An Improved Multiple Competitive Immuno-SERS Sensing Platform and Its Application in Rapid Field Chemical Toxin Screening
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Chemical and Instruments
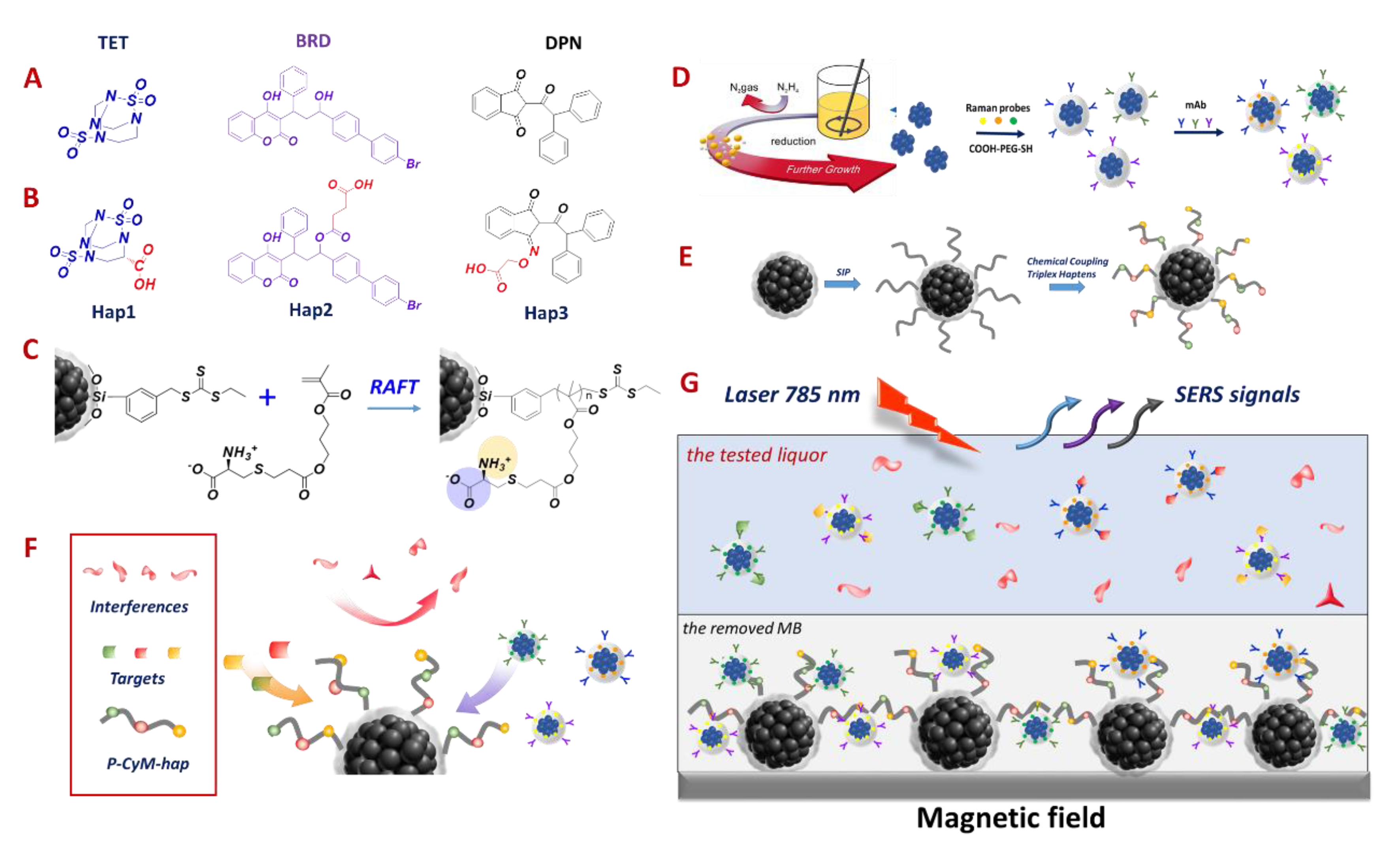
2.2. Preparation of the MB@P-CyM-hap as Multiple Competitive Substrate
2.3. Chemical Conjugation of Triple Haptens on the MB@P-CyM
2.4. Constructing the mAb-Labeled SERS Probe Cocktail
2.5. Detection of DPN, BRD and TET in Buffer
2.6. Screening DPN, BRD and TET in Spiked Biological and Food Matrices
2.7. SERS Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
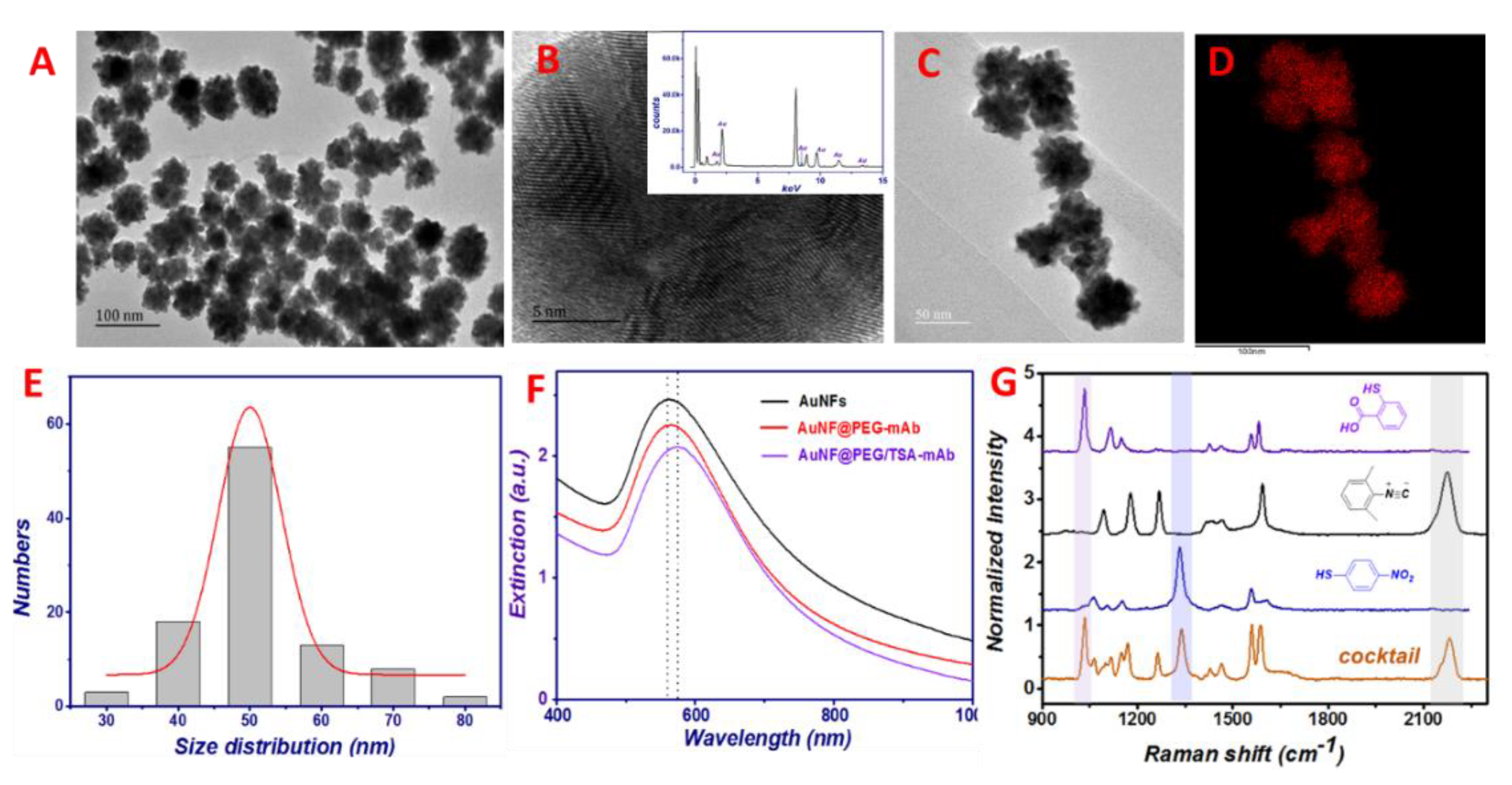
3.1. Characterizations of the Non-Fouling MB@P-CyM-hap
3.2. Fabricating the Specific SERS-Encoding Probes and Examining Their Sensing Capacities
3.3. Sensing Performance of This Assay
3.4. Sample Analysis and Method Validation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dincer, C.; Bruch, R.; Costa-Rama, E.; Fernandez-Abedul, M.T.; Merkoci, A.; Manz, A.; Urban, G.A.; Guder, F. Disposable Sensors in Diagnostics, Food, and Environmental Monitoring. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1806739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.C.; Chou, C.C.; Yang, Y.Q.; Wei-Kai, T.; Wang, Y.T.; Chan, Y.H. Multiplexed Detection of Tumor Markers with Multicolor Polymer Dot-Based Immunochromatography Test Strip. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 2134–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walper, S.A.; Lasarte Aragones, G.; Sapsford, K.E.; Brown, C.W.; Rowland, C.E.; Breger, J.C.; Medintz, I.L. Detecting Biothreat Agents: From Current Diagnostics to Developing Sensor Technologies. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 1894–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heggestad, J.T.; Fontes, C.M.; Joh, D.Y.; Hucknall, A.M.; Chilkoti, A. In Pursuit of Zero 2.0: Recent Developments in Nonfouling Polymer Brushes for Immunoassays. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e1903285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Yan, L.; Zhao, X.; Chen, X.; Li, A.; Zheng, D.; Zhou, X.; Dai, X.; Xu, F.J. Versatile Types of Organic/Inorganic Nanohybrids: From Strategic Design to Biomedical Applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 1666–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Geryak, R.; Geldmeier, J.; Kim, S.; Tsukruk, V.V. Synthesis, Assembly, and Applications of Hybrid Nanostructures for Biosensing. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 12942–13038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elacqua, E.; Zheng, X.; Shillingford, C.; Liu, M.; Weck, M. Molecular Recognition in the Colloidal World. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 2756–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, L.; Walt, D.R. Highly Sensitive and Multiplexed Protein Measurements. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 293–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Koo, K.M.; Wang, Y.; Trau, M. Engineering State-of-the-Art Plasmonic Nanomaterials for SERS-Based Clinical Liquid Biopsy Applications. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1900730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, K.; Zong, S.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, K.; Li, L.; Li, N.; Wang, Z.; Cui, Y. Array-Assisted SERS Microfluidic Chips for Highly Sensitive and Multiplex Gas Sensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Choi, N.; Wang, R.; Lee, S.; Moon, K.C.; Yoon, S.Y.; Chen, L.; Choo, J. Simultaneous Detection of Dual Prostate Specific Antigens Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering-Based Immunoassay for Accurate Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 4926–4933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liang, D.; Feng, J.; Tang, X. Multicolor Cocktail for Breast Cancer Multiplex Phenotype Targeting and Diagnosis Using Bioorthogonal Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Nanoprobes. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 11045–11054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, B.; Xiao, M.; Zou, Y.; Lai, W.; Pei, H.; Alam, M.F.; Zhang, W.; Wan, Y.; Li, L. Fractal SERS Nanoprobes For Multiplexed Quantitative Gene Profiling. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 156, 112130–112136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.X.; Xu, D.; Guo, D.; Han, H.X.; Li, D.W.; Ma, W. Enzyme-Free Amplified SERS Immunoassay For The Ultrasensitive Detection Of Disease Biomarkers. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 2933–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F.; Ella-Menye, J.-R.; Galvan, D.D.; Bai, T.; Hung, H.-C.; Chou, Y.-N.; Zhang, P.; Jiang, S.; Yu, Q. Stealth Surface Modification of Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Substrates for Sensitive and Accurate Detection in Protein Solutions. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 2668–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panikar, S.S.; Ramirez-Garcia, G.; Sidhik, S.; Lopez-Luke, T.; Rodriguez-Gonzalez, C.; Ciapara, I.H.; Castillo, P.S.; Camacho-Villegas, T.; De la Rosa, E. Ultrasensitive SERS Substrate for Label-Free Therapeutic-Drug Monitoring of Paclitaxel and Cyclophosphamide in Blood Serum. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 2100–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panadero, S.; Gomezhens, A.; Perezbendito, D. Simultaneous Determination Of Warfarin And Bromadiolone By Derivative Synchronous Fluorescence Spectrometry. Talanta 1993, 40, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlavacek, A.; Farka, Z.; Hubner, M.; Hornakova, V.; Nemecek, D.; Niessner, R.; Skladal, P.; Knopp, D.; Gorris, H.H. Competitive Upconversion-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for the Sensitive Detection of Diclofenac. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 6011–6018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wen, K.; Dong, B.; Zhang, J.; Bai, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, P.; Mujtaba, M.G.; Yu, X.; Yu, W.; et al. Novel Inner Flter Effect-Based Fluorescence Immunoassay with Gold Nanoclusters for Bromadiolone Detection in Human Serum. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 297, 126787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Yu, W.; Yu, X.; Wen, K.; Shao, B.; Sun, J.; Shen, J.; Wang, Z. Highly Efficient and Precise Two-Step Cell Selection Method for Tetramethylene Disulfotetramine-Specific Monoclonal Antibody Production. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 424, 127689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Liu, S.; Dong, B.; Li, C.; Yang, H.; Zhang, X.; Wen, K.; Yu, X.; Yu, W.; Shen, J.; et al. Production of a Specific Monoclonal Antibody and a Sensitive Immunoassay for yhe Detection of Diphacinone in Biological Samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 6755–6765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, L.L.; Liang, B.; Booth, M.C.; Filigenzi, M.S.; Tkachenko, A.; Gaskill, C.L. Development and Validation of Quantitative Ultraperformance Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Assay for Anticoagulant Rodenticides in Liver. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 6682–6691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erfani, A.; Seaberg, J.; Aichele, C.P.; Ramsey, J.D. Interactions between Biomolecules and Zwitterionic Moieties: A Review. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 2557–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.F.; Ma, Q.; Xue, D.S.; Shan, W.C.; Liu, R.Q.; Dong, B.L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.H.; Shao, B. Polymer/Inorganic Nanohybrids: An Attractive Materials for Analysis and Sensing. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 140, 116273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Qi, D.; Deng, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, D. Superparamagnetic High-Magnetization Microspheres with an Fe3O4@SiO2 Core and Perpendicularly Aligned Mesoporous SiO2 Shell for Removal of Microcystins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 28–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alswieleh, A.M.; Cheng, N.; Canton, I.; Ustbas, B.; Xue, X.; Ladmiral, V.; Xia, S.; Ducker, R.E.; El Zubir, O.; Cartron, M.L.; et al. Zwitterionic Poly(amino acid methacrylate) Brushes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 9404–9413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Hu, F.; Chen, K.; Duan, Z.; Gu, H.; Xu, H. A Facile Route to the Synthesis of Spherical Poly(Acrylic Acid) Brushes via RAFT Polymerization for High-Capacity Protein Immobilization. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 398, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sample | Toxin/Spiked (ng mL−1) | This ci-SERS Assay | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Detected (ng mL−1) | Recovery (%) | ||
| Human Serum | BRD/10.0 | 8.46 | 84.6 |
| TET/10.0 | 11.4 | 114 | |
| DPN/10.0 | 7.32 | 73.2 | |
| Milk | BRD/10.0 | 7.78 | 77.8 |
| TET/10.0 | 11.8 | 118 | |
| DPN/10.0 | 8.24 | 82.4 | |
| Chicken | BRD/10.0 | 7.21 | 72.1 |
| TET/10.0 | 11.8 | 118 | |
| DPN/10.0 | 12.3 | 123 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, J.; Wang, Z.; Yang, L.; He, Y.; Liu, R.; Ran, W.; Wang, Z.; Shao, B. An Improved Multiple Competitive Immuno-SERS Sensing Platform and Its Application in Rapid Field Chemical Toxin Screening. Toxics 2022, 10, 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100605
Sun J, Wang Z, Yang L, He Y, Liu R, Ran W, Wang Z, Shao B. An Improved Multiple Competitive Immuno-SERS Sensing Platform and Its Application in Rapid Field Chemical Toxin Screening. Toxics. 2022; 10(10):605. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100605
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Jiefang, Zixuan Wang, Ling Yang, Yi He, Rui Liu, Wei Ran, Zhanhui Wang, and Bing Shao. 2022. "An Improved Multiple Competitive Immuno-SERS Sensing Platform and Its Application in Rapid Field Chemical Toxin Screening" Toxics 10, no. 10: 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100605
APA StyleSun, J., Wang, Z., Yang, L., He, Y., Liu, R., Ran, W., Wang, Z., & Shao, B. (2022). An Improved Multiple Competitive Immuno-SERS Sensing Platform and Its Application in Rapid Field Chemical Toxin Screening. Toxics, 10(10), 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100605







