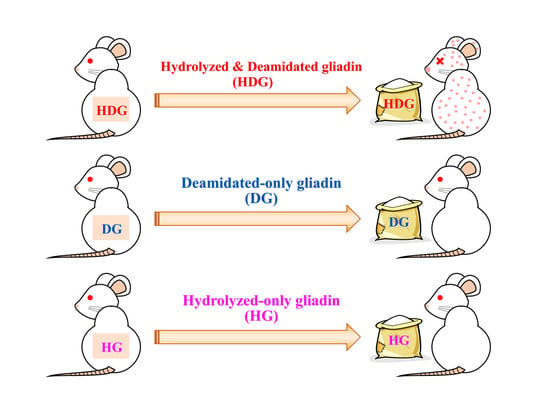
Allergenicity of Deamidated and/or Peptide-Bond-Hydrolyzed Wheat Gliadin by Transdermal Administration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wheat Protein Preparation
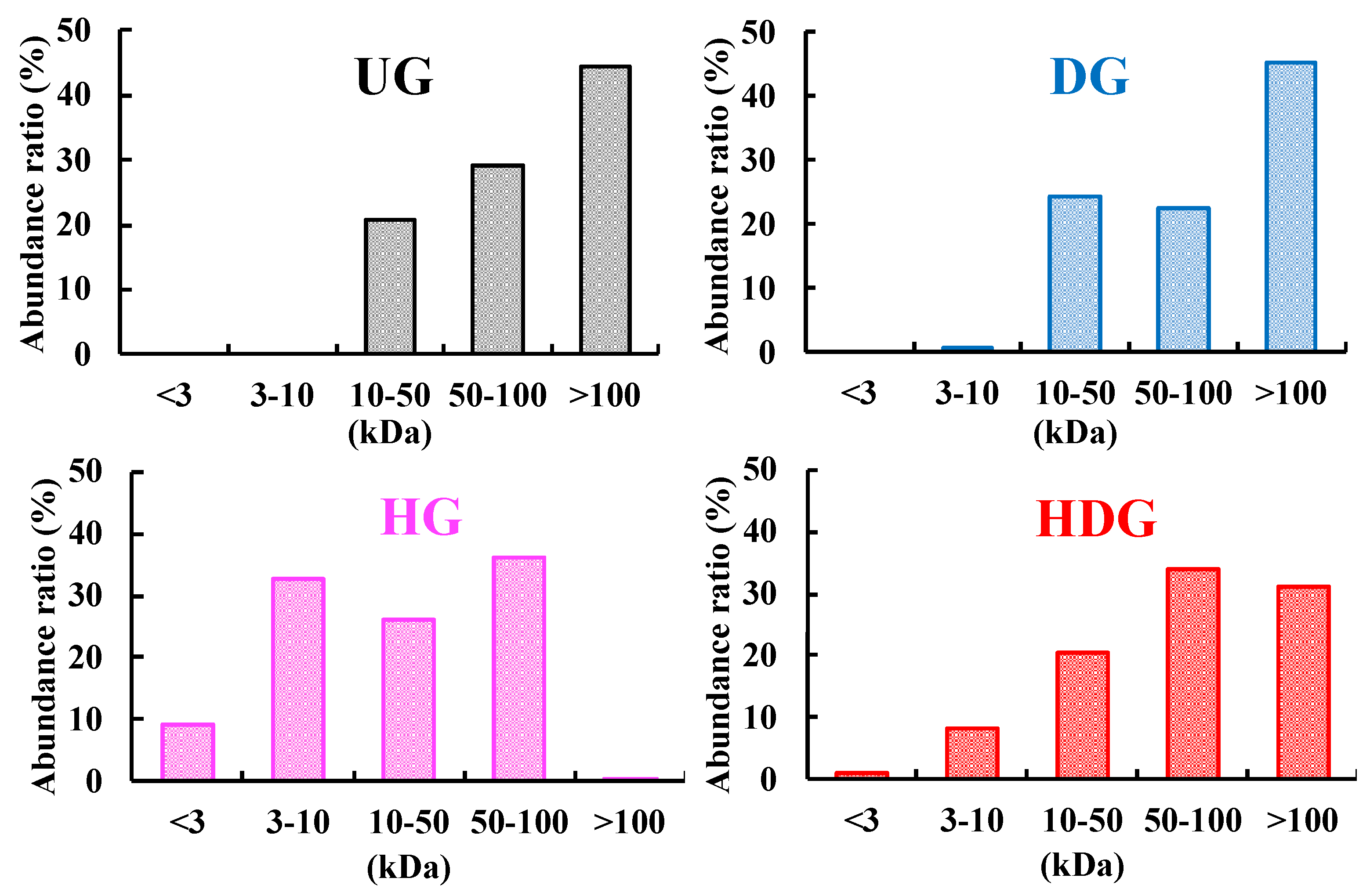
2.2. Apparent Molecular Weight Distribution Measurement
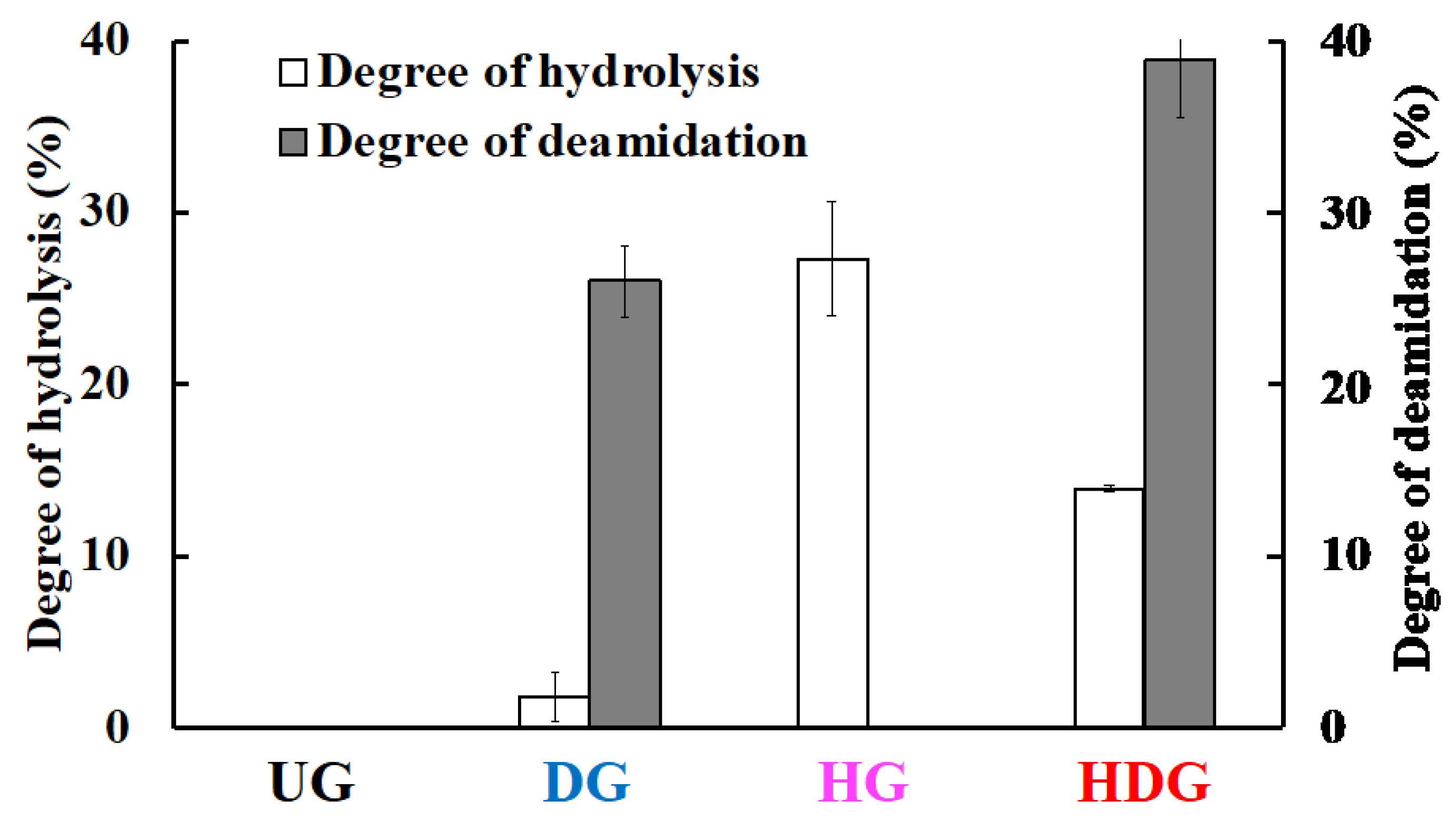
2.3. Degree of Deamidation and Peptide-Bond Hydrolysis
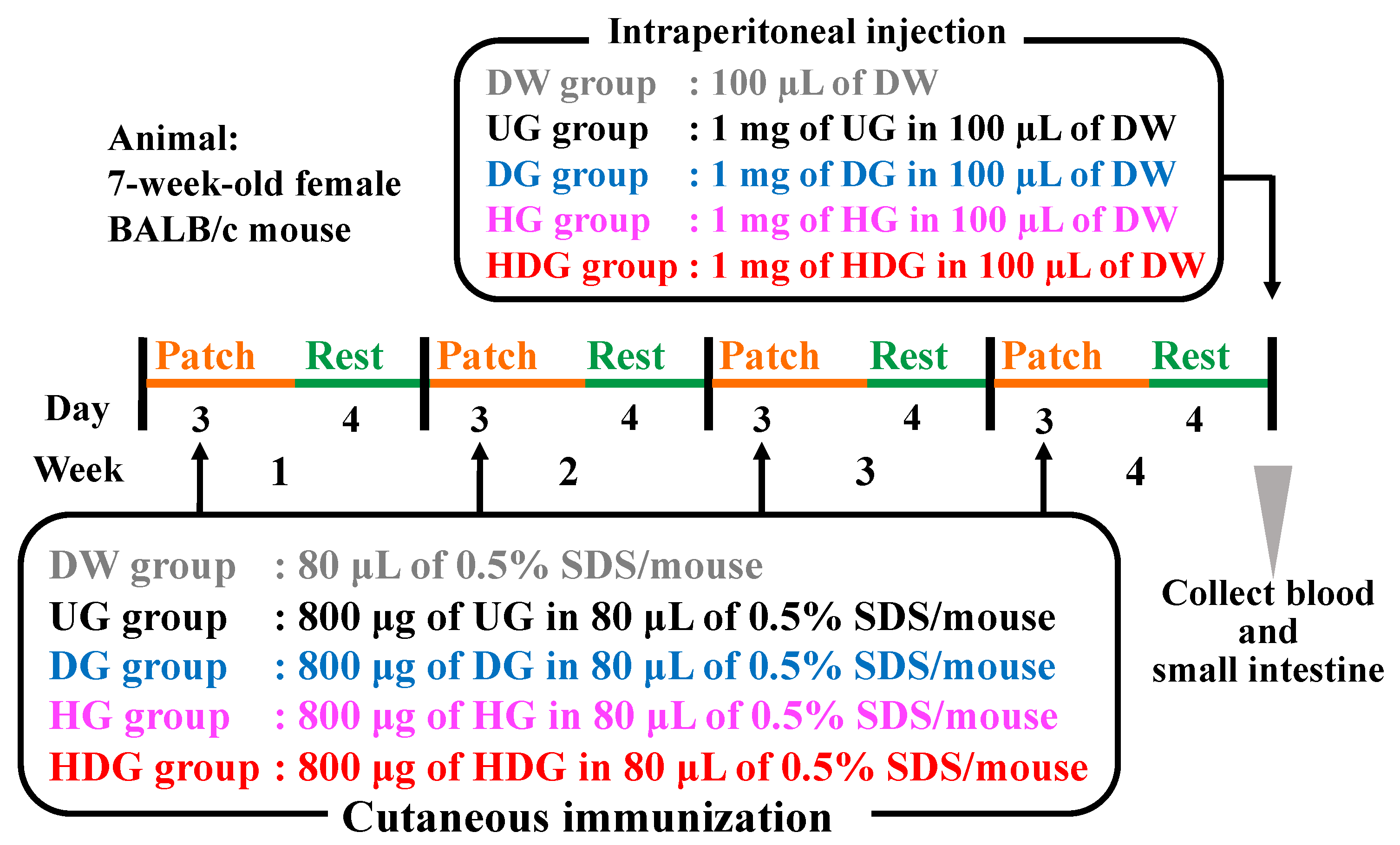
2.4. Animals
2.5. Transdermal Sensitization
2.6. Systemic Anaphylaxis Induction
2.7. Measurement of Serum Histamine and Gliadin Specific IgE and IgG1 Levels
2.8. Measurement of Mcpt8 Expression Level
2.9. In Vitro Skin Sensitization Test
2.10. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Degrees of Deamidation and/or Peptide-Bond Hydrolysis of Wheat Gliadins
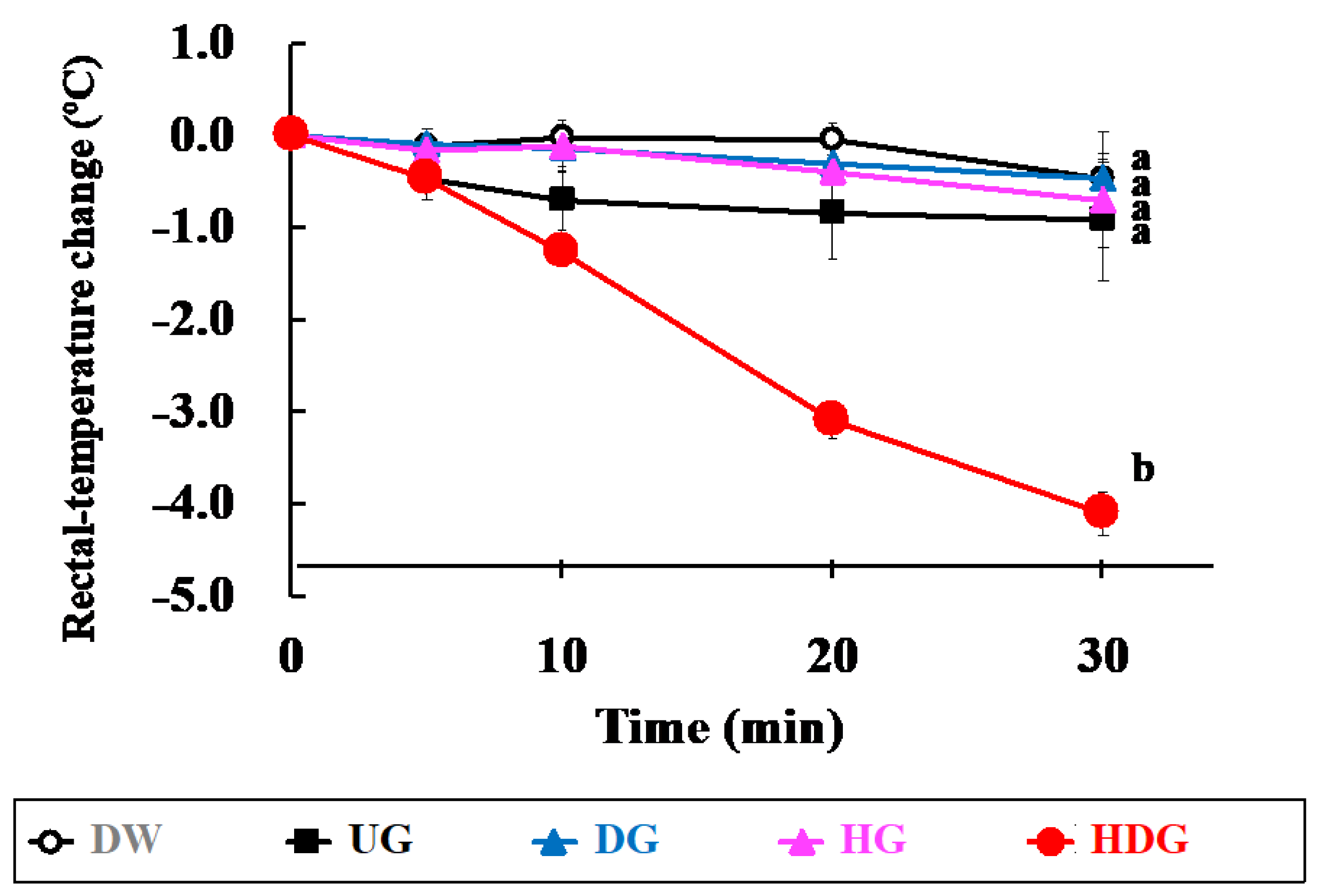
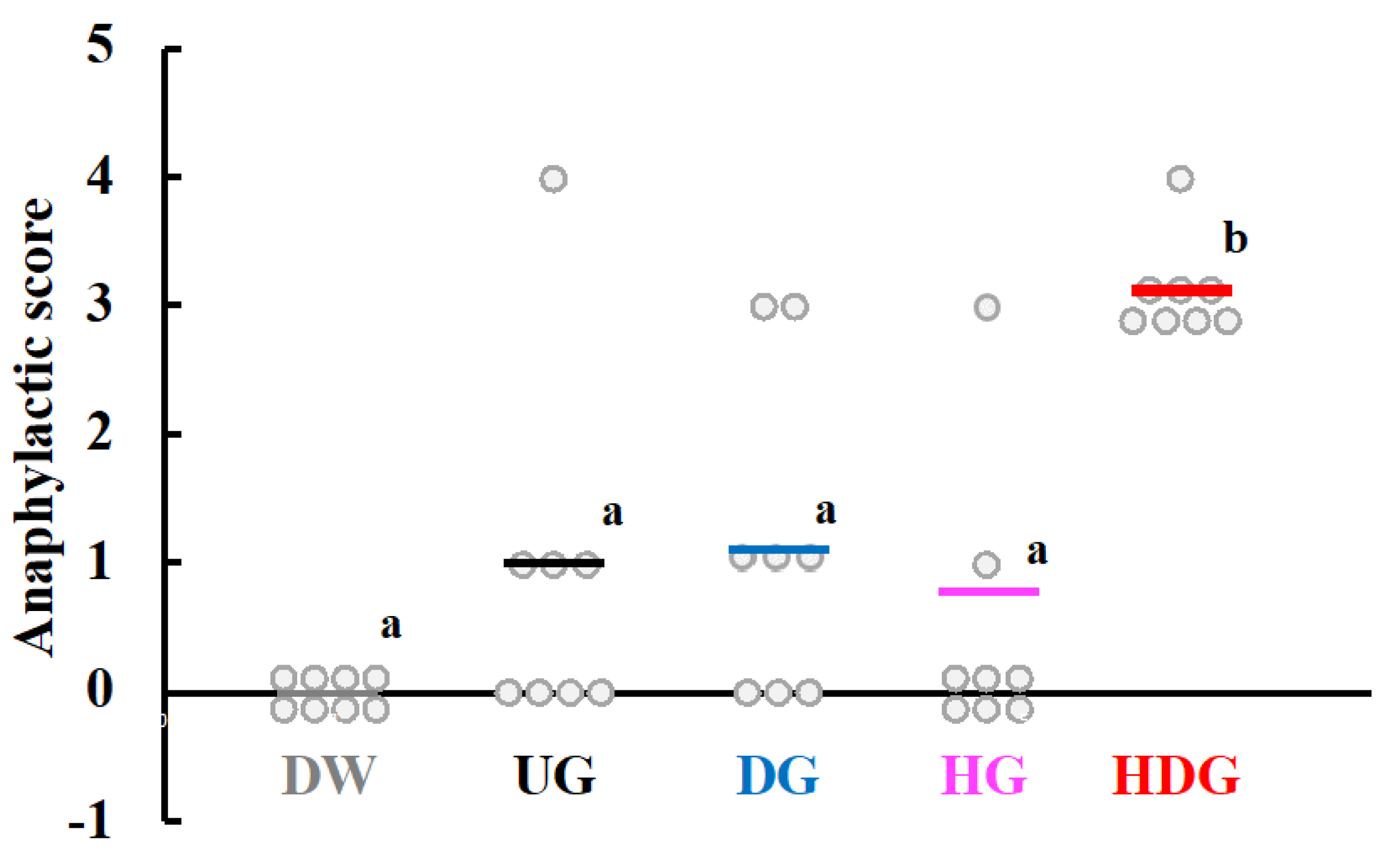
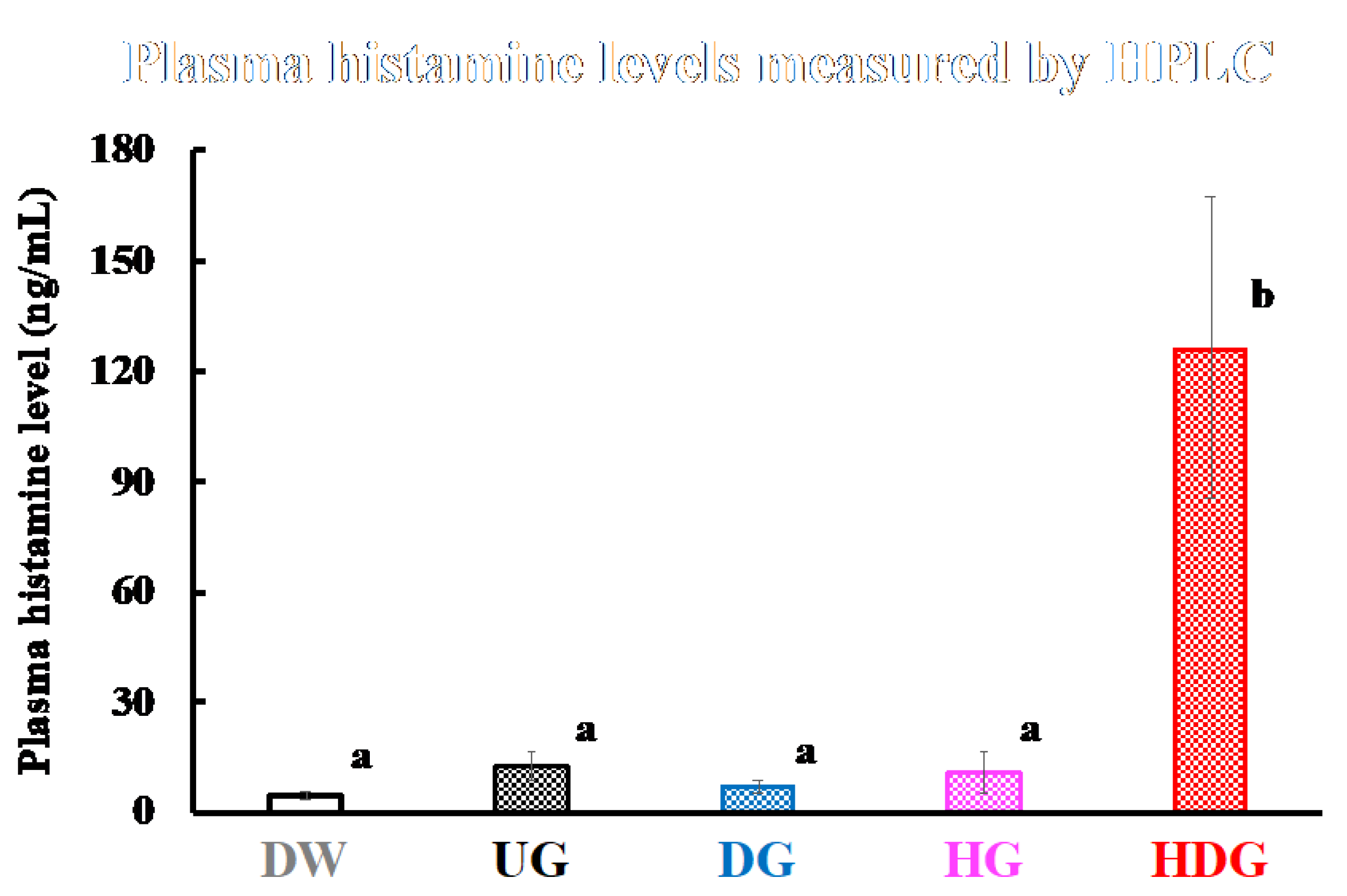
3.2. Cutaneous Sensitivity of Deamidated and/or Peptide-Bond-Hydrolyzed Gliadin
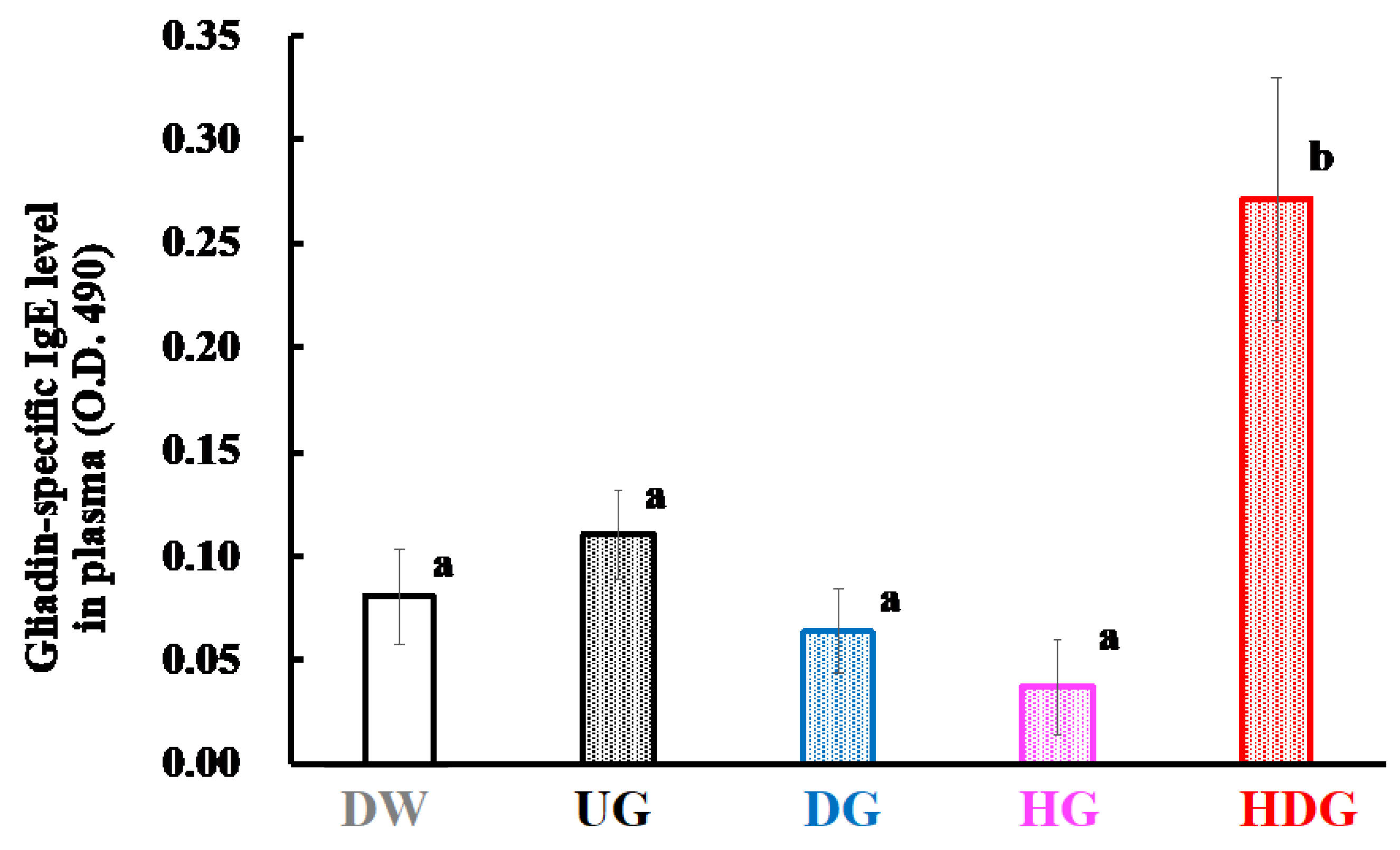
3.3. Gliadin-Specific Immunoglobulin Levels
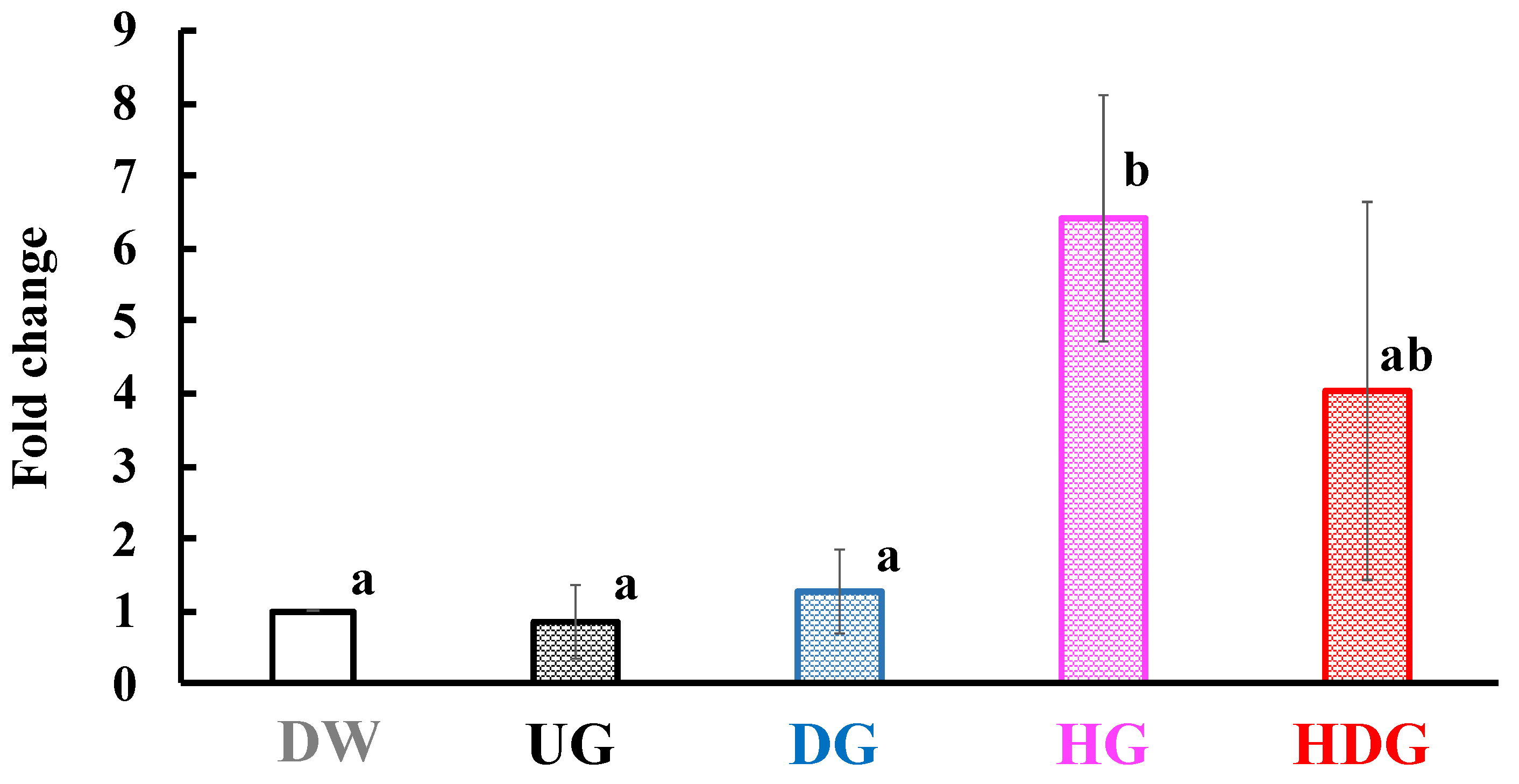
3.4. mRNA Level of Mcpt8 at the Skin Site
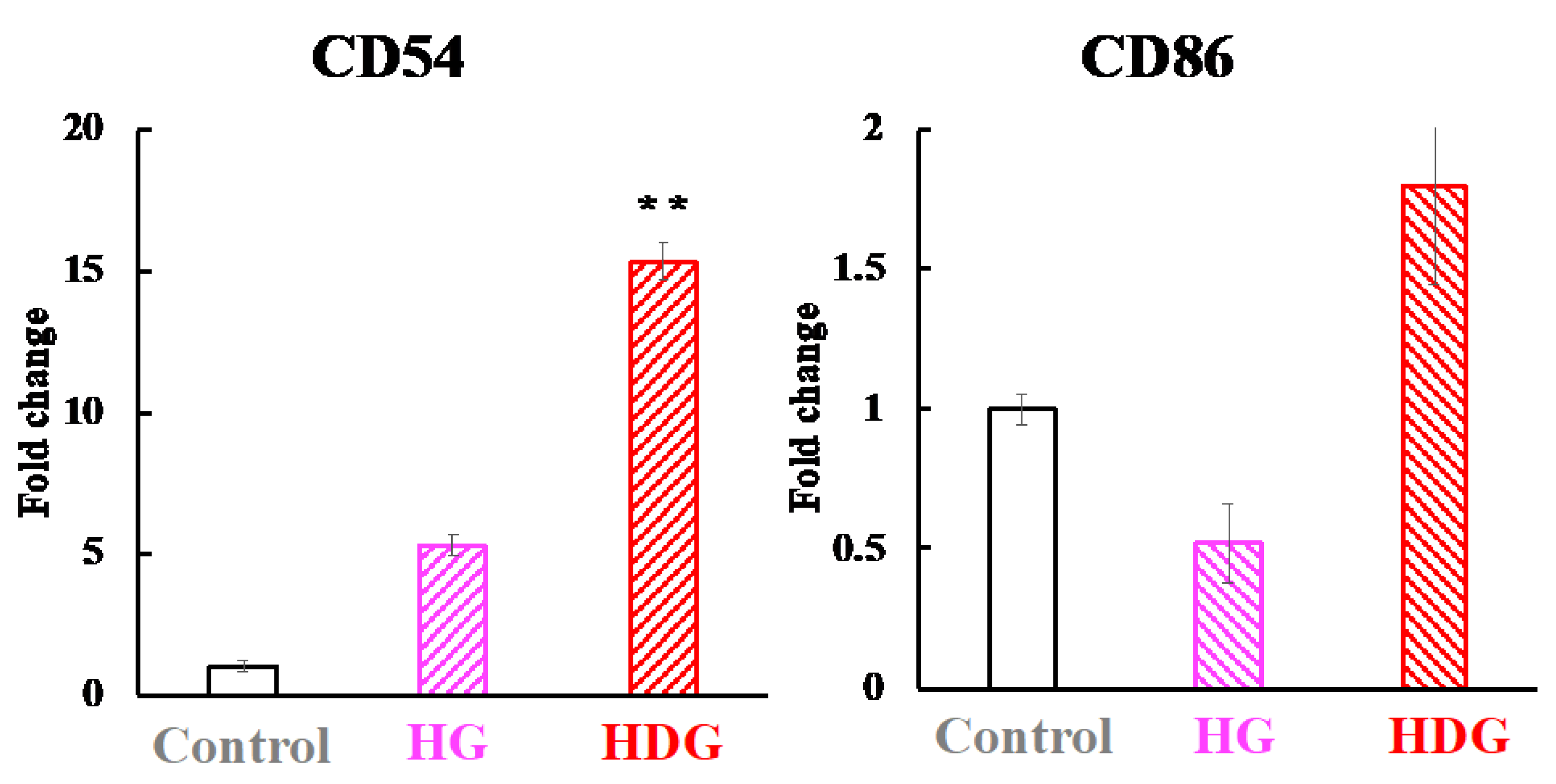
3.5. mRNA Levels of CD54 and CD86 in THP-1 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sarkki, M.-L. Food uses of wheat gluten. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1979, 56, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmedna, M.; Prinyawiwatkul, W.; Rao, R.M. Solubilized wheat protein isolate: Functional properties and potential food applications. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 1340–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, L.; Augustin, M.A.; Batey, I.L.; Wrigley, C.W. Wheat-gluten uses and industry needs. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, H. Wheat proteins and peptides. In Functional Proteins and Peptides, 1st ed.; Mine, Y., Owusu-Apenten, R.K., Jiang, B., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 289–303. [Google Scholar]
- Mimouni, B.; Raymond, J.; Merle-Desnoyers, A.M.; Azanza, J.L.; Ducastaing, A. Combined acid deamidation and enzymic hydrolysis for improvement of the functional properties of wheat gluten. J. Cereal Sci. 1994, 20, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauriere, M.; Pecquet, C.; Bouchez-Mahiout, I.; Snegaroff, J.; Bayrou, O.; Raison-Peyron, N.; Vigan, M. Hydrolysed wheat proteins present in cosmetics can induce immediate hypersensitivities. Contact Derm. 2006, 54, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicherer, S.H. Epidemiology of food allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varjonen, E.; Vainio, E.; Kalimo, K. Antigliadin IgE - indicator of wheat allergy in atopic dermatitis. Allergy 2000, 55, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takizawa, T.; Arakawa, H.; Tokuyama, K.; Morikawa, A. Identification of allergen fractions of wheat flour responsible for anaphylactic reactions to wheat products in infants and young children. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2001, 125, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battais, F.; Pineau, F.; Popineau, Y.; Aparicio, C.; Kanny, G.; Guerin, L.; Moneret-Vautrin, D.A.; Denery-Papini, S. Food allergy to wheat: Identification of immunoglobulin E and immunoglobulin G-binding proteins with sequential extracts and purified proteins from wheat flour. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2003, 33, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, S.; Arai, S.; Yanagihara, Y.; Mita, H.; Takahashi, K.; Watanabe, M. A major wheat allergen has a Gln-Gln-Gln-Pro-Pro motif identified as an IgE-binding epitope. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 219, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, H.; Morita, E.; Tatham, S.A.; Morimoto, K.; Horikawa, T.; Osuna, H.; Ikezawa, Z.; Kaneko, S.; Kohno, K.; Dekio, S. Identification of the IgE binding epitope in ω-5 gliadin, major allergen in wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 12135–12140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumagai, H.; Ishida, S.; Koizumi, A.; Sakurai, H.; Kumagai, H. Preparation of phytate-removed deamidated soybean globulins by ion exchangers and characterization of their calcium-binding ability. J. Agric. Food Sci. 2002, 50, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumagai, H.; Norimatsu, Y.; Hashizume, N.; Sakurai, H.; Kumagai, H. Deamidation of wheat-flour gluten with ion-exchange resin. Nippon Shokuhin Kagaku Kogaku Kaishi 2001, 48, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Norimatsu, Y.; Kumagai, H.; Nagai, R.; Sakurai, H.; Kumagai, H. Deamidation of wheat-flour gluten with ion-exchange resin and its functional properties. Nippon Shokuhin Kagaku Kogaku Kaishi 2002, 49, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, H.; Suda, A.; Sakurai, H.; Kumagai, H.; Arai, S.; Inomata, N.; Ikezawa, Z. Improvement of digestibility, reduction in allergenicity, and induction of oral tolerance of wheat gliadin by deamidation. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2007, 71, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abe, R.; Shimizu, S.; Yasuda, K.; Sugai, M.; Okada, Y.; Chiba, K.; Akao, M.; Kumagai, H.; Kumagai, H. Evaluation of reduced allergenicity of deamidated gliadin in a mouse model of wheat-gliadin allergy using an antibody prepared by a peptide containing three epitopes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 2845–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, R.; Matsukaze, N.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Akao, M.; Kumagai, H.; Kumagai, H. Wheat gliadin deamidated by cation-exchange resins induces oral tolerance in a mouse model of wheat allergy. J. Food Bioact. 2018, 2, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukutomi, Y.; Itagaki, Y.; Taniguchi, M.; Saito, A.; Yasueda, H.; Nakazawa, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Nakamura, H.; Akiyama, K. Rhinoconjunctival sensitization to hydrolyzed wheat protein in facial soap can induce wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 531–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinuki, Y.; Kaneko, S.; Sakieda, K.; Murata, S.; Yoshida, Y.; Morita, E. A case of wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis sensitized with hydrolysed wheat protein in a soap. Contact Derm. 2011, 65, 55–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinuki, Y.; Morita, E. heat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis sensitized with hydrolyzed wheat protein in soap. Allergol. Int. 2012, 61, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adachi, R.; Nakamura, R.; Sakai, S.; Fukutomi, Y.; Teshima, R. Sensitization to acid-hydrolyzed wheat protein by transdermal administration to BALB/C mice, and comparison with gluten. Allergy 2012, 67, 1392–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, S.; Igyártó, B.Z.; Honda, T.; Egawa, G.; Otsuka, A.; Hara-Chikuma, M.; Watanabe, N.; Ziegler, S.F.; Tomura, M.; Inaba, K.; et al. Langerhans cells are critical in epicutaneous sensitization with protein antigen via thymic stromal lymphopoietin receptor signaling. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 1048–1055.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muto, T.; Fukuoka, A.; Kabashima, K.; Ziegler, S.F.; Nakanishi, K.; Matsushita, K.; Yoshimoto, T. The role of basophils and proallergic cytokines, TSLP and IL-33, in cutaneously sensitized food allergy. Int. Immunol. 2014, 26, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsuka, A.; Nakajima, S.; Kubo, M.; Egawa, G.; Honda, T.; Kitoh, A.; Nomura, T.; Hanakawa, S.; Sagita Moniaga, C.; Kim, B.; et al. Basophils are required for the induction of Th2 immunity to haptens and peptide antigens. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valenta, R.; Hochwallner, H.; Linhart, B.; Pahr, S. Food allergies: The basics. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 1120–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tordesillas, L.; Goswami, R.; Benedé, S.; Grishina, G.; Dunkin, D.; Järvinen, K.M.; Maleki, S.J.; Sampson, H.A.; Berin, M.C. Skin exposure promotes a Th2-dependent sensitization to peanut allergens. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 4965–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsieh, K.-Y.; Tsai, C.-C.; Herbert Wu, C.H.; Lin, R.-H. Epicutaneous exposure to protein antigen and food allergy. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2003, 33, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strid, J.; Callard, R.; Strobel, S. Epicutaneous immunization converts subsequent and established antigen-specific T helper type 1 (Th1) to Th2-type responses. Immunology 2006, 119, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokooji, T.; Kurihara, S.; Murakami, T.; Chinuki, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Morita, E.; Harada, S.; Ishii, K.; Hiragun, M.; Hide, M.; et al. Characterization of causative allergens for wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis sensitized with hydrolyzed wheat proteins in facial soap. Allergol. Int. 2013, 62, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kong, X.; Zhou, H.; Qian, H. Enzymatic preparation and functional properties of wheat gluten hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2007, 101, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chobert, J.M.; Briand, L.; Guéguen, J.; Popineau, Y.; Larré, C.; Haertlé, T. Recent advances in enzymatic modifications of food proteins for improving their functional properties. Food Nahrung 1996, 40, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashino, M.; Hirami, K.; Katagiri, T.; Kubota, N.; Ohmukai, Y.; Ishigami, T.; Maruyama, T.; Matsuyama, H. Effects of three natural organic matter types on cellulose acetate butyrate microfiltration membrane fouling. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 379, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, E.J.; Byrne, A. An absorption apparatus for the micro-determination of certain volatile substances. I. The micro-determination of ammonia. Biochem. J. 1933, 27, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Akamatsu, S. Some micromethods for enzyme studies. J. Biochem. 1952, 39, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashikaga, T.; Yoshida, Y.; Hirota, M.; Yoneyama, K.; Itagaki, H.; Sakaguchi, H.; Miyazawa, M.; Ito, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Toyoda, H. Development of an in vitro skin sensitization test using human cell lines: The human cell line activation test (H-CLAT). Toxicol. In Vitro 2006, 20, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casten, L.; Villemin, C.; Claude, M.; Aubert, P.; Durand, T.; Neunlist, M.; Brossard, C.; Magnan, A.; Bodinier, M.; Bouchaud, G. Acid-hydrolyzed gliadins worsen food allergies through early sensitization. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, e1800159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, K.; Shiozawa, N.; Nagao, T.; Yoshikawa, S.; Yamanishi, Y.; Karasuyama, H. Trogocytosis of peptide–MHC class II complexes from dendritic cells confers antigen-presenting ability on basophils. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1111–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chinuki, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Dekio, I.; Kaneko, S.; Tokuda, R.; Nagao, M.; Fujisawa, T.; Morita, E. Higher allergenicity of high molecular weight hydrolysed wheat protein in cosmetics for percutaneous sensitization. Contact Derm. 2012, 68, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villemin, C.; Tranquet, O.; Solé-Jamault, V.; Smit, J.J.; Pieters, R.H.H.; Denery-Papini, S.; Bouchaud, G. Deamidation and enzymatic hydrolysis of gliadins alter their processing by dendritic cells in vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 68, 1447–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashikaga, T.; Sakaguchi, H.; Okamoto, K.; Mizuno, M.; Jun, S.; Yamada, T.; Yoshida, M.; Ota, N.; Hasegawa, S.; Kodama, T.; et al. Assessment of the human cell line activation test (H-CLAT) for skin sensitization; Results of the first Japanese inter-laboratory study. Altern. Anim. Testing Exp. 2008, 13, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abe, R.; Matsukaze, N.; Kobayashi, H.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Uto-Kondo, H.; Kumagai, H.; Kumagai, H. Allergenicity of Deamidated and/or Peptide-Bond-Hydrolyzed Wheat Gliadin by Transdermal Administration. Foods 2020, 9, 635. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9050635
Abe R, Matsukaze N, Kobayashi H, Yamaguchi Y, Uto-Kondo H, Kumagai H, Kumagai H. Allergenicity of Deamidated and/or Peptide-Bond-Hydrolyzed Wheat Gliadin by Transdermal Administration. Foods. 2020; 9(5):635. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9050635
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbe, Ryosuke, Narumi Matsukaze, Hayato Kobayashi, Yusuke Yamaguchi, Harumi Uto-Kondo, Hitoshi Kumagai, and Hitomi Kumagai. 2020. "Allergenicity of Deamidated and/or Peptide-Bond-Hydrolyzed Wheat Gliadin by Transdermal Administration" Foods 9, no. 5: 635. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9050635
APA StyleAbe, R., Matsukaze, N., Kobayashi, H., Yamaguchi, Y., Uto-Kondo, H., Kumagai, H., & Kumagai, H. (2020). Allergenicity of Deamidated and/or Peptide-Bond-Hydrolyzed Wheat Gliadin by Transdermal Administration. Foods, 9(5), 635. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9050635