables. Foods, 9(11), 1703. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9111703






