Organotin Antifouling Compounds and Sex-Steroid Nuclear Receptor Perturbation: Some Structural Insights
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
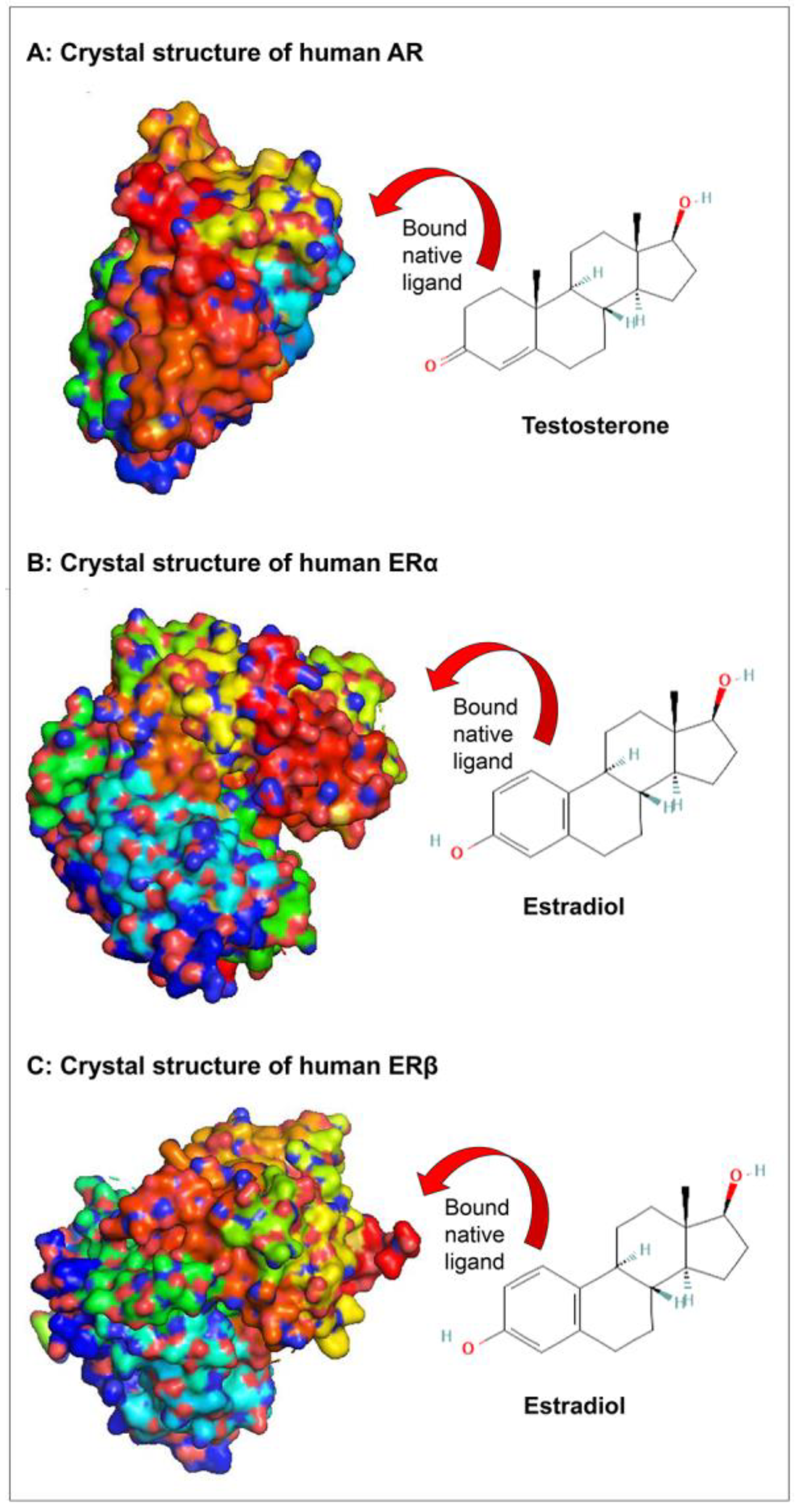
2.1. Data Retrieval
2.2. Molecular Docking
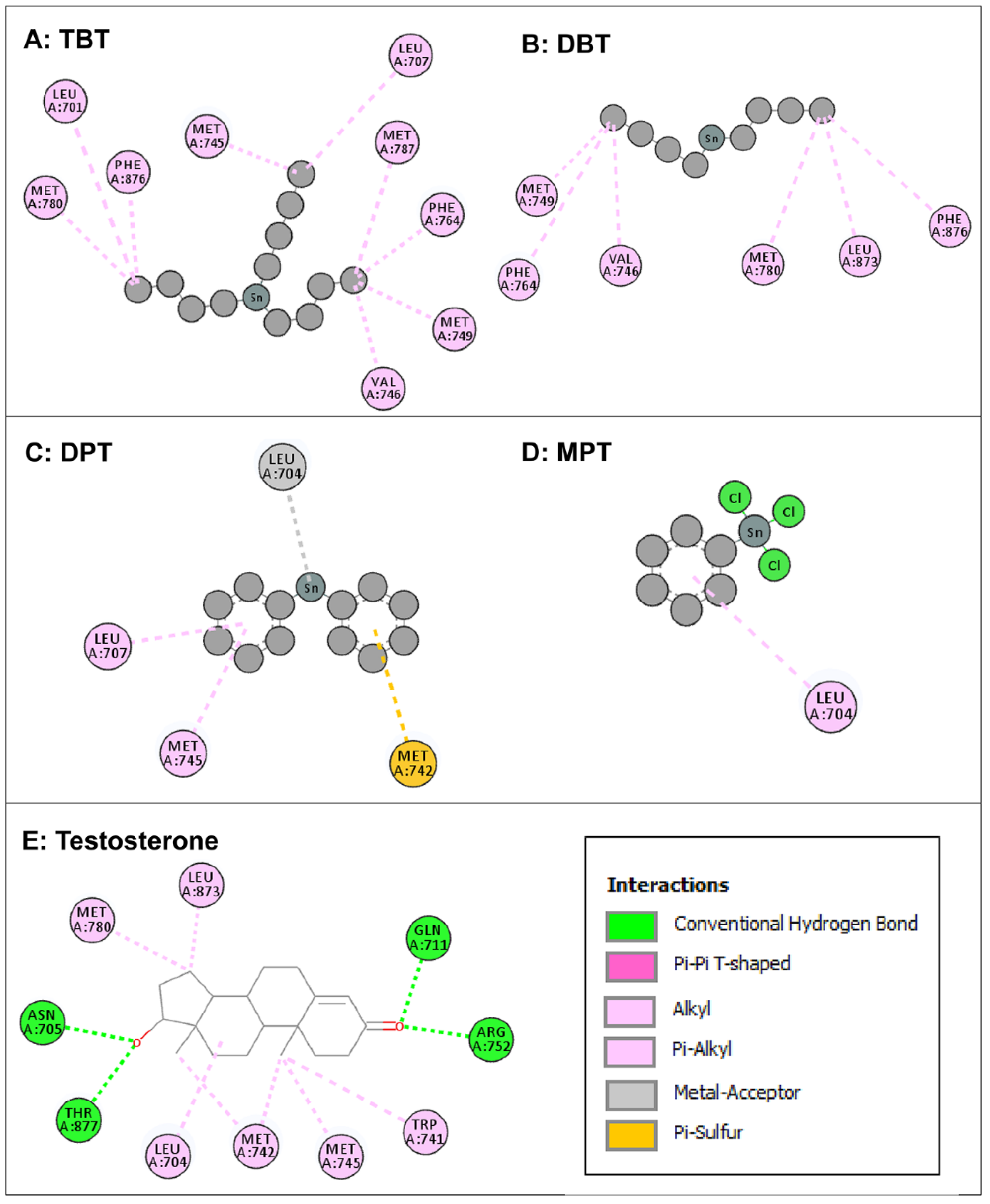
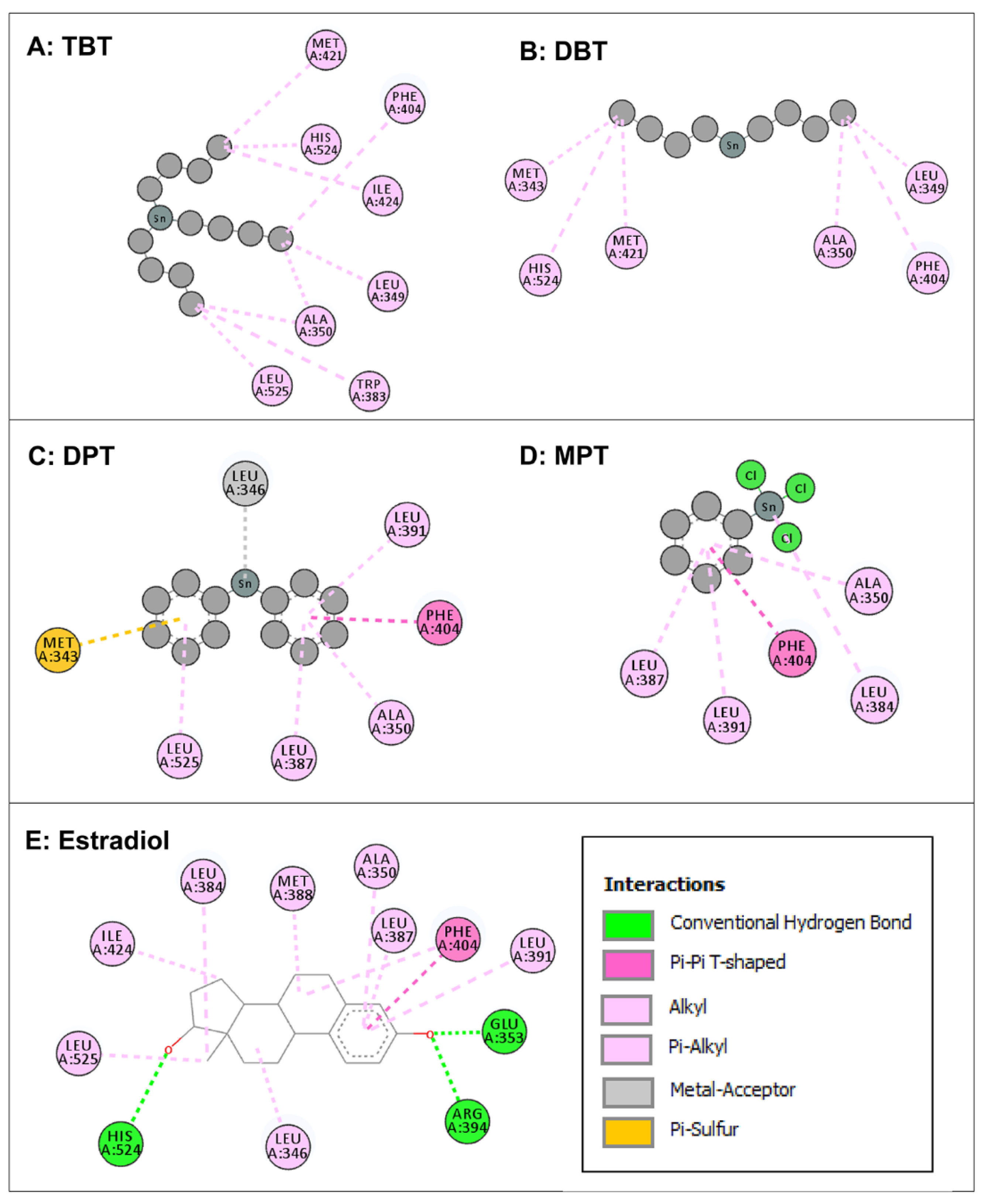
2.3. Protein–Ligand Complex Analysis
2.4. Binding Energy and Dissociation Constant
2.5. Binding-Pose Comparison Analyses
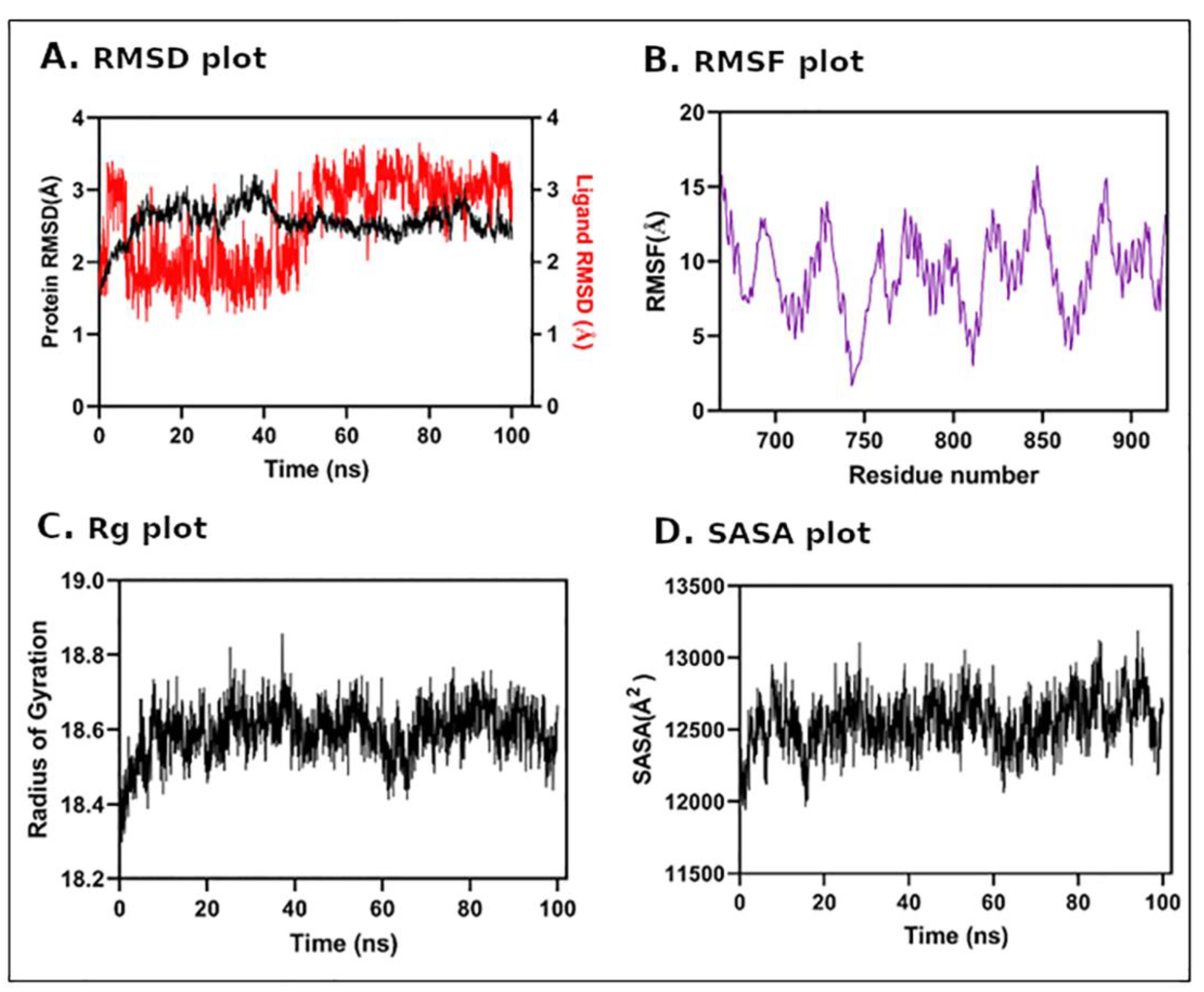
2.6. Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulation Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Docking Analyses
3.2. Molecular Docking of Organotin Compounds with AR
3.3. Molecular Docking of Organotin Compounds with ERα
3.4. Molecular Docking of Organotin Compounds with ERβ
3.5. Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Da Silva, I.F.; Lima, L.F.; Graceli, J.B.; Rodrigues, L.C.D.M. Organotins in Neuronal damage, brain function, and behavior: A short review. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 8, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- WHO. Organotins in Drinking-Water. Background Document for Development of Who Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality. Geneva: World Health Organization (WHO/HEP/ECH/WSH/2020.7). Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO. 2020. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/338068/WHO-HEP-ECH-WSH-2020.7-eng.pdf (accessed on 4 December 2022).
- Barbosa, K.L.; Dettogni, R.S.; da Costa, C.S.; Gastal, E.L.; Raetzman, L.T.; Flaws, J.A.; Graceli, J.B. Tributyltin and the female hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal disruption. Toxicol. Sci. 2022, 186, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyer, J.; Song, Y.; Tollefsen, K.E.; Berge, J.A.; Tveiten, L.; Helland, A.; Øxnevad, S.; Schøyen, M. The ecotoxicology of marine tributyltin (TBT) hotspots: A review. Mar. Envrion. Res. 2022, 179, 105689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metcalfe, C.D.; Bayen, S.; Desrosiers, M.; Muñoz, G.; Sauvé, S.; Yargeau, V. An introduction to the sources, fate, occurrence and effects of endocrine disrupting chemicals released into the environment. Envrion. Res. 2022, 207, 112658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoch, M. Organotin compounds in the environment—An overview. Appl. Geochem. 2001, 16, 719–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graceli, J.B. Editorial: Organotins as a complete physiologic and endocrine disruptor: Role of disease development. Editor. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S&P Global. Organometallics: Chemical Economics Handbook. S&P Global Commodity Insights. 2022. Available online: https://www.spglobal.com/commodityinsights/en/ci/products/organometallics-chemical-economics-handbook.html (accessed on 4 December 2022).
- Okoro, H.K.; Fatoki, O.S.; Adekola, F.A.; Ximba, B.J.; Snyman, R.G.; Opeolu, B. Human exposure, biomarkers, and fate of organotins in the environment. Rev. Envrion. Contam. Toxicol. 2011, 213, 27–54. [Google Scholar]
- He, S.; Li, P.; Li, Z.H. Review on endocrine disrupting toxicity of triphenyltin from the perspective of species evolution: Aquatic, amphibious and mammalian. Chemosphere 2021, 269, 128711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadighara, P.; Jahanbakhsh, M.; Nazari, Z.; Mostashari, P. The organotin contaminants in food: Sources and methods for detection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Food Chem. X 2021, 12, 100154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromme, H.; Mattulat, A.; Lahrz, T.; Rüden, H. Occurrence of organotin compounds in house dust in Berlin (Germany). Chemosphere 2005, 58, 1377–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, K.; Takahashi, S.; Fujiwara, N.; Mizukawa, H.; Tanabe, S. Organotin compounds, including butyltins and octyltins, in house dust from Albany, New York, USA. Arch. Envrion. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 58, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-shatri, M.A.; Nuhu, A.A.; Basheer, C.; Al-Arfaj, A.; Al-Tawabini, B. Assessment of Tributyltin and triphenyltin compounds and their main degradation products in Saudi coastal waters. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2015, 40, 2959–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.T.; Qurban, M.; Manikandan, K.; Tawabini, B.; Basheer, C.; Periyadan, K. Assessment of the organotin pollution in the coastal sediments of the Western Arabian Gulf, Saudi Arabia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 139, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, M.W.; Salam, A.; Mian, A. Levels of organotin compounds in selected fish species from the arabian gulf. Bull. Envrion. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 98, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannan, K.; Senthilkumar, K.; Giesy, J.P. Occurrence of butyltin compounds in human blood. Envrion. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 1776–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, T. Endocrine disruption induced by organotin compounds; organotins function as a powerful agonist for nuclear receptors rather than an aromatase inhibitor. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 33, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graceli, J.B.; Sena, G.C.; Lopes, P.F.; Zamprogno, G.C.; da Costa, M.B.; Godoi, A.F.; Dos Santos, D.M.; de Marchi, M.R.; Dos Santos Fernandez, M.A. Organotins: A review of their reproductive toxicity, biochemistry, and environmental fate. Reprod. Toxicol. 2013, 36, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Silva, A.P.; Andrade, M.N.; Pereira-Rodrigues, P.; Paiva-Melo, F.D.; Soares, P.; Graceli, J.B.; Dias, G.R.M.; Ferreira, A.C.F.; de Carvalho, D.P.; Miranda-Alves, L. Frontiers in endocrine disruption: Impacts of organotin on the hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid axis. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2018, 460, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rantakokko, P.; Main, K.M.; Wohlfart-Veje, C.; Kiviranta, H.; Airaksinen, R.; Vartiainen, T.; Vartiainen, T.; Skakkebæk, N.E.; Toppari, J.; Virtanen, H.E. Association of placenta organotin concentrations with congenital cryptorchidism and reproductive hormone levels in 280 newborn boys from Denmark and Finland. Hum. Reprod. 2013, 28, 1647–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merlo, E.; Silva, I.V.; Cardoso, R.C.; Graceli, J.B. The obesogen tributyltin induces features of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): A review. J. Toxicol. Environ. Healthy B. Crit. Rev. 2018, 21, 181–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternberg, R.M.; Gooding, M.P.; Hotchkiss, A.K.; LeBlanc, G.A. Environmental endocrine control of reproductive maturation in gastropods: Implications for the mechanism of tributyltin-induced imposex in prosobranchs. Ecotoxicology 2010, 19, 4–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, X.R.; Li, Y.W.; Chen, Q.L.; Shen, Y.J.; Liu, Z.H. Tributyltin impaired spermatogenesis and reproductive behavior in male zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2020, 224, 105503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, S.; Srivastava, A.; Khandelwal, S. Long term impact of the endocrine dis ruptor tributyltin on male fertility following a single acute exposure. Environ. Toxicol. 2017, 32, 2295–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daigneault, B.W.; de Agostini Losano, J.D. Tributyltin chloride exposure to post-ejaculatory sperm reduces motility, mitochondrial function and subsequent embryo development. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2022, 34, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Araújo, J.F.P.; Podratz, P.L.; Merlo, E.; Sarmento, I.V.; da Costa, C.S.; Niño, O.M.S.; Faria, R.A.; Freitas Lima, L.C.; Graceli, J.B. Organotin exposure and vertebrate reproduction: A review. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- da Costa, C.S.; Miranda-Alves, L.; La Merrill, M.A.; Silva, I.V.; Graceli, J.B. The tributyltin leads to obesogenic mammary gland abnormalities in adult female rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 307, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podratz, P.L.; Merlo, E.; de Araújo, J.; Ayub, J.; Pereira, A.; Freitas-Lima, L.C.; da Costa, M.B.; Miranda-Alves, L.; Cassa, S.; Carneiro, M.; et al. Disruption of fertility, placenta, pregnancy outcome, and multigenerational inheritance of hepatic steatosis by organotin exposure from contaminated seafood in rats. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 138000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehan, M.; Ahmad, E.; Sheikh, I.A.; Abuzenadah, A.M.; Damanhouri, G.A.; Bajouh, O.S.; AlBasri, S.F.; Assiri, M.M.; Beg, M.A. Androgen and progesterone receptors are targets for bisphenol A (BPA), 4-methyl-2,4-bis-(P-hydroxyphenyl)pent-1-ene—A potent metabolite of BPA, and 4-tert-octylphenol: A computational insight. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beg, M.A.; Sheikh, I.A. Endocrine disruption: Molecular interactions of environmental bisphenol contaminants with thyroid hormone receptor and thyroxine-binding globulin. Toxicol. Ind. Healthy 2020, 36, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehan, M.; Zargar, U.R.; Sheikh, I.A.; Alharthy, S.A.; Almashjary, M.N.; Abuzenadah, A.M.; Beg, M.A. Potential disruption of systemic hormone transport by tobacco alkaloids using computational approaches. Toxics 2022, 10, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeliger, D.; de Groot, B.L. Ligand docking and binding site analysis with PyMOL and Autodock/Vina. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2010, 24, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewing, T.J.; Makino, S.; Skillman, A.G.; Kuntz, I.D. DOCK 4.0: Search strategies for automated molecular docking of flexible molecule databases. J. Comput. Aided. Mol. Des. 2001, 15, 411–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera–a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rehan, M.; Ahmad, E.; Beg, M.A. Structural binding perspectives of a major tobacco alkaloid, nicotine, and its metabolite cotinine with sex-steroid nuclear receptors. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2020, 40, 1410–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Accelrys Software Inc. Discovery Studio Modeling Environment, Release 3.0, Accelrys Software Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA. 2018. Available online: www.accelrys.com (accessed on 4 December 2022).
- Wang, R.; Lu, Y.; Wang, S. Comparative evaluation of 11 scoring functions for molecular docking. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 2287–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, K.J.; Chow, E.; Xu, H.; Dror, R.O.; Eastwood, M.P.; Gregersen, B.A.; Klepeis, J.L.; Kolossvary, I.; Moraes, M.A.; Sacerdoti, F.D.; et al. Scalable algorithms for molecular dynamics simulations on commodity clusters. In Proceedings of the ACM/IEEE Conference on Supercomputing (SC06), Tampa, FL, USA, 11–17 November 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Shivangi, E.M.K.; Meena, L.S. Essential biochemical, biophysical and computational inputs on efficient functioning of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv FtsY. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 171, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beg, M.A.; Sadaf; Shamsi, A.; Sahoo, S.; Yousuf, M.; Najm, M.Z.; Almutawif, Y.A.; Islam, A.; Aloliqi, A.A.; Athar, F. Mechanistic insight into the enzymatic inhibition of β-amyrin against mycobacterial Rv1636: In silico and in vitro approaches. Biology 2022, 11, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.M.; Lee, H.S.; Moon, J.S.; Kim, I.S.; Sim, S.; Ohta, A. Organotin compounds act as inhibitor of transcriptional activation with human estrogen receptor. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 22, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamabe, Y.; Hoshino, A.; Imura, N.; Suzuki, T.; Himeno, S. Enhancement of androgen-dependent transcription and cell proliferation by tributyltin and triphenyltin in human prostate cancer cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2000, 169, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, T.; Nishikawa, J.; Hiromori, Y.; Yokoyama, H.; Koyanagi, M.; Takasuga, S.; Ishizaki, J.; Watanabe, M.; Isa, S.; Utoguchi, N.; et al. Trialkyltin compounds bind retinoid X receptor to alter human placental endocrine functions. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005, 19, 2502–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fodor, I.; Urban, P.; Scott, A.P.; Pirger, Z. A critical evaluation of some of the recent so-called ’evidence’ for the involvement of vertebrate-type sex steroids in the reproduction of mollusks. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2020, 516, 110949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, H.; Wang, J.J.; Wang, M.Y.; Shen, L.; Xiao, L.; Chen, T.J.; Sun, T.Z.; Li, W.J.; Zhu, L.L.; Zhang, X.K. Potent inhibition of tributyltin (TBT) and triphenyltin (TPT) against multiple UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGT): A new potential mechanism underlying endocrine disrupting actions. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 149, 112039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, W.D.; Emmett, E.A.; Steiner, J.; Tureen, R. Neurotoxic effects of occupational exposure to organotins. Am. J. Psychiatry 1981, 138, 1092–1095. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- EFSA. Opinion of the scientific panel on contaminants in the food chain on a request from the commission to assess the health risks to consumers associated with exposure to organotins in foodstuffs. (European Food Safety Authority) (Question N° EFSA-Q-2003-110). EFSA J. 2004, 102, 1–119. Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/pub/102 (accessed on 4 December 2022).
- Lin, T.-J.; Hung, D.-Z.; Kao, C.-H.; Hu, W.-H.; Yang, D.-Y. Unique cerebral dysfunction following triphenyltin acetate poisoning. Hum Exp Toxicol. 1998, 17, 403–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S.; Allera, A.; Albers, P.; Heimbrecht, J.; Jantzen, E.; Klingmuller, D.; Steckelbroeck, S. Dithioerythritol (DTE) prevents inhibitory effects of triphenyltin (TPT) on the key enzymes of the human sex steroid hormone metabolism. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 84, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues-Pereira, P.; Andrade, M.N.; Santos-Silva, A.P.; Teixeira, M.P.; Soares, P.; Graceli, J.B.; de Carvalho, D.P.; Dias, G.; Ferreira, A.; Miranda-Alves, L. Subacute and low-dose tributyltin exposure disturbs the mammalian hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid axis in a sex-dependent manner. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 254, 109279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Mu, Y.; Liu, Y. Triphenyltin disrupts the testicular microenvironment and reduces sperm quality in adult male rats. Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Ma, T.; Chen, X. Tributyltin inhibits development of pubertal Leydig cells in rats. Reprod. Toxicol. 2022, 111, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zuo, Z.; Chen, S.; Yan, F.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, C. Reduction of spermatogenesis in mice after tributyltin administration. Toxicology 2008, 251, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, M.; Delgado, I.F.; Favareto, A.; Lopes, C.; Batista, M.M.; Kempinas, W.D.; Paumgartten, F. Sexual maturation and fertility of mice exposed to triphenyltin during prepubertal and pubertal periods. Toxicol. Rep. 2014, 2, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McAllister, B.G.; Kime, D.E. Early life exposure to environmental levels of the aromatase inhibitor tributyltin causes masculinisation and irreversible sperm damage in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2003, 65, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.N.; Cao, C.Y.; Wang, Q.W.; Gui, W.J.; Zhu, G.N. Effects of azocyclotin on gene transcription and steroid metabolome of hypothalamic–pituitary–gonad axis, and their consequences on reproduction in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 179, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doering, D.D.; Steckelbroeck, S.; Doering, T.; Klingmuller, D. Effects of butyltins on human 5alpha-reductase type 1 and type 2 activity. Steroids 2002, 67, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Chang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, D.; Kang, X. Dibutyltin (DBT) inhibits in vitro androgen biosynthesis of rat immature Leydig cells. Toxicology 2021, 456, 152779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthiessen, P.; Gibbs, P.E. Critical appraisal of the evidence for tributyltin-mediated endocrine disruption in mollusks. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1998, 17, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagadic, L.; Katsiadaki, I.; Biever, R.; Guiney, P.D.; Karouna-Renier, N.; Schwarz, T.; Meador, J.P. Tributyltin: Advancing the science on assessing endocrine disruption with an unconventional endocrine-disrupting compound. Rev. Envrion. Contam. Toxicol. 2018, 245, 65–127. [Google Scholar]
- Vogt, É.L.; Model, J.F.A.; Vinagre, A.S. Effects of Organotins on crustaceans: Update and perspectives. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Araújo, J.; Podratz, P.L.; Sena, G.C.; Merlo, E.; Freitas-Lima, L.C.; Ayub, J.; Pereira, A.; Santos-Silva, A.P.; Miranda-Alves, L.; Silva, I.V.; et al. The obesogen tributyltin induces abnormal ovarian adipogenesis in adult female rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 295, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sena, G.C.; Freitas-Lima, L.C.; Merlo, E.; Podratz, P.L.; de Araújo, J.F.P.; Brandão, P.A.A.; Carneiro, M.T.W.D.; Zicker, M.C.; Ferreira, A.V.M.; Takiya, C.M.; et al. Environmental obesogen tributyltin chloride leads to abnormal hypothalamic- pituitary-gonadal axis function by disruption in kisspeptin/leptin signaling in female rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 319, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Shi, J.; Guo, Z.; Chen, M.; Wang, C.; He, C.; Zuo, Z. A pilot study on polycystic ovarian syndrome caused by neonatal exposure to tributyltin and bisphenol A in rats. Chemosphere 2019, 231, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas-Lima, L.C.; Merlo, E.; Zicker, M.C.; Navia-Pelaez, J.M.; de Oliveira, M.; Capettini, L.D.S.A.; Nogueira, C.R.; Ferreira, A.V.M.; Santos, S.H.S.; Graceli, J.B. Tributyltin impacts in metabolic syndrome development through disruption of angiotensin II receptor signaling pathways in white adipose tissue from adult female rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 299, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podratz, P.L.; Filho, V.S.D.; Lopes, P.F.I.; Sena, G.C.; Matsumoto, S.T.; Samoto, V.Y.; Takiya, C.M.; Miguel, E.D.C.; Silva, I.V.; Graceli, J.B. Tributyltin Impairs the Reproductive Cycle in Female Rats. J. Toxicol. Envrion. Healthy Part A 2012, 75, 1035–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooke, G.M.; Forsyth, D.S.; Bondy, G.S.; Tachon, R.; Tague, B.; Coady, L. Organotin speciation and tissue distribution in rat dams, fetuses, and neonates following oral administration of tributyltin chloride. J. Toxicol. Envrion. Healthy Part A 2008, 71, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Lim, S.; Yun, S.; Yoon, A.; Park, G.; Yang, H. Tributyltin increases the expression of apoptosis- and adipogenesis-related genes in rat ovaries. Clin. Exp. Reprod. Med. 2012, 39, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pu, Y.; Pearl, S.; Gingrich, J.; Jing, J.; Martin, D.; Murga-Zamalloa, C.A.; Veiga-Lopez, A. Multispecies study: Lowdose tributyltin impairs ovarian theca cell cholesterol homeostasis through the RXR pathway in five mammalian species including humans. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 1665–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitoh, M.; Yanase, T.; Morinaga, H.; Tanabe, M.; Mu, Y.M.; Nishi, Y.; Nomura, M.; Okabe, T.; Goto, K.; Takayanagi, R.; et al. Tributyltin or triphenyltin inhibits aromatase activity in the human granulosa-like tumor cell line KGN. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 289, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenfelder, M.; Schams, D.; Einspanier, R. Steroidogenesis during in vitro maturation of bovine cumulus oocyte complexes and possible effects of tri-butyltin on granulosa cells. J. Steroid. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 84, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidrich, D.D.; Steckelbroeck, S.; Klingmuller, D. Inhibition of human cytochrome P450 aromatase activity by butyltins. Steroids 2001, 66, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Organotin Compounds | Androgen Receptor | Estrogen Receptor α | Estrogen Receptor β | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dock Score | BE (Kcal/mol) | pKd | Dock Score | BE (Kcal/mol) | pKd | Dock Score | BE (Kcal/mol) | pKd | |
| Tributyltin | −30.18 | −7.82 | 5.73 | −31.26 | −7.67 | 5.62 | −30.80 | −7.69 | 5.64 |
| Dibutyltin | −27.79 | −6.81 | 4.99 | −26.79 | −6.72 | 4.93 | −27.68 | −6.78 | 4.97 |
| Diphenyltin | −28.40 | −8.17 | 5.99 | −27.64 | −8.10 | 5.94 | −22.76 | −8.13 | 5.96 |
| Monophenyltin | −23.93 | −7.60 | 5.57 | −25.67 | −7.63 | 5.59 | −24.75 | −7.66 | 5.61 |
| Native ligand | - | −10.36 | 7.60 | - | −9.78 | 7.17 | - | −9.95 | 7.29 |
| Monobutyltin | −16.96 | No analysis was performed due to low dock score | −16.94 | No analysis was performed due to low dock score | −16.67 | No analysis was performed due to low dock score | |||
| Triphenyltin | 772.83 | No binding to receptor (dock score high positive) | 122.80 | No binding to receptor (dock score high positive) | 176.40 | No binding to receptor (dock score high positive) | |||
| Azocyclotin | Could not be docked even after varying the default parameters. | ||||||||
| Native (Testosterone) | Tributyltin | Dibutyltin | Diphenyltin | Monophenyltin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | Leu-701 | - | - | - |
| Leu-704 | - | - | Leu-704 | Leu-704 |
| Asn-705 | - | - | - | - |
| - | Leu-707 | - | Leu-707 | - |
| Gln-711 | - | - | - | - |
| Trp-741 | - | - | - | - |
| Met-742 | - | - | Met-742 | - |
| Met-745 | Met-745 | - | Met-745 | - |
| - | Val-746 | Val-746 | - | - |
| - | Val-749 | Met-749 | - | - |
| Arg-752 | - | - | - | - |
| - | Phe-764 | Phe-764 | - | - |
| Met-780 | Met-780 | Met-780 | - | - |
| Met-787 | ||||
| Leu-873 | - | Leu-873 | - | - |
| - | Phe-876 | Phe-876 | - | - |
| Thr-877 | - | - | - | - |
| Native (Estradiol) | Tributyltin | Dibutyltin | Diphenyltin | Monophenyltin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | Met-343 | Met-343 | - |
| Leu-346 | - | - | Leu-346 | - |
| - | Leu-349 | Leu-349 | - | - |
| Ala-350 | Ala-350 | Ala-350 | Ala-350 | Ala-350 |
| Glu-353 | - | - | - | - |
| Leu-384 | - | - | - | Leu-384 |
| - | Trp-383 | - | - | - |
| Leu-387 | - | - | Leu-387 | Leu-387 |
| Met-388 | - | - | - | - |
| Leu-391 | - | - | Leu-391 | Leu-391 |
| Arg-394 | - | - | - | - |
| Phe-404 | Phe-404 | Phe-404 | Phe-404 | Phe-404 |
| - | Met-421 | Met-421 | - | - |
| Ile-424 | Ile-424 | - | - | - |
| His-524 | His-524 | His-524 | - | - |
| Leu-525 | Leu-525 | - | Leu-525 | - |
| Native (Estradiol) | Tributyltin | Dibutyltin | Diphenyltin | Monophenyltin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | Met-295 | - | Met-295 | - |
| Leu-298 | Leu-298 | - | Leu-298 | - |
| - | Leu-301 | Leu-301 | - | - |
| Ala-302 | - | - | Ala-302 | Ala-302 |
| Glu-305 | - | - | - | - |
| Met-336 | - | - | Met-336 | Met-336 |
| Leu-339 | Leu-339 | Leu-339 | Leu-339 | Leu-339 |
| Met-340 | - | - | - | - |
| - | Leu-343 | - | Leu-343 | - |
| Phe-356 | Phe-356 | Phe-356 | Phe-356 | Phe-356 |
| - | Ile-373 | - | - | - |
| Ile-376 | - | - | - | |
| Gly-472 | - | - | - | - |
| His-475 | His-475 | His-475 | - | - |
| Leu-476 | Leu-476 | - | Leu-476 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beg, M.A.; Beg, M.A.; Zargar, U.R.; Sheikh, I.A.; Bajouh, O.S.; Abuzenadah, A.M.; Rehan, M. Organotin Antifouling Compounds and Sex-Steroid Nuclear Receptor Perturbation: Some Structural Insights. Toxics 2023, 11, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11010025
Beg MA, Beg MA, Zargar UR, Sheikh IA, Bajouh OS, Abuzenadah AM, Rehan M. Organotin Antifouling Compounds and Sex-Steroid Nuclear Receptor Perturbation: Some Structural Insights. Toxics. 2023; 11(1):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11010025
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeg, Mohd A., Md A. Beg, Ummer R. Zargar, Ishfaq A. Sheikh, Osama S. Bajouh, Adel M. Abuzenadah, and Mohd Rehan. 2023. "Organotin Antifouling Compounds and Sex-Steroid Nuclear Receptor Perturbation: Some Structural Insights" Toxics 11, no. 1: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11010025
APA StyleBeg, M. A., Beg, M. A., Zargar, U. R., Sheikh, I. A., Bajouh, O. S., Abuzenadah, A. M., & Rehan, M. (2023). Organotin Antifouling Compounds and Sex-Steroid Nuclear Receptor Perturbation: Some Structural Insights. Toxics, 11(1), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11010025








