Fabrication of Concentrated Palm Olein-Based Diacylglycerol Oil–Soybean Oil Blend Oil-In-Water Emulsion: In-Depth Study of the Rheological Properties and Storage Stability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
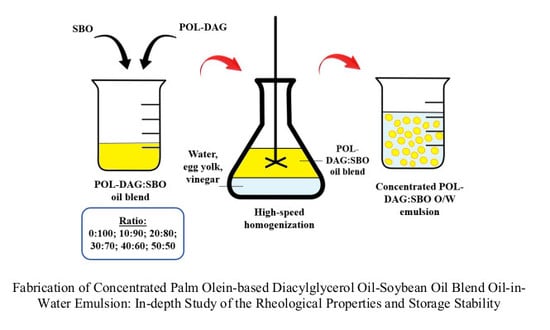
2.2. Production of POL-DAG and Oil Blending
2.3. POL-DAG/SBO-Based O/W Emulsion Preparation
2.4. Textural Properties Analysis
2.5. Color Analysis
2.6. Particle Size Distribution
2.7. Rheological Measurements
2.7.1. Flow Behavior
2.7.2. Thixotropic Profile
2.7.3. Dynamic Viscoelastic Properties
2.8. Microstructural Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Texture and Color Profiles
3.2. Particle Size Distribution
3.3. Rheological Tests
3.3.1. Evaluation of the Flow Property and Thixotropic Profile
3.3.2. Strain Sweep Test
3.3.3. Frequency Strain Sweep and Dynamic Viscoelastic Properties
3.4. Microstructural Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dalgleish, D.G. Food emulsions—Their structures and structure-forming properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2006, 20, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chizawa, Y.; Miyagawa, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Adachi, S. Effect of crystallization of oil phase on the destabilization of O/W emulsions containing vegetable oils with low melting points. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 582, 123824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani Gorji, S.; Calingacion, M.; Smyth, H.E.; Fitzgerald, M. Comprehensive profiling of lipid oxidation volatile compounds during storage of mayonnaise. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 4076–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishibashi, C.; Hondoh, H.; Ueno, S. Influence of morphology and polymorphic transformation of fat crystals on the freeze-thaw stability of mayonnaise-type oil-in-water emulsions. Food Res. Int. 2016, 89, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karupaiah, T.; Chuah, K.-A.; Chinna, K.; Matsuoka, R.; Masuda, Y.; Sundram, K.; Sugano, M. Comparing effects of soybean oil- and palm olein-based mayonnaise consumption on the plasma lipid and lipoprotein profiles in human subjects: A double-blind randomized controlled trial with cross-over design. Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Laszlo, J.A.; Compton, D.L.; Vermillion, K.E. Acyl migration kinetics of vegetable oil 1,2-diacylglycerols. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2008, 85, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linda, T.W. Triglycerides and Cholesterol Research; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Shimida, A.; Ohashi, K. Interfacial and emulsifying properties of diacylglycerol. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2003, 9, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheong, L.-Z.; Tan, C.-P.; Long, K.; Affandi Yusoff, M.S.; Lai, O.-M. Physicochemical, textural and viscoelastic properties of palm diacylglycerol bakery shortening during storage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 2310–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saberi, A.H.; Lai, O.-M.; Miskandar, M.S. Melting and solidification properties of palm-based diacylglycerol, palm kernel olein, and sunflower oil in the preparation of palm-based diacylglycerol-enriched soft tub margarine. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2012, 5, 1674–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Quek, S.Y.; Lam, G.; Easteal, A.J. The rheological behaviour of low fat soy-based salad dressing. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 43, 2204–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.A. Flow and functional models for rheological properties of fluid foods. In Rheology of Fluid and Semisolid Foods; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Nor Hayati, I.; Che Man, Y.B.; Tan, C.P.; Nor Aini, I. Physicochemical characteristics of soybean oil, palm kernel olein, and their binary blends. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 44, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worrasinchai, S.; Suphantharika, M.; Pinjai, S.; Jamnong, P. β-Glucan prepared from spent brewer’s yeast as a fat replacer in mayonnaise. Food Hydrocoll. 2006, 20, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, E.V.; da Silva Lannes, S.C. Chocolate rheology. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 30, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Junqueira, L.A.; Amaral, T.N.; Leite Oliveira, N.; Prado, M.E.T.; de Resende, J.V. Rheological behavior and stability of emulsions obtained from Pereskia aculeata Miller via different drying methods. Int J. Food Prop. 2018, 21, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, H.L.; McGrath, K.M. How does oil type determine emulsion characteristics in concentrated Na-caseinate emulsions? J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 403, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberi, A.H.; Kee, B.B.; Oi-Ming, L.; Miskandar, M.S. Physico-chemical properties of various palm-based diacylglycerol oils in comparison with their corresponding palm-based oils. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Food Emulsions: Principles, Practices, and Techniques; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chantrapornchai, W.; Clydesdale, F.; McClements, D.J. Influence of droplet characteristics on the optical properties of colored oil-in-water emulsions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1999, 155, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouaou, I.; Shamaei, S.; Koutchoukali, M.S.; Bouhelassa, M.; Tsotsas, E.; Kharaghani, A. Impact of operating conditions on a single droplet and spray drying of hydroxypropylated pea starch: Process performance and final powder properties. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 14, e2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pal, R. Viscosity and storage/loss moduli for mixtures of fine and coarse emulsions. Chem. Eng. J. 1997, 67, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peressini, D.; Sensidoni, A.; de Cindio, B. Rheological characterization of traditional and light mayonnaises. J. Food Eng. 1998, 35, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesch, S.; Schubert, H. Influence of increasing viscosity of the aqueous phase on the short-term stability of protein stabilized emulsions. J. Food Eng. 2002, 52, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatsisvili, N.T.; Amvrosiadis, I.; Kiosseoglou, V. Physicochemical properties of a dressing-type o/w emulsion as influenced by orange pulp fiber incorporation. LW-Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roopa, B.S.; Bhattacharya, S. Characterisation and modelling of time-independent and time-dependent flow behaviour of sodium alginate dispersions. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 44, 2583–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, L.-S.; Lin, P.-H. Application of decolourised hsian-tsao leaf gum to low-fat salad dressing model emulsions: A rheological study. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2004, 84, 1307–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tárrega, A.; Durán, L.; Costell, E. Flow behaviour of semi-solid dairy desserts. Effect of temperature. Int. Dairy J. 2004, 14, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štern, P.; Valentová, H.; Pokorný, J. Rheological properties and sensory texture of mayonnaise. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2001, 103, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadros, T. Application of rheology for assessment and prediction of the long-term physical stability of emulsions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 108–109, 227–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fomuso, L.B.; Corredig, M.; Akoh, C.C. A comparative study of mayonnaise and italian dressing prepared with lipase-catalyzed transesterified olive oil and caprylic acid. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2001, 78, 771–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, F.; Montanari, L.; Peressini, D.; Fantozzi, P. Influence of alginate concentration and molecular weight on functional properties of mayonnaise. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2002, 35, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Boye, J.I. Advances in the design and production of reduced-fat and reduced-cholesterol salad dressing and mayonnaise: A review. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013, 6, 648–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brummer, R. Rheology Essentials of Cosmetic and Food Emulsions; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gunasekaran, S.; Ak, M.M. Dynamic oscillatory shear testing of foods—Selected applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2000, 11, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, J.R.; Telford, J.H. Measuring the yield behaviour of structured fluids. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 2004, 124, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E. Structure formation in casein-based gels, foams, and emulsions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2006, 288, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Storage Period | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Samples | One-Day | 30 Days | One-Day | 30 Days | ||||||
| Texture Properties | Color Profiles | |||||||||
| POL-DAG/SBO | Firmness (N) | Hardness (kg/s) | Firmness (N) | Hardness (kg/s) | L* | a* | b* | L* | a* | b* |
| Control (0:100) | 13.94 ± 0.09 c | 0.34 ± 0.01 c | 11.39 ± 0.06 e | 0.24 ± 0.01 c | 82.88 ± 0.05 b | −1.99 ± 0.02 a | 9.47 ± 0.10 c | 86.77 ± 0.01 a | −2.50 ± 0.01 a | 14.40 ± 0.01 f |
| A (10:90) | 15.59 ± 0.92 c | 0.37 ± 0.02 c | 13.81 ± 0.20 e | 0.35 ± 0.01 c | 83.07 ± 0.06 a | −1.95 ± 0.02 a | 10.29 ± 0.10 b,c | 83.86 ± 0.01 e | −2.75 ± 0.01 b | 16.44 ± 0.02 b |
| B (20:80) | 15.33 ± 0.16 c | 0.36 ± 0.01 c | 42.38 ± 2.30 d | 0.85 ± 0.70 b,c | 82.44 ± 0.01 c | −2.27 ± 0.03 b | 11.27 ± 0.10 a,b | 83.06 ± 0.02 f | −3.38 ± 0.03 e | 16.95 ± 0.27 a |
| C (30:70) | 44.51 ± 2.69 b | 0.95 ± 0.04 b | 75.97 ± 2.40 c | 1.68 ± 0.25 b | 82.41 ± 0.03 c | −2.31 ± 0.02 b | 11.32 ± 0.10 a,b | 84.80 ± 0.01 d | −3.08 ± 0.03 d | 16.31 ± 0.21 c |
| D (40:60) | 44.85 ± 0.47 b | 0.99 ± 0.02 b | 133.85 ± 6.80 b | 2.78 ± 0.44 a | 82.28 ± 0.02 d | −2.23 ± 0.03 b | 10.47 ± 0.10 b,c | 85.00 ± 0.03 c | −3.00 ± 0.02 c | 15.79 ± 0.10 d |
| E (50:50) | 55.23 ± 0.99 a | 1.06 ± 0.03 a | 160.13 ± 12.42 a | 3.39 ± 0.64 a | 81.70 ± 0.02 e | −2.32 ± 0.06 b | 11.62 ± 0.10 a | 85.32 ± 0.02 b | −2.77 ± 0.02 b | 15.94 ± 0.12 e |
| Storage Period | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Samples | One-Day | 30 Days | ||||||||
| POL-DAG/SBO | d[10] | d[50] | d[90] | Span Index | d4,3 (µm) | d[10] | d[50] | d[90] | Span Index | d4,3 (µm) |
| Control (0:100) | 0.15 ± 0.03 b | 5.74 ± 0.23 c | 9.91 ± 0.03 e | 1.70 ± 0.01 c | 5.78 ± 0.03 c | 2.29 ± 0.13 b | 7.65 ± 0.92 c | 13.73 ± 0.45 d | 1.50 ± 0.04 d | 8.43 ± 0.36 c |
| A (10:90) | 0.18 ± 0.02 a,b | 5.43 ± 0.01 c | 10.03 ± 0.65 e,d | 1.81 ± 0.03 b,c | 5.46 ± 0.35 c | 2.94 ± 0.17 a | 17.14 ± 1.73 a | 30.60 ± 6.06 b | 1.61 ± 0.15 d | 17.08 ± 2.97 b |
| B (20:80) | 0.25 ± 0.07 a | 5.67 ± 0.25 c | 10.61 ± 0.60 d | 1.83 ± 0.03 b,c | 6.19 ± 0.50 c | 0.09 ± 0.01 c | 5.95 ± 0.11 d | 16.78 ± 0.50 c,d | 2.81 ± 0.34 c | 7.75 ± 0.16 c |
| C (30:70) | 0.17 ± 0.02 b | 8.61 ± 0.65 b | 15.84 ± 0.69 c | 1.82 ± 0.05 b,c | 8.17 ± 0.94 b | 0.09 ± 0.01 c | 6.14 ± 0.62 c,d | 21.25 ± 0.50 c | 3.45 ± 0.54 b | 8.46 ± 0.33 c |
| D (40:60) | 0.17 ± 0.02 b | 8.81 ± 0.66 b | 17.09 ± 0.79 b | 1.92 ± 0.04 a,b | 9.09 ± 0.90 a,b | 0.12 ± 0.01 c | 13.23 ± 1.21 b | 46.45 ± 5.90 a | 3.50 ± 0.87 a | 22.58 ± 2.63 a |
| E (50:50) | 0.16 ± 0.02 b | 9.96 ± 0.99 a | 19.77 ± 0.84 a | 1.98 ± 0.12 a | 10.03 ± 1.24 a | 0.14 ± 0.02 c | 13.78 ± 1.19 b | 44.65 ± 5.95 a | 3.23 ± 0.55 b,c | 23.93 ± 2.67 a |
| Samples | Power Law Model | Herschel–Bulkley Model | Casson Model | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| POL-DAG/SBO | K (Pa·s) | n | R2 | K (Pa·s) | n | R2 | R2 | ||||
| Control (0:100) | 2.72 ± 0.50 d | 0.494 ± 0.024 a | 0.999 | 1.98 ± 0.15 c | 0.567 ± 0.032 a | 1.59 ± 0.16 a | 0.999 | 3.93 ± 0.57 d | 0.111 ± 0.010 a | 0.996 | 0.38 ± 0.03 e |
| A (10:90) | 2.95 ± 0.55 d | 0.454 ± 0.024 a | 0.997 | 2.35 ± 0.17 c | 0.461 ± 0.022 b | 0.67 ± 0.04 a | 0.999 | 4.96 ± 0.60 d | 0.062 ± 0.040 b | 0.992 | 0.32 ± 0.03 e |
| B (20:80) | 11.29 ± 1.60 c | 0.263 ± 0.021 b | 0.998 | 12.66 ± 0.70 c | 0.239 ± 0.015 c | 2.01 ± 0.24 a | 0.998 | 13.56 ± 1.58 c | 0.065 ± 0.042 b | 0.991 | 0.63 ± 0.02 d |
| C (30:70) | 27.05 ± 3.70 b | 0.135 ± 0.015 c,d | 0.859 | 619.27 ± 66.60 b | 0.010 ± 0.005 d | −593.30 ± 115.80 b | 0.981 | 30.77 ± 0.90 b | 0.025 ± 0.009 c | 0.854 | 1.04 ± 0.03 c |
| D (40:60) | 30.83 ± 2.90 b | 0.158 ± 0.018 c | 0.954 | 651.60 ± 72.40 b | 0.120 ± 0.010 d | −617.40 ± 108.60 b | 0.915 | 33.96 ± 0.80 b | 0.054 ± 0.001 b | 0.838 | 1.23 ± 0.03 b |
| E (50:50) | 52.75 ± 6.14 a | 0.097 ± 0.002 d | 0.916 | 702.60 ± 122.49 a | 0.002 ± 0.001 d | −715.23 ± 122.90 c | 0.834 | 50.23 ± 1.99 a | 0.050 ± 0.001 b | 0.819 | 1.46 ± 0.06 a |
| Storage | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Samples | One-day | 30 days | ||||||||
| POL-DAG/SBO | Thixotropy Area (Pa/s) | G’G” Crossover (Pa) | G’ (Pa) | G” (Pa) | tan δ | Thixotropy Area (Pa/s) | G’G” Crossover (Pa) | G’ (Pa) | G” (Pa) | Tan δ |
| Control (0:100) | 76.80 ± 8.50 a | 16.36 ± 0.09 d | 120.70 ± 8.60 d | 26.91 ± 3.39 d | 0.22 ± 0.00 c | 37.20 ± 1.20 d | 6.63 ± 0.23 c | 34.80 ± 8.70 c | 9.20 ± 2.00 c | 0.26 ± 0.00 c |
| A (10:90) | 436.30 ± 24.80 b | 15.69 ± 0.09 d | 119.70 ± 7.40 d | 38.97 ± 5.60 d | 0.33 ± 0.01 a | 181.70 ± 11.22 d | 7.78 ± 0.36 c | 138.40 ± 12.66 c | 50.70 ± 7.80 c | 0.37 ± 0.02 a |
| B (20:80) | 1510.70 ± 110.30 c | 61.09 ± 12.20 c | 541.40 ± 25.20 c | 159.40 ± 10.80 c | 0.29 ± 0.00 b | 373.50 ± 20.20 d | 27.18 ± 3.42 c | 402.50 ± 26.80 b,c | 126.40 ± 13.30 c | 0.31 ± 0.02 b |
| C (30:70) | 3722.00 ± 171.80 d | 226.47 ± 24.15 a | 1425.70 ± 50.00 a | 453.23 ± 22.20 a | 0.32 ± 0.01 a,b | 1398.30 ± 98.20 c | 44.41 ± 6.80 c | 954.10 ± 64.80 b | 326.80 ± 16.40 b | 0.34 ± 0.01 a,b |
| D (40:60) | 3347.70 ± 134.60 e | 183.97 ± 12.22 b | 1160.30 ± 39.40 b | 354.36 ± 18.80 b | 0.31 ± 0.01 a,b | 4021.10 ± 220.20 b | 179.97 ± 11.22 b | 3691.70 ± 412.00 a | 1267.00 ± 128.20 a | 0.34 ± 0.01 a,b |
| E (50:50) | 2481.70 ± 122.40 f | 174.62 ± 12.68 b | 1182.10 ± 38.80 b | 381.90 ± 19.40 b | 0.32 ± 0.01 a,b | 5022.00 ± 396.10 a | 456.20 ± 35.35 a | 3554.00 ± 368.80 a | 1172.30 ± 72.50 a | 0.33 ± 0.01 a,b |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ng, S.P.; Khor, Y.P.; Lim, H.K.; Lai, O.M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cheong, L.Z.; Arbi Nehdi, I.; Mansour, L.; Ping Tan, C. Fabrication of Concentrated Palm Olein-Based Diacylglycerol Oil–Soybean Oil Blend Oil-In-Water Emulsion: In-Depth Study of the Rheological Properties and Storage Stability. Foods 2020, 9, 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9070877
Ng SP, Khor YP, Lim HK, Lai OM, Wang Y, Wang Y, Cheong LZ, Arbi Nehdi I, Mansour L, Ping Tan C. Fabrication of Concentrated Palm Olein-Based Diacylglycerol Oil–Soybean Oil Blend Oil-In-Water Emulsion: In-Depth Study of the Rheological Properties and Storage Stability. Foods. 2020; 9(7):877. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9070877
Chicago/Turabian StyleNg, Siou Pei, Yih Phing Khor, Hong Kwong Lim, Oi Ming Lai, Yong Wang, Yonghua Wang, Ling Zhi Cheong, Imededdine Arbi Nehdi, Lamjed Mansour, and Chin Ping Tan. 2020. "Fabrication of Concentrated Palm Olein-Based Diacylglycerol Oil–Soybean Oil Blend Oil-In-Water Emulsion: In-Depth Study of the Rheological Properties and Storage Stability" Foods 9, no. 7: 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9070877
APA StyleNg, S. P., Khor, Y. P., Lim, H. K., Lai, O. M., Wang, Y., Wang, Y., Cheong, L. Z., Arbi Nehdi, I., Mansour, L., & Ping Tan, C. (2020). Fabrication of Concentrated Palm Olein-Based Diacylglycerol Oil–Soybean Oil Blend Oil-In-Water Emulsion: In-Depth Study of the Rheological Properties and Storage Stability. Foods, 9(7), 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9070877