Seasonal Distribution of Atmospheric Coarse and Fine Particulate Matter in a Medium-Sized City of Northern China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
3. Results and Discussion
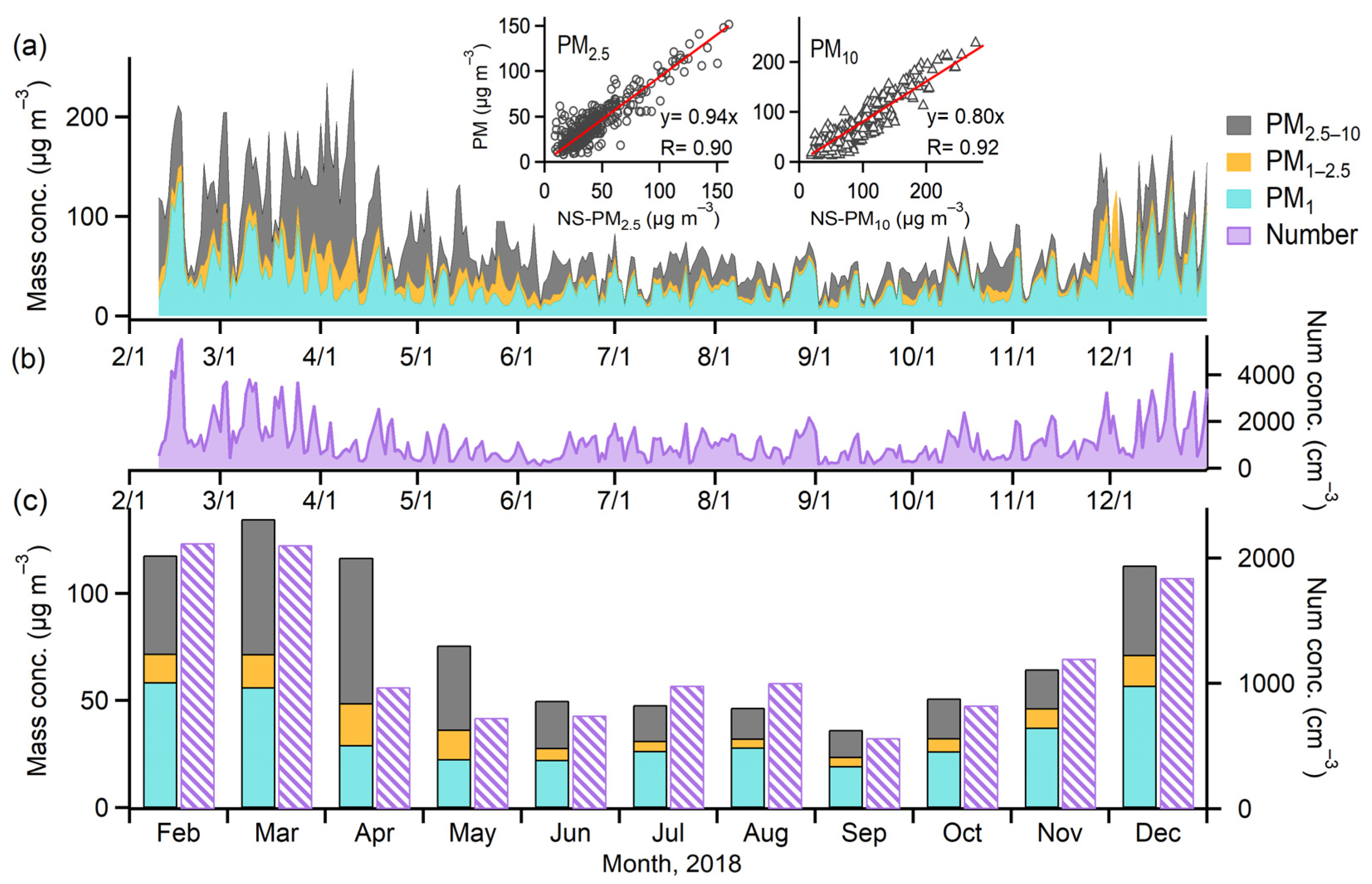
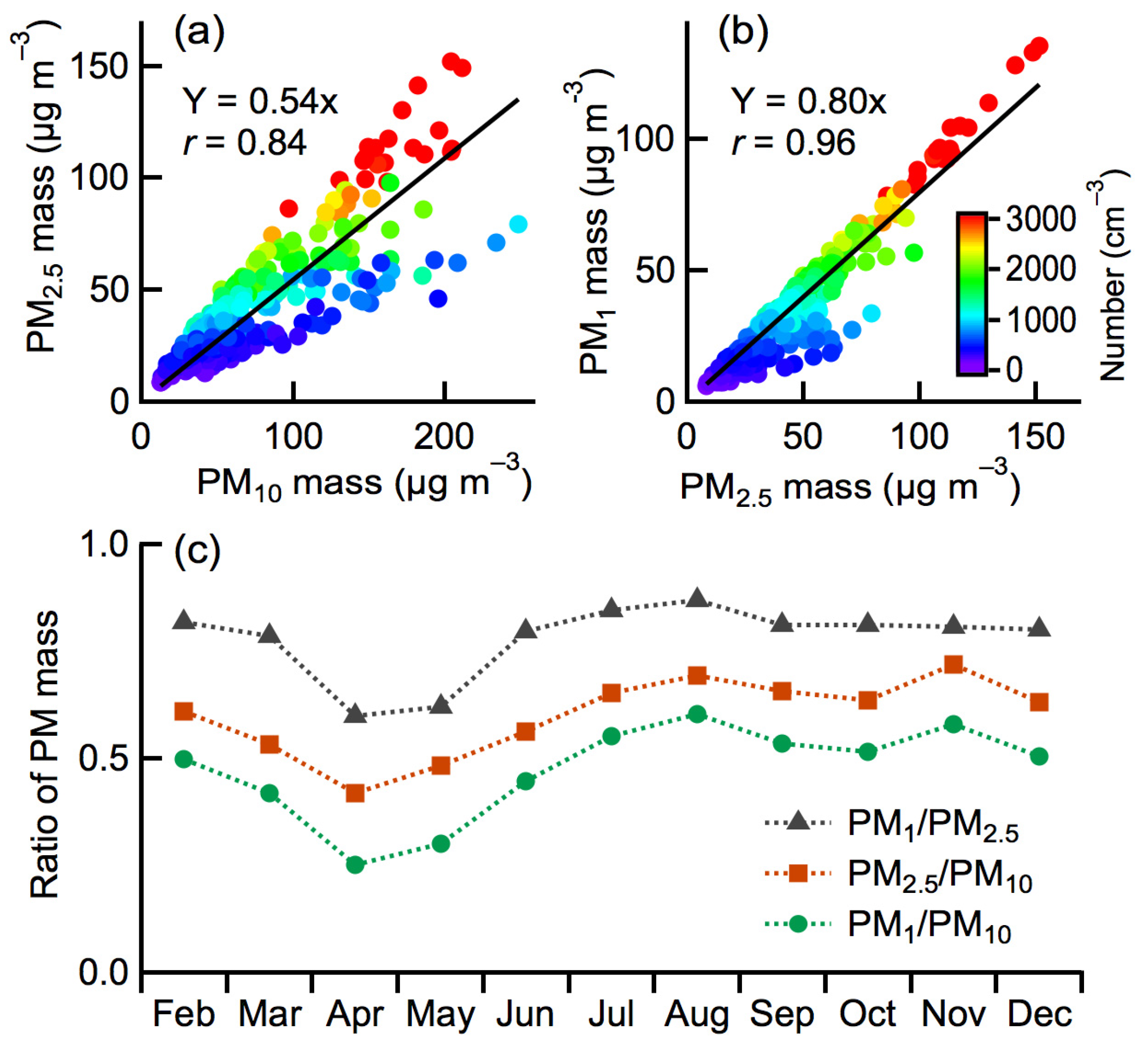
3.1. Seasonal Variation Profiles of PM
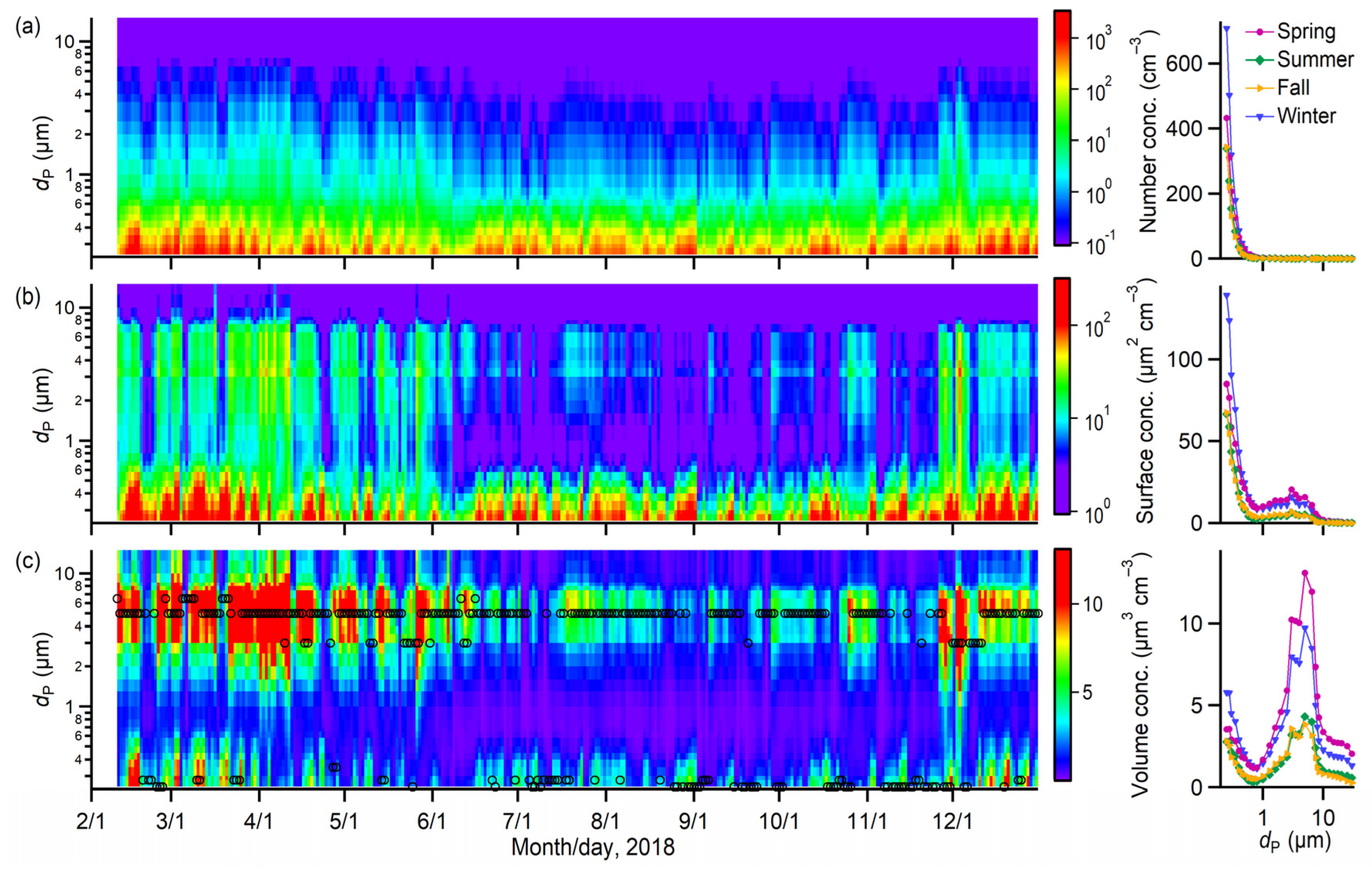
3.2. Size Distributions of PM
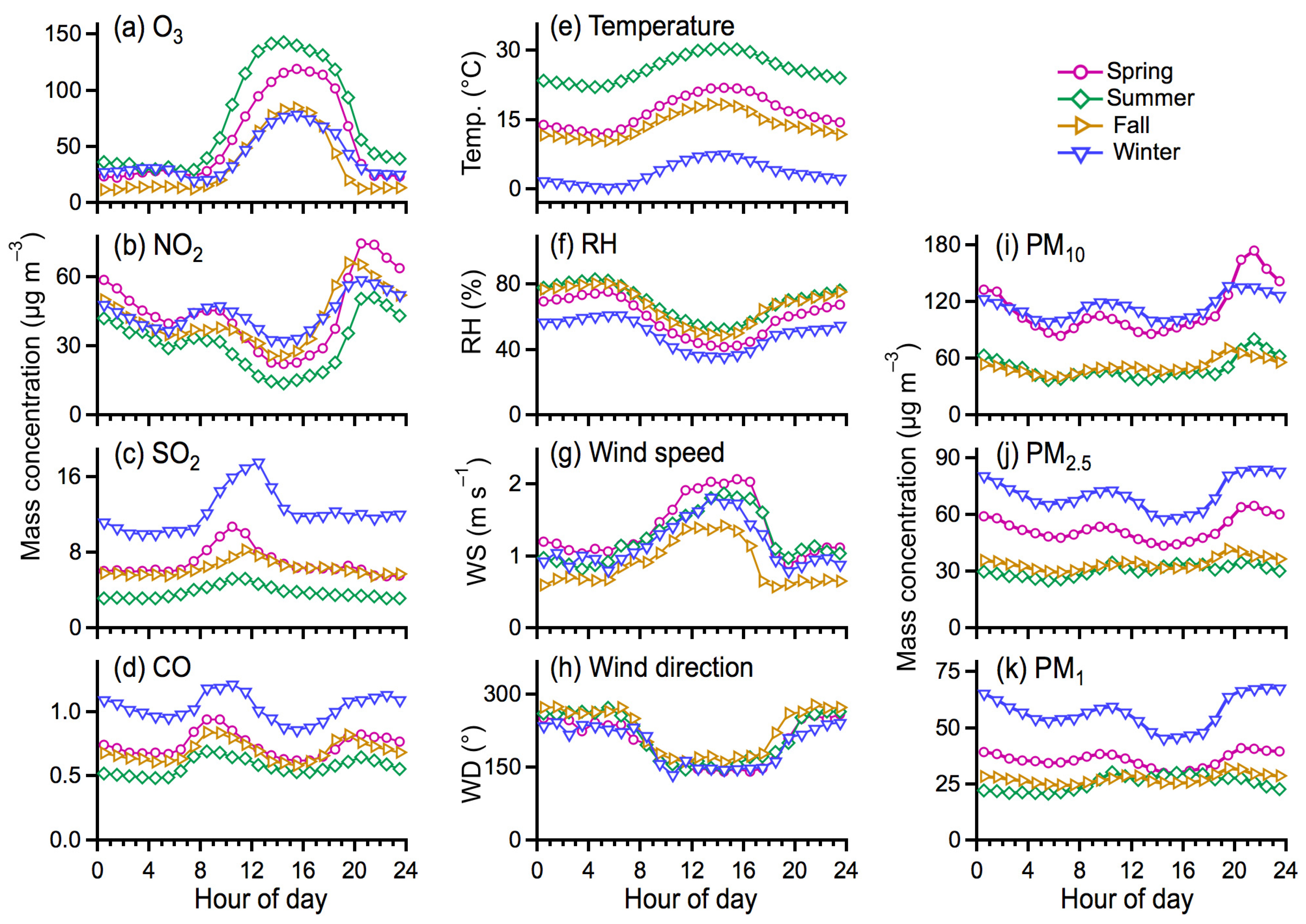
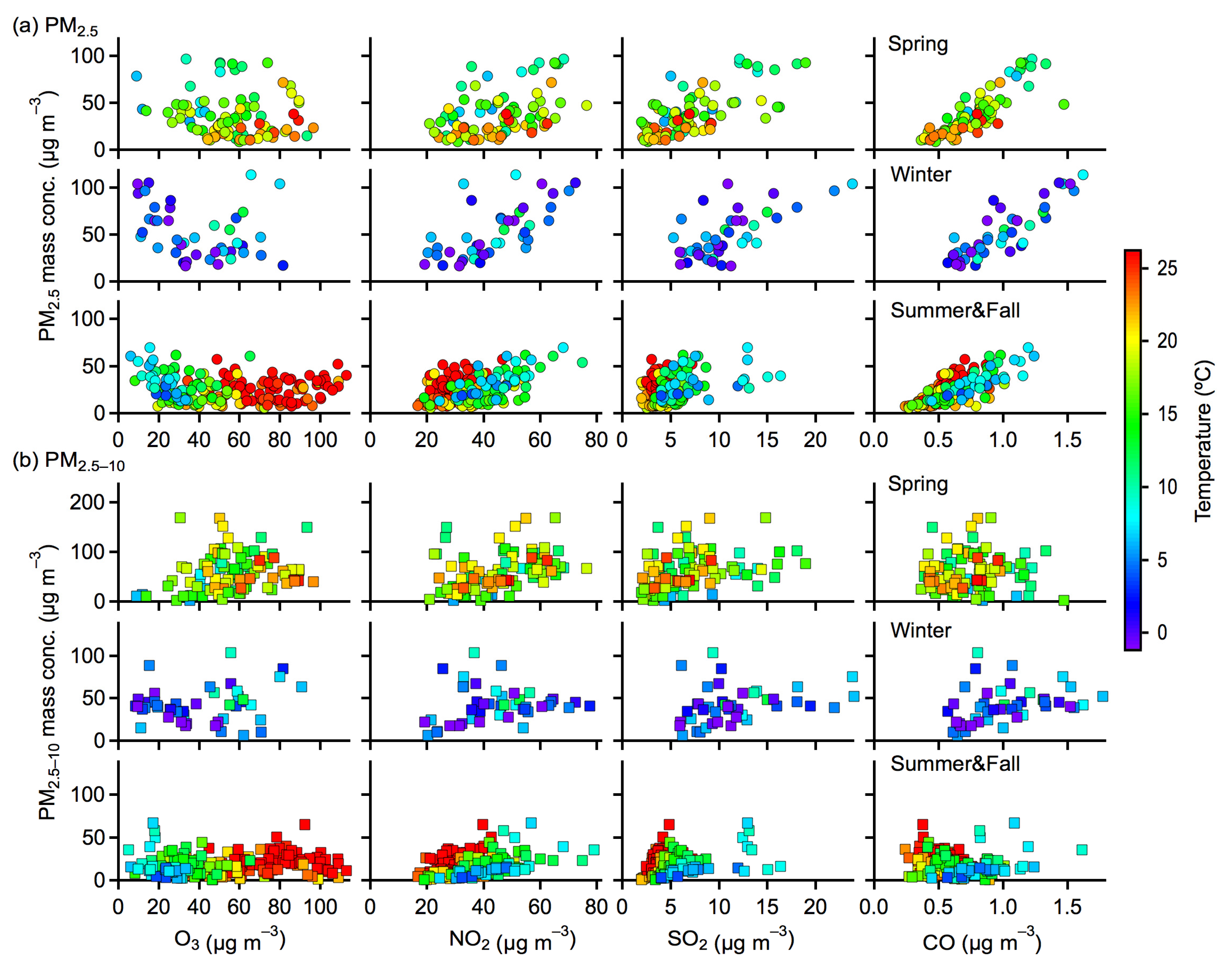
3.3. Influences on PM Concentration and Distribution
4. Summary and Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liang, L.; Gong, P. Urban and Air Pollution: A Multi-City Study of Long-Term Effects of Urban Landscape Patterns on Air Quality Trends. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, H.; Chen, J. Formation, Features and Controlling Strategies of Severe Haze-Fog Pollutions in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 578, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, F.; Xu, D.; Cheng, Y.; Dong, S.; Guo, C.; Jiang, X.; Zheng, X. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Adverse Health Effects of Ambient PM2.5 and PM10 Pollution in the Chinese Population. Environ. Res. 2015, 136, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, R.; Yu, W. The Effects of PM2.5 Concentrations and Relative Humidity on Atmospheric Visibility in Beijing. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 2235–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.J.; Zhang, Y.; Bozzetti, C.; Ho, K.F.; Cao, J.J.; Han, Y.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Slowik, J.G.; Platt, S.M.; Canonaco, F.; et al. High Secondary Aerosol Contribution to Particulate Pollution during Haze Events in China. Nature 2014, 514, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- An, Z.; Huang, R.J.; Zhang, R.; Tie, X.; Li, G.; Cao, J.; Zhou, W.; Shi, Z.; Han, Y.; Gu, Z.; et al. Severe Haze in Northern China: A Synergy of Anthropogenic Emissions and Atmospheric Processes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 8657–8666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Xue, Y.; Guang, J.; de Leeuw, G.; Self, R.; She, L.; Fan, C.; Xie, Y.; Chen, G. Spatial and Temporal Distribution Characteristics of Haze Days and Associated Factors in China from 1973 to 2017. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 214, 116862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bei, N.; Li, G.; Huang, R.J.; Cao, J.; Meng, N.; Feng, T.; Liu, S.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Molina, L.T. Typical Synoptic Situations and Their Impacts on the Wintertime Air Pollution in the Guanzhong Basin, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 7373–7387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.C.; Huang, R.J.; Ni, H.Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Q.Y.; Li, G.H.; Tie, X.X.; Shen, Z.X.; Huang, Y.; Liu, S.X.; et al. Chemical Composition, Sources and Secondary Processes of Aerosols in Baoji City of Northwest China. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 158, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, B.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, G.; Fang, N.; Li, M.; Cao, J. Seasonal Characteristics of Black Carbon Aerosol and Its Potential Source Regions in Baoji, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Wang, Q.Y.; Cao, J.J.; Huang, R.J.; Chen, W.D.; Han, Y.M.; Xu, H.M.; Liu, S.X.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Wang, P.; et al. Long-Term Trends in Visibility and Impacts of Aerosol Composition on Visibility Impairment in Baoji, China. Atmos. Res. 2014, 149, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Wang, G.; Hu, S.; Han, Q.; Xu, Y.; Gao, Z. Aliphatic Alkanes and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Atmospheric PM10 Aerosols from Baoji, China: Implications for Coal Burning. Atmos. Res. 2009, 93, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, H.; Eatough, D.J. Aerosol Measurement: The Use of Optical Light Scattering for the Determination of Particulate Size Distribution, and Particulate Mass, Including the Semi-Volatile Fraction. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2009, 59, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draxier, R.R.; Hess, G.D. An Overview of the HYSPLIT_4 Modelling System for Trajectories, Dispersion and Deposition. Aust. Meteorol. Mag. 1998, 47, 295–308. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.Y.; Draxler, R.R. TrajStat: GIS-Based Software That Uses Various Trajectory Statistical Analysis Methods to Identify Potential Sources from Long-Term Air Pollution Measurement Data. Environ. Model. Softw. 2009, 24, 938–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Yang, Y.; Luo, H.; Zhao, R.; Pan, N.; Lin, J.; Yang, L. Transport Pathways of PM10 during the Spring in Northwest China and Its Characteristics of Potential Dust Sources. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 237, 117746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Guan, Q.; Pan, N.; Wang, Q.; Li, H.; Lin, J.; Tan, Z.; Shao, W. Using Composite Fingerprints to Quantify the Potential Dust Source Contributions in Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 742, 140560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Shen, Z.; Cao, J.; Zhang, L.; Wu, T.; Zhang, Q.; Yin, X.; Lei, Y.; Huang, Y.; Huang, R.J.; et al. Particulate Matters Emitted from Maize Straw Burning for Winter Heating in Rural Areas in Guanzhong Plain, China: Current Emission and Future Reduction. Atmos. Res. 2017, 184, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerminen, V.M.; Chen, X.; Vakkari, V.; Petäjä, T.; Kulmala, M.; Bianchi, F. Atmospheric New Particle Formation and Growth: Review of Field Observations. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 103003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, Y.; Liu, X.; Dai, J.; Wang, Z.; Dong, Z.; Dong, Y.; Chen, C.; Li, X.; Zhao, N.; Fan, C. Aerosol Size Distribution and New Particle Formation Events in the Suburb of Xi’an, Northwest China. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 153, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xue, L.; Brimblecombe, P.; Lam, Y.F.; Li, L.; Zhang, L. Ozone Pollution in China: A Review of Concentrations, Meteorological Influences, Chemical Precursors, and Effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 1582–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Gu, D.; Zhao, C.; Huey, L.G.; Stickel, R.; Liao, J.; Shao, M.; Zhu, T.; Zeng, L.; et al. Summertime Photochemistry during CAREBeijing-2007: RO x Budgets and O3 Formation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 7737–7752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, P.; Ye, C.; Xue, C.; Zhang, C.; Mu, Y.; Sun, X. Formation Mechanisms of Atmospheric Nitrate and Sulfate during the Winter Haze Pollution Periods in Beijing: Gas-Phase, Heterogeneous and Aqueous-Phase Chemistry. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 4153–4165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, W.; Shao, M.; Granier, C.; Liu, Y.; Ye, C.S.; Zheng, J.Y. Long-Term Trends of Anthropogenic SO2, NOx, CO, and NMVOCs Emissions in China. Earth’s Future 2018, 6, 1112–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, K.; Jacob, D.J.; Liao, H.; Zhu, J.; Shah, V.; Shen, L.; Bates, K.H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhai, S. A Two-Pollutant Strategy for Improving Ozone and Particulate Air Quality in China. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 906–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Bei, N.; Tie, X.; Molina, L.T. Aerosol Effects on the Photochemistry in Mexico City during MCMA-2006/MILAGRO Campaign. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 5169–5182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Y.; He, K.B.; Du, Z.Y.; Zheng, M.; Duan, F.K.; Ma, Y.L. Humidity Plays an Important Role in the PM2.5 Pollution in Beijing. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 197, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, S.; Jacob, D.J.; Wang, X.; Shen, L.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Gui, K.; Zhao, T.; Liao, H. Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) Trends in China, 2013–2018. Separating Contributions from Anthropogenic Emissions and Meteorology. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 11031–11041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Zhou, B.; Li, Z.; Lin, Y.; Li, L.; Han, Y. Seasonal Distribution of Atmospheric Coarse and Fine Particulate Matter in a Medium-Sized City of Northern China. Toxics 2022, 10, 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10050216
Zhang X, Zhou B, Li Z, Lin Y, Li L, Han Y. Seasonal Distribution of Atmospheric Coarse and Fine Particulate Matter in a Medium-Sized City of Northern China. Toxics. 2022; 10(5):216. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10050216
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xin, Bianhong Zhou, Zhiyu Li, Yue Lin, Lijuan Li, and Yuemei Han. 2022. "Seasonal Distribution of Atmospheric Coarse and Fine Particulate Matter in a Medium-Sized City of Northern China" Toxics 10, no. 5: 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10050216
APA StyleZhang, X., Zhou, B., Li, Z., Lin, Y., Li, L., & Han, Y. (2022). Seasonal Distribution of Atmospheric Coarse and Fine Particulate Matter in a Medium-Sized City of Northern China. Toxics, 10(5), 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10050216




