Inter-Relationships between Test Weight, Thousand Kernel Weight, Kernel Size Distribution and Their Effects on Durum Wheat Milling, Semolina Composition and Pasta Processing Quality
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wheat Samples
2.2. Wheat Physical Properties
2.3. Wheat Milling
2.4. Wheat and Semolina Analysis
2.5. Spaghetti Processing and Measurement of Quality
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Impact of Kernel Size on Durum Wheat Milling Quality
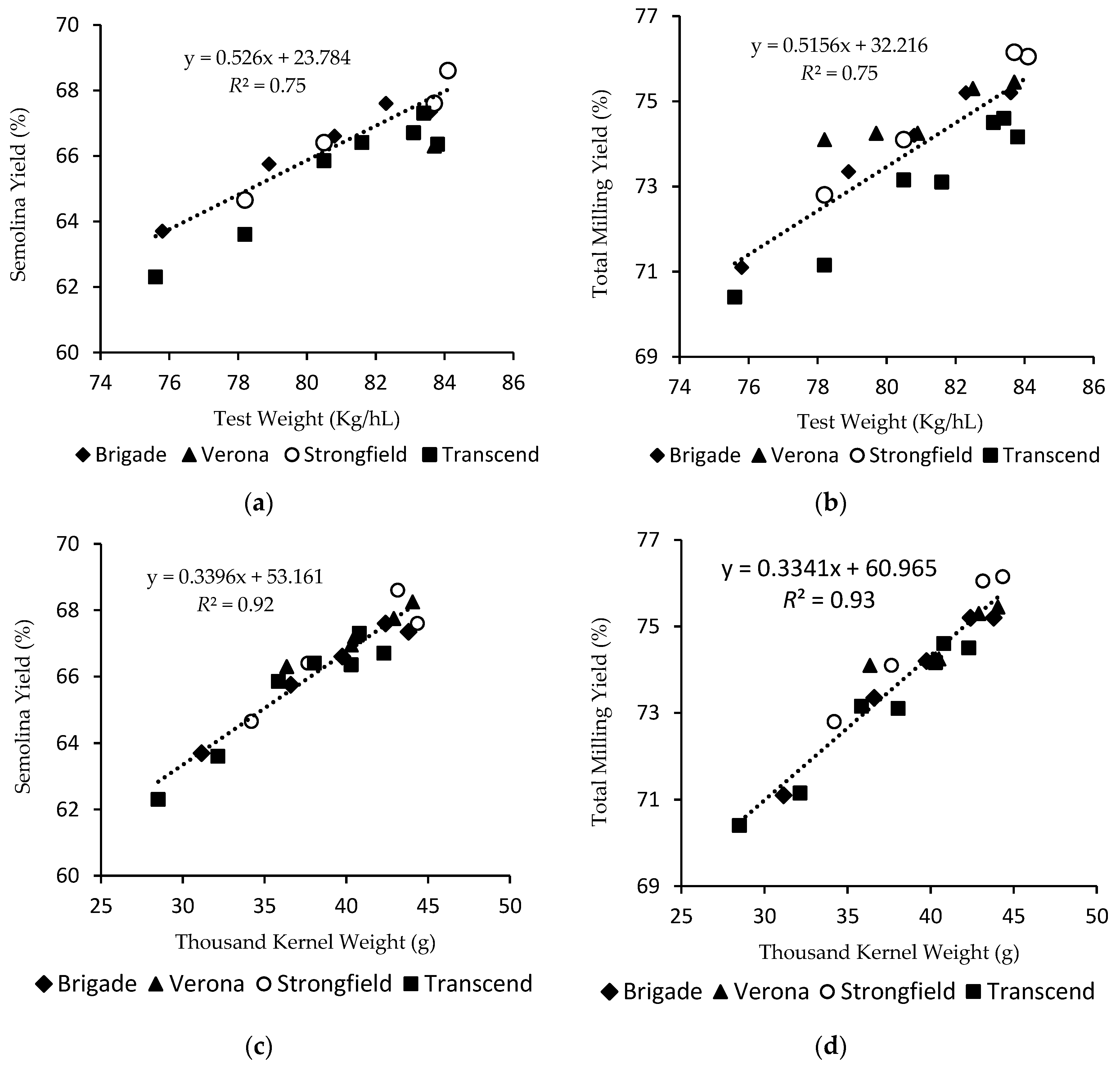
3.2. Effect of Genotype on the Relationship between TW, TKW and KSD
3.3. TW, TKW, KSD in Relation to Durum Milling Quality
3.4. The Potential of Kernel Size as a Grading Factor for Durum Wheat
3.5. Yellow Pigment and Color Characteristics of Semolina and Pasta in Relation to Durum Kernel Size
3.6. Cooking Characteristics of Pasta Made from Durum with Different Kernel Sizes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baker, D.; Fifield, C.C.; Hartsing, T.F. Factors related to the flour-yielding capacity of wheat. Northwest. Miller 1965, 272, 16–18. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo, R.R.; Dexter, J.E. Relationship between some durum wheat physical characteristics and semolina milling properties. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1980, 60, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexter, J.E.; Matsuo, R.R.; Martin, D.G. The relationship of durum wheat test weight to milling performance and spaghetti quality. Cereals Foods World 1987, 32, 772–777. [Google Scholar]
- Hook, S.C. Specific weight and wheat quality. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1984, 35, 1136–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkachuk, R.; Kuzina, F.D. Wheat: Relationship between some physical and chemical properties. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1979, 59, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, A.L.; Jordan, M.C.; Larson, G.; Somers, D.J.; Humphreys, D.G.; McCartney, C.A. Relationships between QTL for grain shape, grain weight, test weight, milling yield, and plant height in the spring wheat cross RL4452/’AC Domain’. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, D.R.; Ellison, F.W.; Mares, D.J. Effects of grain shape and size on milling yields in wheat. I. Theoretical analysis based on simple geometric models. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1984, 35, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabwalo, D.N.; Berzonsky, W.A.; Brabec, D.; Pearson, T.; Glover, K.D.; Kleinjan, J.L. Impact of grain morphology and the genotype by environment interactions on test weight of spring and winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Euphytica 2018, 214, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troccoli, A.; di Fonzo, N. Relationship between kernel size features and test weight in Triticum durum. Cereal Chem. 1999, 76, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaan, J.; EI-Khayat, G.H.; Manthey, F.A.; Fuller, M.P.; Brennan, C.S. Durum wheat quality: II. The relationship of kernel physicochemical composition to semolina quality and end product utilization. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 41, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexter, J.E.; Symons, S.J. Impact of durum wheat test weight, kernel size, kernel weight and protein content on semolina milling potential. Int. Miller 2007, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Dziki, D.; Laskowski, J. Wheat kernel physical properties and milling process. Acta Agrophys. 2005, 6, 59–71. [Google Scholar]
- Lyford, C.P.; Kidd, W.; Rayas-Duarte, P.; Deyoe, C. Prediction of flour extraction rate in hard red winter wheat using the single kernel characterization. J. Food Qual. 2005, 28, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, A.; Badiali, O.; Cantarero, M.; Leon, A.; Ribotta, P.; Rubiolo, O. Relationship of test weight and kernel properties to milling and baking quality in Agrentine Triticales. Cereal Res. Commun. 2002, 30, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baasandorj, T.; Ohm, J.; Simsek, S. Effect of kernel vitreousness and protein level on protein molecular weight distribution, milling quality, and breadmaking quality in hard red spring wheat. Cereal Chem. 2016, 93, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexter, J.E.; Matsuo, R.R. Effect of starchy kernels, immaturity, and shrunken kernels on durum wheat quality. Cereal Chem. 1981, 58, 395–400. [Google Scholar]
- Dexter, J.E.; Edwards, N.M. The implications of frequently encountered grading factors on the processing quality of durum wheat. Assoc. Oper. Millers Bull. 1998, 7165–7171. [Google Scholar]
- Canadian Grain Commission. Wheat: Export Grade Determinants Tables for Canada Western Amber Durum (CWAD) Wheat. 2020. Available online: https://www.grainscanada.gc.ca/en/grain-quality/official-grain-grading-guide/04-wheat/export-grade-determinants/cwad-en.html (accessed on 15 May 2020).
- Wang, K.; Taylor, D.; Pozniak, C.; Fu, B. Developing a high-throughput micromilling protocol for evaluating durum wheat milling performance and semolina quality. Cereal Chem. 2019, 96, 802–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexter, J.E.; Matsuo, R.R.; Kruger, J.E. The spaghetti-making quality of commercial durum wheat samples with variable α-amylase activity. Cereal Chem. 1990, 67, 405–412. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, P.; Sobering, D.; Antoniszyn, J. Protein testing methods. In Wheat Protein Production and Marketing; Fowler, D.B., Geddes, W.E., Johnston, A.M., Preston, K.R., Eds.; University Extension Press: Saskatoon, SK, Canada, 1998; pp. 37–47. [Google Scholar]
- AACC International. Approved Methods of Analysis (11th Ed.) Methods 76-31.01 (2014) and 38-12.02 (2000); AACC International: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, B.; Schlichting, L.; Pozniak, C.J.; Singh, A.K. Pigment loss from semolina to dough: Rapid measurement and relationship with pasta color. J. Cereal Sci. 2013, 57, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Wang, K.; Dupuis, B.; Taylor, D.; Nam, S. Kernel vitreousness and protein content: Relationship, interaction and synergistic effects on durum wheat quality. J. Cereal Sci. 2017, 78, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feillet, P.; Autran, J.C.; Icard-Verniere, C. Pasta brownness: An assessment. J. Cereal Sci. 2000, 32, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquistucci, R. Influence of Maillard reaction on protein modification and color development in pasta. Comparison of different drying conditions. LWT 2000, 33, 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Anese, M.; Nicoli, M.C.; Massini, R.; Lerici, C.R. Effects of drying processing on the Maillard reaction in pasta. Food Res. Int. 1999, 32, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ames, N.P.; Clarke, J.M.; Marchylo, B.A.; Dexter, J.E.; Woods, S.M. Effect of environment and genotype on durum wheat gluten strength and pasta viscoelasticity. Cereal Chem. 1999, 76, 582–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ames, N.P.; Clarke, J.M.; Marchylo, B.A.; Dexter, J.E.; Schlichting, L.M.; Woods, S.M. The effect of extra-strong gluten on quality parameters in durum wheat. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2003, 83, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Egidio, M.G.; Mariani, B.M.; Nardi, S.; Novaro, P.; Cubadda, R. Chemical and technological variables and their relationships: A predictive equation for pasta cooking quality. Cereal Chem. 1990, 67, 275–281. [Google Scholar]
- Malcolmson, L.J.; Matsuo, R.R.; Balshaw, R. Textural optimization of spaghetti using response surface methodology: Effects of drying temperature and durum protein level. Cereal Chem. 1993, 70, 417–423. [Google Scholar]





| Sample Description | Grade | Wheat Protein (%) | TW (kg/hL) | TKW (g) | Wheat Ash (%) | Semolina Ash (%) | Semolina Yield (%) | Total Milling Yield (%) | Granule Ash Score (%) | Semolina Size Distribution (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <150 µm | 150 < 250 µm | >250 µm | ||||||||||
| Unsorted Sample | 1 | 15.1c | 80.9b | 37.7c | 1.48d | 0.70c | 65.8bc | 74.1b | 65.8b | 6.9d | 25.4b | 67.7b |
| >no.8 a | 2 b | 14.1d | 82.6a | 61.9a | 1.52c | 0.67d | 67.9a | 76.5a | 71.4a | 4.7e | 25.4b | 70.0a |
| >no.7 | 1 | 14.0d | 82.6a | 47.4b | 1.46d | 0.66d | 66.4b | 74.2b | 70.7a | 6.5d | 25.6b | 67.9b |
| >no.6 | 1 | 15.2c | 81.1b | 35.8d | 1.49d | 0.71c | 65.2c | 73.1c | 65.2b | 8.0c | 25.4b | 66.6c |
| >no.5 | 3 c | 17.1b | 78.3c | 27.8e | 1.61b | 0.80b | 62.5d | 70.2d | 54.7c | 11.2b | 25.7b | 63.1d |
| <no.5 | 5 d | 18.6a | 73.5d | 19.3f | 1.86a | 0.95a | 59.8e | 67.5e | 39.1d | 13.0a | 26.6a | 60.4e |
| F Value | 2226.6 **** | 4797.1 **** | 12,482.5 **** | 480.0 **** | 525.7 **** | 302.2 **** | 477.1 **** | 5232.7 **** | 1749.9 **** | 34.4 *** | 701.7 **** | |
| Sample Description | Grade | Wheat Protein (%) | TW (Kg/hL) | TKW (g) | Kernel Size Distribution (%) | Semolina Yield (%) | Total Milling Yield (%) | Granules Ash Score (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| >no.8 | >no.7 | >no.6 | >no.5 | <no.5 | <no.6 | ||||||||
| Brigade 1 | 1 | 12.7m | 83.6bc | 43.8a | 9.0b | 48.7ab | 31.8k | 9.0m | 1.5kl | 10.6mn | 67.4bcde | 75.2abc | 76.0b |
| Brigade 2 | 1 | 13.5k | 82.3f | 42.4abc | 6.9cd | 41.2e | 36.6ghi | 13.3j | 2.0k | 15.3k | 67.6bcd | 75.2abc | 73.6c |
| Brigade 3 | 1 | 14.4i | 80.8h | 39.8de | 3.8fgh | 29.1g | 42.5b | 21.1g | 3.5fg | 24.6h | 66.6efghi | 74.2de | 70.9e |
| Brigade 4 | 3 a | 16.4e | 78.9k | 36.6fg | 3.5fgh | 18.7i | 42.3bc | 29.7d | 5.8d | 35.5e | 65.8i | 73.4efg | 65.8i |
| Brigade 5 | 5 b | 17.4c | 75.8m | 31.2j | 0.9ij | 11.0j | 27.9l | 41.7b | 18.5b | 60.2b | 63.7k | 71.1h | 56.8l |
| Verona 1 | 1 | 12.1o | 83.7b | 44.1a | 10.9a | 47.3abc | 31.7k | 8.6m | 1.5kl | 10.1m | 68.3ab | 75.5ab | 73.4c |
| Verona 2 | 1 | 13.1l | 82.5e | 42.9ab | 6.6de | 44.6cd | 34.8hij | 11.6k | 2.4ij | 14.0l | 67.8abc | 75.3ab | 73.8c |
| Verona 3 | 1 | 14.0j | 80.9h | 40.3cd | 4.8ef | 37.7f | 37.4efgh | 17.3i | 2.7hi | 20.1j | 67.0cdefg | 74.3cde | 68.7g |
| Verona 4 | 2 a | 14.8h | 79.7j | 40.5cd | 4.3fg | 36.3f | 39.6cdef | 16.7i | 3.1gh | 19.8j | 67.2cdefg | 74.3cde | 69.8f |
| Verona 5 | 3 a | 17.1d | 78.2l | 36.2fgh | 1.9ghi | 24.1h | 41.4bc | 27.4e | 5.1e | 32.5f | 66.3ghi | 74.1def | 60.3k |
| Strongfield 1 | 1 | 11.3p | 84.1a | 43.2a | 8.7bc | 48.9ab | 32.6jk | 8.3m | 1.6kl | 9.9n | 68.6a | 76.1a | 78.1a |
| Strongfield 2 | 1 | 13.9j | 83.7b | 44.3a | 11.5a | 49.0a | 31.6k | 6.4n | 1.4l | 7.8o | 67.6bcd | 76.2a | 77.9a |
| Strongfield 3 | 1 | 13.9j | 80.5i | 37.6efg | 2.5ghi | 29.1g | 46.1a | 19.8h | 2.5hij | 22.3i | 66.4fghi | 74.1de | 74.2c |
| Strongfield 4 | 3 a | 17.1d | 78.2l | 34.2hi | 2.3hij | 20.2i | 39.8bcde | 32.2c | 5.7de | 37.8d | 64.7j | 72.8g | 64.7j |
| Transcend 1 | 1 | 10.6q | 83.8b | 40.3cd | 7.4bcd | 42.2de | 36.9fghi | 12.0k | 1.6kl | 13.5l | 66.4fghi | 74.2de | 74.1c |
| Transcend 2 | 1 | 12.5n | 83.4c | 40.8bcd | 6.9cd | 41.3e | 38.1defg | 12.3k | 1.5kl | 13.8l | 67.3cdef | 73.1g | 74.2c |
| Transcend 3 | 1 | 15.4g | 83.1d | 42.3abc | 8.6bcd | 45.8bc | 34.3ijk | 10.3l | 1.1l | 11.3m | 66.7defgh | 74.6bcd | 71.9d |
| Transcend 4 | 1 | 12.6mn | 81.6g | 38.1ef | 3.2fgh | 29.0g | 40.8bcd | 23.3f | 3.7f | 27.1g | 66.4fghi | 73.2fg | 68.1g |
| Transcend 5 | 1 | 15.6f | 80.5i | 35.9gh | 1.0ij | 19.3i | 46.6a | 29.6d | 3.5fg | 33.1f | 65.9hi | 74.5bcd | 66.7h |
| Transcend 6 | 3 a | 17.6b | 78.2l | 32.2ij | 0.6j | 8.3jk | 33. jk1 | 46.4a | 11.6c | 58.0c | 63.6k | 71.0h | 56.7l |
| Transcend 7 | 5 b | 19.3a | 75.6m | 28.5k | 0.5j | 6.7k | 26.3l | 47.3a | 19.2a | 66.5a | 62.3l | 70.4h | 45.9m |
| TW | TKW | Semolina Yield | Total Milling Yield | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat Properties | ||||
| Protein | −0.96 *** | −0.94 *** | −0.93 *** | −0.91 *** |
| TW | - | 0.92 *** | 0.87 *** | 0.87 *** |
| TKW | 0.92 *** | - | 0.97 *** | 0.96 *** |
| Kernel Fractions | ||||
| >no.8 | 0.88 *** | 0.90 *** | 0.79 *** | 0.85 *** |
| >no.7 | 0.93 *** | 0.97 *** | 0.91 *** | 0.93 *** |
| >no.6 | 0.03 ns | 0.01 ns | 0.19 ns | 0.13 ns |
| >no.5 | −0.93 *** | −0.98 *** | −0.94 *** | −0.96 *** |
| <no.5 | −0.86 *** | −0.88 *** | −0.89 *** | −0.88 *** |
| Combined Kernel Fractions | ||||
| >no.7 | 0.93 *** | 0.97 *** | 0.90 *** | 0.93 *** |
| >no.6, <no.8 | 0.90 *** | 0.95 *** | 0.95 *** | 0.94 *** |
| >no.5, <no.7 | −0.86 *** | −0.90 *** | −0.81 *** | −0.85 *** |
| <no.6 | −0.93 *** | −0.97 *** | −0.95 *** | −0.96 *** |
| Sample Description | Wheat Protein | Semolina Protein (%) | Semolina (70% Extraction) | Semolina (>180 um) | Spaghetti | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TYP (ppm) | L* | a* | b* | L* | a* | b* | TYP (ppm) | L* | a* | b* | |||
| All kernels | 15.1c | 14.2c | 10.0d | 83.6b | −2.6cd | 32.3bc | 82.9b | −2.6cd | 34.5b | 8.1d | 72.2b | 5.2c | 64.2b |
| >no.8 ∆ | 14.1d | 12.9d | 8.1f | 84.1a | −2.7de | 30.7d | 83.7a | −2.7cd | 32.2c | 6.6f | 73.6a | 3.9d | 62.1c |
| >no.7 | 14.0d | 13.1d | 9.0e | 84.1a | −2.8e | 31.9c | 83.4ab | −2.7d | 34.1b | 7.6e | 73.6a | 4.0d | 64.6ab |
| >no.6 | 15.2c | 14.3c | 10.3c | 83.7b | −2.6c | 33.1a | 82.9b | −2.5c | 35.2ab | 8.7c | 72.2b | 5.2c | 65.3a |
| >no.5 | 17.1b | 16.2b | 11.5b | 83.3b | −2.4b | 32.8ab | 82.0c | −2.2b | 36.0a | 9.9b | 70.2c | 7.0b | 64.6ab |
| <no.5 | 18.6a | 17.8a | 12.6a | 82.6c | −2.0a | 32.1bc | 81.0d | −1.7a | 35.6a | 10.8a | 66.7d | 9.9a | 61.7c |
| F value | 2226.6 **** | 1736.2 **** | 6423.4 **** | 63.3 **** | 139.8 **** | 58.0 **** | 175.9 **** | 155.5 **** | 58.4 **** | 4274.7 **** | 1340.1 **** | 1473.3 **** | 98.3 **** |
| Sample Description | Wheat Protein (%) | Semolina Protein (%) | Wheat Ash (%) | Semolina Ash (%) | Semolina (70% Extraction) | Semolina (>180 µm) | Spaghetti | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TYP (ppm) | L* | a* | b* | L* | a* | b* | TYP (ppm) | L* | a* | b* | |||||
| Brigade 1 | 12.7m | 11.7m | 1.31kl | 0.61hi | 8.2h | 84.3bc | −2.8hi | 30.6gh | 83.6b | −2.9j | 33.0def | 6.5i | 74.3 | 3.1 | 61.6 |
| Brigade 2 | 13.5k | 12.5l | 1.36j | 0.64fgh | 8.6e | 83.9defg | −2.7fg | 31.4bcd | 83.4bc | −2.7ij | 33.4cde | 7.1f | 73.4 | 3.6 | 62.6 |
| Brigade 3 | 14.4i | 13.4i | 1.38i | 0.66f | 9.5b | 83.8defgh | −2.7fg | 32.3a | 83.0cde | −2.6ghi | 34.4ab | 7.5d | 72.7 | 4.8 | 63.6 |
| Brigade 4 | 16.4e | 15.4e | 1.41fg | 0.71cd | 10.1a | 83.4hijk | −2.3cd | 32.0ab | 82.5efg | −2.2cd | 34.7a | 8.2ab | 71.5 | 6.0 | 63.5 |
| Brigade 5 | 17.4c | 16.5c | 1.51d | 0.79b | 10.2a | 83.5fghij | −2.4de | 31.6bcd | 82.2gh | −2.2bc | 34.8a | 8.3a | 70.3 | 7.2 | 62.1 |
| Verona 1 | 12.1o | 11.2n | 1.38hi | 0.65fg | 8.1hi | 84.0cde | −2.7fg | 31.3cde | 83.4bc | −2.7hi | 32.7f | 6.6hi | 74.0 | 3.4 | 61.6 |
| Verona 2 | 13.1l | 12.4l | 1.34j | 0.64fgh | 8.6ef | 83.9def | −2.7fg | 31.3cdef | 83.2bcd | −2.6fghi | 33.5cde | 7.1f | 73.2 | 3.6 | 62.9 |
| Verona 3 | 14.0j | 13.2ij | 1.43ef | 0.69de | 8.9d | 83.4hijk | −2.5e | 31.6abc | 82.9cde | −2.4efg | 33.5cd | 7.2f | 72.6 | 4.9 | 62.0 |
| Verona 4 | 14.8h | 13.9h | 1.40gh | 0.68e | 8.8de | 83.7efghi | −2.5e | 31.0defg | 82.9cde | −2.4de | 33.1def | 7.2f | 72.3 | 5.2 | 62.1 |
| Verona 5 | 17.1d | 16.4c | 1.55c | 0.78b | 9.3c | 83.3jk | −2.2bc | 30.5ghi | 82.2gh | −2.0b | 33.5cde | 7.3ef | 70.8 | 6.5 | 61.1 |
| Strongfield 1 | 11.3p | 10.4o | 1.30l | 0.60ij | 7.7j | 84.3bc | −2.9hi | 30.3hi | 83.6b | −2.7ij | 31.9h | 5.9k | 74.2 | 3.3 | 59.2 |
| Strongfield 2 | 13.9j | 12.8k | 1.32kl | 0.59j | 7.7j | 84.0bcd | −2.7gh | 29.9i | 83.4bc | −2.6ghi | 31.9h | 6.1j | 74.3 | 3.0 | 60.3 |
| Strongfield 3 | 13.9j | 13.1j | 1.31kl | 0.62gh | 8.4fg | 83.8defg | −2.5ef | 30.5ghi | 83.2bcd | −2.5efgh | 32.7fg | 6.8g | 72.4 | 4.4 | 61.9 |
| Strongfield 4 | 17.1d | 16.2d | 1.51d | 0.71c | 8.8de | 83.4ijk | −2.2b | 30.3hi | 82.5efg | −2.1bc | 32.8f | 6.9g | 71.2 | 6.0 | 60.7 |
| Transcend 1 | 10.6q | 9.8p | 1.31kl | 0.62hi | 8.1hi | 84.7a | −2.9i | 30.7fgh | 84.1a | −2.8j | 32.7fg | 6.8h | 74.3 | 3.5 | 61.7 |
| Transcend 2 | 12.5n | 11.6m | 1.33k | 0.63fgh | 8.3gh | 84.4ab | −2.8ghi | 30.6gh | 83.5b | −2.7hi | 32.9ef | 7.1f | 73.7 | 3.7 | 62.9 |
| Transcend 3 | 15.4g | 14.4g | 1.41fg | 0.65f | 8.0i | 83.9de | −2.4de | 30.3ghi | 83.3bcd | −2.4def | 32.2gh | 6.8gh | 72.9 | 4.3 | 61.7 |
| Transcend 4 | 12.6mn | 11.6m | 1.44e | 0.69de | 8.8de | 84.3bc | −2.7gh | 31.4bcd | 83.4bc | −2.6ghi | 33.5cde | 7.4de | 72.9 | 4.7 | 62.7 |
| Transcend 5 | 15.6f | 14.6f | 1.41fg | 0.70cde | 9.5bc | 83.8defg | −2.5e | 31.4bcd | 82.8def | −2.3de | 33.9bc | 7.8c | 72.0 | 5.2 | 63.4 |
| Transcend 6 | 17.6b | 16.7b | 1.58b | 0.79b | 9.5b | 83.5ghijk | −2.1b | 30.8efgh | 82.3fg | −2.0b | 33.8c | 8.1b | 70.7 | 6.5 | 62.6 |
| Transcend 7 | 19.3a | 18.6a | 1.79a | 0.90a | 10.0a | 83.2k | −1.9a | 30.6fgh | 81.8h | −1.7a | 33.8c | 8.2a | 69.0 | 8.3 | 61.2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, K.; Fu, B.X. Inter-Relationships between Test Weight, Thousand Kernel Weight, Kernel Size Distribution and Their Effects on Durum Wheat Milling, Semolina Composition and Pasta Processing Quality. Foods 2020, 9, 1308. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9091308
Wang K, Fu BX. Inter-Relationships between Test Weight, Thousand Kernel Weight, Kernel Size Distribution and Their Effects on Durum Wheat Milling, Semolina Composition and Pasta Processing Quality. Foods. 2020; 9(9):1308. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9091308
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Kun, and Bin Xiao Fu. 2020. "Inter-Relationships between Test Weight, Thousand Kernel Weight, Kernel Size Distribution and Their Effects on Durum Wheat Milling, Semolina Composition and Pasta Processing Quality" Foods 9, no. 9: 1308. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9091308
APA StyleWang, K., & Fu, B. X. (2020). Inter-Relationships between Test Weight, Thousand Kernel Weight, Kernel Size Distribution and Their Effects on Durum Wheat Milling, Semolina Composition and Pasta Processing Quality. Foods, 9(9), 1308. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9091308





