Quality and Shelf-Life Modeling of Frozen Fish at Constant and Variable Temperature Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Material
2.2. Color Measurement
2.3. Total Volatile Basic Nitrogen (TVBN) Determination
2.4. Sensory Analysis
2.5. Microbiological Analysis
2.6. Data Analysis
- (a)
- A primary kinetic model, where values obtained from the different measured quality parameters were plotted vs. time for all the tested storage temperatures. The apparent order of quality loss was estimated, based on the least square statistical fit.
- (b)
- A secondary model, which reflects the effect of storage temperature on the parameters of the primary model. The temperature dependence of the deterioration rate constants, k, was modeled by the Arrhenius Equation (1)
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Frozen Storage on Appearance and Color of Fish Fillets
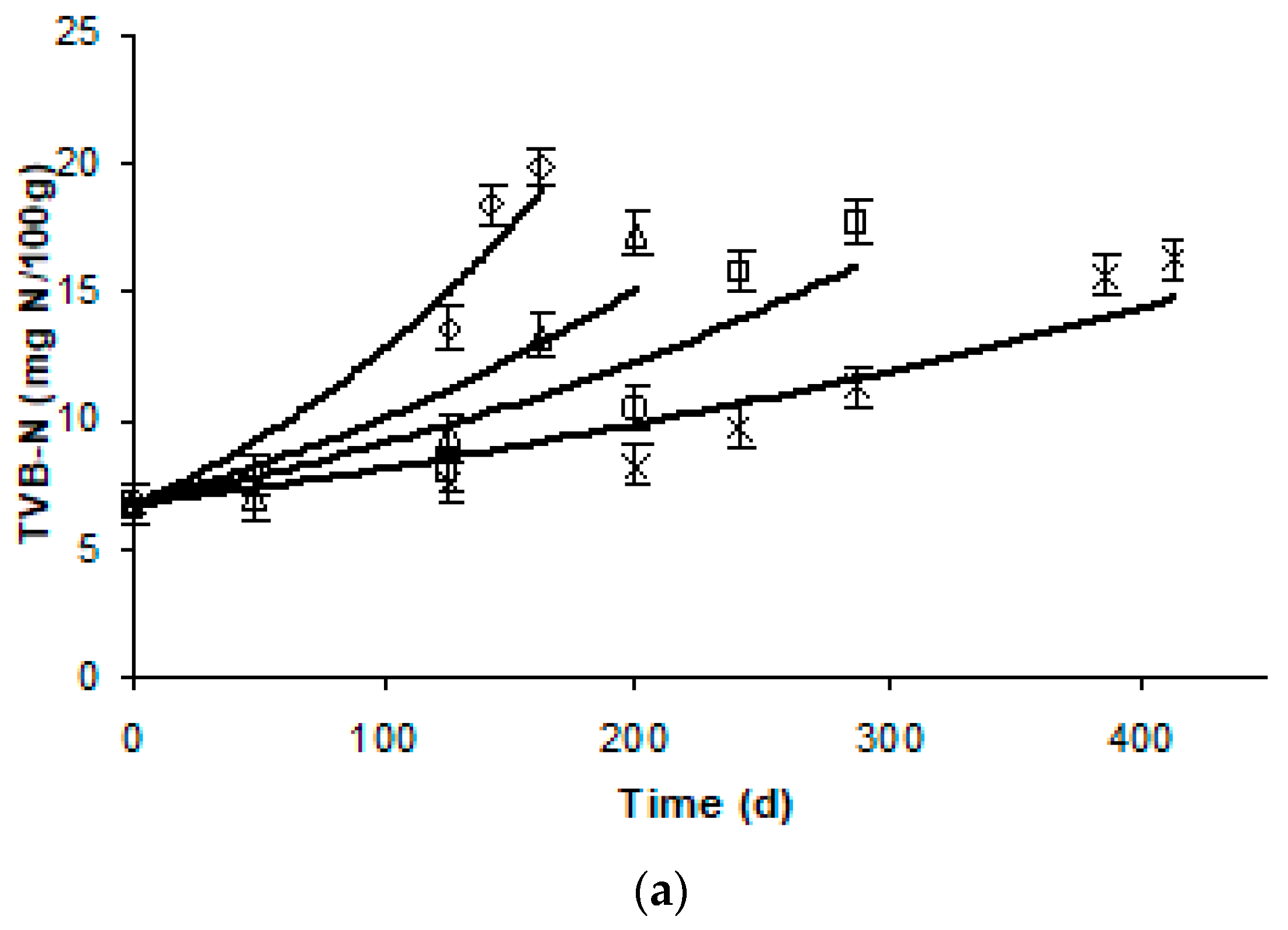
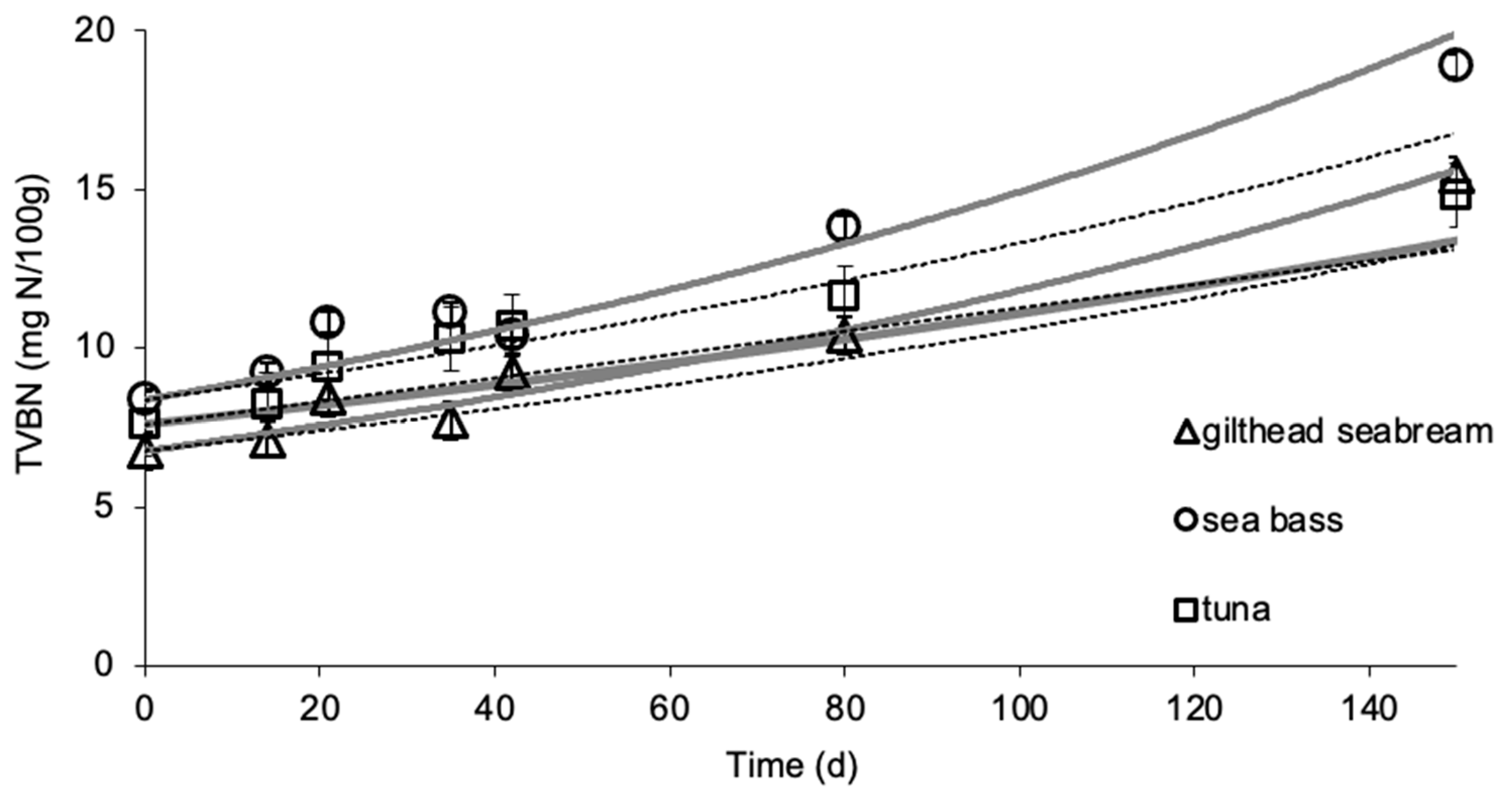
3.2. Effect of Frozen Storage on TVBN
3.3. Sensory Evaluation
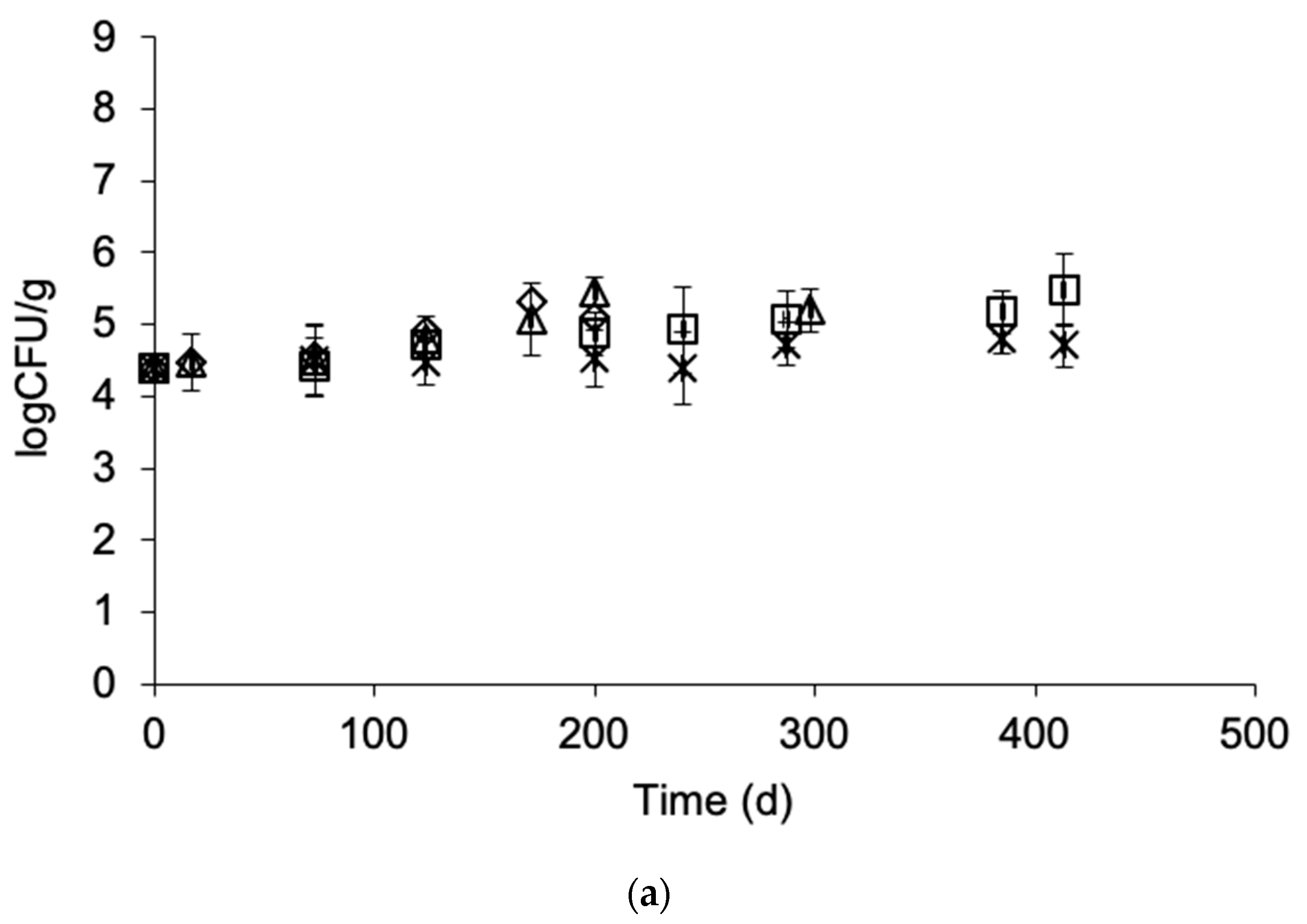
3.4. Effect of Frozen Storage on Microbial Load
3.5. Application of the Validated Models for Shelf-Life Prediction during the Distribution of Frozen Fish
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haard, N.F. Biochemical reactions in fish muscle during frozen storage. In Seafood Science and Technology; Bligh, E.G., Ed.; Fishing News Books: Oxford, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Rehbein, H. Measuring the shelf-life of frozen fish. In Safety and Quality Issues in Fish Processing; Bremner, H.A., Ed.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000; p. 407. [Google Scholar]
- Nikkilä, O.E.; Linko, R. Freezing, packaging and frozen storage of fish. J. Food Res. 1954, 21, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBlanc, E.L.; LeBlanc, R.J.; Blum, I.E. Prediction of quality in frozen cod (Gadus morhua). J. Food Sci. 1988, 53, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogou, E.; Katsaros, G.; Derens, E.; Alvarez, G.; Taoukis, P.S. Cold chain database development and application as a tool for the cold chain management and food quality evaluation. Int. J. Refrig. 2015, 52, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsironi, T.; Giannoglou, M.; Platakou, E.; Taoukis, P.S. Training of SMEs for frozen food shelf life testing and novel smart packaging application for cold chain monitoring. Int. J. Food Stud. 2015, 4, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronsivalli, L.J. A recommended procedure for assuring the quality of fish fillets at point of consumption. Mar. Fish. Rev. 1982, 44, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Giannoglou, M.; Touli, A.; Platakou, E.; Tsironi, T.; Taoukis, P.S. Predictive modeling and selection of TTI smart labels for monitoring the quality and shelf life of frozen seafood. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2014, 26, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licciardello, J.J.; Ravesi, E.M.; Lundstrom, R.C.; Wilhelm, K.A.; Correia, F.F.; Allsup, M.G. Time-temperature tolerance and physical-chemical quality tests for frozen red hake. J. Food Qual. 1982, 5, 215–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josephson, D.B.; Lindsay, R.C.; Stuiber, D.A. Effect of handling and packaging on the quality of frozen whitefish. J. Food Sci. 1985, 50, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurling, R.; McArthur, H. Thawing, refreezing and frozen storage effects on muscle functionality and sensory attributes of frozen cod (Gadus morhua). J. Food Sci. 1996, 61, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warm, K.; Boknaes, N.; Nielsen, J. Development of quality index methods for evaluation of frozen cod (Gadus morhua) and cod fillets. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 1998, 7, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-gigirey, B.; Vieites Baptista De Sousa, J.M.; Villa, T.G.; Barros-velazquez, J. Chemical changes and visual appearance of albacore tuna as related to frozen storage. J. Food Sci. 1999, 64, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderssen, K.E.; Stormo, S.K.; Skåra, T.; Skjelvareid, M.H.; Heia, K. Predicting liquid loss of frozen and thawed cod from hyperspectral imaging. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 133, 110093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymczak, M.; Kamiński, P.; Felisiak, K.; Szymczak, B.; Dmytrów, I.; Sawicki, T. Effect of constant and fluctuating temperatures during frozen storage on quality of marinated fillets from Atlantic and Baltic herrings (Clupea harengus). LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 133, 109961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sveinsdóttir, H.I.; Karlsdóttir, M.G.; Arason, S.; Stefánsson, G.; Sone, I.; Skåra, T.; Rustad, T.; Larsson, K.; Undeland, I.; Gudjónsdóttir, M. Effect of antioxidants on the sensory quality and physicochemical stability of Atlantic mackerel (Scomber scombrus) fillets during frozen storage. Food Chem. 2020, 321, 126744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, N.; Okazaki, E. Recent research on factors influencing the quality of frozen seafood. Fish. Sci. 2020, 86, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aubourg, S.P.; Medina, I. Influence of storage time and temperature on lipid deterioration during cod (Gadus morhua) and haddock (Melanogrammus aeglefinus) frozen storage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1999, 79, 1943–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsironi, T.; Dermesonlouoglou, E.; Giannakourou, M.; Taoukis, P. Shelf life modelling of frozen shrimp at variable temperature conditions. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 42, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taoukis, P.S.; Labuza, T.P. Applicability of time temperature indicators as shelf life monitors of food products. J. Food Sci. 1989, 54, 783–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakourou, M.C.; Taoukis, P.S. Systematic application of time temperature integrators as tools for control of frozen quality. J. Food Sci. 2002, 67, 2221–2228. [Google Scholar]
- Tsironi, T.; Giannoglou, M.; Platakou, E.; Taoukis, P. Evaluation of time temperature integrators for shelf-life monitoring of frozen seafood under real cold chain conditions. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2016, 10, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivarnik, L.; Ellis, P.; Wang, X.; Reilly, T. Standardization of the ammonia electrode method for evaluating seafood quality by correlation to sensory analysis. J. Food Sci. 2001, 66, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsironi, T.; Maltezou, I.; Tsevdou, M.; Katsaros, G.; Taoukis, P. High-pressure cold pasteurization of gilthead seabream fillets: Selection of process conditions and validation of shelf life extension. Food Bioprocess. Technol. 2015, 8, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakourou, M.C.; Stoforos, N.G. A theoretical analysis for assessing the variability of secondary model thermal inactivation kinetic parameters. Foods 2017, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giannakourou, M.; Taoukis, P. Holistic approach to the uncertainty in shelf life prediction of frozen foods at dynamic cold chain conditions. Foods 2020, 9, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, B.; Labuza, T.P. Shelf life testing: Procedures and prediction methods. In Quality in Frozen Food; Erickson, M.C., Hung, Y.C., Eds.; Chapman & Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1997; p. 377. [Google Scholar]
- Giannakourou, M.C.; Taoukis, P.S. Kinetic modelling of vitamin C loss in frozen green vegetables under variable storage conditions. Food Chem. 2003, 83, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakourou, M.C.; Taoukis, P.S. Meta-analysis of kinetic parameter uncertainty on shelf life prediction in the frozen fruits and vegetable chain. Food Eng. Rev. 2019, 11, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labuza, T.P. Application of chemical kinetics to deterioration of foods. J. Chem. Educ. 1984, 61, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taoukis, P.S.; Tsironi, T.N.; Giannakourou, M.C. Reaction kinetics, chapter 15. In Food Engineering Handbook: Food Engineering Fundamentals; Varzakas, T., Tzia, C., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 529–569. [Google Scholar]
- Oscar, T.P. Validation of lag time and growth rate models for Salmonella Typhimurium: Acceptable prediction zone method. J. Food Sci. 2005, 70, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, T.; Dalgaard, P.; Tienungoon, S. Predictive modeling of the growth and sur-vival of Listeria in fishery products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2000, 62, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, L.; Sun, Y.; Chen, S.; Wu, C.; Hu, Y. A study of fractal dimension as a quality indicator of hairtail (Trichiurus haumela) samples during frozen storage. Sci. Rep. 2018, 1, 16468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Yang, Z.; Gong, B.; Wang, J.; Xiao, K.; Yang, S.-T. Quality evaluation focusing on tissue fractal dimension and chemical changes for Frozen Tilapia with Treatment by Tangerine Peel Extract. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Deng, S.; Lin, H. Changes in the physicochemical and volatile flavor characteristics of scomberomorus niphonius during chilled and Frozen storage. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2012, 5, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Topic Popovic, N.; Skukan, A.B.; Dzidara, P.; Coz-Rakovac, R.; Strunjak-Perovic, I.; Kozacinski, L.; Jadan, M.; Brlek-Gorski, D. Microbiological quality of marketed fresh and frozen seafood caught off the Adriatic coast of Croatia. Vet. Med. 2010, 55, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Labuza, T.P.; Schmidl, M.K. Accelerated shelf-life testing of foods. Food Technol. 1985, 39, 57–62. [Google Scholar]








| L-Value | TVBN | Taste | Ov. Acceptability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gilthead sea bream fillets | Ea (kJ/mol) | 48.9 ± 2.1 a | 65.9 ± 7.0 a | 65.2 ± 2.8 a | 65.3 ± 14.9 a |
| R2 | 0.997 | 0.978 | 0.996 | 0.999 | |
| Sea bass fillets | Ea (kJ/mol) | 64.4 ± 6.4 a | 60.8 ± 2.7 a | 64.5 ± 2.7 a | 64.3 ± 0.5 a |
| R2 | 0.980 | 0.996 | 0.997 | 0.998 | |
| Yellowfin tuna slices | Ea (kJ/mol) | 83.9 ± 10.4 a | 69.9 ± 8.5 a | 69.4 ± 3.5 a | 77.9 ± 13.7 a |
| R2 | 0.970 | 0.971 | 0.995 | 0.942 |
| L-Value | TVBN | Taste | Ov. Acceptability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gilthead sea bream fillets | Af | 1.0012 | 1.0018 | 1.0061 | 1.0075 |
| Bf | 1.0015 | 0.9277 | 0.9447 | 0.9212 | |
| RE | −0.008 to 0.010 | −0.030 to 0.140 | 0.036 to 0.075 | 0.044 to 0.109 | |
| Sea bass fillets | Af | 1.0002 | 1.0051 | 1.0062 | 1.0048 |
| Bf | 1.0010 | 0.9079 | 1.0329 | 0.9743 | |
| RE | −0.011 to 0.008 | 0.022 to 0.046 | −0.073 to −0.010 | −0.029 to 0.077 | |
| Yellowfin tuna slices | Af | 1.0042 | 1.0046 | 1.0032 | 1.0029 |
| Bf | 1.0103 | 0.9093 | 0.9725 | 0.9606 | |
| RE | −0.0065 to 0.019 | 0.023 to 0.144 | −0.104 to −0.033 | −0.124 to 0.084 |
| L-Value | TVBN | Taste | Ov. Acceptability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gilthead sea bream fillets | Af | 1.0012 | 1.0019 | 1.0055 | 1.0076 |
| Bf | 1.0016 | 0.9292 | 0.9660 | 0.9199 | |
| RE | −0.007 to 0.008 | −0.027 to 0.144 | −0.025 to 0.062 | 0.044 to 0.110 | |
| Sea bass fillets | Af | 1.0003 | 1.0050 | 1.0064 | 1.0045 |
| Bf | 1.0014 | 0.9082 | 1.0337 | 0.9740 | |
| RE | −0.011 to 0.008 | 0.022 to 0.145 | −0.073 to −0.010 | −0.028 to 0.076 | |
| Yellowfin tuna slices | Af | 1.0030 | 1.0056 | 1.0047 | 1.0052 |
| Bf | 1.0094 | 0.9086 | 0.9821 | 0.9832 | |
| RE | −0.066 to 0.019 | −0.104 to −0.032 | −0.104 to −0.032 | −0.124 to 0.084 |
| −5 °C | −8 °C | −12 °C | −15 °C | −18 °C | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gilthead sea bream fillets | TVBN (limit = 15 mg N/100 g) | 130 | 182 | 287 | 408 | 586 |
| Sensory (limit = 5 score for overall acceptability) | 134 | 186 | 293 | 415 | 594 | |
| Sea bass fillets | TVBN (limit = 20 mg N/100 g) | 140 | 191 | 291 | 403 | 563 |
| Sensory (limit = 5 score for overall acceptability) | 133 | 185 | 290 | 408 | 580 | |
| Yellowfin tuna slices | TVBN (limit = 22 mg N/100 g) | 156 | 212 | 323 | 448 | 624 |
| Sensory (limit = 5 score for overall acceptability) | 152 | 208 | 320 | 445 | 623 |
| 1st Stage Duration: 25 Days | 2nd Stage Duration: 25 Days | 3rd Stage Duration: 50 Days | 4th Stage Duration: 50 Days | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Teff (°C) | −15.6 | −13.3 | −11.8 | −10.4 |
| Frozen gilthead sea bream fillets | ||||
| Sensory Scoring | 8.77 | 8.48 | 7.78 | 6.96 |
| RSLpredicted (d) | 391 | 361 | 288 | 204 |
| Frozen sea bass fillets | ||||
| Sensory Scoring | 8.72 | 8.25 | 7.61 | 6.85 |
| RSLpredicted (d) | 384 | 353 | 281 | 197 |
| Frozen yellowfin tuna slices | ||||
| Sensory Scoring | 8.79 | 8.50 | 7.80 | 6.95 |
| RSLpredicted (d) | 421 | 389 | 311 | 217 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsironi, T.N.; Stoforos, N.G.; Taoukis, P.S. Quality and Shelf-Life Modeling of Frozen Fish at Constant and Variable Temperature Conditions. Foods 2020, 9, 1893. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9121893
Tsironi TN, Stoforos NG, Taoukis PS. Quality and Shelf-Life Modeling of Frozen Fish at Constant and Variable Temperature Conditions. Foods. 2020; 9(12):1893. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9121893
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsironi, Theofania N., Nikolaos G. Stoforos, and Petros S. Taoukis. 2020. "Quality and Shelf-Life Modeling of Frozen Fish at Constant and Variable Temperature Conditions" Foods 9, no. 12: 1893. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9121893
APA StyleTsironi, T. N., Stoforos, N. G., & Taoukis, P. S. (2020). Quality and Shelf-Life Modeling of Frozen Fish at Constant and Variable Temperature Conditions. Foods, 9(12), 1893. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9121893






