Multi-Omics Analyses Reveal the Mechanisms of Early Stage Kidney Toxicity by Diquat
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Chemical Reagents Treatments
2.2. Histopathologic Examination
2.3. Transcriptome Analysis
2.4. Proteomics Analysis
2.5. Untargeted LC–MS Metabolomics Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Establishment and Validation of DQ-Treated Mouse Model
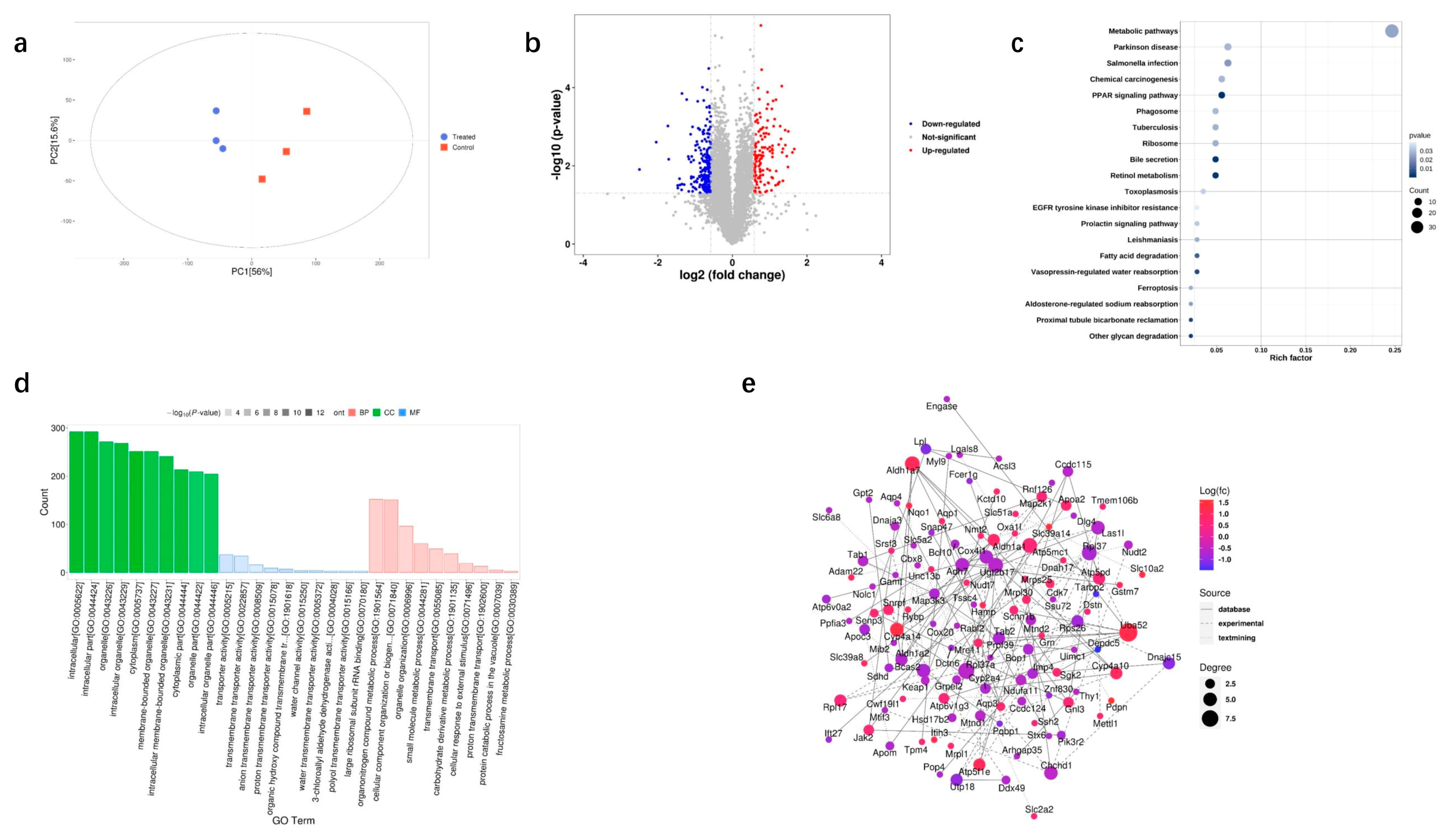
3.2. Transcriptomic Analysis of DQ-Treated Mice
3.3. Proteomic Analysis of DQ-Treated Mice
3.4. Integrated Transcriptome and Proteome Datasets
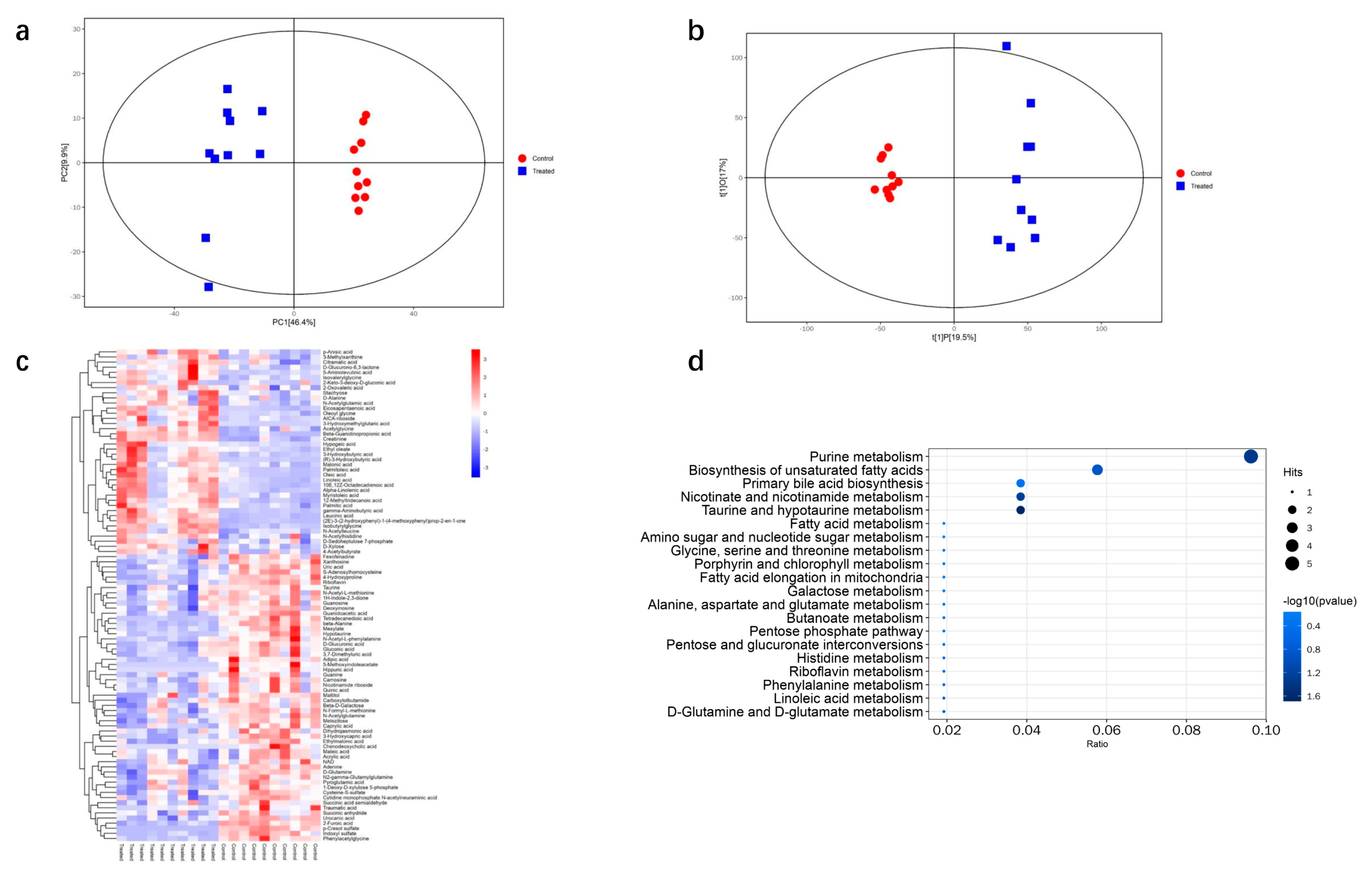
3.5. Metabolomic Analysis of DQ-Treated Mice
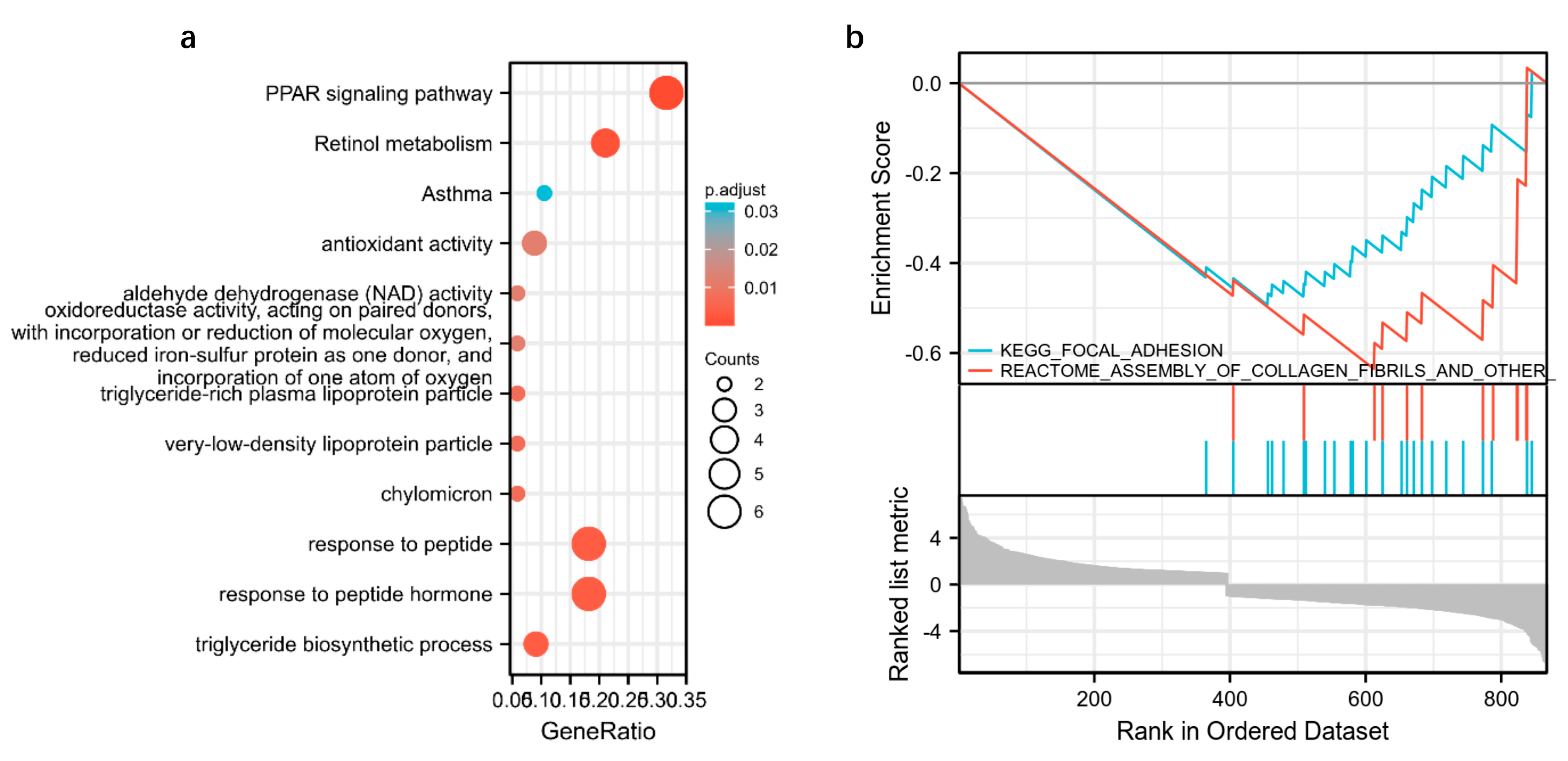
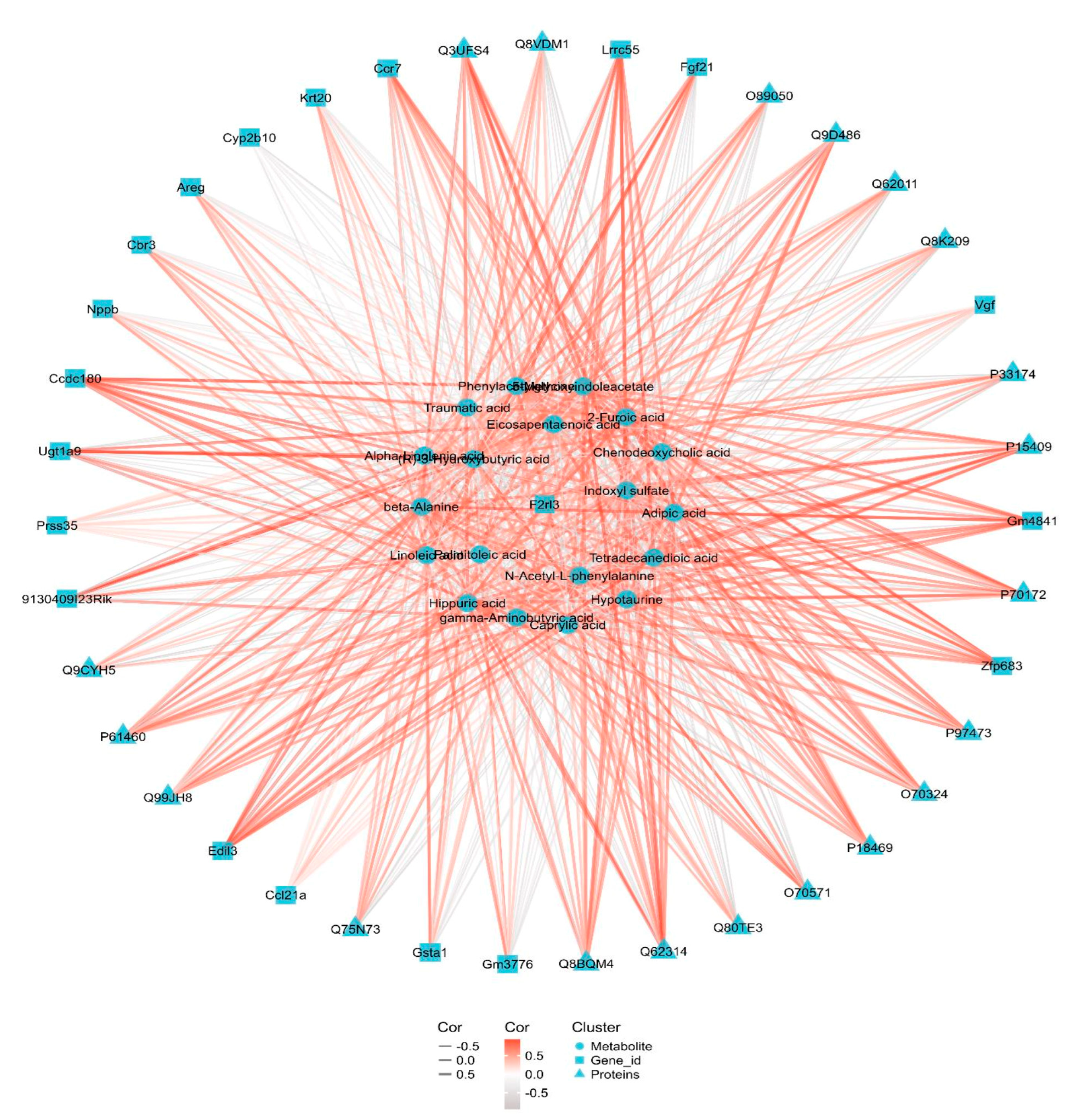
3.6. Integrated Transcriptomic, Proteomic and Metabolomics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, G.; Jian, T.; Cui, S.; Shi, L.; Kan, B.; Jian, X. Acute diquat poisoning resulting in toxic encephalopathy: A report of three cases. Clin. Toxicol. (Phila.) 2022, 60, 647–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhaes, N.; Carvalho, F.; Dinis-Oliveira, R.J. Human and experimental toxicology of diquat poisoning: Toxicokinetics, mechanisms of toxicity, clinical features, and treatment. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2018, 37, 1131–1160. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guck, D.; Hernandez, R.; Moore, S.; Van de Louw, A.; Haouzi, P. Rapid Glomerulotubular Nephritis as an Initial Presentation of a Lethal Diquat Ingestion. Case Rep. Nephrol. 2021, 2021, 4723092. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hantson, P.; Wallemacq, P.; Mahieu, P. A case of fatal diquat poisoning: Toxicokinetic data and autopsy findings. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 2000, 38, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petejova, N.; Martinek, A.; Zadrazil, J.; Teplan, V. Acute toxic kidney injury. Ren. Fail. 2019, 41, 576–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronco, C.; Bellomo, R.; Kellum, J.A. Acute kidney injury. Lancet 2019, 394, 1949–1964. [Google Scholar]
- Kellum, J.A.; Romagnani, P.; Ashuntantang, G.; Ronco, C.; Zarbock, A.; Anders, H.J. Acute kidney injury. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2021, 7, 52. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, H.C.; Chen, Y.Y.; Tsai, I.J.; Shiao, C.C.; Huang, T.M.; Chan, C.K.; Liao, H.W.; Lai, T.S.; Chueh, Y.; Wu, V.C.; et al. Accelerated versus standard initiation of renal replacement therapy for critically ill patients with acute kidney injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis of RCT studies. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, B.; Wu, W.; Chen, M.; Gu, H.; Tang, Q.; Guo, D.; Chen, T.; Chen, Y.; Lu, C.; Song, L.; et al. From the Cover: Metabolomics Reveals a Role of Betaine in Prenatal DBP Exposure-Induced Epigenetic Transgenerational Failure of Spermatogenesis in Rats. Toxicol. Sci. 2017, 158, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Cui, S.; Jian, T.; Kan, B.; Jian, X. Diquat poisoning in a pregnant woman resulting in a miscarriage and maternal death. Clin. Toxicol. (Phila.) 2021, 59, 1275–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahri-Joutey, M.; Andreoletti, P.; Surapureddi, S.; Nasser, B.; Cherkaoui-Malki, M.; Latruffe, N. Mechanisms Mediating the Regulation of Peroxisomal Fatty Acid Beta-Oxidation by PPARalpha. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaki, T.; Bennion, B.G.; Stenson, E.K.; Lynn, J.C.; Otinga, C.; Djukovic, D.; Raftery, D.; Fei, L.; Wong, H.R.; Liles, W.C.; et al. PPARalpha contributes to protection against metabolic and inflammatory derangements associated with acute kidney injury in experimental sepsis. Physiol. Rep. 2019, 7, e14078. [Google Scholar]
- Luan, Z.L.; Zhang, C.; Ming, W.H.; Huang, Y.Z.; Guan, Y.F.; Zhang, X.Y. Nuclear receptors in renal health and disease. EBioMedicine 2022, 76, 103855. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Zeng, W.; Wu, B.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Tian, H.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Clay, R.; Wei, X.; et al. PPARalpha Inhibition Overcomes Tumor-Derived Exosomal Lipid-Induced Dendritic Cell Dysfunction. Cell Rep. 2020, 33, 108278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marechal, L.; Sicotte, B.; Caron, V.; Brochu, M.; Tremblay, A. Fetal Cardiac Lipid Sensing Triggers an Early and Sex-related Metabolic Energy Switch in Intrauterine Growth Restriction. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, 3295–3311. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Yan, Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Du, J.; Chen, L. The Role of Mitochondria in Liver Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: From Aspects of Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress, Mitochondrial Fission, Mitochondrial Membrane Permeable Transport Pore Formation, Mitophagy, and Mitochondria-Related Protective Measures. Oxid Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 2021, 6670579. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, L.; Li, T.S.; Zhang, J.Z.; Liu, Z.H.; Yang, J.; Wang, B.H.; Wang, Y.M.; Zhou, J.; Kong, L.D. Fructose drives mitochondrial metabolic reprogramming in podocytes via Hmgcs2-stimulated fatty acid degradation. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2021, 6, 253. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, W.; Xie, X.; Du, M.; Bu, Y.; Wu, N.; Yang, H.; Tian, C.; Xu, F.; Xiang, S.; Zhang, P.; et al. Green Tea Polyphenols Ameliorate the Early Renal Damage Induced by a High-Fat Diet via Ketogenesis/SIRT3 Pathway. Oxid Med. Cell Longev. 2017, 2017, 9032792. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Yang, H.; Kong, X.; Wang, K.; Mao, X.; Yan, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; et al. Proteomics analysis reveals diabetic kidney as a ketogenic organ in type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 300, E287–E295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capdevila, J.H.; Falck, J.R. The arachidonic acid monooxygenase: From biochemical curiosity to physiological/pathophysiological significance. J. Lipid Res. 2018, 59, 2047–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, Y.; Carrino, S.; Lin, F.; Ferlin, A.; Lad, H.V.; Mazzacuva, F.; Falcone, S.; Rivers, N.; Banks, G.; Concas, D.; et al. Tissue Proteome of 2-Hydroxyacyl-CoA Lyase Deficient Mice Reveals Peroxisome Proliferation and Activation of omega-Oxidation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 987. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Smalling, R.V.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Kusumanchi, P.; Bogaert, W.; Wang, L.; Delker, D.A.; Skill, N.J.; Han, S.; et al. The role of SHP/REV-ERBalpha/CYP4A axis in the pathogenesis of alcohol-associated liver disease. JCI Insight. 2021, 6, e140687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Zaritsky, J.J.; Fornoni, A.; Smoyer, W.E. Dyslipidaemia in nephrotic syndrome: Mechanisms and treatment. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sidhom, E.H.; Kim, C.; Kost-Alimova, M.; Ting, M.T.; Keller, K.; Avila-Pacheco, J.; Watts, A.J.; Vernon, K.A.; Marshall, J.L.; Reyes-Bricio, E.; et al. Targeting a Braf/Mapk pathway rescues podocyte lipid peroxidation in CoQ-deficiency kidney disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.J.; Li, Z.H.; Zhang, Y.D.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, F.Q.; Wang, W.; Cui, Z.J.; Chen, G.Q. Ketone Body 3-Hydroxybutyrate Ameliorates Atherosclerosis via Receptor Gpr109a-Mediated Calcium Influx. Adv. Sci. (Weinh.) 2021, 8, 2003410. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Mao, Z.; Qian, J.; Zong, C.; Sun, H.; Yuan, B. Multi-Omics Analyses Reveal the Mechanisms of Early Stage Kidney Toxicity by Diquat. Toxics 2023, 11, 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11020184
Zhang H, Zhang J, Li J, Mao Z, Qian J, Zong C, Sun H, Yuan B. Multi-Omics Analyses Reveal the Mechanisms of Early Stage Kidney Toxicity by Diquat. Toxics. 2023; 11(2):184. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11020184
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Huazhong, Jinsong Zhang, Jinquan Li, Zhengsheng Mao, Jian Qian, Cheng Zong, Hao Sun, and Beilei Yuan. 2023. "Multi-Omics Analyses Reveal the Mechanisms of Early Stage Kidney Toxicity by Diquat" Toxics 11, no. 2: 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11020184
APA StyleZhang, H., Zhang, J., Li, J., Mao, Z., Qian, J., Zong, C., Sun, H., & Yuan, B. (2023). Multi-Omics Analyses Reveal the Mechanisms of Early Stage Kidney Toxicity by Diquat. Toxics, 11(2), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11020184





