Juvenile Exposure to BPA Alters the Estrous Cycle and Differentially Increases Anxiety-like Behavior and Brain Gene Expression in Adult Male and Female Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
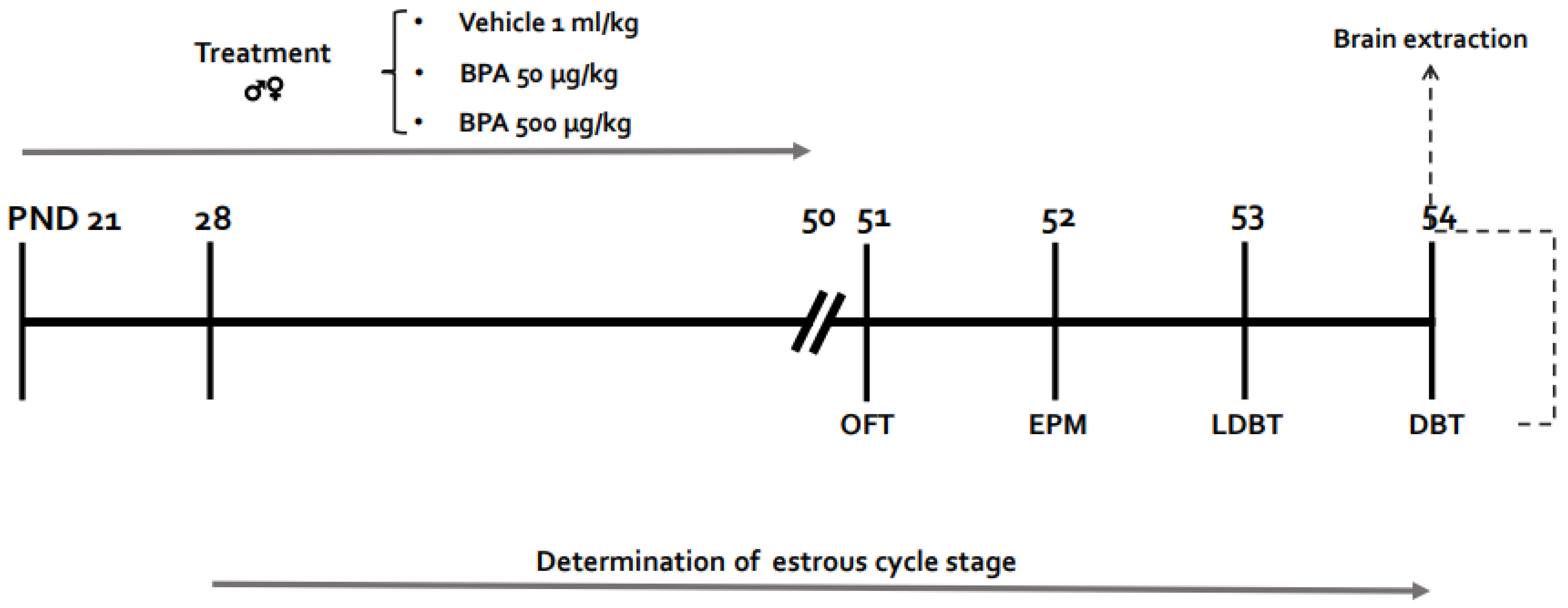
2. Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. BPA Preparation and Administration
2.3. Estrous Cycle Evaluation
2.4. Behavioral Tests
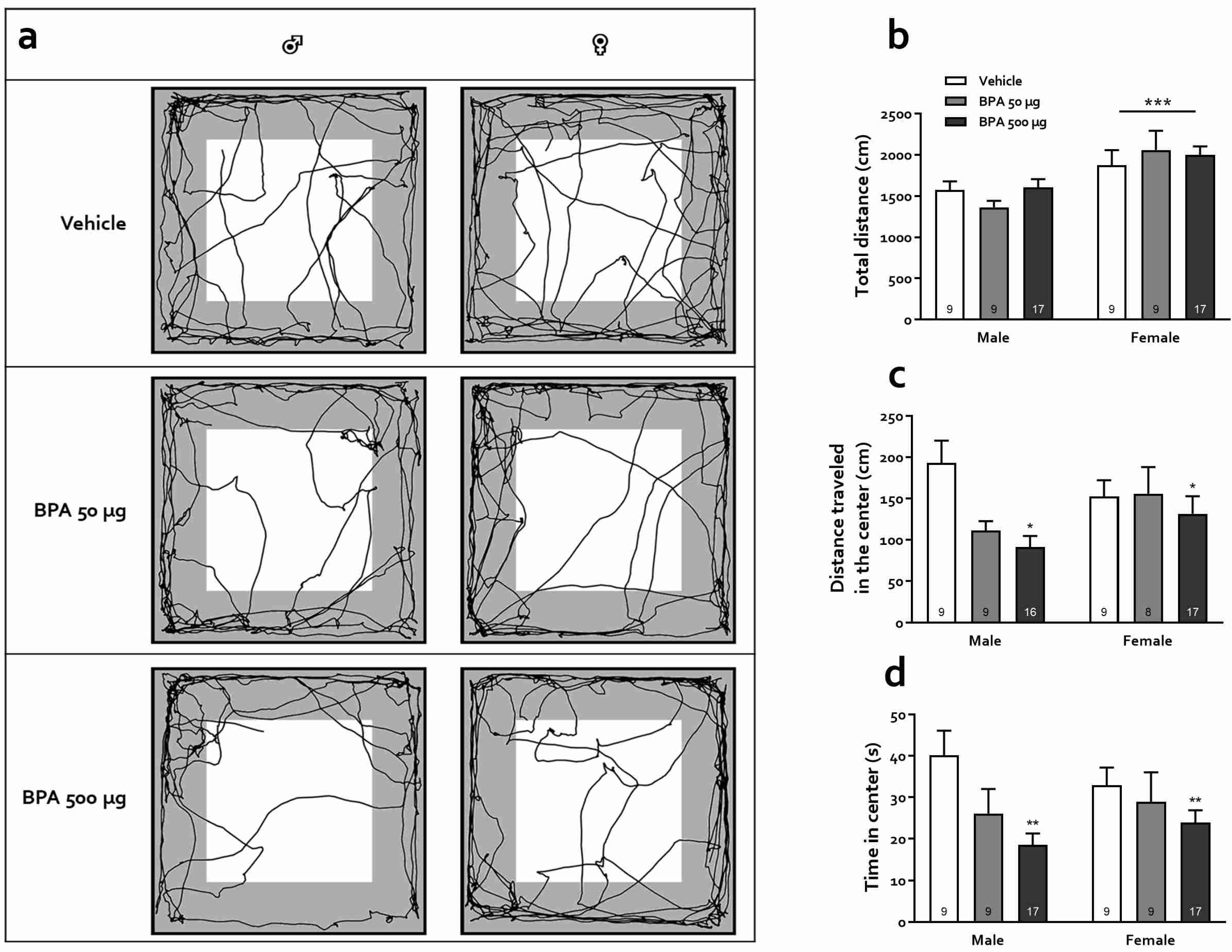
2.5. Open-Field Test (OFT)
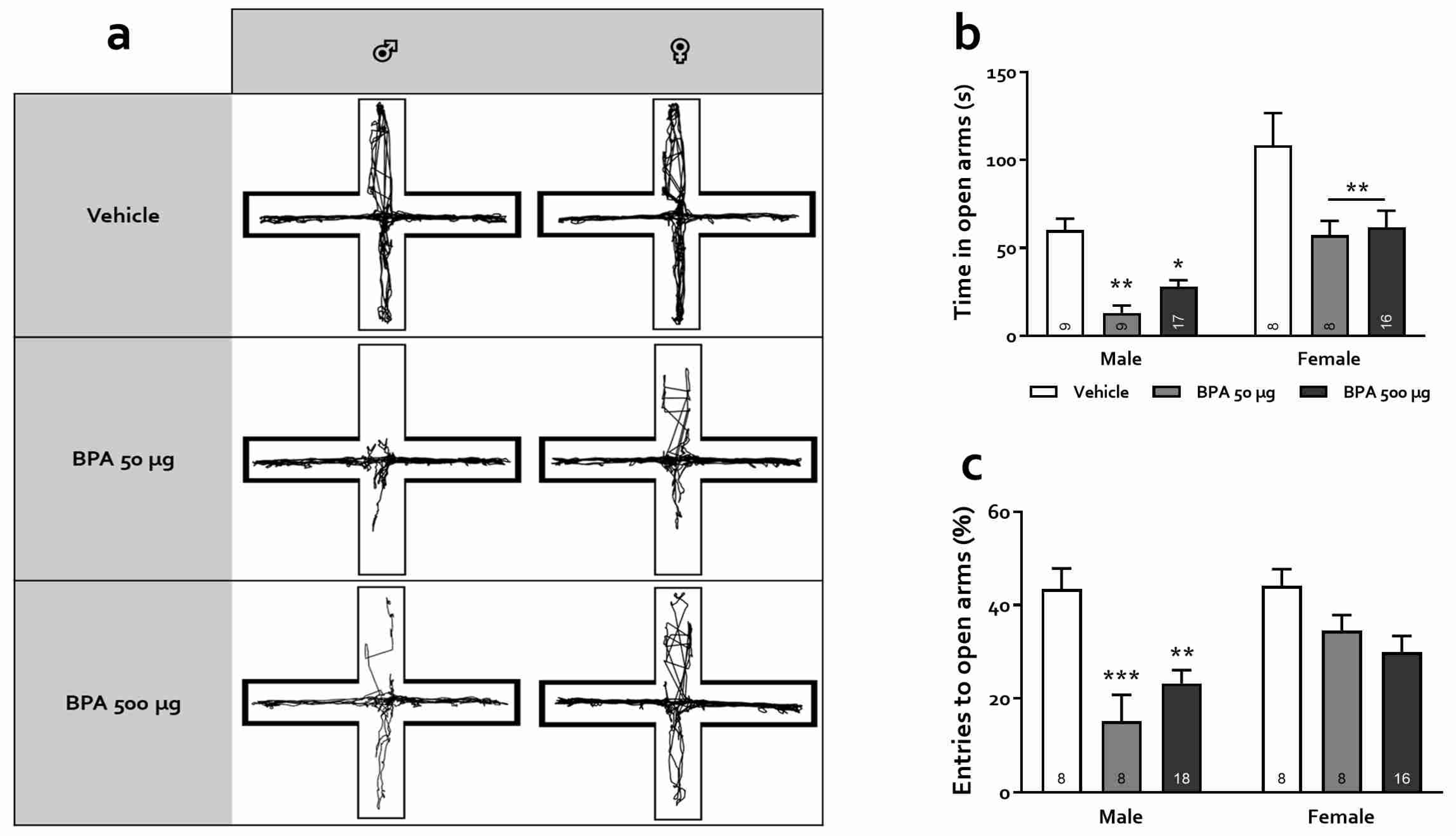
2.6. Elevate-Plus Maze (EPM)
2.7. Light-Dark Box Test (LDBT)
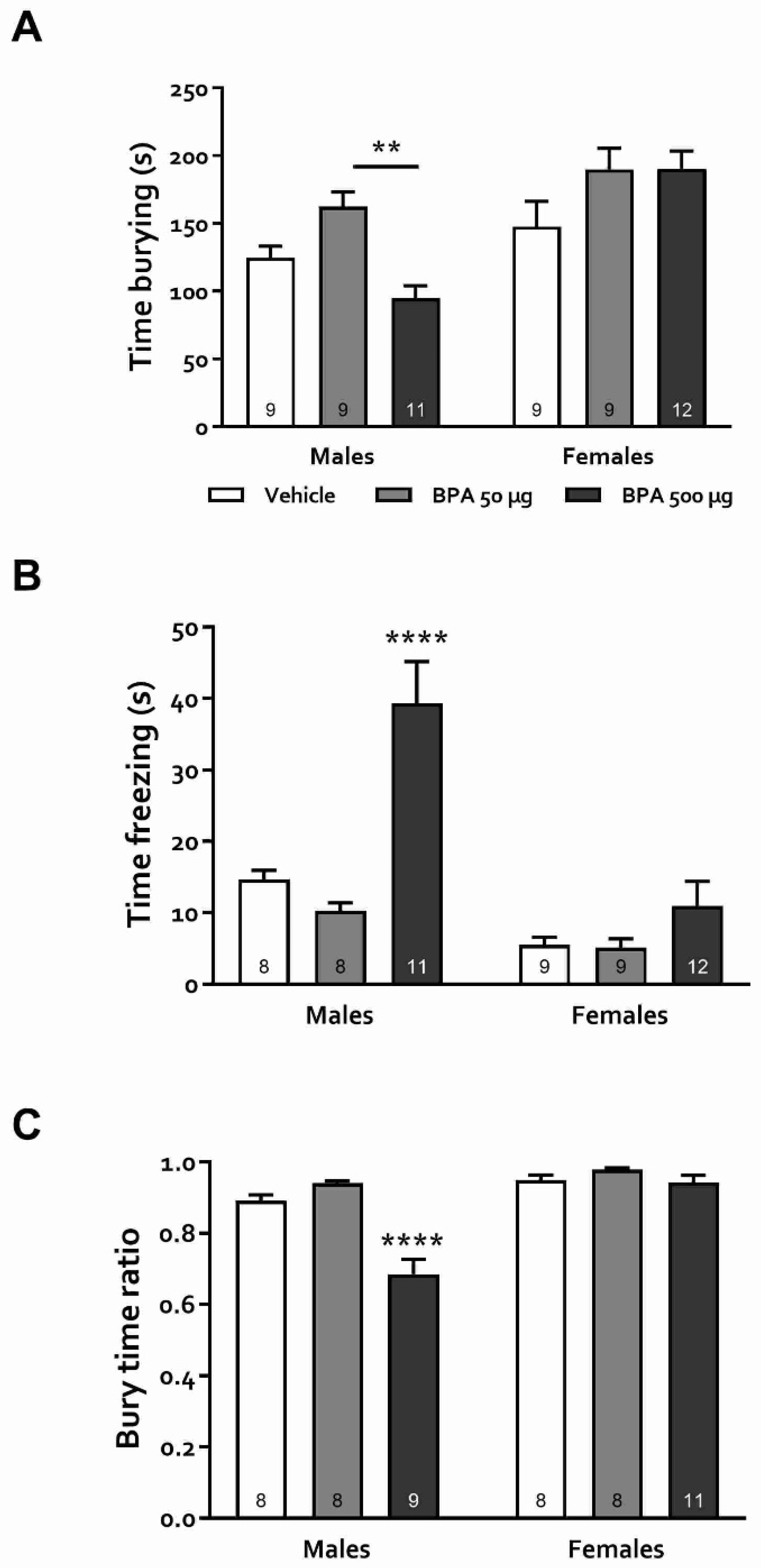
2.8. Defensive Burying Test (DBT)
2.9. RNA Isolation and Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Body Weight
3.2. Estrous Cycle
3.3. Anxiety-like Behavior
3.3.1. Open Field Test (OFT)
3.3.2. Elevated Plus Maze (EPM)
3.3.3. Light-Dark Box Test (LDBT)
3.3.4. Defensive Burying Test (DBT)
3.4. Juvenile BPA Exposure Alters Gene Expression in the Hippocampus and the Hypothalamus
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carwile, J.L.; Luu, H.T.; Bassett, L.S.; Driscoll, D.A.; Yuan, C.; Chang, J.Y.; Ye, X.; Calafat, A.M.; Michels, K.B. Polycarbonate Bottle Use and Urinary Bisphenol A Concentrations. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 1368–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejaredar, M.; Lee, Y.; Roberts, D.J.; Sauve, R.; Dewey, D. Bisphenol A Exposure and Children’s Behavior: A Systematic Review. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2017, 27, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P. Role of Plastics on Human Health. Indian J. Pediatr. 2018, 85, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welshons, W.V.; Nagel, S.C.; vom Saal, F.S. Large Effects from Small Exposures. III. Endocrine Mechanisms Mediating Effects of Bisphenol A at Levels of Human Exposure. Endocrinology 2006, 147, s56–s69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beausoleil, C.; Emond, C.; Cravedi, J.P.; Antignac, J.P.; Applanat, M.; Appenzeller, B.M.R.; Beaudouin, R.; Belzunces, L.P.; Canivenc-Lavier, M.C.; Chevalier, N.; et al. Regulatory Identification of BPA as an Endocrine Disruptor: Context and Methodology. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2018, 475, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, A.; Cofini, M.; Rigante, D.; Lucchetti, L.; Cipolla, C.; Penta, L.; Esposito, S. The Effect of Bisphenol A on Puberty: A Critical Review of the Medical Literature. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Song, H.; Choi, J.; Sim, S.; Kojima, H.; Park, J.; Iida, M.; Lee, Y.J. The Mixture Effects of Bisphenol Derivatives on Estrogen Receptor and Androgen Receptor. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotidou, E.; Zerva, S.; Mitsiou, D.J.; Alexis, M.N.; Kitraki, E. Perinatal Exposure to Low-Dose Bisphenol A Affects the Neuroendocrine Stress Response in Rats. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 220, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhou, L.; Bai, Y.; Zhou, R.; Chen, L. Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis Hyperactivity Accounts for Anxiety- and Depression-like Behaviors in Rats Perinatally Exposed to Bisphenol A. J. Biomed. Res. 2015, 29, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga-Lopez, A.; Beckett, E.M.; Salloum, B.A.; Ye, W.; Padmanabhan, V. Developmental Programming: Prenatal BPA Treatment Disrupts Timing of LH Surge and Ovarian Follicular Wave Dynamics in Adult Sheep. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2014, 279, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Chen, Q.F.; Liu, Z.P.; Xu, H.F.; Zhang, X.P.; Xiang, Q.; Zhang, W.Z.; Cui, W.M.; Zhang, X.; Li, N. Estrogen Receptor α and β Expressions in Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Ovary Axis in Rats Exposed Lactationally to Soy Isoflavones and Bisphenol A. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2010, 23, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, M.; Bianchi, M.; Lux-Santos, V.; Libertun, C. Neonatal Exposure to Bisphenol A Alters Reproductive Parameters and Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone Signaling in Female Rats. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. FDA Food Additives & Ingredients—Bisphenol A (BPA). Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/ingredientspackaginglabeling/foodadditivesingredients/ucm166145.htm (accessed on 27 June 2018).
- EFSA BPA Update: Working Group to Start Reviewing New Studies|European. Available online: http://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/press/news/180904 (accessed on 4 September 2018).
- Valentino, R.; D’Esposito, V.; Ariemma, F.; Cimmino, I.; Beguinot, F.; Formisano, P. Bisphenol A Environmental Exposure and the Detrimental Effects on Human Metabolic Health: Is It Necessary to Revise the Risk Assessment in Vulnerable Population? J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2016, 39, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitku, J.; Chlupacova, T.; Sosvorova, L.; Hampl, R.; Hill, M.; Heracek, J.; Bicikova, M.; Starka, L. Development and Validation of LC–MS/MS Method for Quantification of Bisphenol A and Estrogens in Human Plasma and Seminal Fluid. Talanta 2015, 140, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harley, K.G.; Gunier, R.B.; Kogut, K.; Johnson, C.; Bradman, A.; Calafat, A.M.; Eskenazi, B. Prenatal and Early Childhood Bisphenol A Concentrations and Behavior in School-Aged Children. Environ. Res. 2013, 126, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heredia, L.; Bellés, M.; LLovet, M.I.; Domingo, J.L.; Linares, V. Behavioral Effects in Mice of Postnatal Exposure to Low-Doses of 137-Cesium and Bisphenol A. Toxicology 2016, 340, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-B.; Hong, Y.-C.; Kim, J.-W.; Park, E.-J.; Shin, M.-S.; Kim, B.-N.; Yoo, H.-J.; Cho, I.-H.; Bhang, S.-Y.; Cho, S.-C. Bisphenol A in Relation to Behavior and Learning of School-Age Children. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2013, 54, 890–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtani, N.; Iwano, H.; Suda, K.; Tsuji, E.; Tanemura, K.; Inoue, H.; Yokota, H. Adverse Effects of Maternal Exposure to Bisphenol F on the Anxiety- and Depression-like Behavior of Offspring. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2017, 79, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Alderman, M.H.; Asgari, C.; Taylor, H.S. Fetal Bisphenol-A Induced Changes in Murine Behavior and Brain Gene Expression Persisted in Adult-Aged Offspring. Endocrinology 2020, 161, bqaa164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiersielis, K.R.; Samuels, B.A.; Roepke, T.A. Perinatal Exposure to Bisphenol A at the Intersection of Stress, Anxiety, and Depression. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2020, 79, 106884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, F.; Vishnevetsky, J.; Herbstman, J.B.; Calafat, A.M.; Xiong, W.; Rauh, V.; Wang, S. Prenatal Bisphenol a Exposure and Child Behavior in an Inner-City Cohort. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1190–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, F.; Nolte, E.L.R.; Wang, Y.; Margolis, A.E.; Calafat, A.M.; Wang, S.; Garcia, W.; Hoepner, L.A.; Peterson, B.S.; Rauh, V.; et al. Bisphenol A Exposure and Symptoms of Anxiety and Depression among Inner City Children at 10–12 Years of Age. Environ. Res. 2016, 151, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roen, E.L.; Wang, Y.; Calafat, A.M.; Wang, S.; Margolis, A.; Herbstman, J.; Hoepner, L.A.; Rauh, V.; Frederica, P.P. Bisphenol A Exposure and Behavioral Problems among Inner City Children at 7–9 Years of Age. Environ. Res. 2015, 142, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, J.M.; Yolton, K.; Dietrich, K.N.; Hornung, R.; Ye, X.; Calafat, A.M.; Lanphear, B.P. Prenatal Bisphenol A Exposure and Early Childhood Behavior. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 1945–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, J.M.; Kalkbrenner, A.E.; Calafat, A.M.; Yolton, K.; Ye, X.; Dietrich, K.N.; Lanphear, B.P. Impact of Early-Life Bisphenol A Exposure on Behavior and Executive Function in Children. Pediatrics 2011, 128, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebolledo-Solleiro, D.; Castillo, L.Y.; Solleiro-Villavicencio, H. Impact of BPA on Behavior, Neurodevelopment and Neurodegeneration. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed) 2021, 26, 363–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Tai, F.; Song, Z.; Wu, R.; Zhang, X.; He, F. Pubertal Exposure to Bisphenol A Disrupts Behavior in Adult C57BL/6J Mice. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2011, 31, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Wei, R.; Niu, R.; Wang, C.; Wang, J. Pubertal Exposure to Bisphenol A Increases Anxiety-like Behavior and Decreases Acetylcholinesterase Activity of Hippocampus in Adult Male Mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 60, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Tian, D.; Hong, X.; Chen, L.; Xie, L. Sex-Specific Influence of Exposure to Bisphenol-A between Adolescence and Young Adulthood on Mouse Behaviors. Neuropharmacology 2011, 61, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstein, S.D.; Villafane, J.J.; Juliano, N.; Bowman, R.E. Adolescent Exposure to Bisphenol-A Increases Anxiety and Sucrose Preference but Impairs Spatial Memory in Rats Independent of Sex. Brain Res. 2013, 1529, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, R.E.; Luine, V.; Weinstein, S.D.; Khandaker, H.; DeWolf, S.; Frankfurt, M. Bisphenol-A Exposure during Adolescence Leads to Enduring Alterations in Cognition and Dendritic Spine Density in Adult Male and Female Rats. Horm. Behav. 2015, 69, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Li, T.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Hu, F. Bisphenol A Exposure Remodels Cognition of Male Rats Attributable to Excitatory Alterations in the Hippocampus and Visual Cortex. Toxicology 2018, 410, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohmura, Y.; Kuniyoshi, Y. A Translational Model to Determine Rodent’s Age from Human Foetal Age. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semple, B.D.; Blomgren, K.; Gimlin, K.; Ferriero, D.M.; Noble-Haeusslein, L.J. Brain Development in Rodents and Humans: Identifying Benchmarks of Maturation and Vulnerability to Injury across Species. Prog. Neurobiol. 2013, 106–107, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, J.M.; Murr, A.S.; Cooper, R.L. The Rodent Estrous Cycle: Characterization of Vaginal Cytology and Its Utility in Toxicological Studies. Birth Defects Res. Part B Dev. Reprod. Toxicol. 2007, 80, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebolledo-Solleiro, D.; Roldán-Roldán, G.; Díaz, D.; Velasco, M.; Larqué, C.; Rico-Rosillo, G.; Vega-Robledo, G.B.; Zambrano, E.; Hiriart, M.; Pérez de la Mora, M. Increased Anxiety-like Behavior Is Associated with the Metabolic Syndrome in Non-Stressed Rats. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellow, S.; Chopin, P.; File, S.E.; Briley, M. Validation of Open: Closed Arm Entries in an Elevated plus-Maze as a Measure of Anxiety in the Rat. J. Neurosci. Methods 1985, 14, 149–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henniger, M.S.; Ohl, F.; Hölter, S.M.; Weissenbacher, P.; Toschi, N.; Lörscher, P.; Wigger, A.; Spanagel, R.; Landgraf, R. Unconditioned Anxiety and Social Behaviour in Two Rat Lines Selectively Bred for High and Low Anxiety-Related Behaviour. Behav. Brain Res. 2000, 111, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costall, B.; Jones, B.J.; Kelly, M.E.; Naylor, R.J.; Tomkins, D.M. Exploration of Mice in a Black and White Test Box: Validation as a Model of Anxiety. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1989, 32, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez de la Mora, M.; Gallegos-Cari, A.; Crespo-Ramirez, M.; Marcellino, D.; Hansson, A.C.; Fuxe, K. Distribution of Dopamine D 2-like Receptors in the Rat Amygdala and Their Role in the Modulation of Unconditioned Fear and Anxiety. Neuroscience 2012, 201, 252–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda, S.R.; Skinner, M.K. CHAPTER 38—Puberty in the Rat. In Knobil and Neill’s Physiology of Reproduction, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ojeda, S.R.; Wheaton, J.E.; Jameson, H.E.; McCann, S.M. The Onset of Puberty in the Female Rat: Changes in Plasma Prolactin, Gonadotropins, Luteinizing Hormone-Releasing Hormone (LHRH), and Hypothalamic LHRH Content. Endocrinology 1976, 98, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fucich, E.; Morilak, D. Shock-Probe Defensive Burying Test to Measure Active versus Passive Coping Style in Response to an Aversive Stimulus in Rats. Bio-Protocol 2018, 8, e2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatherall, L.; Sánchez, C.; Morilak, D.A. Chronic Vortioxetine Treatment Reduces Exaggerated Expression of Conditioned Fear Memory and Restores Active Coping Behavior in Chronically Stressed Rats. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017, 20, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, M.K.; Bingham, B.; Shah, A.; Joshi, A.; Frazer, A.; Strong, R.; Morilak, D.A. Effects of Chronic plus Acute Prolonged Stress on Measures of Coping Style, Anxiety, and Evoked HPA-Axis Reactivity. Neuropharmacology 2012, 63, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, S.; Dussaubat, N.; Díaz-Véliz, G. Effects of the Estrous Cycle and Ovarian Hormones on Behavioral Indices of Anxiety in Female Rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology 1996, 21, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcondes, F.K.; Miguel, K.J.; Melo, L.L.; Spadari-Bratfisch, R.C. Estrous Cycle Influences the Response of Female Rats in the Elevated Plus-Maze Test. Physiol. Behav. 2001, 74, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayin, A.; Derinöz, O.; Yüksel, N.; Şahin, S.; Bolay, H. The Effects of the Estrus Cycle and Citalopram on Anxiety-like Behaviors and c-Fos Expression in Rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2014, 124, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viguié, C.; Mhaouty-Kodja, S.; Habert, R.; Chevrier, C.; Michel, C.; Pasquier, E. Evidence-Based Adverse Outcome Pathway Approach for the Identification of BPA as En Endocrine Disruptor in Relation to Its Effect on the Estrous Cycle. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2018, 475, 10–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakae, D.Y.; Sakae, T.M.; Paschoalini, M.A.; Faria, M.S. Relative Luminosity in the plus Maze upon the Exploratory Behaviour of Female Wistar Rats. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2015, 73, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholl, J.L.; Afzal, A.; Fox, L.C.; Watt, M.J.; Forster, G.L. Sex Differences in Anxiety-like Behaviors in Rats. Physiol. Behav. 2019, 211, 112670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howdeshell, K.L.; Hotchkiss, A.K.; Thayer, K.A.; Vandenbergh, J.G.; vom Saal, F.S. Exposure to Bisphenol A Advances Puberty. Nature 1999, 401, 763–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adewale, H.B.; Jefferson, W.N.; Newbold, R.R.; Patisaul, H.B. Neonatal Bisphenol-a Exposure Alters Rat Reproductive Development and Ovarian Morphology without Impairing Activation of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Neurons. Biol. Reprod. 2009, 81, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nah, W.H.; Park, M.J.; Gye, M.C. Effects of Early Prepubertal Exposure to Bisphenol A on the Onset of Puberty, Ovarian Weights, and Estrous Cycle in Female Mice. Clin. Exp. Reprod. Med. 2011, 38, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Tian, C.; Liu, Q.; Zhen, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, L.; Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, S.; He, D.; et al. Preconception Paternal Bisphenol A Exposure Induces Sex-Specific Anxiety and Depression Behaviors in Adult Rats. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtani, N.; Suda, K.; Tsuji, E.; Tanemura, K.; Yokota, H.; Inoue, H.; Iwano, H. Late Pregnancy Is Vulnerable Period for Exposure to BPA. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2018, 80, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Dong, F.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Shen, X. Sex-Specific Effects of Long-Term Exposure to Bisphenol-A on Anxiety- and Depression-like Behaviors in Adult Mice. Chemosphere 2015, 120, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, E.P.; Allardice, H.A.; Schenk, A.K.; Rissman, E.F. Effects of Maternal or Paternal Bisphenol A Exposure on Offspring Behavior. Horm. Behav. 2018, 101, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Hong, X.; Xie, L.; Li, T.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, G.; Liu, X. Gestational and Lactational Exposure to Bisphenol-A Affects Anxiety- and Depression-like Behaviors in Mice. Horm. Behav. 2012, 62, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boersma, G.J.; Moghadam, A.A.; Cordner, Z.A.; Tamashiro, K.L. Prenatal Stress and Stress Coping Style Interact to Predict Metabolic Risk in Male Rats. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 1302–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craske, M.G.; Stein, M.B.; Eley, T.C.; Milad, M.R.; Holmes, A.; Rapee, R.M.; Wittchen, H.U. Anxiety Disorders. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, E.I.; Ressler, K.J.; Binder, E.; Nemeroff, C.B. The Neurobiology of Anxiety Disorders: Brain Imaging, Genetics, and Psychoneuroendocrinology. Psychiatr. Clin. North Am. 2009, 32, 549–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.; Wang, M.; Xia, W.; Chen, T.; Huo, W.; Mao, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, S. Perinatal Exposure to Low-Dose Bisphenol A Disrupts Learning/Memory and DNA Methylation of Estrogen Receptor Alpha in the Hippocampus. Toxicol. Res. 2016, 5, 828–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.-B.; He, Y.; Song, C.; Ke, X.; Fan, S.-J.; Peng, W.-J.; Tan, R.; Kawata, M.; Matsuda, K.-I.; Pan, B.-X.; et al. Bisphenol a Regulates the Estrogen Receptor Alpha Signaling in Developing Hippocampus of Male Rats through Estrogen Receptor. Hippocampus 2014, 24, 1570–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinch, C.D.; Ibhazehiebo, K.; Jeong, J.-H.; Habibi, H.R.; Kurrasch, D.M. Low-Dose Exposure to Bisphenol A and Replacement Bisphenol S Induces Precocious Hypothalamic Neurogenesis in Embryonic Zebrafish. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 1475–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhou, L.; Bai, Y.; Zhou, R.; Chen, L. Sex Differences in the Adult HPA Axis and Affective Behaviors Are Altered by Perinatal Exposure to a Low Dose of Bisphenol A. Brain Res. 2014, 1571, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castillo, L.Y.; Ríos-Carrillo, J.; González-Orozco, J.C.; Camacho-Arroyo, I.; Morin, J.-P.; Zepeda, R.C.; Roldán-Roldán, G. Juvenile Exposure to BPA Alters the Estrous Cycle and Differentially Increases Anxiety-like Behavior and Brain Gene Expression in Adult Male and Female Rats. Toxics 2022, 10, 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10090513
Castillo LY, Ríos-Carrillo J, González-Orozco JC, Camacho-Arroyo I, Morin J-P, Zepeda RC, Roldán-Roldán G. Juvenile Exposure to BPA Alters the Estrous Cycle and Differentially Increases Anxiety-like Behavior and Brain Gene Expression in Adult Male and Female Rats. Toxics. 2022; 10(9):513. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10090513
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastillo, Laura Yesenia, Jorge Ríos-Carrillo, Juan Carlos González-Orozco, Ignacio Camacho-Arroyo, Jean-Pascal Morin, Rossana C. Zepeda, and Gabriel Roldán-Roldán. 2022. "Juvenile Exposure to BPA Alters the Estrous Cycle and Differentially Increases Anxiety-like Behavior and Brain Gene Expression in Adult Male and Female Rats" Toxics 10, no. 9: 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10090513
APA StyleCastillo, L. Y., Ríos-Carrillo, J., González-Orozco, J. C., Camacho-Arroyo, I., Morin, J.-P., Zepeda, R. C., & Roldán-Roldán, G. (2022). Juvenile Exposure to BPA Alters the Estrous Cycle and Differentially Increases Anxiety-like Behavior and Brain Gene Expression in Adult Male and Female Rats. Toxics, 10(9), 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10090513






