A Novel Pseudomonas geniculata AGE Family Epimerase/Isomerase and Its Application in d-Mannose Synthesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains, Chemicals, and Enzymes
2.2. Construction of Recombinant Plasmid
2.3. Expression of Recombinant P. geniculata AGEase
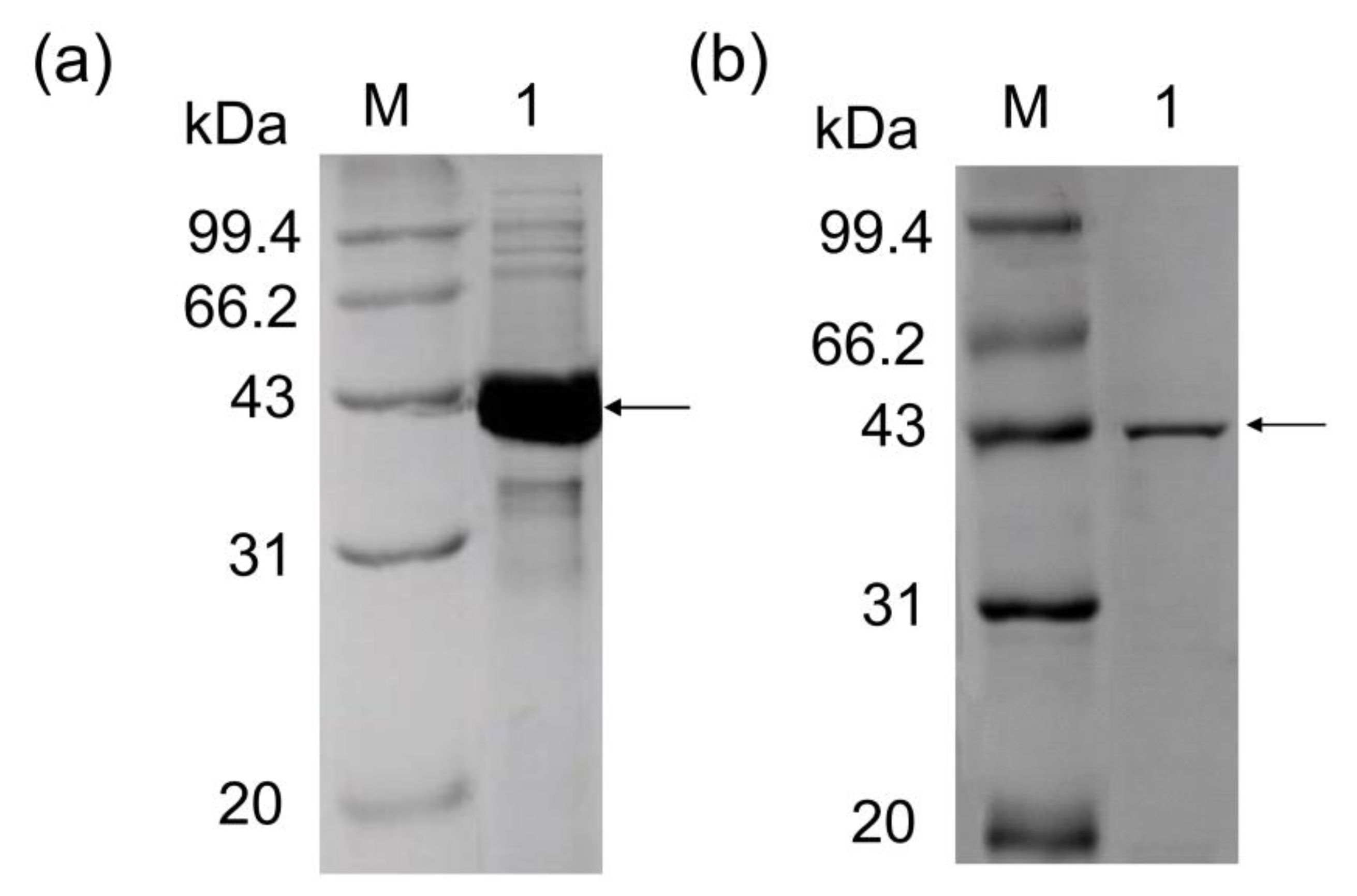
2.4. Purification of Recombinant P. geniculata AGEase
2.5. Recombinant P. geniculata AGEase Activity Assay
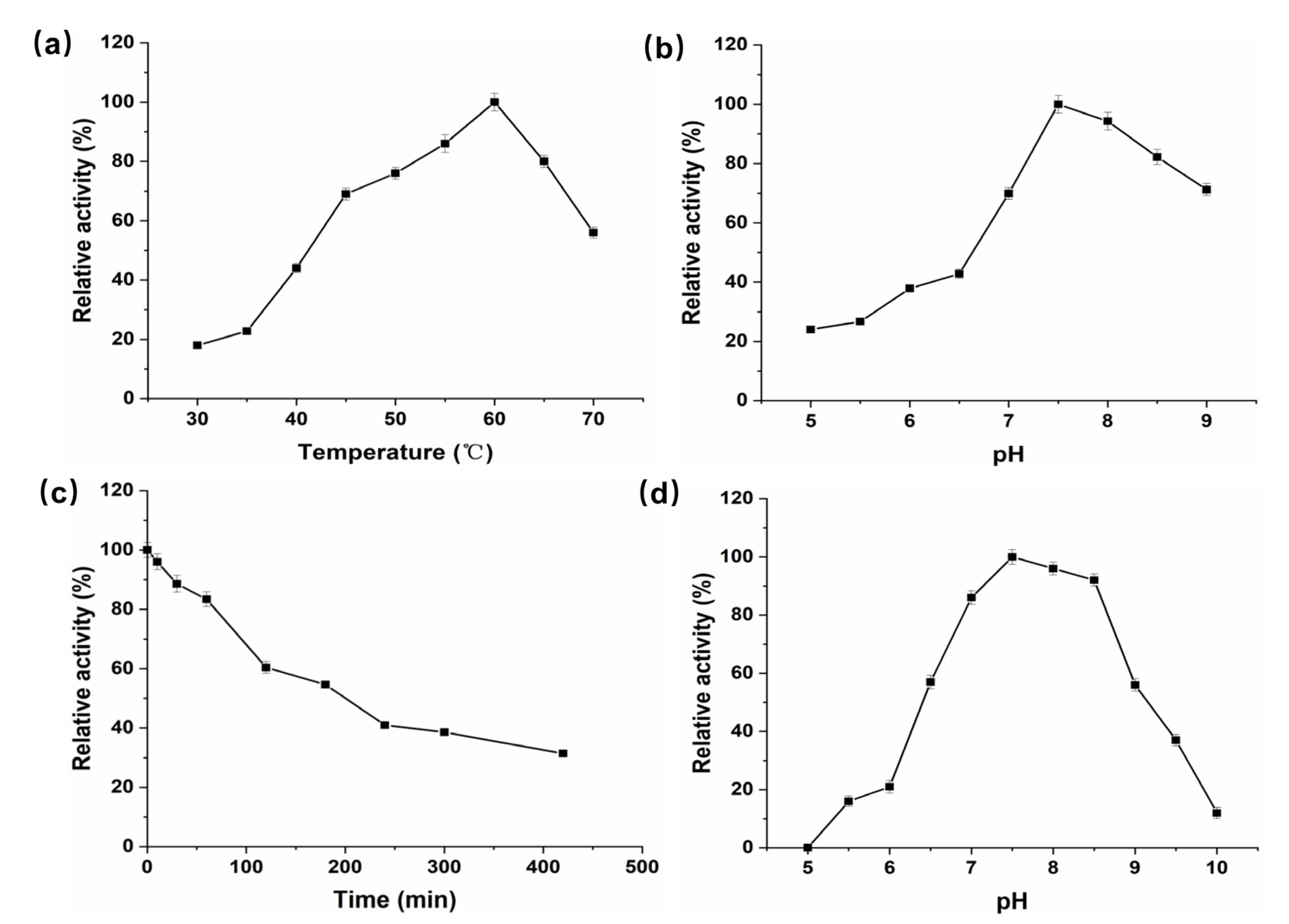
2.6. Characterization of Purified P. geniculata AGEase
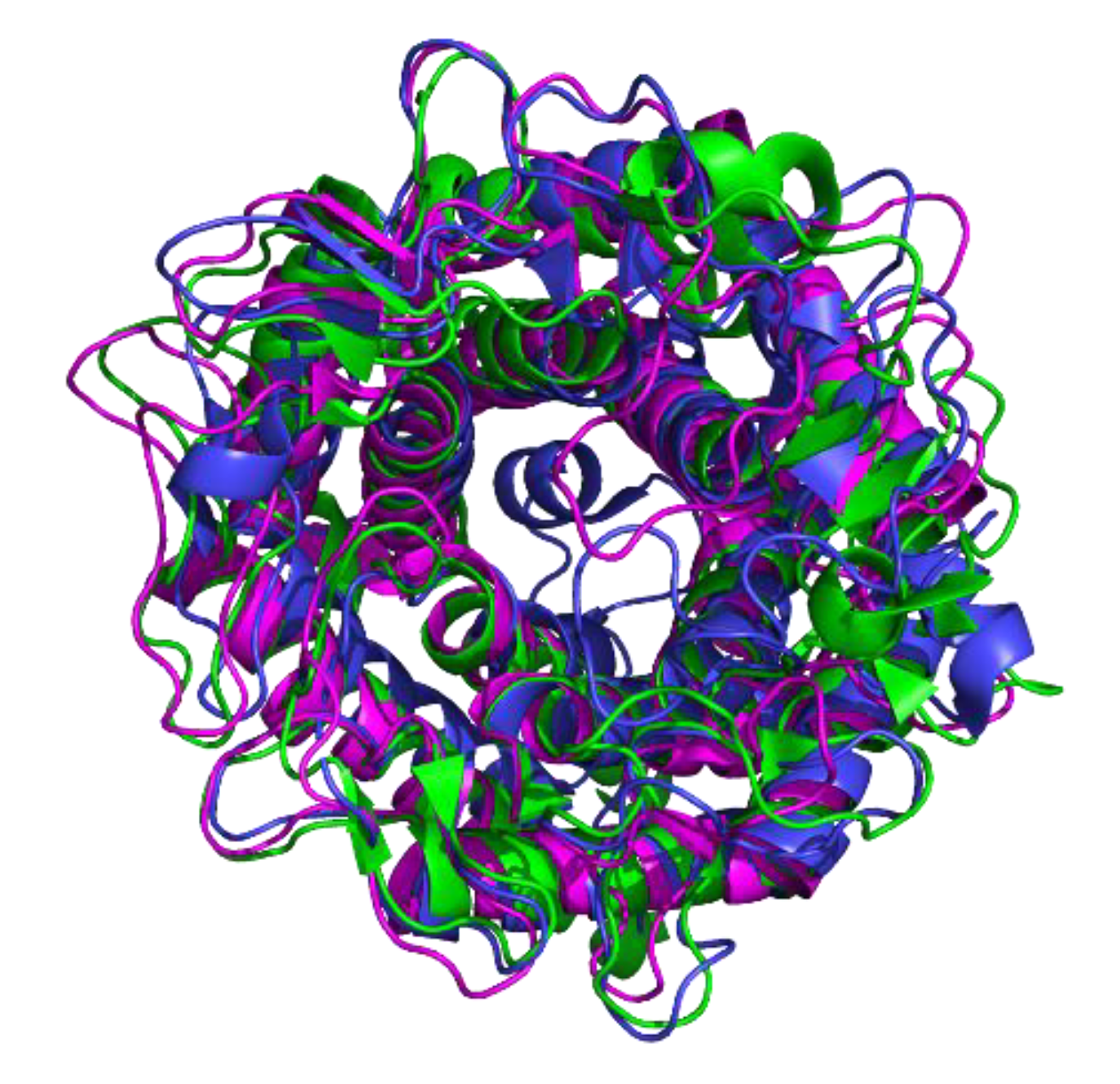
2.7. Structure Modeling
2.8. Determination of the Kinetic Parameters
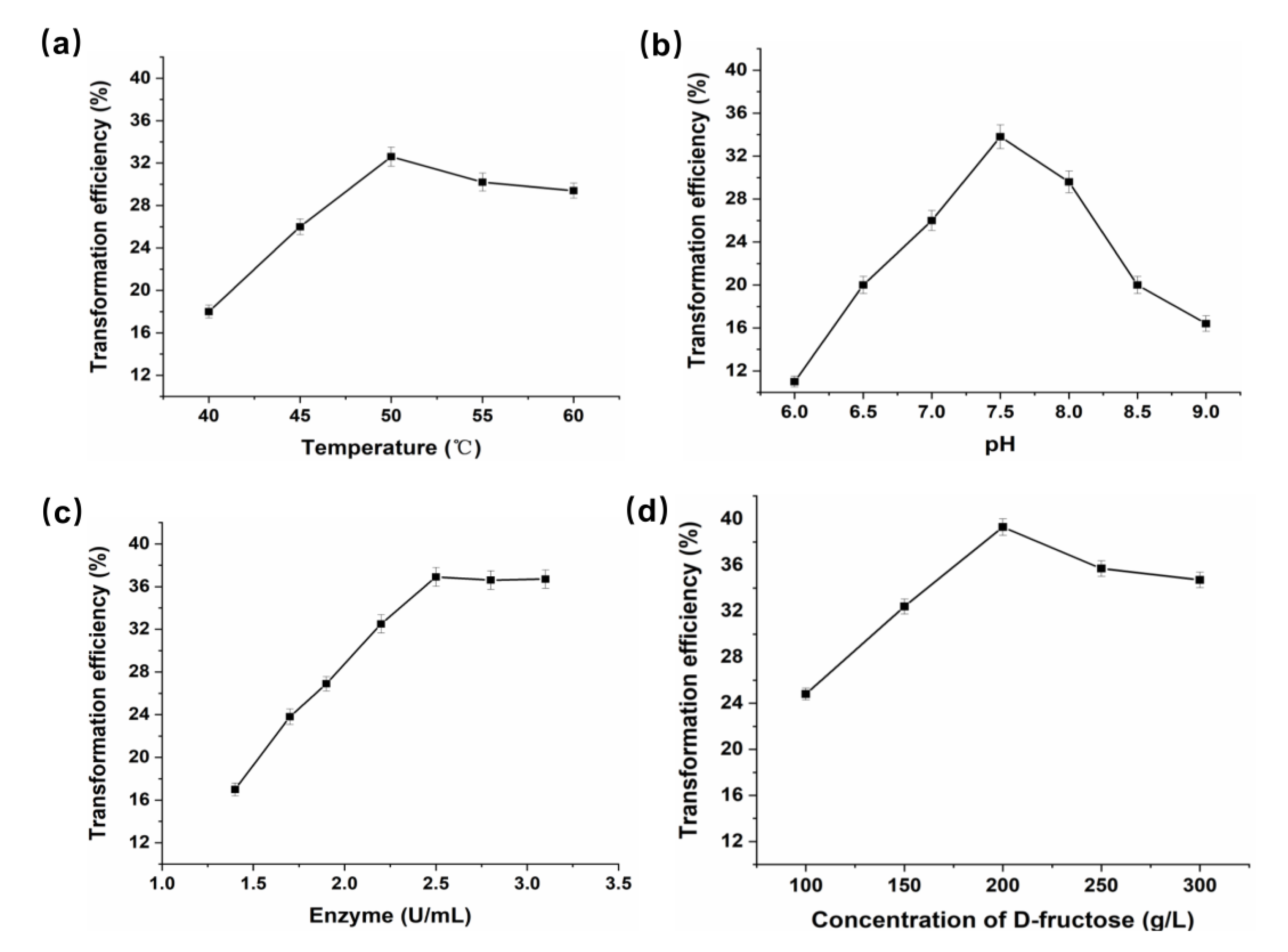
2.9. Production of d-Mannose from d-Fructose by P. geniculata AGEase
2.10. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Analysis of Products
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Cloning and Expression of P. geniculata AGEase
3.2. Purification of P. geniculata AGEase and Identification of Biochemical Properties
3.3. P. geniculata AGEase Substrate Specificity
3.4. Preparation of D-Mannose Using P. geniculata AGEase with d-Fructose as Substrate
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, P.; Miao, M.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, B. d-Mannose: Properties, production, and applications: An overview. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ichikawa, M.; Scott, D.A.; Losfeld, M.E.; Freeze, H.H. The metabolic origins of mannose in glycoproteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 6751–6761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, W.; Mu, W. Recent studies on the biological production of d-mannose. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 8753–8761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scribano, D.; Sarshar, M.; Prezioso, C.; Lucarelli, M.; Angeloni, A.; Zagaglia, C.; Palamara, A.T.; Ambrosi, C. d-Mannose treatment neither affects uropathogenic Escherichia coli properties nor induces stable FimH modifications. Molecules 2020, 25, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sarshar, M.; Behzadi, P.; Ambrosi, C.; Zagaglia, C.; Palamara, A.T.; Scribano, D. FimH and anti-adhesive therapeutics: A disarming strategy against uropathogens. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B. Chemical characterization and ameliorating effect of polysaccharide from Chinese jujube on intestine oxidative injury by ischemia and reperfusion. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 48, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheyas, F.; Blankenship, S.M.; Young, E.; McFeeters, R. Dietary fibre content of thirteen apple cultivars. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1997, 75, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravantinos-Zafiris, G.; Oreopoulou, V.; Tzia, C.; Thomopoulos, C. Fibre fraction from orange peel residues after Pectin extraction. LWT 1994, 27, 468–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.H.; Wang, G.B.; Li, J.P.; Cao, Y.H. The orthogonal experiment analysis on the producing mannose from dextrose by catalyzig effect of ammonium molybdate. Contemp. Chem. Ind. 2005, 34, 39–41. [Google Scholar]
- Bicas, J.L.; Silva, J.C.; Dionísio, A.P.; Pastore, G.M. Biotechnological production of bioflavors and functional sugars. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 30, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.C.; Wu, H.M.; Chang, Y.N.; Wang, W.C.; Hsu, W.H. The central cavity from the (alpha/alpha)6 barrel structure of Anabaena sp. CH1 N-Acetyl-d-glucosamine 2-epimerase contains two key histidine residues for reversible conversion. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 367, 895–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, T.; Saburi, W.; Matsui, H.; Mori, H.; Yao, M. Structural insights into the epimerization of β-1,4-linked oligosaccharides catalyzed by cellobiose 2-epimerase, the sole enzyme epimerizing non-anomeric hydroxyl groups of unmodified sugars. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 3405–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Itoh, T.; Mikami, B.; Hashimoto, W.; Murata, K. Crystal structure of YihS in complex with d-Mannose: Structural annotation of Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica yihS-encoded proteins to an aldose–ketose isomerase. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 377, 1443–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palleroni, N.J.; Doudoroff, M. Mannose isomerase of Pseudomonas saccharophila. J. Biol. Chem. 1956, 218, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q. The construction of recombinant Escherichia coli of expression d-mannose ketol isomerase and study of enzymic characterization. Master’s thesis, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J. Study on d-mannose isomerase produced by Pseudomonas sp. No. 2120. Master’s thesis, Jiangnan University, Jiangsu, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Chen, M.; Guang, C.; Zhang, W.; Mu, W. Characterization of a recombinant d-mannose-producing d-lyxose isomerase from Caldanaerobius polysaccharolyticus. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2020, 138, 109553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.S.; Kim, J.E.; Choi, J.G.; Oh, D.K. Characterization of a recombinant cellobiose 2-epimerase from Caldicellulosiruptor saccharolyticus and its application in the production of mannose from glucose. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 92, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dische, Z.; Borenfreund, E. A new spectrophotometric method for the detection and determination of keto sugars and trioses. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 192, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Waterhouse, A.; Bertoni, M.; Bienert, S.; Studer, G.; Tauriello, G.; Gumienny, R.; Heer, F.T.; de Beer, T.A.P.; Rempfer, C.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W296–W303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 2.0 Schrodinger, LLC. Available online: https://pymol.org/2/ (accessed on 29 September 2020).
| Source | Substrate | Conditions | Transformation Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudomonas saccharophilad-MIase | 1.1 g/L d-fructose | 30 °C, pH 7.4 | 29.0 [14] |
| Agrobacterium radiobactord-MIase | 250 g/L d-fructose | 45 °C, pH 7.5, 2 h | 29.2 [15] |
| Pseudomonas sp. d-MIase | 200 g/L d-fructose | 55 °C, pH 7.5, 32 h | 36.7 [16] |
| Caldanaerobius polysaccharolyticusd-LIase | 100 g/L d-fructose | 65 °C, pH 6.5, 4 h | 25.6 [17] |
| Caldicellulosiruptor saccharolyticus CEase | 500 g/L d-glucose | 75 °C, pH 7.5, 3 h | 15.0 [18] |
| Substrates | Products | Transformation Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|
| d-glucose | d-fructose | 5.4 |
| d-fructose | d-mannose | 33.8 |
| d-mannose | d-fructose | 67.9 |
| d-xylulose | d-lyxose | 23.1 |
| d-lyxose | d-xylulose | 12.4 |
| cellobiose | N.D. | N.D. |
| d-xylose | N.D. | N.D. |
| N-acetyl-d-mannosamine | N.D. | N.D. |
| N-acetyl-d-glucosamine | N.D. | N.D. |
| Substrates | kcat (s−1) | Km (mM) | kcat/Km (s−1·mM−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| d-mannose | 476.3 ± 4.0 | 49.2 ± 8.5 | 9.7 ± 0.5 |
| d-fructose | 176.5 ± 1.2 | 117.0 ± 22.5 | 1.5 ± 0.1 |
| d-glucose | 67.2 ± 0.9 | 382.0 ± 88.1 | 0.2 ± 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Chen, S. A Novel Pseudomonas geniculata AGE Family Epimerase/Isomerase and Its Application in d-Mannose Synthesis. Foods 2020, 9, 1809. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9121809
Liu Z, Li Y, Wu J, Chen S. A Novel Pseudomonas geniculata AGE Family Epimerase/Isomerase and Its Application in d-Mannose Synthesis. Foods. 2020; 9(12):1809. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9121809
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zhanzhi, Ying Li, Jing Wu, and Sheng Chen. 2020. "A Novel Pseudomonas geniculata AGE Family Epimerase/Isomerase and Its Application in d-Mannose Synthesis" Foods 9, no. 12: 1809. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9121809
APA StyleLiu, Z., Li, Y., Wu, J., & Chen, S. (2020). A Novel Pseudomonas geniculata AGE Family Epimerase/Isomerase and Its Application in d-Mannose Synthesis. Foods, 9(12), 1809. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9121809




