Ecotoxicological Differences of Antimony (III) and Antimony (V) on Earthworms Eisenia fetida (Savingy)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Soils, Earthworms, and Chemicals
2.2. Toxicity Assessments Assay
2.2.1. Acute Contact Test
2.2.2. Earthworm Avoidance Test
2.2.3. Chronic Toxicity Test
2.3. Determination of Water-Soluble Sb Concentration
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Behavior and Morphological Changes in Earthworms during the Toxicity Tests
3.2. Mortality and Dose-Response Relationship in Acute Contact Toxic Test
3.3. Avoidance Responses
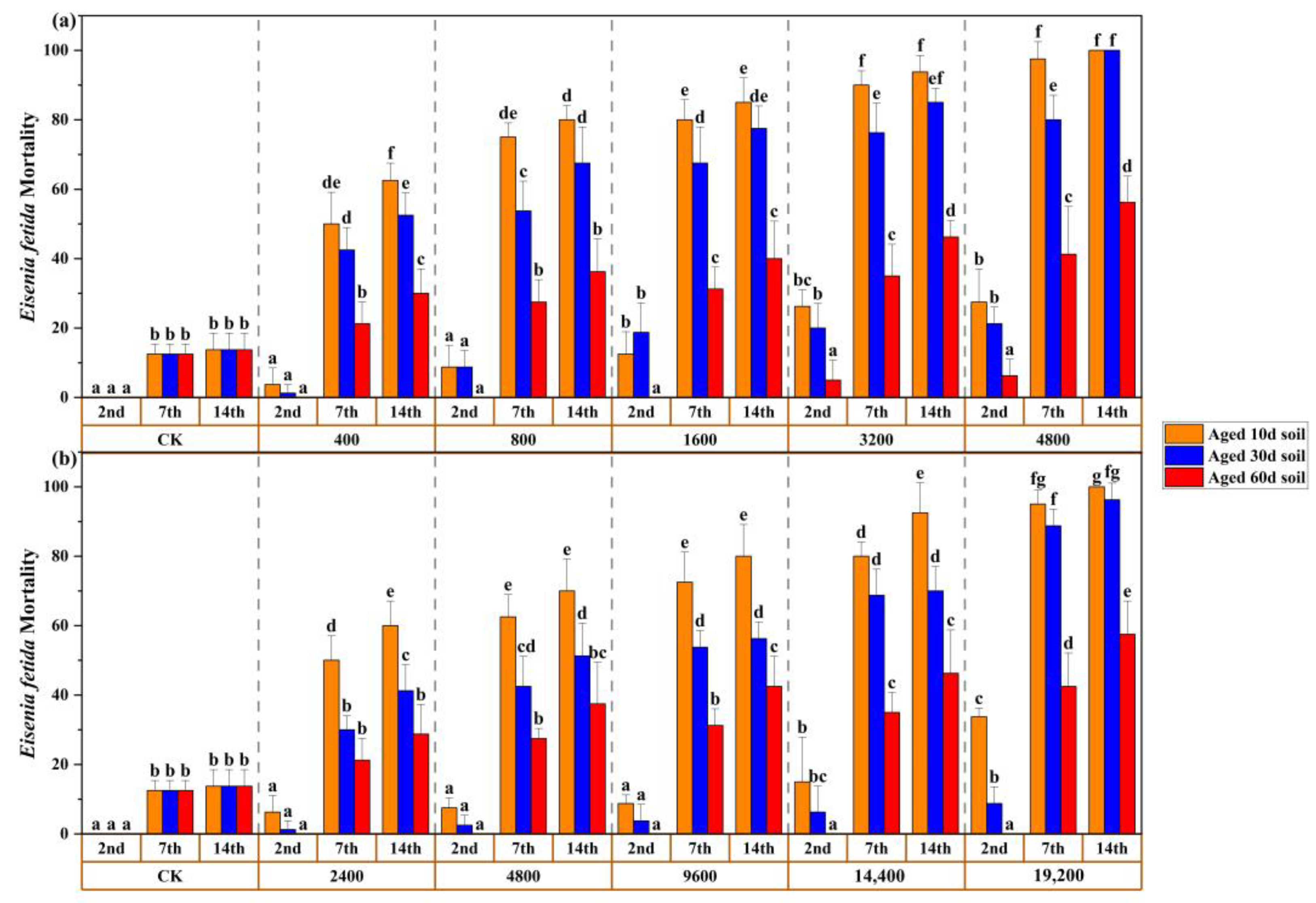
3.4. Mortality and Aging Relationship in Chronic Toxic Test
3.5. Mortality and Water-Soluble Sb Relationship after the Aging Process
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Sb (III) and Sb (V) on the Morphological Variation in E. fetida
4.2. Effects of Sb (III) and Sb (V) on the Mortality of E. fetida
4.3. Effects of Sb (III) and Sb (V) on the Avoidance Responses of E. fetida
4.4. Effects of the Aging Process on the Toxicity of Sb in Soil
4.5. Effects of the Aging Process on Speciation of Sb in Soil
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, N.; Wang, A.; Kong, L.; He, M. Calculation and application of Sb toxicity coefficient for potential ecological risk assessment. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 610–611, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, W.A. Antimony in the environment—The new global puzzle. Environ. Chem. 2009, 6, 93–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, C.; Zhao, D.; Gao, J.; Hao, J.; He, M.; Liu, K.; Wang, K.; Hua, S. A Comprehensive Global Inventory of Atmospheric Antimony Emissions from Anthropogenic Activities, 1995–2010. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 10235–10241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Wang, X.; Wu, F.; Fu, Z. Antimony pollution in China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2012, 421–422, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolan, N.; Kumar, M.; Singh, E.; Kumar, A.; Singh, L.; Kumar, S.; Keerthanan, S.; Hoang, S.A.; El-Naggar, A.; Vithanage, M.; et al. Antimony contamination and its risk management in complex environmental settings: A review. Environ. Int. 2021, 158, 106908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, W.; Xiang, G.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Sushkova, S.; Minkina, T.; Duan, R. Implications of Soil Potentially Toxic Elements Contamination, Distribution and Health Risk at Hunan’s Xikuangshan Mine. Processes 2021, 9, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filella, M.; Belzile, N.; Chen, Y.-W. Antimony in the environment: A review focused on natural waters: I. Occurrence. Earth-Science Rev. 2002, 57, 125–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschan, M.; Robinson, B.H.; Schulin, R. Antimony in the soil—Plant system—A review. Environ. Chem. 2009, 6, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filella, M.; Belzile, N.; Chen, Y.-W. Antimony in the environment: A review focused on natural waters: II. Relevant solution chemistry. Earth-Science Rev. 2002, 59, 265–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tserenpil, S.; Liu, C.-Q. Study of antimony (III) binding to soil humic acid from an antimony smelting site. Microchem. J. 2011, 98, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Zhou, S. Kinetic modeling of antimony(V) adsorption–desorption and transport in soils. Chemosphere 2014, 111, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Mi, Y.; Zhang, H. Kinetic modeling of antimony(III) oxidation and sorption in soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 316, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierart, A.; Shahid, M.; Séjalon-Delmas, N.; Dumat, C. Antimony bioavailability: Knowledge and research perspectives for sustainable agricultures. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 289, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Qin, L.; Wang, L.; Sun, X.; Yu, L.; Wang, M.; Chen, S. Ecological risk thresholds for Zn in Chinese soils. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 833, 155182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otomo, P.V.; Owojori, O.; Reinecke, S.; Daniels, S.; Reinecke, A. Using estimates of metal bioavailability in the soil and genetic variation of allozymes to investigate heavy metal tolerance in the earthworm Eisenia fetida (Oligochaeta). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 2070–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.C.; Bisson, M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donner, E.; Broos, K.; Heemsbergen, D.; Warne, M.S.J.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Hodson, M.E.; Nortcliff, S. Biological and chemical assessments of zinc ageing in field soils. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.B.; Uren, N.C. Effect of aging on the availability of zinc added to a calcareous clay soil. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2006, 76, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Han, H.; Hu, Y.; Wang, J.; Feng, Y.; Yu, B.; Xia, X.; Darma, A. Differential transformation mechanisms of exotic Cr(VI) in agricultural soils with contrasting physio-chemical and biological properties. Chemosphere 2021, 279, 130546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; O’Loughlin, E.J.; Kwon, M.J. Antimony redox processes in the environment: A critical review of associated oxidants and reductants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 431, 128607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Jiang, Q.; Yan, T.; Xu, S.; Shi, H.; Peng, L.; Du, R.; Zhao, X.; Hu, C.; Wang, X.; et al. Antimony symplastic and apoplastic absorption, compartmentation, and xylem translocation in Brassica parachinensis L. under antimonate and antimonite. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 197, 110621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obiakor, M.O.; Wilson, S.C.; Tighe, M.; Pereg, L. Antimony Causes Mortality and Induces Mutagenesis in the Soil Functional Bacterium Azospirillum brasilense Sp7. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Yan, X.; Weng, W.; Xu, S.; Xu, G.; Gu, T.; Guan, X.; Liu, S.; Chen, P.; Wu, Y.; et al. Extracellular proteins of Desulfovibrio vulgaris as adsorbents and redox shuttles promote biomineralization of antimony. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 426, 127795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, G.G.; Barois, I.; Lavelle, P. Regulation of soil organic matter dynamics and microbial activityin the drilosphere and the role of interactionswith other edaphic functional domains. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2000, 36, 177–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, P.; Bali, S.; Sharma, A.; Kohli, S.K.; Vig, A.P.; Bhardwaj, R.; Thukral, A.K.; Abd_Allah, E.F.; Wijaya, L.; Alyemeni, M.N.; et al. Cd induced generation of free radical species in Brassica juncea is regulated by supplementation of earthworms in the drilosphere. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 655, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.-J.; Bai, J.; Li, W.; Murrell, J.C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Luo, C.; Li, Y. Mechanisms of the enhanced DDT removal from soils by earthworms: Identification of DDT degraders in drilosphere and non-drilosphere matrices. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404, 124006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Lin, K.; Ji, R. Antioxidant and gene expression responses of Eisenia fetida following repeated exposure to BDE209 and Pb in a soil-earthworm system. Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 556, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Chen, L.; Liang, J.; Lin, K. Biological effects of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE209) and Pb on earthworm (Eisenia fetida) in a soil system. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 207, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, T.; Shu, W. Toxicity of soil antimony to earthworm Eisenia fetida (Savingy) before and after the aging process. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 207, 111278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Liu, C.; Li, J.; Luo, Y.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Yang, P.; Feng, B. Responses of rhizosphere soil properties, enzyme activities and microbial diversity to intercropping patterns on the Loess Plateau of China. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 195, 104355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gérard, F. Clay minerals, iron/aluminum oxides, and their contribution to phosphate sorption in soils—A myth revisited. Geoderma 2016, 262, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Test No. 207: Earthworm, Acute Toxicity Tests; OECD: Paris, France, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- International Organization For Standardization. I. Soil quality—Effects of pollutants on earthworms—Part 1: Determination of acute toxicity to Eisenia fetida/Eisenia andrei. In 11268-1, Characterization; I.T.S.B., Ed.; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- International Organization For Standardization. I. Soil quality—Avoidance test for determining the quality of soils and effects of chemicals on behaviour—Part 1: Test with earthworms (Eisenia fetida and Eisenia andrei). In ISO 17512-1, Characterization; I.T.S.B., Ed.; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ettler, V.; Mihaljevič, M.; Šebek, O.; Nechutný, Z. Antimony availability in highly polluted soils and sediments—A comparison of single extractions. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Li, C. Effect of lead on survival, locomotion and sperm morphology of Asian earthworm, Pheretima guillelmi. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obiakor, M.O.; Tighe, M.; Wang, Z.; Ezeonyejiaku, C.D.; Pereg, L.; Wilson, S.C. The relative sensitivity of freshwater species to antimony(III): Implications for water quality guidelines and ecological risk assessments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 25276–25290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Zhong, Z.; Liu, W.; Deng, H.; Lin, Z. Removal of Sb(III) from wastewater by magnesium oxide and the related mechanisms. Environ. Res. 2020, 186, 109489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, L.; Lin, Z.; Dai, J.; Wang, R.; Yu, Y.; Liu, H.; Rensing, C.; Feng, R. Factors influencing the uptake and speciation transformation of antimony in the soil-plant system, and the redistribution and toxicity of antimony in plants. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 738, 140232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Yang, J. Effects of different forms of antimony on rice during the period of germination and growth and antimony concentration in rice tissue. Sci. Total. Environ. 1999, 243–244, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamaru, Y.M.; Altansuvd, J. Speciation and bioavailability of selenium and antimony in non-flooded and wetland soils: A review. Chemosphere 2014, 111, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Ma, C.; Chu, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Ouyang, W.; Lin, C.; He, M. Toxicity and bioavailability of antimony in edible amaranth (Amaranthus tricolor Linn.) cultivated in two agricultural soil types. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 257, 113642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuz, A.-K.; Mönch, H.; Johnson, C.A. Sorption of Sb(III) and Sb(V) to Goethite: Influence on Sb(III) Oxidation and Mobilization. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7277–7282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loni, P.C.; Wu, M.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Ma, L.; Liu, C.; Song, Y.; Tuovinen, O.H. Mechanism of microbial dissolution and oxidation of antimony in stibnite under ambient conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, Y.-W.; Lee, W.-M.; Jeong, S.-W.; An, Y.-J. Ecological effects of soil antimony on the crop plant growth and earthworm activity. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frohne, T.; Rinklebe, J.; Diaz-Bone, R.A.; Du Laing, G. Controlled variation of redox conditions in a floodplain soil: Impact on metal mobilization and biomethylation of arsenic and antimony. Geoderma 2011, 160, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Steinman, A.D.; Yao, L.; Xie, L. Toxicological and biochemical responses of the earthworm Eisenia fetida to cyanobacteria toxins. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijver, M.G.; Vink, J.P.; Miermans, C.J.; van Gestel, C.A. Oral sealing using glue: A new method to distinguish between intestinal and dermal uptake of metals in earthworms. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Du, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, J. Acute Toxicity of Imidazole Nitrate Ionic Liquids with Varying Chain Lengths to Earthworms (Eisenia foetida). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 99, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Li, L.; He, M.; Ouyang, W.; Lin, C.; Liu, X. Toxicity and bioavailability of antimony to the earthworm (Eisenia fetida) in different agricultural soils. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 291, 118215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, M.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, D.; Wang, Y. Effects of soil properties and aging process on the acute toxicity of cadmium to earthworm Eisenia fetida. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 3708–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, M.B.; van Gestel, C.A. Toxicity of Copper to the Collembolan Folsomia fimetaria in Relation to the Age of Soil Contamination. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2001, 49, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Tian, T.; Dai, Z.; Shao, T.; Zhang, W.; Liu, M. Assessment of Cd bioavailability using chemical extraction methods, DGT, and biological indicators in soils with different aging times. Chemosphere 2022, 296, 133931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conesa, H.; Wieser, M.; Gasser, M.; Hockmann, K.; Evangelou, M.; Studer, B.; Schulin, R. Effects of three amendments on extractability and fractionation of Pb, Cu, Ni and Sb in two shooting range soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Sun, X.; Häggblom, M.M.; Kolton, M.; Lan, L.; Li, B.; Dong, Y.; Xu, R.; Li, F. Identification of Antimonate Reducing Bacteria and Their Potential Metabolic Traits by the Combination of Stable Isotope Probing and Metagenomic-Pangenomic Analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 13902–13912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Sun, Z.; Zhao, L.; Ma, J.; Li, X.; He, F.; Hou, H. Toxicity of exogenous hexavalent chromium to soil-dwelling springtail Folsomia candida in relation to soil properties and aging time. Chemosphere 2019, 224, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Gao, B.; Zhou, H.; Xu, D.; Wang, Q.; Yin, S. Assessing the remobilization of Antimony in sediments by DGT: A case study in a tributary of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Luo, M.; Wei, S.; Jiang, Z.; He, M. The vital function of humic acid with different molecular weight in controlling Cd and Pb bioavailability and toxicity to earthworm (Eisenia fetida) in soil. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buschmann, J.; Canonica, S.; Sigg, L. Photoinduced Oxidation of Antimony(III) in the Presence of Humic Acid. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 5335–5341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora, P.; Seugé, C.; Chotte, J.L.; Rouland, C. Physico-chemical typology of the biogenic structures of termites and earthworms: A comparative analysis. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2003, 37, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| pH | Organic Matter (g/kg) | Total Nitrogen (g/kg) | Available Nitrogen (mg/kg) | Total Phosphorus (mg/kg) | Available Phosphorus (mg/kg) | Total Potassium (g/kg) | Available Potassium (mg/kg) | Soil Mechanical Composition | Total Sb (mg/kg) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sand/% | Silt/% | Clay/% | |||||||||
| 7.28 | 30.34 | 1.77 | 128.53 | 1.06 | 23.63 | 15.79 | 185.15 | 20.12 | 35.80 | 44.08 | 3.57 |
| Exposure Time | Sb (III) | Sb (V) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LC50 | 95% Confidence Interval | LC50 | 95% Confidence Interval | |
| 24 h | 2581 | 2248–3022 | 4675 | 3824–6483 |
| 48 h | 1427 | 1175–1723 | 2223 | 1920–2608 |
| 72 h | 666 | 323–1071 | 1126 | 733–1627 |
| Tests | Exposure Time | Sb (III) | Sb (V) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LC50 | 95% Confidence Interval | LC50 | 95% Confidence Interval | ||
| Aged 10 d Soil | 7 d | 370 | 92–632 | 2730 | 582–4556 |
| 14 d | 254 | 31–482 | 2040 | 457–3416 | |
| Aged 30 d Soil | 7 d | 614 | 81–1142 | 6033 | 3540–8786 |
| 14 d | 399 | 99–680 | 4391 | 1746–6738 | |
| Aged 60 d Soil | 7 d | >4800 | >19,200 | ||
| 14 d | 3547 | 2294–8222 | 14,640 | 9751–35,023 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, J.; Lu, D.; Chen, L.; Liu, W.; Zheng, Y.; Xiang, G.; Meng, G.; Lin, Z.; Duan, R. Ecotoxicological Differences of Antimony (III) and Antimony (V) on Earthworms Eisenia fetida (Savingy). Toxics 2023, 11, 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11030230
Bai J, Lu D, Chen L, Liu W, Zheng Y, Xiang G, Meng G, Lin Z, Duan R. Ecotoxicological Differences of Antimony (III) and Antimony (V) on Earthworms Eisenia fetida (Savingy). Toxics. 2023; 11(3):230. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11030230
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Jing, Dan Lu, Linyu Chen, Weiying Liu, Yu Zheng, Guohong Xiang, Guiyuan Meng, Zhong Lin, and Renyan Duan. 2023. "Ecotoxicological Differences of Antimony (III) and Antimony (V) on Earthworms Eisenia fetida (Savingy)" Toxics 11, no. 3: 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11030230
APA StyleBai, J., Lu, D., Chen, L., Liu, W., Zheng, Y., Xiang, G., Meng, G., Lin, Z., & Duan, R. (2023). Ecotoxicological Differences of Antimony (III) and Antimony (V) on Earthworms Eisenia fetida (Savingy). Toxics, 11(3), 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11030230







