Comparison of Chemical Composition and Safety Issues in Fish Roe Products: Application of Chemometrics to Chemical Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Chemical Analyses
2.3. Microbiological Analysis
2.4. Determination of Organic Acids
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
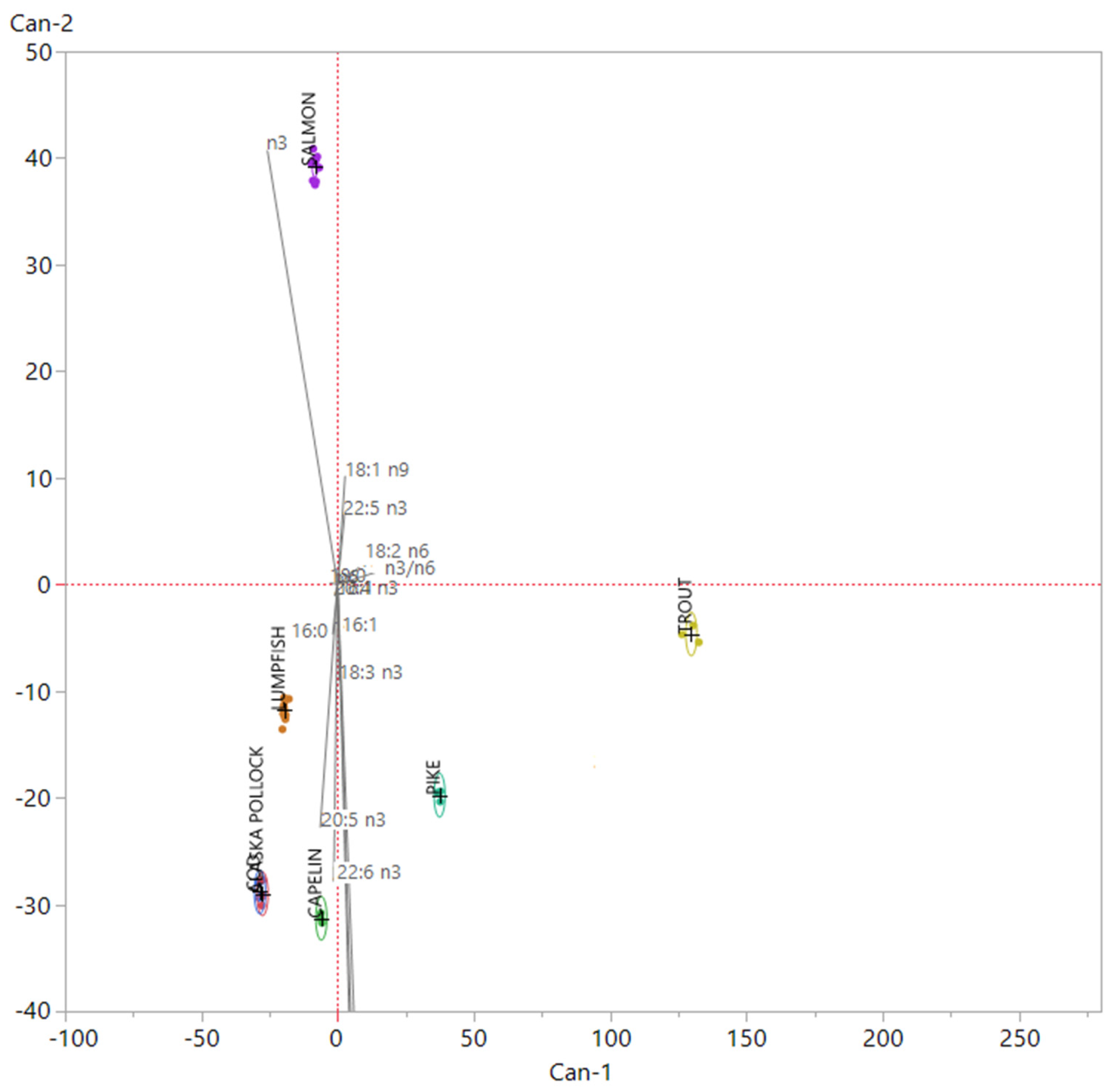
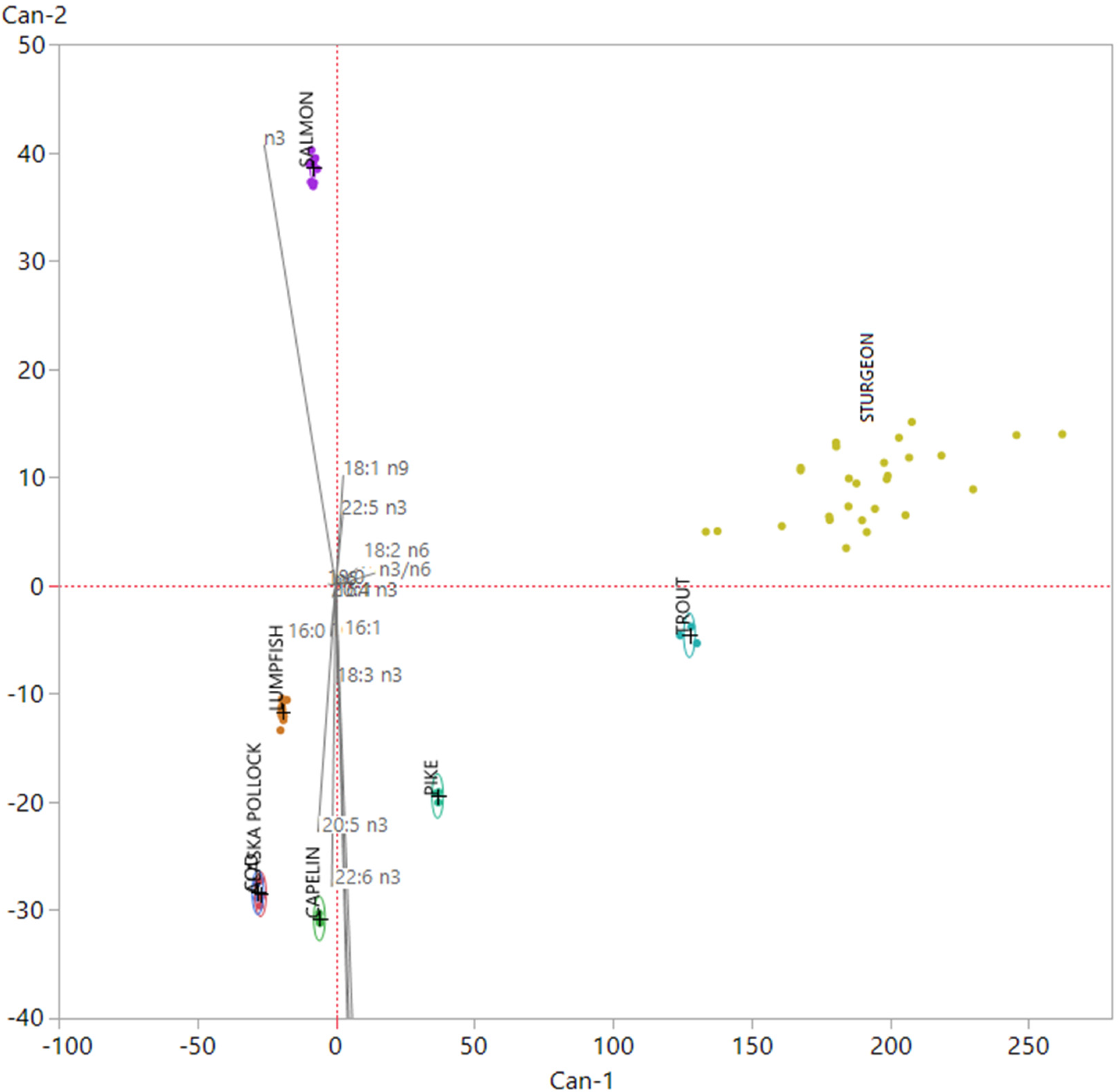
3.1. Nutritional Quality and Authenticity of Fish Roes
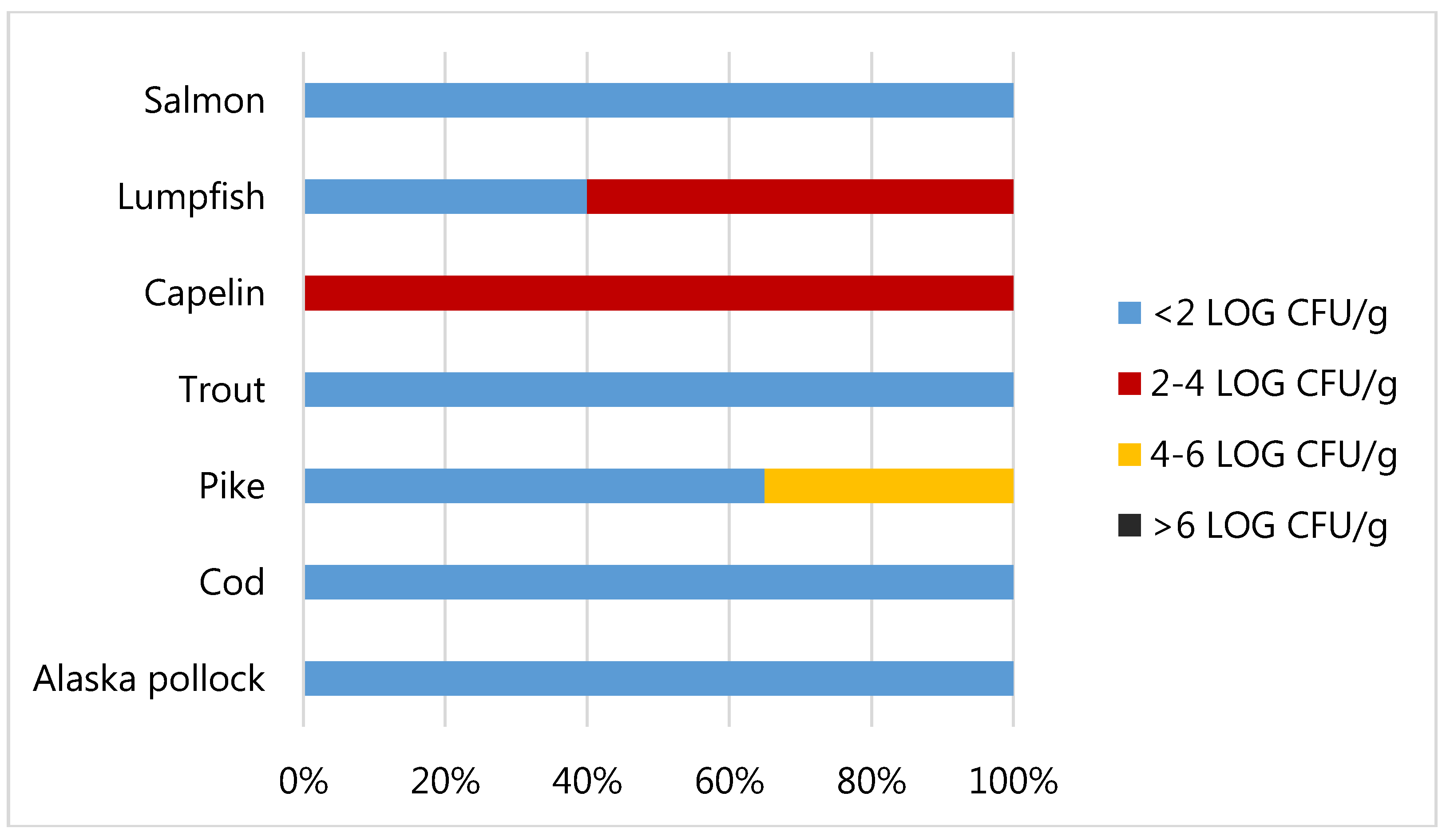
3.2. Food Safety of Fish Roes Products
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shirai, N.; Higuchi, T.; Suzuki, H. Analysis of lipid classes and the fatty acid composition of the salted fish roe food products, Ikura, Tarako, Tobiko and Kazunoko. Food Chem. 2006, 94, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bledsoe, G.; Bledsoe, C.D.; Rasco, B. Caviars and Fish Roe Products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2003, 43, 317–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codex Alimentarius. Guidelines on Nutrition Labelling CAC/GL 2-1985 as Last Amended 2010; Joint FAO/WHO Food Standards Programme, Secretariat of the Codex Alimentarius Commission; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bronzi, P.; Rosenthal, H. Present and future sturgeon and caviar production and marketing: A global market overview. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2014, 30, 1536–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronzi, P.; Chebanov, M.; Michaels, J.T.; Wei, Q.; Rosenthal, H.; Gessner, J. Sturgeon meat and caviar production: Global update 2017. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2019, 35, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sicuro, B. The future of caviar production on the light of social changes: A new dawn for caviar? Rev. Aquac. 2019, 11, 204–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monfort, M.C. Fish Roe in Europe: Supply and Demand Conditions; FAO/GLOBEFISH Research Programme; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2002; Volume 72, p. 47. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, J.H.; Rasco, B. Effect of Water Phase Salt Content and Storage Temperature on Listeria monocytogenes Survival in Chum Salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) Roe and Caviar (Ikura). J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, M160–M165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilhelmsson, O. The state of enzyme biotechnology in the fish processing industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1997, 8, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, P. Enzymes in Fish and Seafood Processing. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2016, 4, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johannesson, J. Lumpfish Caviar-from Vessel to Consumer; FAO Fisheries Technical Paper; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2006; p. 485. [Google Scholar]
- Da Costa, M.P.; Conte-Junior, C.A. Chromatographic methods for determination of carbohydrates and organic acids in foods of animal origin. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2015, 14, 586–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defernez, M.; Kemsley, E.K. The use and misuse of chemometrics for treating classification problems. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 1997, 16, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Association of Official Analytical Chemists. Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Arlington, VA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane Stanley, G.H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Christie, W.W. Preparation of Derivatives of Fatty Acid. In Lipid Analysis Isolation, Separation, Identification and Structural Analysis of Lipids; Christie, W.W., Ed.; The Oily Press: Bridgwater, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Microorganisms—Part 1: Colony Count at 30 Degrees by the Pour Plate Technique; ISO 4833-1:2013; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Methods for the Enumeration of Mesophilic Lactic Acid Bacteria—Colony-Count Technique at 30 Degrees C; ISO 15214:1998; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Methods for the Detection and Enumeration of Enterobacteriaceae—Part 2: Colony-Count Method; ISO 21528-2:2004; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Methods for the Enumeration of Yeasts and Moulds—Part 1: Colony Count Technique in Products with Water Activity Greater than 0, 95; ISO 21527-1:2008; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Coagulase-Positive Staphylococci (Staphylococcus Aureus and Other Species)—Part 1: Technique Using Baird-Parker Agar Medium AMENDMENT 2: Inclusion of an Alternative Confirmation Test Using RPFA Stab Method; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Association Française de Normalisation (AFNOR). Detection of Listeria Monocytogenes and Listeria spp. AFNOR BRD 07/04–09/98; AFNOR: Cedex, Saint-Denis, France, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Tirloni, E.; Stella, S.; Bernardi, C.; Dalgaard, P.; Rosshaug, P.S. Predicting growth of Listeria monocytogenes in fresh ricotta. Food Microbiol. 2019, 78, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- European Medicines Agency. Validation of Analytical Procedures: Note for Guidance on Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology (CPMP/ICH/381/95); European Medicines Agency: Amsterdam, The Nederlands, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Burana-osot, J.; Arunsingkharat, L.; Naksuk, M.; Naungnamjai, S.; Saetun, T. Validation of a HPLC Method for the Determination of Benzoic Acid and Sorbic Acid in Noodles. Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2014, 41, 370–382. [Google Scholar]
- Scano, P.; Rosa, A.; Mereu, S.; Piras, C.; Atzeri, A.; Dessì, M.A. Multivariate fatty acid and fatty alcohol profile of mullet bottarga. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2010, 112, 1369–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borella, L.; Vasconi, M.; Caprino, F.; Bellagamba, F.; Pazzaglia, M.; Moretti, V.M. La qualità del caviale prodotto da storioni allevati in Italia. Ind. Aliment. 2016, 565, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, A.; Vasconi, M.; Bellagamba, F.; Mentasti, T.; Moretti, V.M. Sturgeon meat and caviar quality from different cultured species. Fishes 2020, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duarte, C.M.; Alcaraz, M. To produce many small or few large eggs: A size-independent reproductive tactic of fish. Oecologia 1989, 80, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tocher, D.R.; Sargent, J.R. Analyses of lipids and fatty acids in ripe roes of some Northwest European marine fish. Lipids 1984, 19, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basby, M.; Jappesen, V.F.; Huss, H.H. Chemical composition of fresh and salted lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus) roe. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 1998, 7, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogeropoulos, N.; Mikellidi, A.; Nomikos, T.; Chiou, A. Screening of macro-and bioactive microconstituents of commercial finfish and sea urchin eggs. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 4, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- V’uorela, R.; Kaitaranta, J.; Linko, R. Proximate composition of fish roe in relation to maturity. Can. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. J. 1979, 12, 186–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sayed Mahmoud, K.; Linder, M.; Fanni, J.; Parmentier, M. Characterization of the lipid fractions obtained by proteolytic and chemical extractions from rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) roe. Process Biochem. 2008, 43, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubring, R. Differential scanning calorimetric (DSC) measurements on the roe of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): Influence of maturation and technological treatment. Thermochim. Acta 2004, 415, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İnanli, A.G.; Coban, Ö.E.; Dartay, M. The chemical and sensorial changes in rainbow trout caviar salted in different ratios during storage. Fish. Sci. 2010, 76, 879–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaitaranta, J.K.; Ackman, R.G. Total lipids and lipid classes of fish roe. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Comp. Biochem. 1981, 69, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, T.K.; Matsui, T.; Konosu, S. Purification and properties of an aminopeptidase from Alaska pollack, Theragra chalcogramma, roe. J. Biochem. 1989, 105, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, R.B.; Kroeger, E.L.; Reichert, W.L.; Carter, C.S.; Rust, M.B. Uptake and selective partitioning of dietary lipids to ovarian and muscle tissue of maturing female coho salmon, Oncorhynchus kisutch, during secondary oocyte growth. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 2017, 208–209, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.; Tan, Q.; Zhang, L.; Yao, J.; Zhou, H.; Hu, P.; Liang, X.; Liu, H. The migration of docosahexenoic acid (DHA) to the developing ovary of female zebrafish (Danio rerio). Comp. Biochem. Physiol.-Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2019, 233, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tocher, D.R. Metabolism and Functions of lipids and fatty acids in teleost fish. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2003, 11, 107–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turchini, G.; Torstensen, B.E.; Ng, W.K. Fish oil replacement in finfish nutrition. Rev. Aquac. 2009, 1, 10–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliu, F.; Leoni, B.; Della Pergola, R. Lipid classes and fatty acids composition of the roe of wild Silurus glanis from subalpine freshwater. Food Chem. 2017, 232, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izquierdo, M.S. Essential fatty acid requirements of cultured marine fish larvae. Aquac. Nutr. 1996, 2, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyprian, O.O.; Sveinsdottir, K.; Nguyen, M.V.; Tomasson, T.; Thorkelsson, G.; Arason, S. Influence of lipid content and packaging methods on the quality of dried capelin (Mallotus villosus) during storage. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Der Meeren, T.; Klungsoyr, J.; Wilhelmsen, S.; Kvensenth, P.G. Fatty Acid Composition of Unfed and Growing Cod Larvae, Gadus Morhua L., Feeding on Natural Plankton in Large Enclosures; Physiological and Biochemical Aspects of Fish Development; Walther, B.T., Fyhn, H.J., Eds.; Univ. of Bergen: Bergen, Norway, 1991; pp. 34–35. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y.; Kaeriyama, M. Feeding Habits and Trophic Levels of Pacific Salmon (Oncorhynchus spp.) in the North Pacific Ocean. North Pac. Anadromous Fish Comm. Bull. No 2016, 6, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caredda, M.; Addis, M.; Pes, M.; Fois, N.; Sanna, G.; Piredda, G.; Sanna, G. Physico-chemical, colorimetric, rheological parameters and chemometric discrimination of the origin of Mugil cephalus’ roes during the manufacturing process of Bottarga. Food Res. Int. 2018, 108, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapa-Guimarães, J.; Trattner, S.; Pickova, J. Effect of processing on amine formation and the lipid profile of cod (Gadus morhua) roe. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EC) No 2073/2005 of 15 November 2005 on microbiological criteria for foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Union 2005, 338, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Miya, S.; Takahashi, H.; Ishikawa, T.; Fujii, T.; Kimura, B. Risk of Listeria monocytogenes contamination of raw ready-to-eat seafood products available at retail outlets in Japan. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 3383–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Handa, S.; Kimura, B.; Takahashi, H.; Koda, T.; Hisa, K.; Fujii, T. Incidence of Listeria monocytogenes in raw seafood products in Japanese retail stores. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olafsdottir, G.; Chaine, E.; Westad, F.; Jonsdottir, R.; Thalmann, C.R.; Bazzo, S.; Labreche, S.; Marcq, P.; Lundby, M.; Haugen, J.H. Prediction of microbial and sensory quality of cold smoked Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) by Electronic Nose. J. Food Sci. 2005, 70, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oeleker, K.; Alter, T.E.; Kleer, J.; Pund, R.; Goelz, G.; Hildebrandt, G.; Huehn, S. Microbiological and chemical investigation of caviar at retail. J. für Verbrauch. und Lebensm. 2015, 10, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altug, G.; Bayrak, Y. Microbiological analysis of caviar from Russia and Iran. Food Microbiol. 2003, 20, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himelbloom, B.H.; Crapo, C.A. Microbial evaluation of Alaska salmon caviar. J. Food Protection. G 1998, 1, 626–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jay, J.M. (Ed.) Modern Food Microbiology, 6th ed.; Aspen Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 1–53. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EU) No 1129/2011 of 11 November 2011 amending Annex II to Regulation (EC) N 1333/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council by establishing a Union list of food additives. Off. J. Eur. Union 2011, 295, 11–12.
- Mejlholm, O.; Dalgaard, P. Development and Validation of an Extensive Growth and Growth Boundary Model for Listeria monocytogenes in Lightly Preserved and Ready-to-Eat Shrimp. J. Food Prot. 2009, 72, 2132–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Species | Samples | Different Preparations | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Number | Number Per Producer | NaCl * | Stabilizers | Preservatives | Antioxidants | Color Additives | Others | |
| Salmon Oncorhynchus keta | 12 | 3 | 2.5% | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 3 | 3.5% | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ||
| 3 | 2.5% | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ||
| 3 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ||
| Lumpfish Cyclopterus lumpus | 11 | 2 | ND | E413 | E211 | E330 | E120, E160c | Chartamus |
| 3 | ND | E413 | E211 | E330 | E150d, E151 | |||
| 3 | ND | E412, E422 | E202, E211 | E331 | E141, E150d, E163, E151 | E621 (flavour enhancer) | ||
| Capelin Mallosus villosus | 3 | 3 | ND | E412, E422 | E202, E212 | E330 | E120, E160c | E622 (flavour enhancer) |
| 1 | ND | E202, E211 | E330 | E150d | Sugar | |||
| 1 | ND | E413 | E202, E211 | E330 | E160a, E120 | Sugar, soy | ||
| Rainbow trout Oncorynchus mykiss | 3 | 3 | <6% | ND | E200 | ND | ND | ND |
| Pike Esox lucius | 3 | 3 | ND | E415 | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Cod Gadus morhua | 3 | 3 | ND | ND | E200 | ND | ND | ND |
| Alaska Pollock Theragra chalcogramma | 3 | 3 | ND | ND | E200 | ND | ND | ND |
| Fish Species | Salmon n = 12 | Lumpfish n = 11 | Capelin n = 3 | Trout n = 3 | Pike n = 3 | Cod n = 3 | Alaska Pollock n = 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight mg | 217.3 ± 31.33 | 6.0 ± 1.07 | 0.7 ± 0.09 | 54.7 ± 7.36 | 4.7 ± 0.50 | 0.2 ± 0.04 | 0.2 ± 0.02 |
| Moisture g/100 g | 53.5 ± 1.68 | 79.7 ± 0.92 | 81.7 ± 0.77 | 59.2 ± 0.03 | 64.0 ± 0.83 | 71.6 ± 0.55 | 73.5 ± 0.42 |
| Protein g/100 g | 29.6 ± 0.85 | 10.8 ± 0.40 | 8.1 ± 0.56 | 23.8 ± 0.07 | 19.4 ± 1.12 | 19.6 ± 0.27 | 19.2 ± 0.50 |
| Lipid g/100 g | 12.8 ± 0.85 | 4.3 ± 0.58 | 4.5 ± 0.23 | 12.5 ± 0.08 | 12.7 ± 0.57 | 3.2 ± 0.17 | 2.8 ± 0.10 |
| Ash g/100 g | 4.2 ± 0.79 | 5.2 ± 0.89 | 5.7 ± 0.02 | 4.6 ± 0.05 | 3.9 ± 0.04 | 5.5 ± 0.11 | 4.4 ± 0.05 |
| NaCl g/100 g | 2.7 ± 0.64 | 2.7 ± 0.64 | 2.5 ± 0.32 | 2.3 ± 0.06 | 3.3 ± 0.00 | 3.1 ± 0.06 | 2.8 ± 0.04 |
| Fish Species | Salmon n = 12 | Lumpfish n = 11 | Capelin n = 3 | Trout n = 3 | Pike n = 3 | Cod n = 3 | Alaska Pollak n = 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14:0 | 3.44 ± 0.51 b | 1.37 ± 0.11 c | 4.54 ± 0.01 a | 1.58 ± 0.04 c | 1.76 ± 0.03 c | 1.47 ± 0.04 c | 1.68 ± 0.19 c |
| 15:0 | 0.54 ± 0.11a | 0.27 ± 0.03 bc | 0.36 ± 0.00 bc | 0.19 ± 0.00 c | 0.27 ± 0.00 bc | 0.30 ± 0.01 bc | 0.38 ± 0.11 b |
| 16:0 | 10.63 ± 0.43 d | 14.19 ± 0.37 c | 17.07 ± 0.09 ab | 10.85 ± 0.20 d | 16.05 ± 0.12 b | 17.59 ± 0.81 a | 17.44 ± 0.56 ab |
| 16:1 n7 | 4.83 ± 0.53 c | 1.82 ± 0.25 e | 10.59 ± 0.10 b | 2.93 ± 0.10 d | 13.15 ± 0.30 a | 4.89 ± 0.21 c | 4.93 ± 0.14 c |
| 16:2 n4 | 0.14 ± 0.03 c | 0.02 ± 0.06 d | 0.36 ± 0.00 b | 0.13 ± 0.02 c | 0.70 ± 0.03 a | nd | nd |
| 17:0 | 0.51 ± 0.10 a | 0.41 ± 0.07 ab | 0.08 ± 0.13 d | 0.19 ± 0.00 bcd | 0.40 ± 0.01 abc | 0.25 ± 0.29 bcd | 0.14 ± 0.24 cd |
| 16:3 n4 | 0.85 ± 0.33 a | 0.02 ± 0.06 c | nd | 0.05 ± 0.04 bc | 0.53 ± 0.02 ab | 0.08 ± 0.13 bc | nd |
| 18:0 | 4.76 ± 0.23 a | 4.37 ± 0.19 b | 2.29 ± 0.01 b | 3.90 ± 0.06 c | 2.36 ± 0.04 de | 2.83 ± 0.18 d | 2.90 ± 0.28 d |
| 18:1 n9 | 18.25 ± 1.55 c | 17.07 ± 1.81 c | 11.21 ± 0.11 d | 27.11 ± 0.22 a | 21.65 ± 0.20 b | 12.50 ± 0.60 d | 12.82 ± 0.59 d |
| 18:1 n7 | 2.85 ± 0.40 b | 4.02 ± 0.45 b | 4.43 ± 0.04 ab | 3.28 ± 0.06 b | 7.67 ± 0.14 a | 4.25 ± 3.68 b | 2.09 ± 3.62 b |
| 18:2 n6 | 1.32 ± 0.11 d | 1.04 ± 0.21 e | 1.72 ± 0.01 c | 9.35 ± 0.19 a | 3.50 ± 0.04 b | 0.53 ± 0.03 f | 0.61 ± 0.04 f |
| 18:3 n3 | 1.22 ± 0.14 c | 0.39 ± 0.06 e | 0.78 ± 0.01 d | 3.53 ± 0.04 a | 2.20 ± 0.11 b | nd | nd |
| 18:4 n3 | 1.07 ± 0.11 c | 0.88 ± 0.26 cd | 3.08 ± 0.02 a | 0.66 ± 0.02 de | 1.73 ± 0.05 b | 0.46 ± 0.03 e | 0.47 ± 0.04 e |
| 18:4 n1 | 0.34 ± 0.10 a | nd | nd | 0.19 ± 0.00 b | nd | nd | nd |
| 20:1 n11 | 0.43 ± 0.15 c | nd | nd | nd | nd | 1.69 ± 0.03 b | 2.01 ± 0.23 a |
| 20:1 n9 | 0.85 ± 0.27 d | 4.06 ± 0.92 ab | 5.10 ± 0.08 a | 2.85 ± 0.06 c | 0.41 ± 0.02 d | 2.79 ± 0.05 c | 3.05 ± 0.17 bc |
| 20:1 n7 | 0.32 ± 0.03 b | 0.54 ± 0.20 a | nd | 0.03 ± 0.05 cd | 0.26 ± 0.01 bcd | 0.34 ± 0.02 abc | 0.12 ± 0.21 bcd |
| 20:2 n6 | 0.32 ± 0.05 a | nd | nd | 1.64 ± 0.03 a | 0.36 ± 0.00 a | nd | 0.16 ± 0.28 c |
| 20:3 n6 | 0.12 ± 0.05 c | nd | nd | 0.75 ± 0.02 a | 0.42 ± 0.00 b | nd | nd |
| 20:4 n6 | 1.42 ± 0.23 c | 0.64 ± 0.16 d | 0.68 ± 0.00 d | 1.40 ± 0.04 c | 2.34 ± 0.02 b | 3.07 ± 0.16 a | 3.07 ± 0.19 a |
| 20:4 n3 | 2.51 ± 0.19 a | 0.97 ± 0.15 b | 0.73 ± 0.00 bc | 0.94 ± 0.02 bc | 0.62 ± 0.01 c | 0.12 ± 0.22 d | nd |
| 20:5 n3 | 15.41 ± 0.53 b | 18.93 ± 0.77 a | 16.07 ± 0.07 b | 6.42 ± 0.02 d | 9.03 ± 0.03 c | 17.80 ± 1.07 a | 18.18 ± 0.56 a |
| 22:1 n9 | 0.19 ± 0.12 b | 0.49 ± 0.18 a | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd |
| 22:5 n3 | 5.56 ± 0.47 a | 1.70 ± 0.16 c | 1.64 ± 0.02 c | 2.02 ± 0.01 bc | 2.38 ± 0.01 b | 1.90 ± 0.15 bc | 1.90 ± 0.07 bc |
| 22:6 n3 | 22.04 ± 1.20 b | 26.81 ± 1.53 a | 19.27 ± 0.39 c | 20.01 ± 0.37 bc | 11.91 ± 0.29 c | 27.14 ± 1.21 a | 28.05 ± 1.09 a |
| SFA | 19.88 ± 0.41 e | 20.61 ± 0.63 d | 24.33 ± 0.18 a | 16.70 ± 0.22 f | 20.84 ± 0.17 cd | 22.44 ± 1.05 bc | 22.54 ± 1.24 b |
| MUFA | 27.72 ± 1.71 cd | 28.00 ± 1.78 d | 31.34 ± 0.23 c | 36.21 ± 0.29 b | 43.14 ± 0.24 a | 26.47 ± 2.83 d | 25.02 ± 2.82 d |
| PUFA | 52.40 ± 1.66 a | 51.39 ± 1.28 a | 44.33 ± 0.36 b | 47.09 ± 0.47 b | 36.02 ± 0.40 c | 51.09 ± 2.51 a | 52.44 ± 1.79 a |
| n3 | 47.88 ± 1.43 a | 49.68 ± 1.06 a | 41.57 ± 0.37 b | 33.57 ± 0.34 c | 28.17 ± 0.41 d | 47.43 ± 2.44 a | 48.60 ± 1.71 a |
| n6 | 3.19 ± 0.31 d | 1.67 ± 0.35 e | 2.40 ± 0.01 d | 13.15 ± 0.22 a | 6.62 ± 0.03 b | 3.59 ± 0.18 c | 3.84 ± 0.47 c |
| n3/n6 | 15.14 ± 1.26 b | 30.63 ± 5.19 a | 17.35 ± 0.24 b | 2.55 ± 0.05 c | 4.26 ± 0.07 c | 13.20 ± 0.18 b | 12.78 ± 1.53 b |
| Salmon | Lumpfish | Capelin | Trout | Pike | Cod | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lumpfish | 52.3 | |||||
| Capelin | 70.6 | 23.7 | ||||
| Trout | 144.9 | 149.4 | 138.3 | |||
| Pike | 74.7 | 57.4 | 44.9 | 93.6 | ||
| Cod | 71.0 | 19.3 | 22.7 | 160.1 | 66.6 | |
| Alaska pollock | 17.3 | 6.9 | 21.6 | 157.2 | 64.9 | 0.9 * |
| Fish Species | Salmon n = 12 | Lumpfish n = 11 | Capelin n = 3 | Trout n = 3 | Pike n = 3 | Cod n = 3 | Alaska Pollock n = 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 6.28 ± 0.08 | 5.77 ± 0.09 | 6.19 ± 0.06 | 5.95 ± 0.03 | 5.88 ± 0.05 | 5.96 ± 0.06 | 5.95 ± 0.03 |
| Citric acid ppm | nd | nd | 1356 ± 68 | 898 ± 75 | 2695 ± 192 | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| Lactic acid ppm | 676 ± 261 | 5343 ± 2472 | 1546 ± 172 | 10,812 ± 746 | 232 ± 7 | 11,072 ± 370 | 11,752 ± 2168 |
| Acetic acid ppm | 263 ± 92 | nd | nd | 713 ± 50 | <LOD | 875 ± 75 | 1177 ± 56 |
| Sorbic acid ppm | nd | nd | 607 ± 70 | 2021 ± 35 | <LOD | 2050 ± 118 | 2573 ± 491 |
| Benzoic acid ppm | <LOD | 858 ± 347 | 598 ± 120 | <LOD | <LOD | 285 ± 68 | <LOD |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vasconi, M.; Tirloni, E.; Stella, S.; Coppola, C.; Lopez, A.; Bellagamba, F.; Bernardi, C.; Moretti, V.M. Comparison of Chemical Composition and Safety Issues in Fish Roe Products: Application of Chemometrics to Chemical Data. Foods 2020, 9, 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9050540
Vasconi M, Tirloni E, Stella S, Coppola C, Lopez A, Bellagamba F, Bernardi C, Moretti VM. Comparison of Chemical Composition and Safety Issues in Fish Roe Products: Application of Chemometrics to Chemical Data. Foods. 2020; 9(5):540. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9050540
Chicago/Turabian StyleVasconi, Mauro, Erica Tirloni, Simone Stella, Chiara Coppola, Annalaura Lopez, Federica Bellagamba, Cristian Bernardi, and Vittorio Maria Moretti. 2020. "Comparison of Chemical Composition and Safety Issues in Fish Roe Products: Application of Chemometrics to Chemical Data" Foods 9, no. 5: 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9050540
APA StyleVasconi, M., Tirloni, E., Stella, S., Coppola, C., Lopez, A., Bellagamba, F., Bernardi, C., & Moretti, V. M. (2020). Comparison of Chemical Composition and Safety Issues in Fish Roe Products: Application of Chemometrics to Chemical Data. Foods, 9(5), 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9050540








