Determination of the Spatial Distribution of Air Pollutants in Bucheon, Republic of Korea, in Winter Using a GIS-Based Mobile Laboratory
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
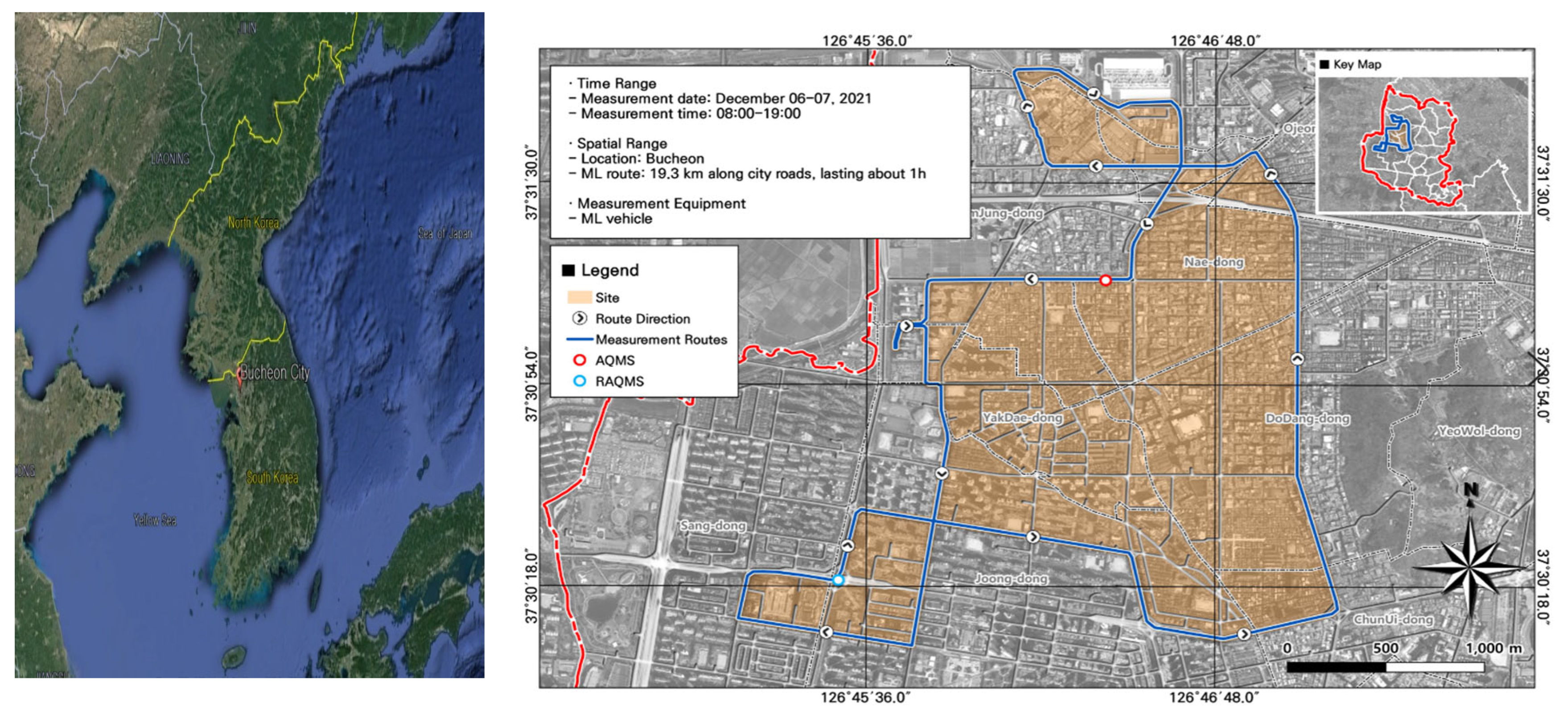
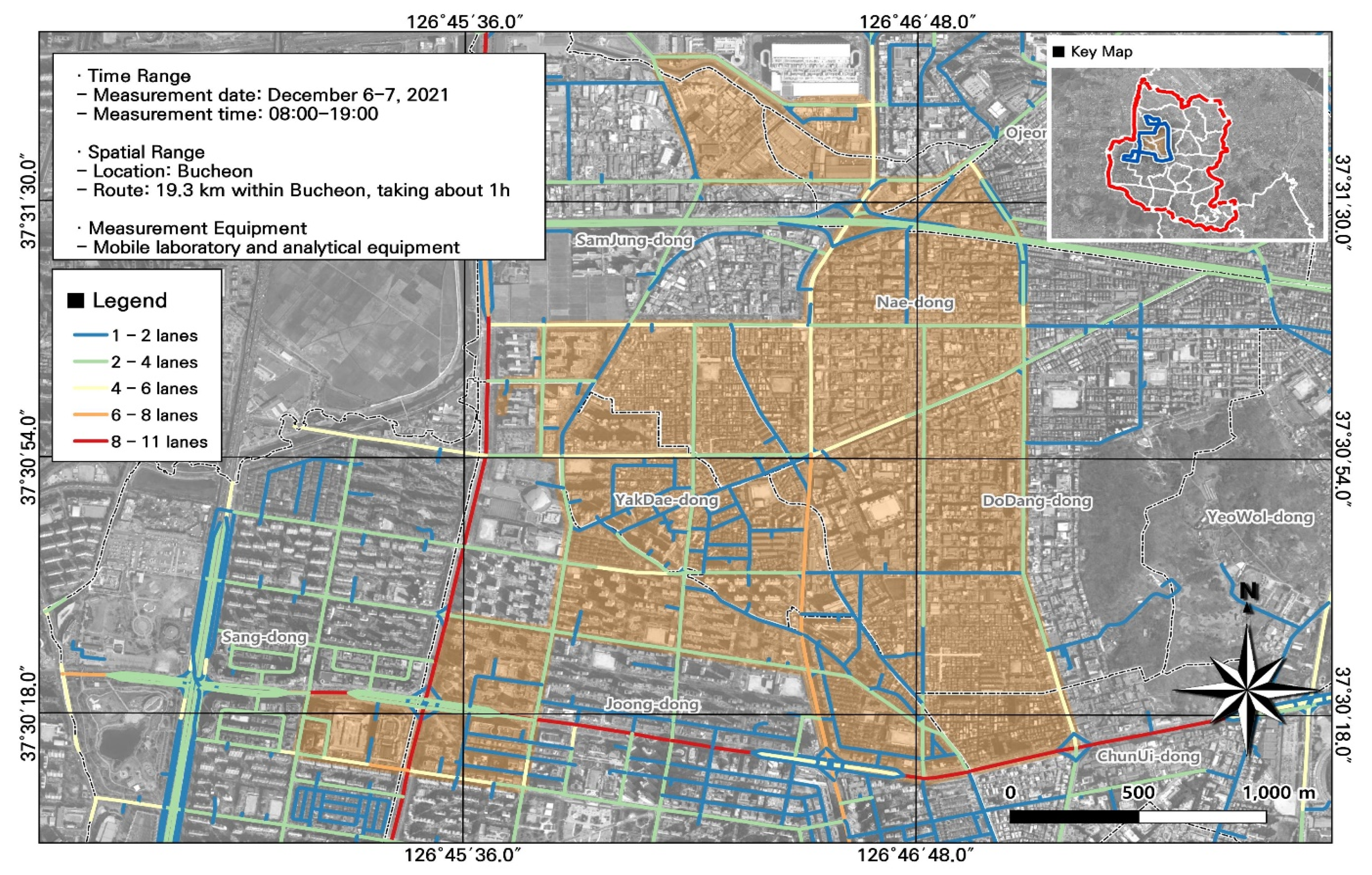
2.1. Research Site
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.2.1. Mobile Laboratory
2.2.2. Measurement Procedure
2.2.3. GIS Analysis
3. Results
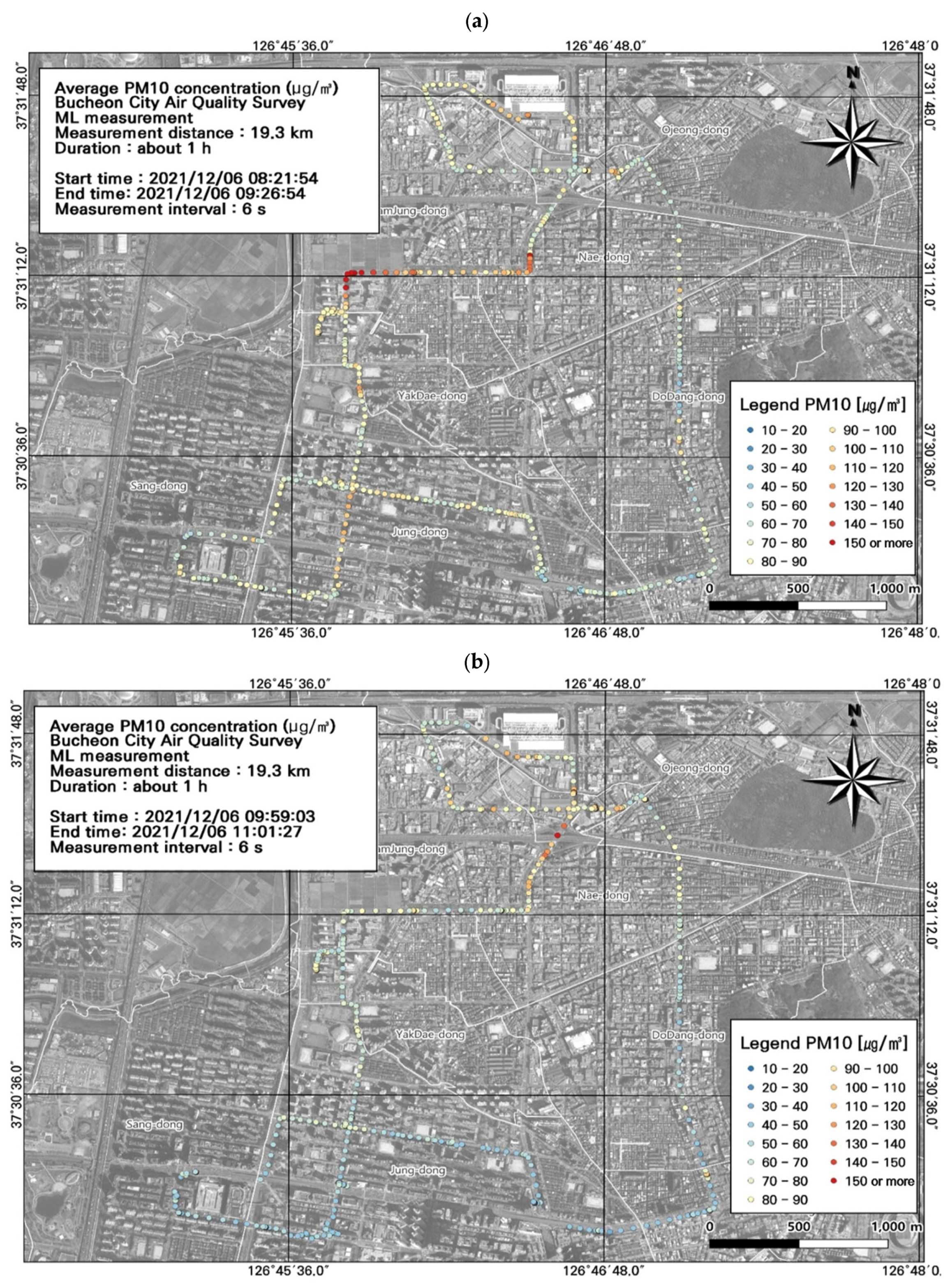
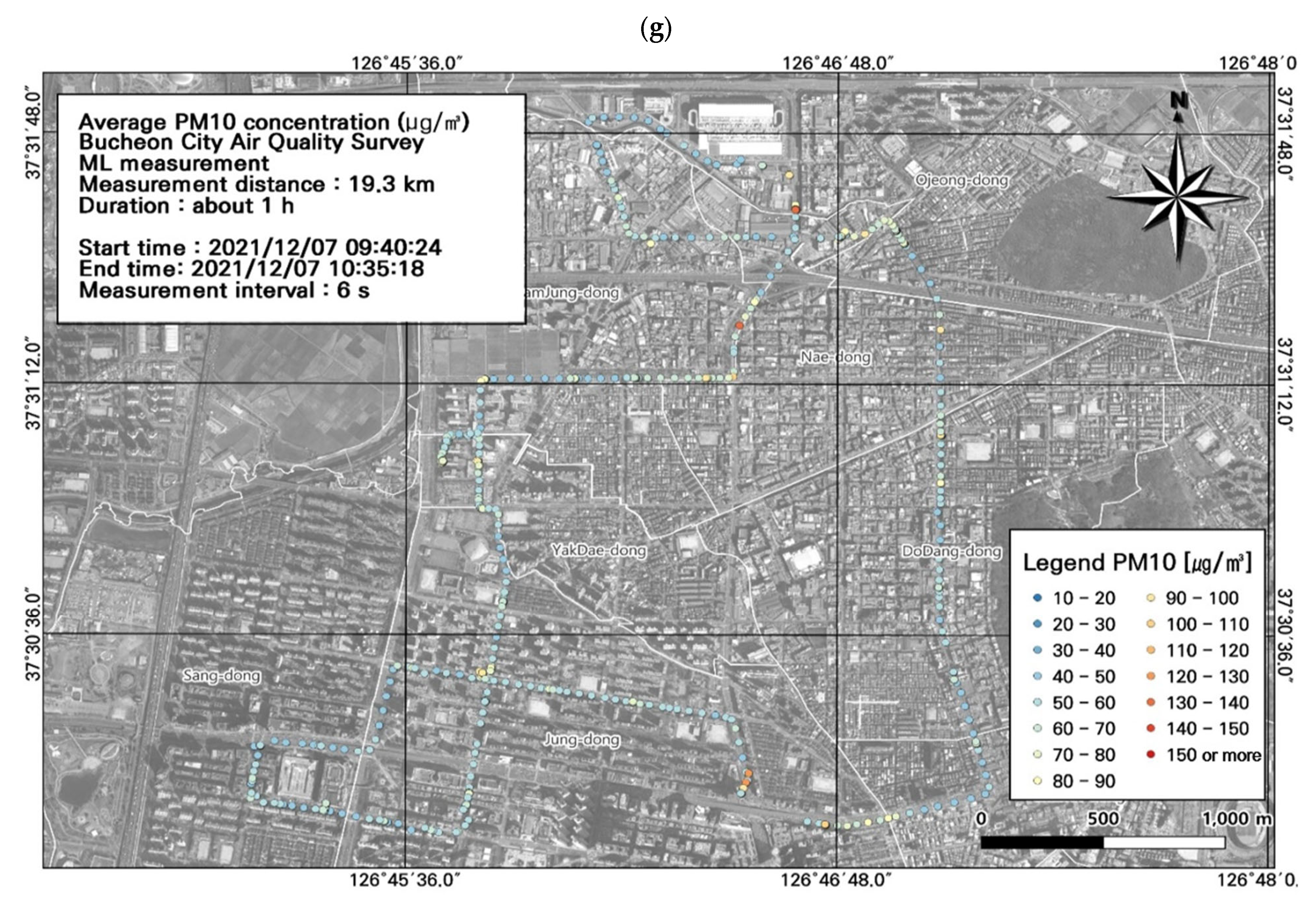
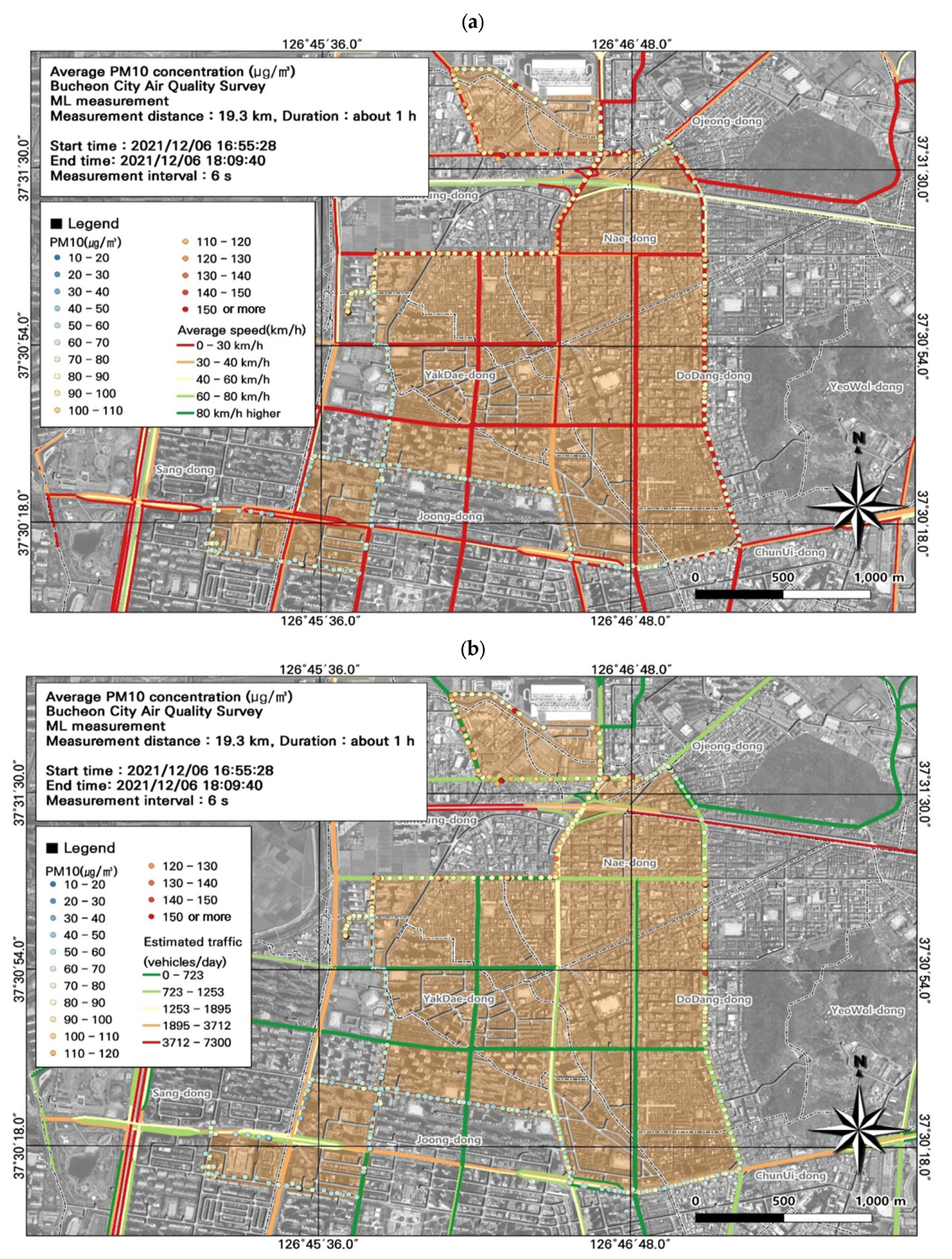
3.1. Particulate Pollution in Bucheon
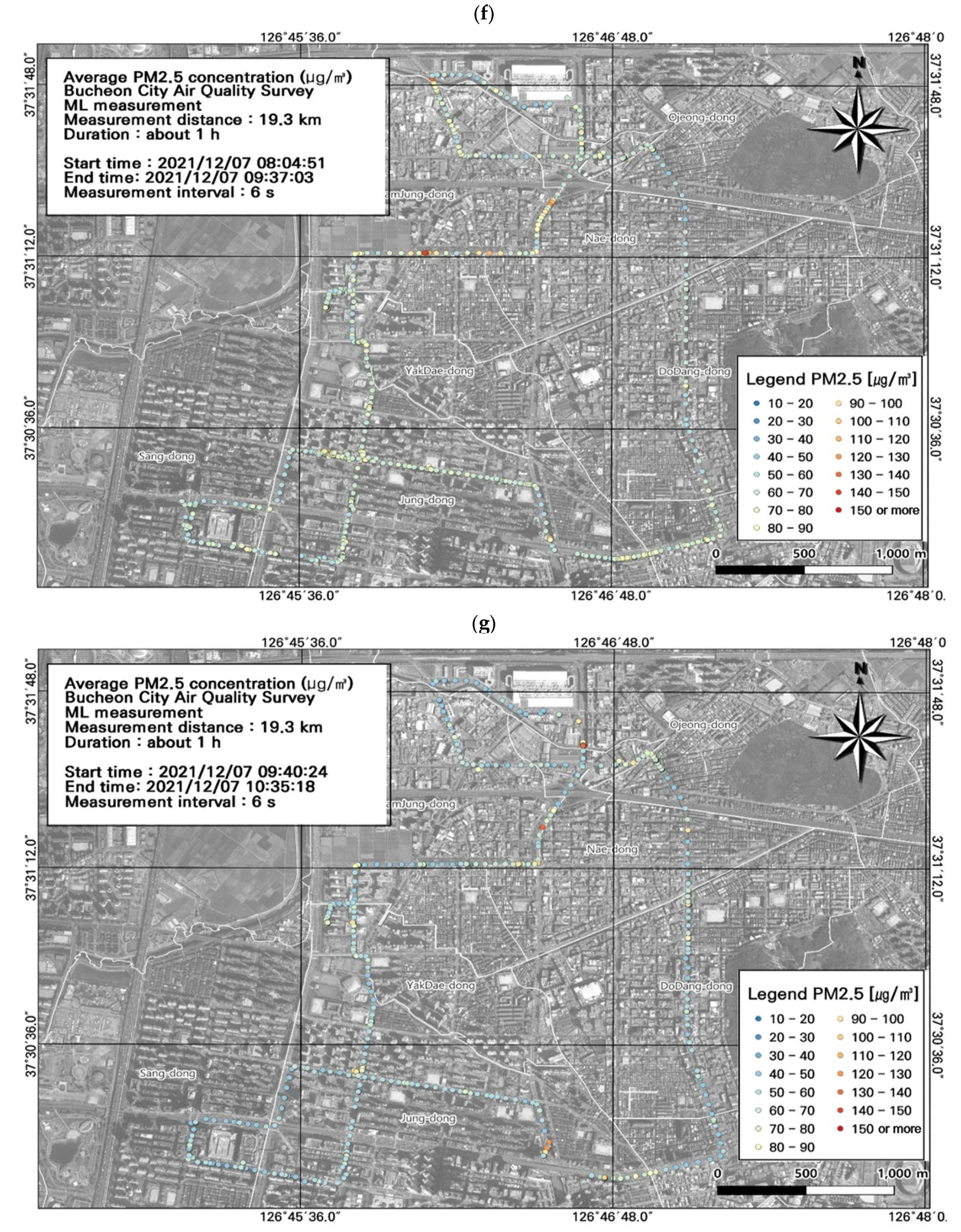
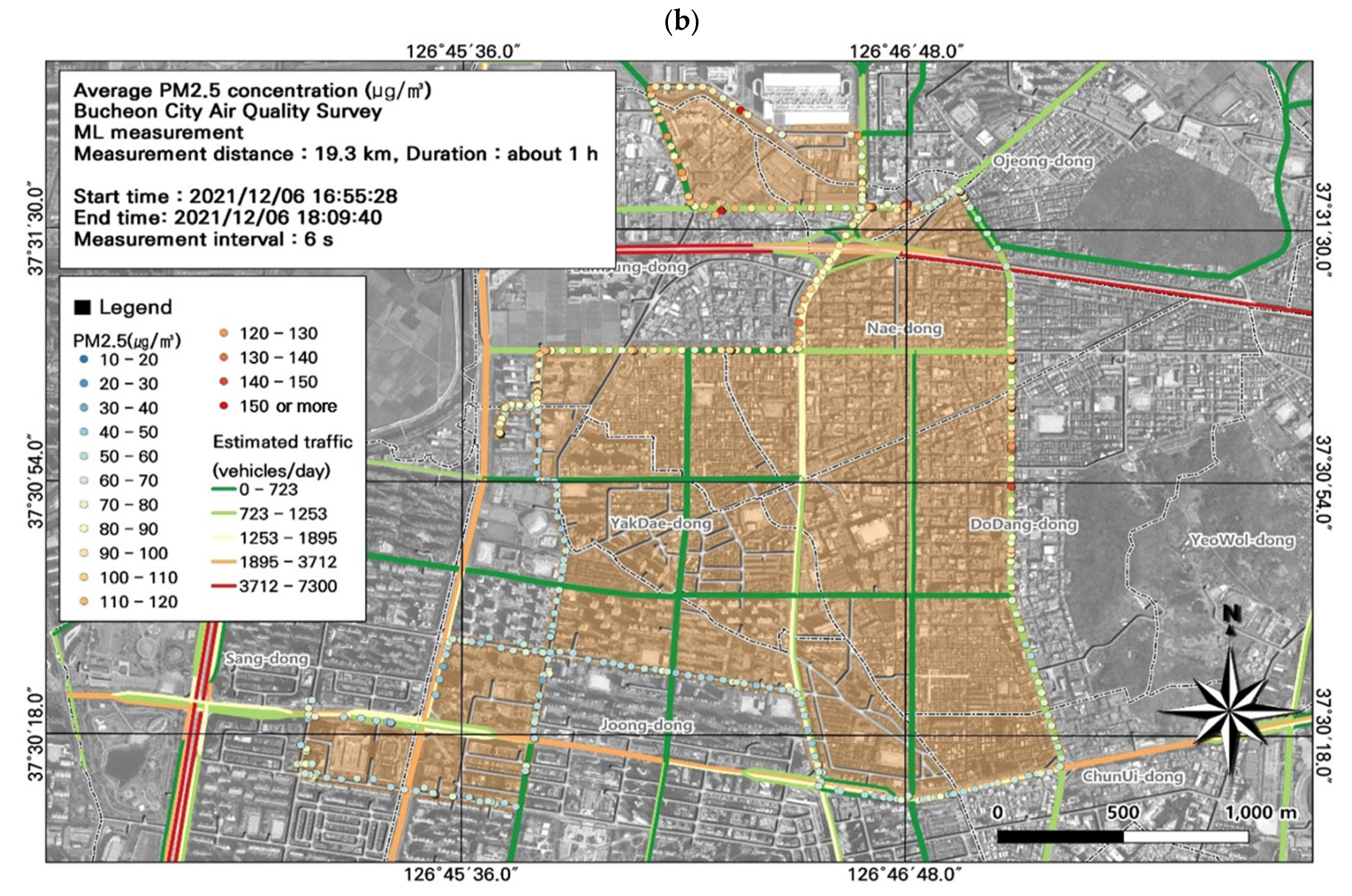
3.2. Spatiotemporal Patterns of PM2.5 and PM10 Concentrations
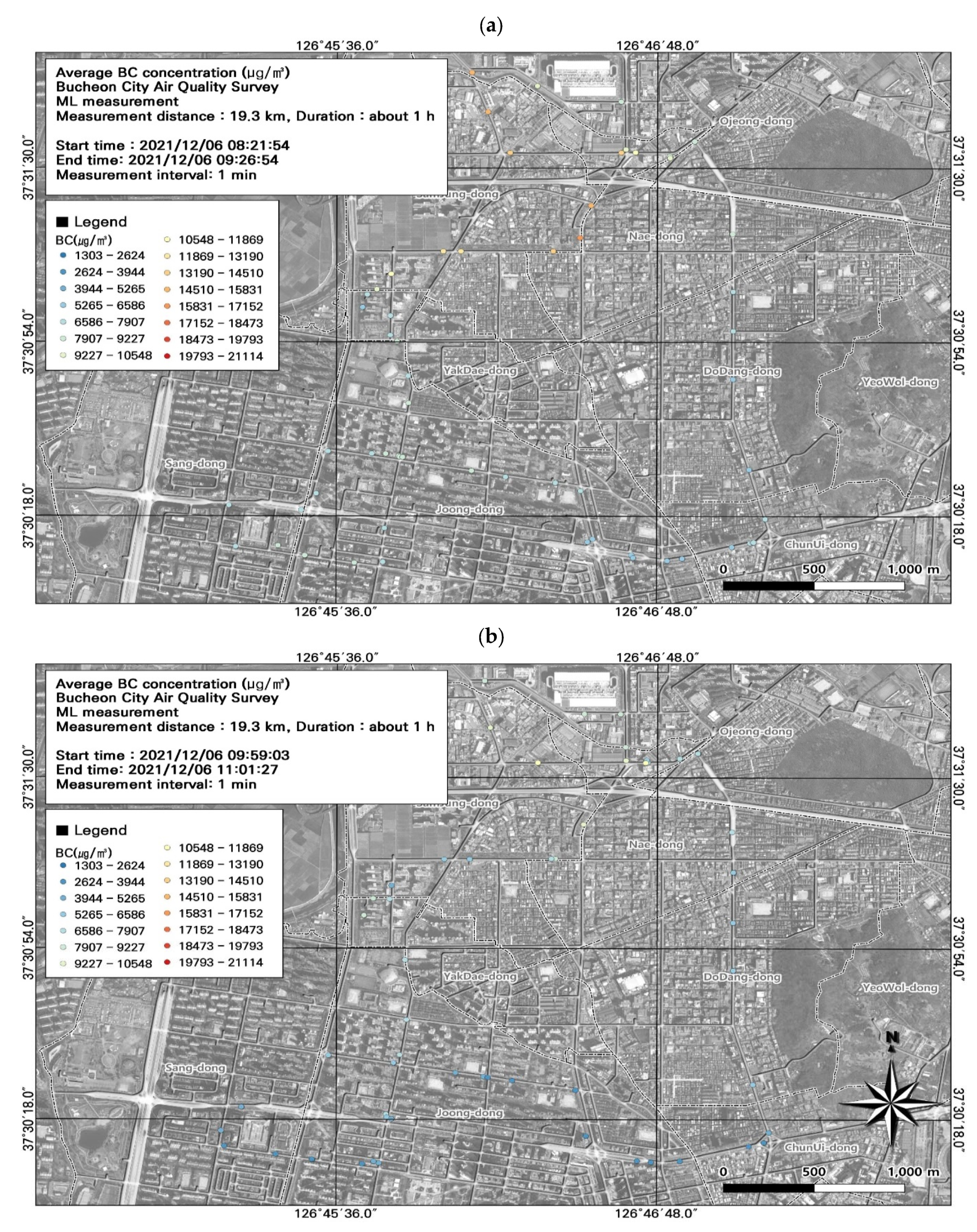
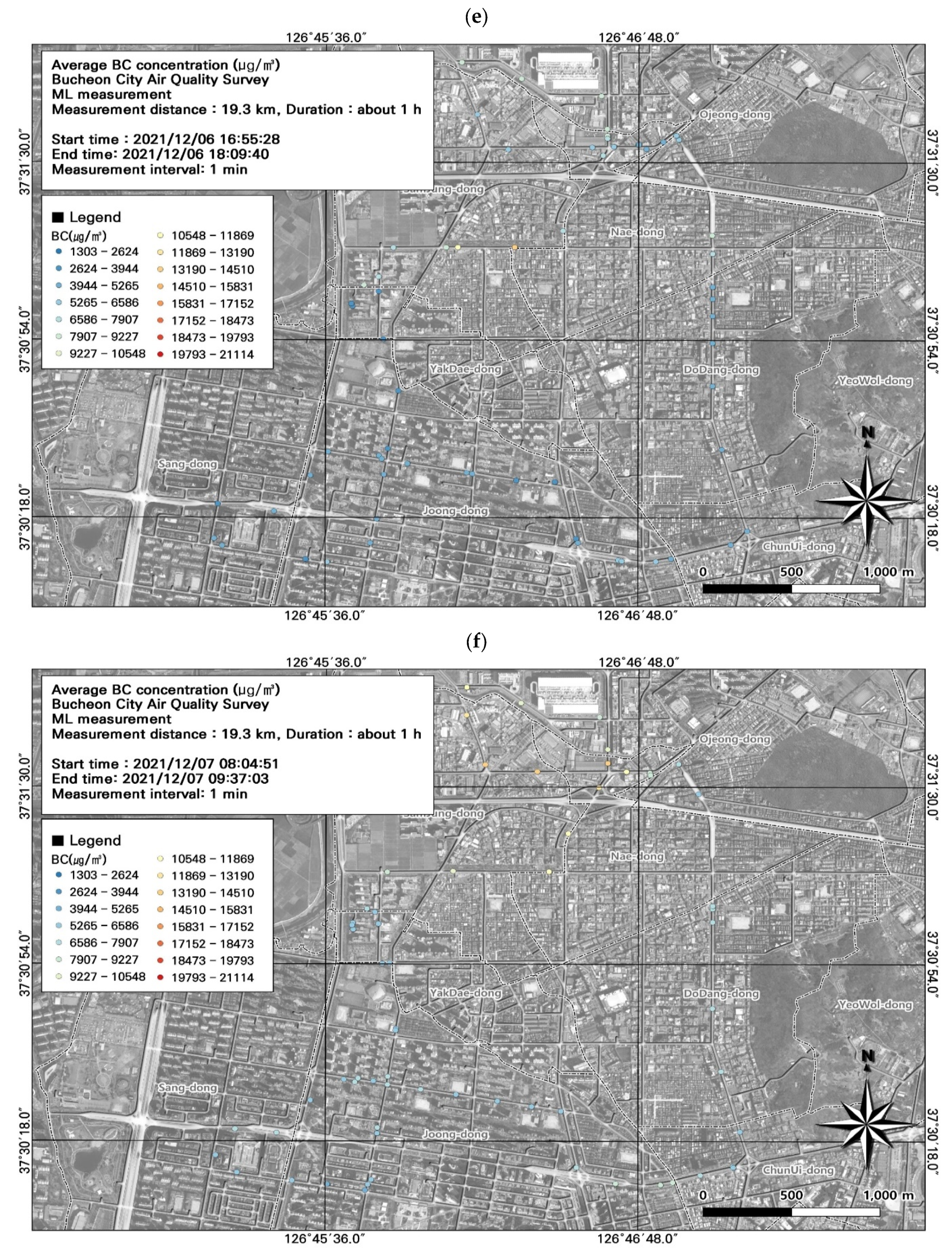
3.3. Spatiotemporal Patterns of BC Concentrations
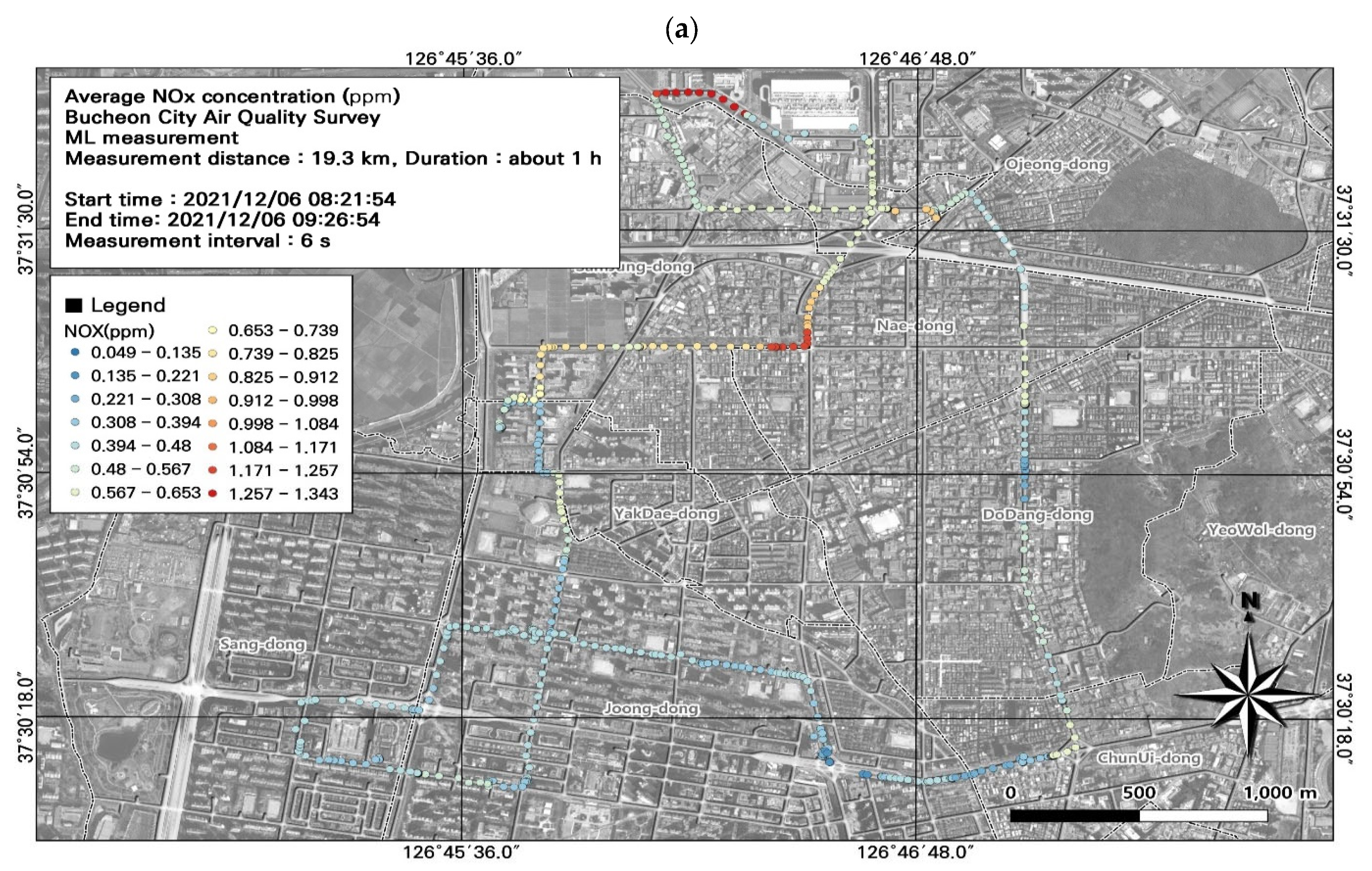
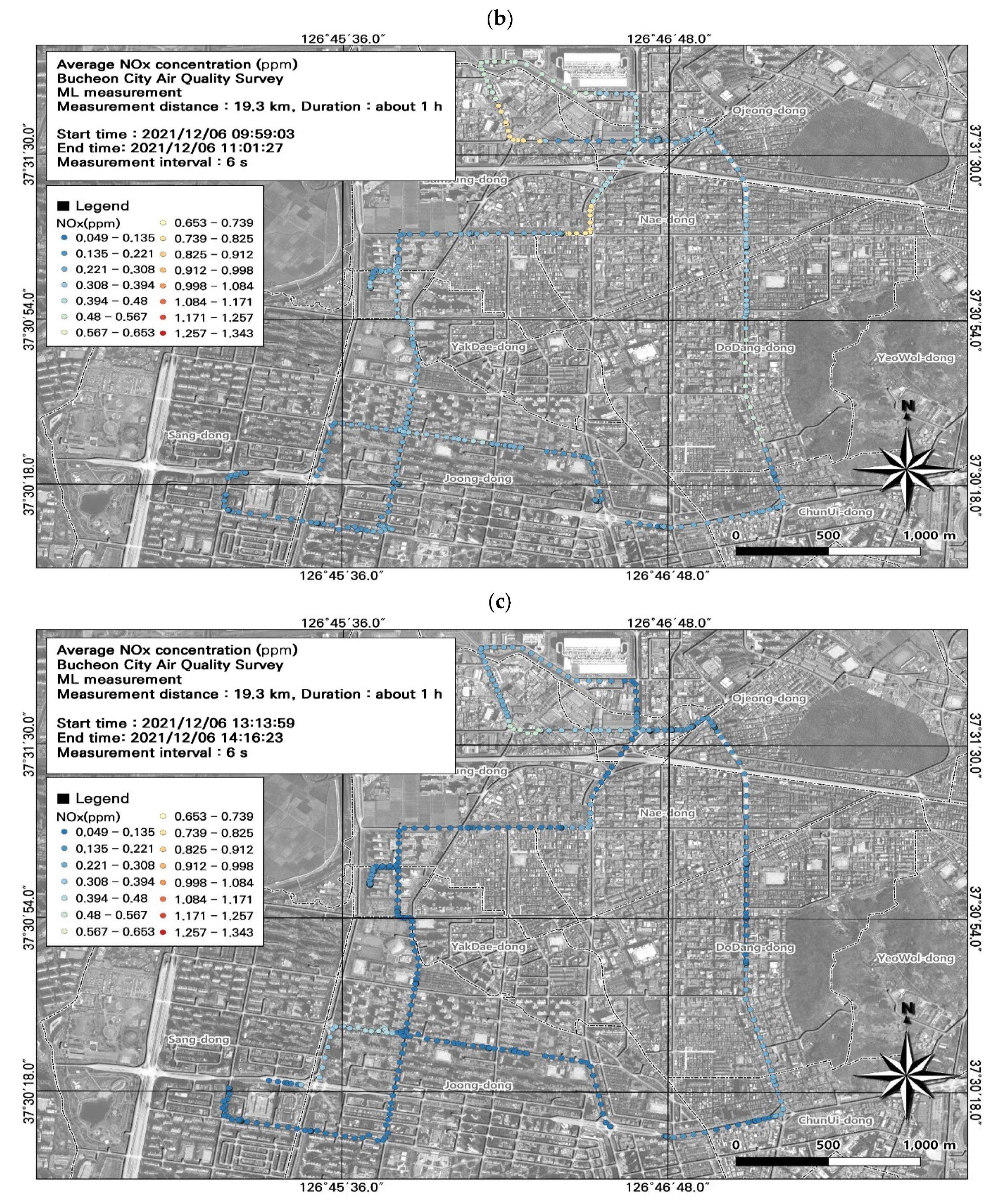
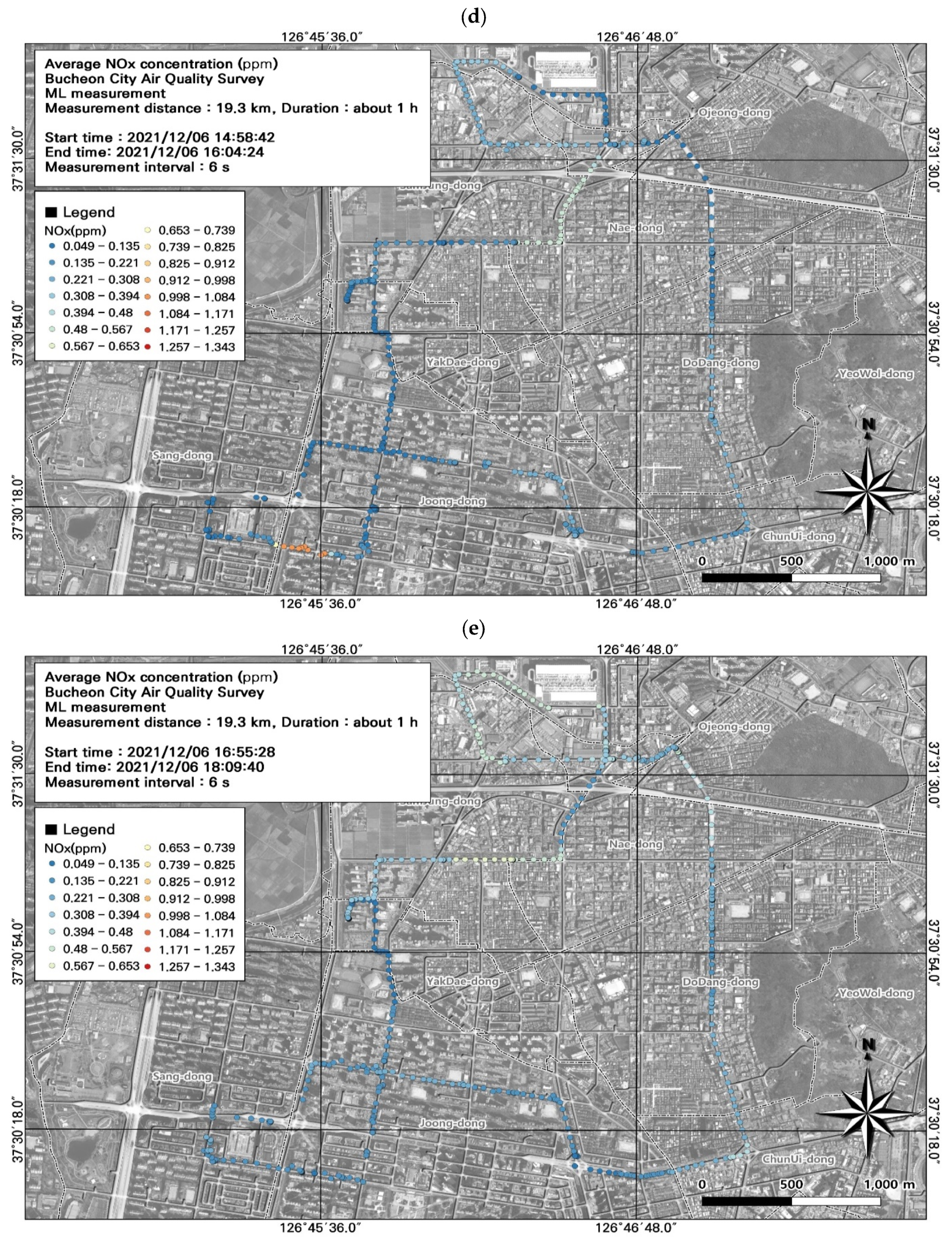
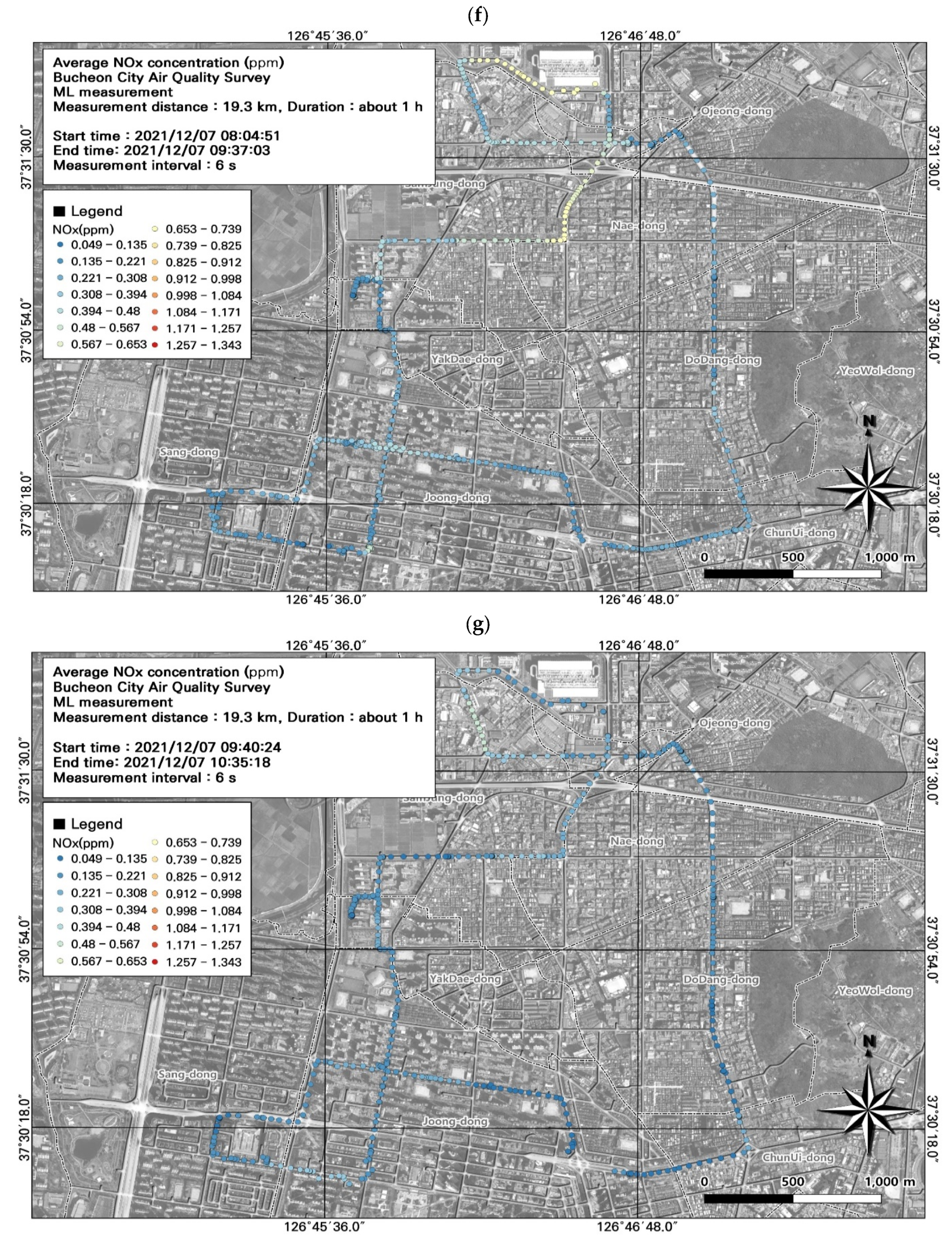
3.4. Spatiotemporal Patterns of NOx Concentrations
3.5. GIS-Based Pollution Hotspot Analysis
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, J.I.; Cho, Y.S. Urban air pollution problems and control strategies. J. Environ. Sanit. Eng. 1992, 7, 69–82. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Choi, C.I.; Kim, J.H. An international comparative study on the relationship between economic growth and environmental pollution: Testing the existence of EKC in CO2. J. Korea Plan. Assoc. 2006, 41, 153–166. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.J.; Jun, M.J. Analysis on relationship between urban development characteristics and air pollution level. J. Korea Plan. Assoc. 2014, 49, 151–167. (In Korean) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.B.; Kim, C.H.; Noh, S.J.; Hwang, E.Y.; Park, D.S.; Lee, J.J.; Kim, J.H. A study on spatial distribution characteristics of air pollutants in Bucheon-si using mobile laboratory. J. Part. Aerosol Res. 2020, 17, 9–20. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.B.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, S.B.; Kim, K.H.; Yoo, J.W.; Bae, G.N. Characteristics of spatial and temporal air pollution on bicycle way along the Han river in Seoul, Korea. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 35, 184–194. (In Korean) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myong, J.P. Health effects of particulate matter. Korean J. Med. 2016, 91, 106–113. (In Korean) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environment. Installation and Management Guideline of Air Pollution Measurement Network; Ministry of Environment: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2019. (In Korean)
- Dong, J.I.; Lee, W.J. Air Pollution Measurement Network Management: Real-Time Air Quality Measurement System. 2015. Available online: https://seoulsolution.kr/en/content/6540 (accessed on 27 October 2023).
- Do, W.G.; Jung, W.S.; Yoo, E.C.; Kwak, J. An investigation into air quality of main roads in Busan using mobile platform measurement. J. Environ. Sci. Int. 2013, 22, 1199–1211. (In Korean) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocker, D.; Johnson, K.C.; Miller, J.W. Development and application of mobile laboratory for measuring emissions from diesel engines. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 182–189. [Google Scholar]
- Hochheiser, S.; Storlazzi, M.; Basbagill, W.J. Use of a mobile laboratory in air pollution studies. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 2007, 26, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Zhu, T.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, R.Y.; Zhang, S.Q.; Xie, X.X.; Han, Y.Q.; Li, Y. Use of mobile laboratory to evaluate changes in on-road air pollutants during the Beijing 2008 summer Olympics. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 8247–8263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.; Bae, G.N. A mobile emission laboratory for car chasing experiment. Trans. Korean Soc. Automot. Eng. 2011, 19, 109–116. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.H.; Shin, J.S.; Shin, W.G.; Lee, S.G.; Kim, C.; Lee, C. Road dust emissions from paved roads measured by road dust monitoring vehicle and analysis of trace elements. Part. Aerosol Res. 2012, 8, 47–54. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, S.J.; Jo, K.H.; Kim, H.S.; Song, G.B.; Lee, S.B.; Jeong, J.Y. Measurement of hazardous air pollutants in industrial complex using mobile measurement system with SIFT-MS. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 36, 507–521. (In Korean) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.B.; Bae, G.N. Monitoring of onroad air pollution using a mobile laboratory. J. Korean Soc. Automob. Eng. 2013, 35, 31–34. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Samad, A.; Vogt, U. Mobile air quality measurements using bicycle to obtain spatial distribution and high temporal resolution in and around the city center of Stuttgart. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 244, 117915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitchins, J.; Morawska, L.; Wolff, R.; Gilbert, D. Concentration of submicrometre particles from vehicle emissions near a major road. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerdahl, D.; Fruin, S.; Sax, T.; Fine, P.M.; Sioutas, C. Mobile platform measurements of ultrafine particles and associated pollutant concentrations of freeways and residential streets in Los Angeles. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 3597–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, D.; Lee, S.B.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Jin, H.C.; Kim, T.S.; Bae, G.N. Spatial distribution of on-road ultrafine particle number concentration on Naebu Express Way in Seoul during Winter season. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 29, 10–26. (In Korean) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossche, J.V.D.; Peters, J.; Verwaeren, J.; Botteldooren, D.; Theunis, J.; Baets, B.D. Mobile monitoring for mapping spatial variation in urban air quality: Development and validation of a methodology based on ana extensive dataset. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 105, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Kwak, K.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Woo, S.H.; Kim, J.B.; Lee, S.B.; Ryu, S.H.; Kim, C.H.; Bae, G.N.; Oh, I.B. Spatial mapping of a highly non-uniform distribution of particle-bound PAH in a densely polluted urban area. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 496. (In Korean) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APM Engineering Co., Ltd. Test Report of Inlet System Installed for ML; APM Engineering Co., Ltd.: Bucheon-si, Republic of Korea, 2019. [Google Scholar]
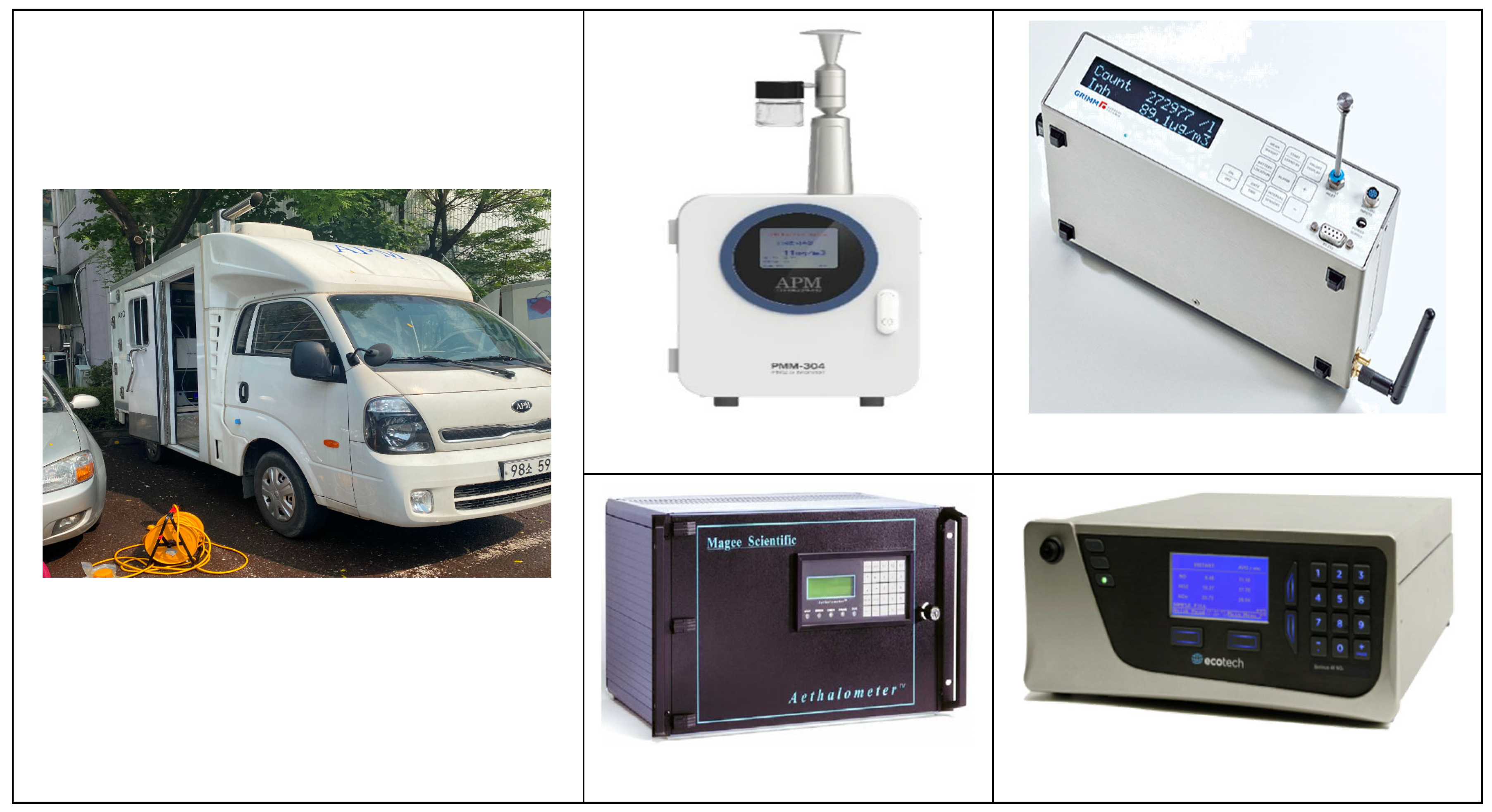












| Measurement Item | Instrument | Measurement Range | Interval |
|---|---|---|---|
| Latitude, Longitude, Altitude, Speed | GPS system | - | 1 s |
| PM10, PM2.5 | Grimm 11-D (Grimm Aerosol Technik) | 0.253–35.15 μm | 6 s |
| PM2.5 | PMM-304 (APM) | 0–200 µg/m3 | 60 s (1 m) |
| NOx | Serinus 40 (Ecotech) | 0–20 ppm | 1 s |
| Black carbon | AE51 aethalometer (Magee Scientific) | 0–1000 µg/m3 | 60 s (1 m) |
| Measurement Item | Unit | ML | AQMS | RAQMS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM10 | µg/m3 | 78.7 ± 26.2 | 85.1 ± 21.5 | 63.5 ± 12.6 |
| PM2.5 | µg/m3 | 55.7 ± 13.0 | 52.7 ± 15.1 | 38.9 ± 8.3 |
| Black carbon | µg/m3 | 6205.7 ± 3020.1 | - | - |
| NO | ppm | 0.21 ± 0.16 | - | - |
| NO2 | ppm | 0.07 ± 0.03 | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 0.05 ± 0.01 |
| NOx | ppm | 0.28 ± 0.18 | - | - |
| Temperature | °C | - | 6.4 ± 3.8 | - |
| Relative humidity | % | - | 60. 6 ± 13.7 | - |
| Wind speed | Km/h | - | 0.4 ± 0.3 | - |
| Number of Measurements | PM10 (µg/m3) | PM2.5 (µg/m3) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 79.6 ± 19.7 | 62.7 ± 13.0 |
| 2 | 69.1 ± 21.6 | 52.6 ± 11.7 |
| 3 | 57.1 ± 38.8 | 39.5 ± 14.2 |
| 4 | 63.6 ± 34.5 | 42.9 ± 11.5 |
| 5 | 91.8 ± 17.6 | 59.2 ± 8.8 |
| 6 | 71.2 ± 13.8 | 59.5 ± 6.8 |
| 7 | 67.4 ± 25.8 | 57.6 ± 17.4 |
| Number of Measurements | BC (µg/m3) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 8722.0 ± 2660.7 |
| 2 | 6005.6 ± 2197.0 |
| 3 | 3300.2 ± 1780.7 |
| 4 | 4580.8 ± 3064.2 |
| 5 | 5624.0 ± 2016.2 |
| 6 | 7187.2 ± 2321.0 |
| 7 | 7889.2 ± 3283.4 |
| Number of Measurements | NO (ppm) | NO2 | NOx (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.43 ± 0.18 | 0.08 ± 0.03 | 0.50 ± 0.20 |
| 2 | 0.24 ± 0.12 | 0.07 ± 0.03 | 0.31 ± 0.14 |
| 3 | 0.09 ± 0.09 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.15 ± 0.10 |
| 4 | 0.14 ± 0.13 | 0.07 ± 0.05 | 0.21 ± 0.17 |
| 5 | 0.20 ± 0.11 | 0.08 ± 0.03 | 0.28 ± 0.12 |
| 6 | 0.21 ± 0.12 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.27 ± 0.14 |
| 7 | 0.15 ± 0.08 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.20 ± 0.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, M.; Kim, D.; Jang, Y.; Lee, J.; Ko, S.; Kim, K.; Park, C.; Park, D. Determination of the Spatial Distribution of Air Pollutants in Bucheon, Republic of Korea, in Winter Using a GIS-Based Mobile Laboratory. Toxics 2023, 11, 932. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110932
Kim M, Kim D, Jang Y, Lee J, Ko S, Kim K, Park C, Park D. Determination of the Spatial Distribution of Air Pollutants in Bucheon, Republic of Korea, in Winter Using a GIS-Based Mobile Laboratory. Toxics. 2023; 11(11):932. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110932
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Minkyeong, Daeho Kim, Yelim Jang, Jooyeon Lee, Sangwon Ko, Kyunghoon Kim, Choonsoo Park, and Duckshin Park. 2023. "Determination of the Spatial Distribution of Air Pollutants in Bucheon, Republic of Korea, in Winter Using a GIS-Based Mobile Laboratory" Toxics 11, no. 11: 932. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110932
APA StyleKim, M., Kim, D., Jang, Y., Lee, J., Ko, S., Kim, K., Park, C., & Park, D. (2023). Determination of the Spatial Distribution of Air Pollutants in Bucheon, Republic of Korea, in Winter Using a GIS-Based Mobile Laboratory. Toxics, 11(11), 932. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110932









