Study on the Influence of Bio-Based Packaging System on Sodium Benzoate Release Kinetics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chitosan Film Preparation
2.2. Sodium Alginate Film Preparation
2.3. Active Beads Preparation
2.4. Active Monolayer Films Preparation
2.5. Multilayer Films Preparation
2.6. Determination of Sodium Benzoate Release Kinetic
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dilucia, F.; Lacivita, V.; Conte, A.; Del Nobile, M.A. Sustainable use of fruit and vegetable by-products to enhance food packaging performance. Foods 2020, 9, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafarzadeh, S.; Jafari, S.M.; Salehabadi, A.; Nafchi, A.M.; Uthaya Kumar, U.S.; Khalil, H.P.S.A. Biodegradable green packaging with antimicrobial functions based on the bioactive compounds from tropical plants and their by-products. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 100, 262–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Jafari, S.M.; Sharma, S. Antimicrobial bio-nanocomposites and their potential applications in food packaging. Food Cont. 2020, 112, 107086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Rubio, A.; Almenar, E.; Hernandez-Munoz, P.; Lagaron, J.M.; Catala, R.; Gavara, R. Overview of active polymer-based packaging technologies for food applications. Food Rev. Int. 2004, 20, 357–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suppakul, P.; Miltz, J.; Sonneveld, K.; Bigger, S.W. Active packaging technologies with an emphasis on antimicrobial packaging and its applications. J. Food Sci. 2003, 68, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Del Nobile, M.A.; Conte, A. Packaging for food preservation; Food Engineering Series; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 80–100. [Google Scholar]
- Novello, J.; Sillankorva, S.; Pires, P.; Azeredo, J.; Wanke, C.H.; Tondo, E.C.; Bianchi, O. Inactivation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in mineral water by DP1 bacteriophage immobilized on ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer used as seal caps of plastic bottles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 49009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scannel, A.; Hill, C.; Ross, R.; Marx, S.; Hartmeier, W.; Arendt, E. Development of bioactive food packaging materials using immobilized bacteriocins lacticin 3147 and Nisaplin. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2000, 60, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Fogliano, V.; Heising, J.; Meulenbroeks, E.; Dekker, M. Volatile antimicrobial absorption in food gel depends on the food matrix characteristics. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 107, 105933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, S.; Ilberg, V.; Blum, U.; Langowski, H.C. Release of silver from silver doped PET bottles. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2020, 25, 100517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecitoglu, C.; Yemenicioglu, A.; Arslanoglu, A.; Elmaci, Z.S.; Korel, F.; Cetin, A.E. Incorporation of partially purified hen egg white lysozyme into zein films for antimicrobial food packaging. Food Res. Int. 2006, 39, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buonocore, G.G.; Del Nobile, M.A.; Panizza, A.; Corbo, M.R.; Nicolais, L. A general approach to describe the antimicrobial agent release from highly swellable films intended for food packaging applications. J. Control. Release 2003, 90, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristiana, M.; Yoshida, P.; Bastos, C.E.N.; Telma, T.F. Modeling of potassium sorbate diffusion through chitosan films. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 584–589. [Google Scholar]
- Maderuelo, C.; Zarzuelo, A.; Lanao, J.M. Critical factor in the release of drugs from sustained release hydrophilic matrices. J. Control. Release 2011, 154, 2–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaCoste, A.; Schaich, K.M.; Zumbrunnen, D.; Yam, K.L. Advancing controlled release packaging through smart blending. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2005, 18, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastromatteo, M.; Mastromatteo, M.; Conte, A.; Del Nobile, M.A. Advances in controlled release devices for food packaging applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 21, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemili, S.; Yemenicioğlu, A.; Altınkaya, S.A. Development of cellulose acetate based antimicrobial food packaging materials for controlled release of lysozyme. J. Food Eng. 2009, 90, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mastromatteo, M.; Barbuzzi, G.; Conte, A.; Del Nobile, M.A. Controlled release of thymol from zein based film. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2009, 10, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siepmann, J.; Streubel, A.; Peppas, N.A. Understanding and predicting drug delivery from hydrophilic matrix tablets using the sequential layer model. Pharm. Res. 2002, 19, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonocore, G.G.; Conte, A.; Corbo, M.R.; Sinigaglia, M.; Del Nobile, M.A. Mono- and multilayer active films containing lysozyme as antimicrobial agent. Inn. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2005, 6, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.U.; Kim, Y.M.; Lee, D.S. Multilayered antimicrobial polyethylene films applied to the packaging of ground beef. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2001, 14, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anukiruthika, T.; Sethupathy, P.; Wilson, A.; Kashampur, K.; Moses, J.A.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Multilayer packaging: Advances in preparation techniques and emerging food applications. Compreh. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 1156–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdalla, K.F.; Kamoun, E.A.; El Maghraby, G.M. Optimization of the entrapment efficiency and release of ambroxol hydrochloride alginate beads. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 5, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Anal, A.K.; Stevens, W.F. Chitosan-alginate multilayer beads for controlled release of ampillicin. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 290, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Jafari, S.M.; Aadil, R.M.; Assadpour, E.; Randhawa, M.A.; Mahmood, S. Development of active food packaging via incorporation of biopolymeric nanocarriers containing essential oils. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 101, 106–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimala Bharathi, S.K.; Moses, J.A.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Nano and microencapsulation using food grade polymers. In Polymers for Food Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 357–400. [Google Scholar]
- Liakos, I.; Rizzello, L.; Bayer, I.S.; Pompa, P.P.; Cingolani, R.; Athanassiou, A. Controlled antiseptic release by alginate polymer films and beads. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, C.H.; Heng, P.W.S.; Chan, L.W. Alginates as a useful natural polymer for microencapsulation and therapeutic applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, M.T.; Tzortzis, G.; Charalampopoulos, D.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Production and evaluation of dry alginate-chitosan microcapsules as an enteric delivery vehicle for probiotic bacteria. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 2834–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karzar Jeddi, M.; Mahkam, M. Magnetic nano carboxymethyl cellulose-alginate/chitosan hydrogel beads as biodegradable devices for controlled drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 135, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzioł, A.; Mazgała, A.; Michna, J.; Regiel-Futyra, A.; Sebastian, V. Preparation and characterization of alginate/chitosan formulations for ciprofloxacin-controlled delivery. J. Biomater. Appl. 2017, 32, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balanč, B.; Trifković, K.; Đorđević, V.; Marković, S.; Pjanović, R.; Nedović, V.; Bugarski, B. Novel resveratrol delivery systems based on alginate-sucrose and alginate-chitosan microbeads containing liposomes. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 832–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donhowe, E.G.; Flores, F.P.; Kerr, W.L.; Wicker, L.; Kong, F. Characterization and invitro bioavailability of β-carotene: Effects of microencapsulation method and food matrix. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 57, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djaenudin, E.; Budianto, E.; Saepudin, E.; Nasir, M. The encapsulation of Lactobacillus casei probiotic bacteria based on sodium alginate and chitosan. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Saint Petersburg, Russia, 17–18 April 2019; p. 012043. [Google Scholar]
- Pacheco, M.S.; Kano, G.E.; Paulo, L.D.A.; Lopes, P.S.; De Moraes, M.A. Silk fibroin/chitosan/alginate multilayer membranes as a system for controlled drug release in wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 152, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Shu, C.; Chen, Q.; Cao, J.; Jiang, W. The multi-layer film system improved the release and retention properties of cinnamon essential oil and its application as coating in inhibition to penicillium expansion of apple fruit. Food Chem. 2019, 299, 125109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, Y.S.; Bae, M.S.; Kim, S.; Noh, I.; Suh, J.K.F.; Lee, K.B.; Kwon, I.K. Mechanism of albumin release from alginate and chitosan beads fabricated in dual layers. Macromol. Res. 2011, 19, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Nobile, M.A.; Mensitieri, G.; Netti, P.A.; Nicolais, L. Anomalous diffusion in poly-ether-ether-ketone (PEEK). Chem. Eng. Sci. 1994, 49, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, S.; Conte, A.; Campos, C.; Gerschenson, L.; Del Nobile, M.A. Mass transport properties of tapioca-based active edible films. J. Food Eng. 2007, 81, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonocore, G.G.; Del Nobile, M.A.; Panizza, A.; Bove, S.; Battaglia, G.; Nicolais, L. Modeling the lysozyme release kinetics from antimicrobial films intended for food packaging applications. J. Food Sci. 2003, 68, 1365–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Nobile, M.A.; Massera, M. Modeling of water sorption kinetic in spaghetti during overcooking. Cereal Chem. 2000, 77, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iordanskii, A.L.; Zaikov, G.E.; Berlin, A.A. Diffusion kinetics of hydrolysis of biodegradable polymers. Weight loss and control of the release of low molecular weight substances. Polym. Sci. 2015, 8, 211–218. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.H. Antimicrobial Food Packaging. Food Technol. 2000, 54, 56–65. [Google Scholar]
- Krishna Rao, K.S.V.; Subha, M.C.S.; Vijaya Kumar Naidu, B.; Sairam, M.; Mallikarjuna, N.N.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Controlled release of diclofenac sodium and ibuprofen through beads of sodium alginate and hydroxy ethyl cellulose blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 102, 5708–5718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Ling, Y.; Cao, C.; Li, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, X. Chitosan derivatives/reduced graphene oxide/alginate beads for small-molecule drug delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 69, 1222–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Yu, S.; Lin, D.; Wu, Z.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J.; Ding, Z.; Miao, Y.; Liu, T.; Chen, T.; et al. Preparation, characterization, and release behavior of doxorubicin hydrochloride from dual cross-linked chitosan/alginate hydrogel beads. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 3057–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranenko, D.A.; Kolodyaznaya, V.S.; Zabelina, N.A. Effect of composition and properties of chitosan-based edible coatings on microflora of meat and meat products. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2013, 12, 149–157. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, M.; Neetoo, H.; Chen, H. Control of Listeria monocytogenes on ham steaks by antimicrobials incorporated into chitosan-coated plastic films. Food Microbiol. 2008, 25, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Neetoo, H.; Chen, H. Effectiveness of chitosan-coated plastic films incorporating antimicrobials in inhibition of Listeria monocytogenes on cold-smoked salmon. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 127, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
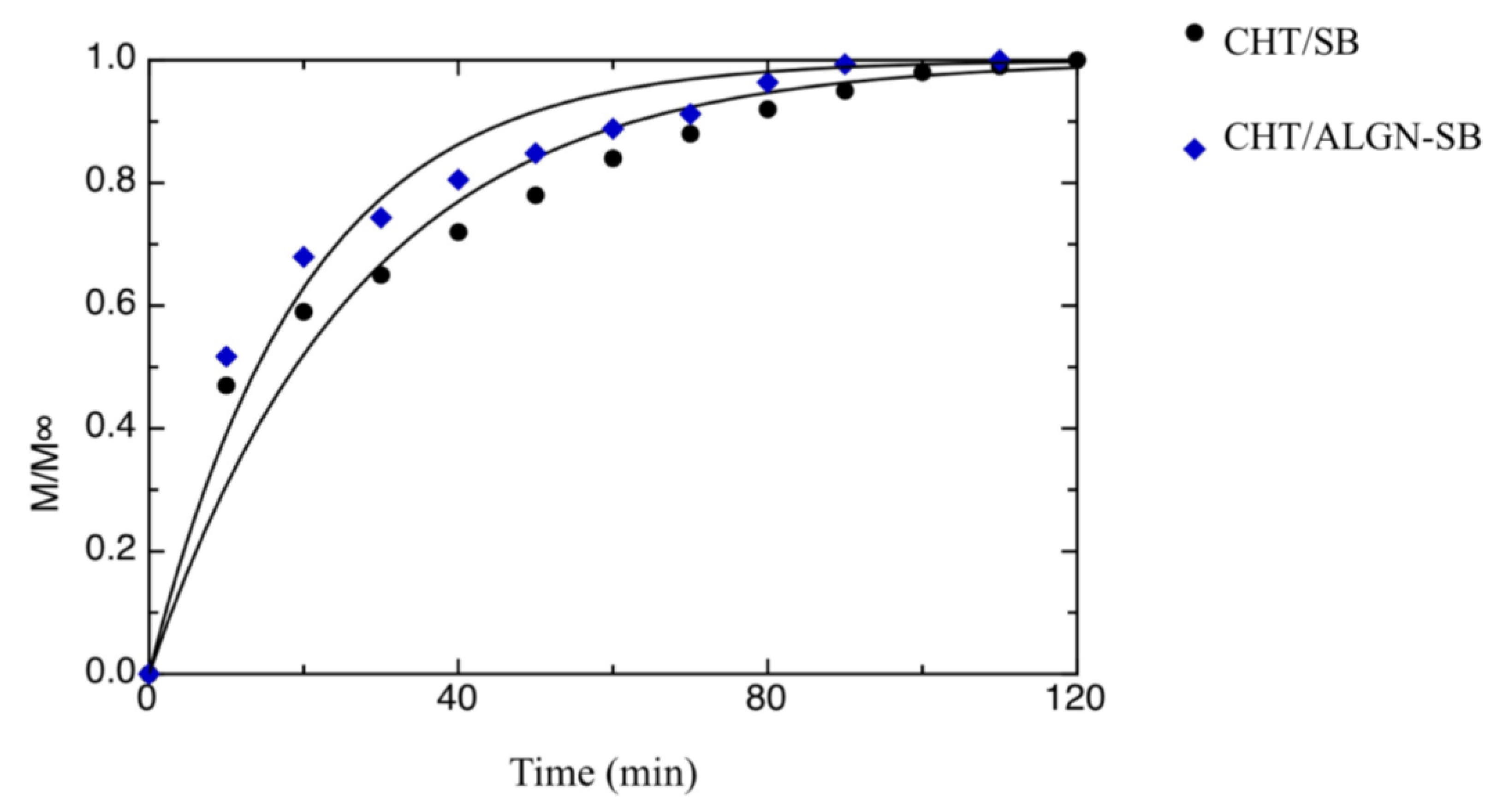
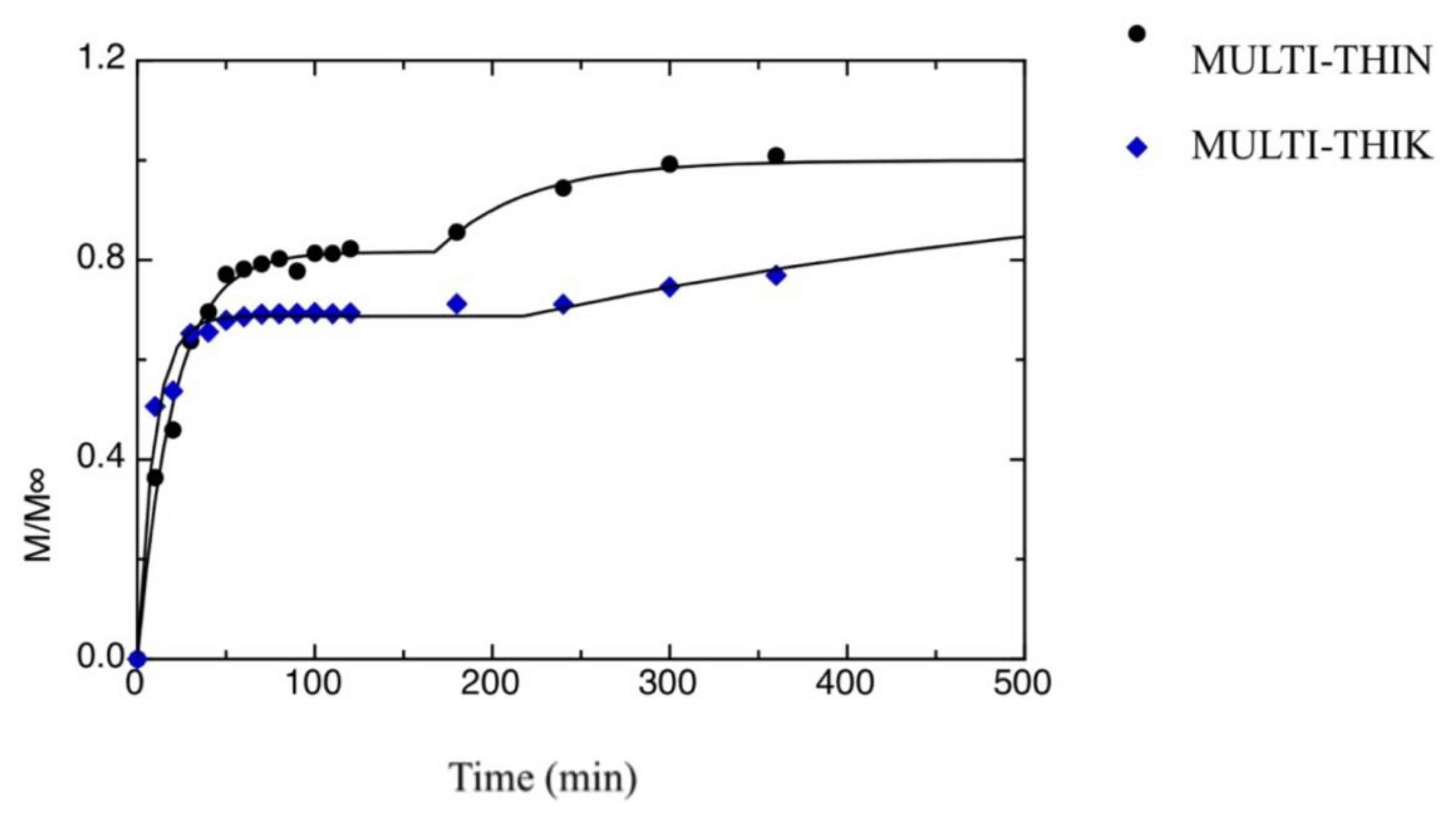
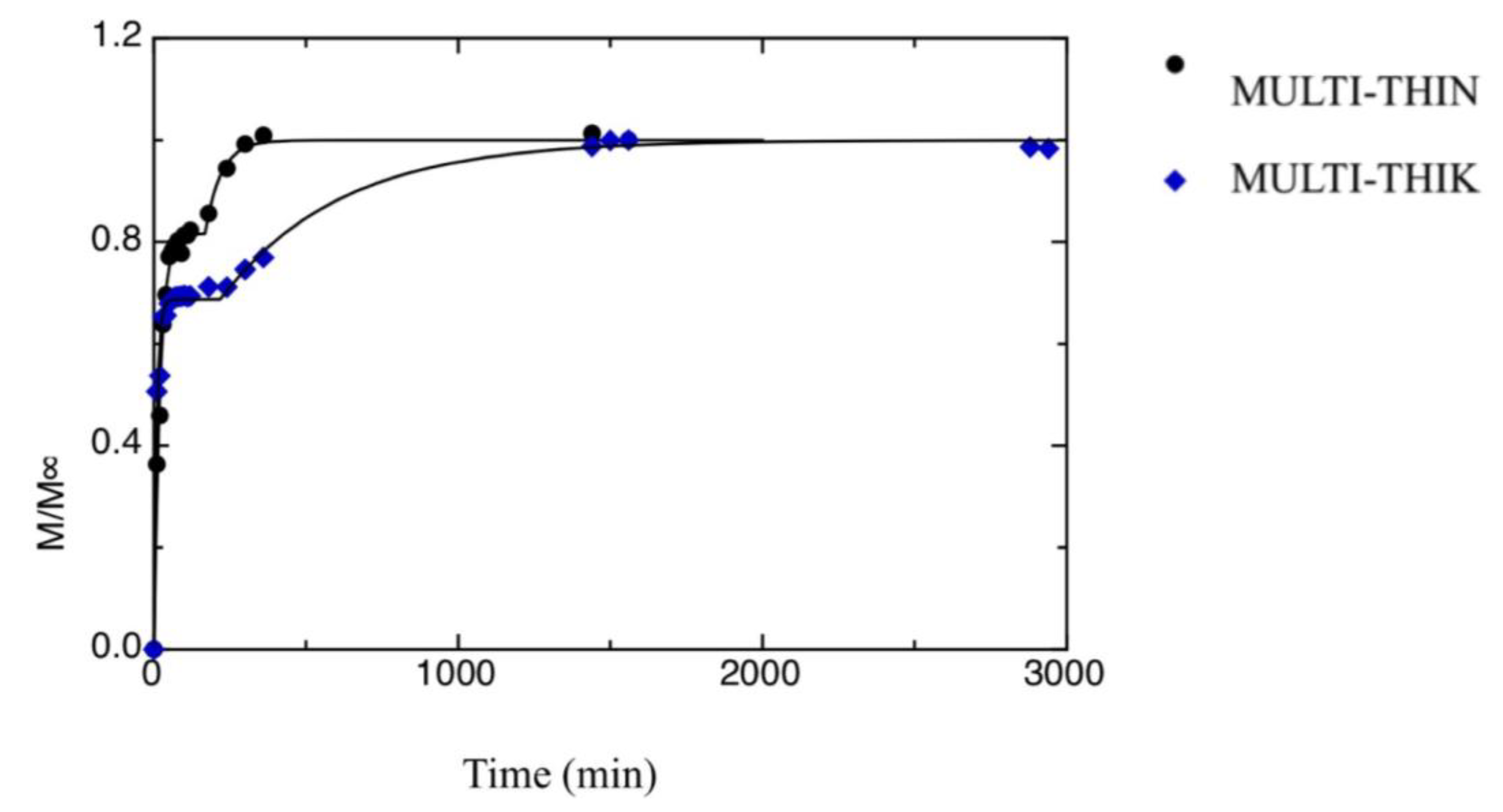
| a[1] [min−1] | a[3] [min−1] | M1∞/M∞ | t0 [min] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MULT-THIN | 20.3 ± 1.03 a | 52.6 ± 18.4 b | 0.816 ± 9.62 × 10−3 a | 168 ± 10.3 b |
| MULT-THIK | 9.32 ± 0.757 b | 393 ± 110 a | 0.687 ± 7.51 × 10−3 b | 219 ± 30.3 a |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Conte, A.; Lecce, L.; Iannetti, M.; Del Nobile, M.A. Study on the Influence of Bio-Based Packaging System on Sodium Benzoate Release Kinetics. Foods 2020, 9, 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9081010
Conte A, Lecce L, Iannetti M, Del Nobile MA. Study on the Influence of Bio-Based Packaging System on Sodium Benzoate Release Kinetics. Foods. 2020; 9(8):1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9081010
Chicago/Turabian StyleConte, Amalia, Lucia Lecce, Mariapia Iannetti, and Matteo Alessandro Del Nobile. 2020. "Study on the Influence of Bio-Based Packaging System on Sodium Benzoate Release Kinetics" Foods 9, no. 8: 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9081010
APA StyleConte, A., Lecce, L., Iannetti, M., & Del Nobile, M. A. (2020). Study on the Influence of Bio-Based Packaging System on Sodium Benzoate Release Kinetics. Foods, 9(8), 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9081010








