Acute Exposure to Arsenic Affects Pupal Development and Neurological Functions in Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fly Husbandry, Breeding, and Collection of Flies
2.2. Chemicals
Materials
2.3. Treatment and Estimation of the Lethal Concentration (LC50)
2.4. Morphological Changes in the Pupae
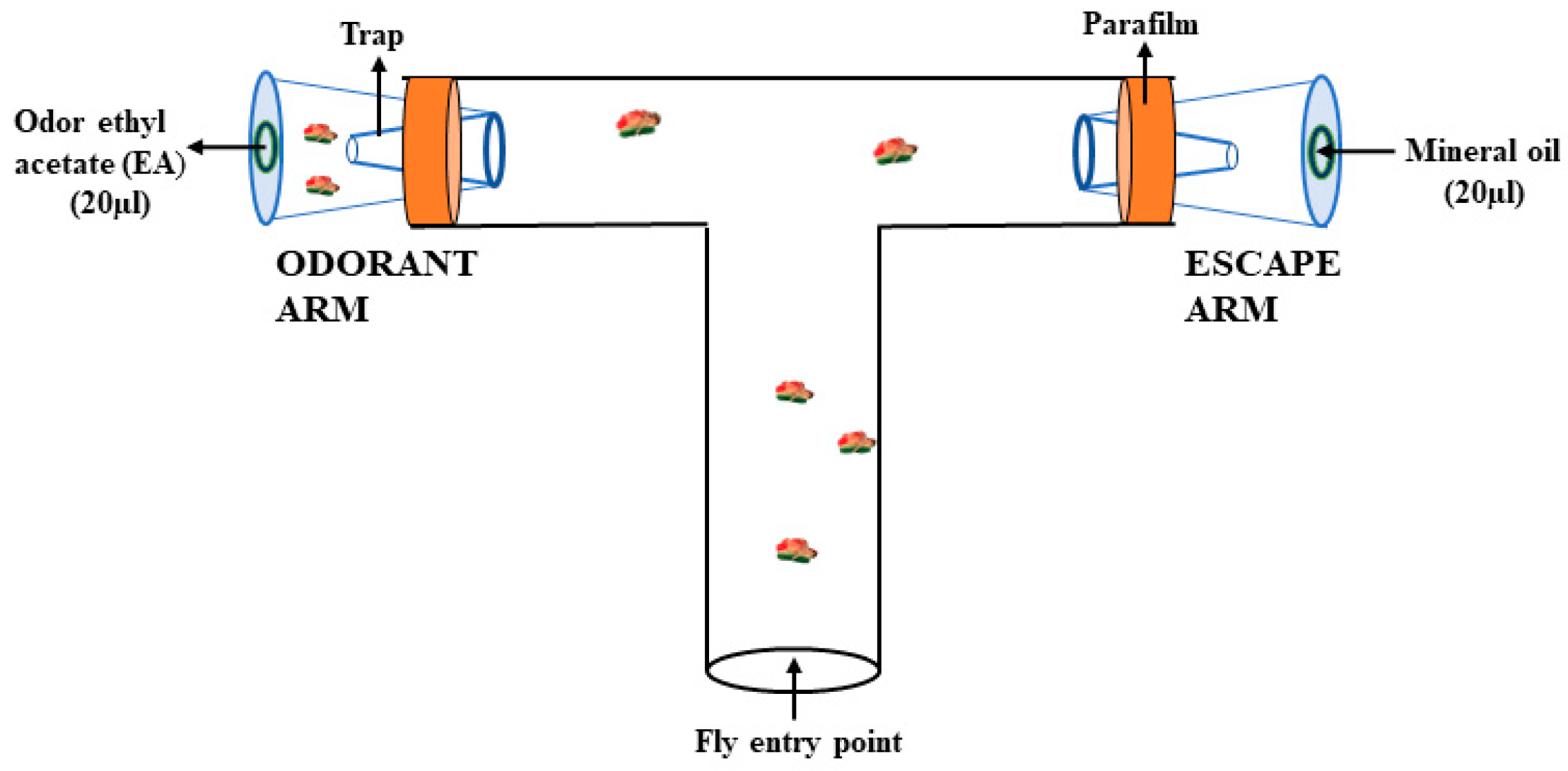
2.5. Behavioral Experimental Setup
2.5.1. Climbing Assay
2.5.2. Olfactory Two-Choice Assay
2.5.3. Learning Assay
2.6. Statistics
3. Results
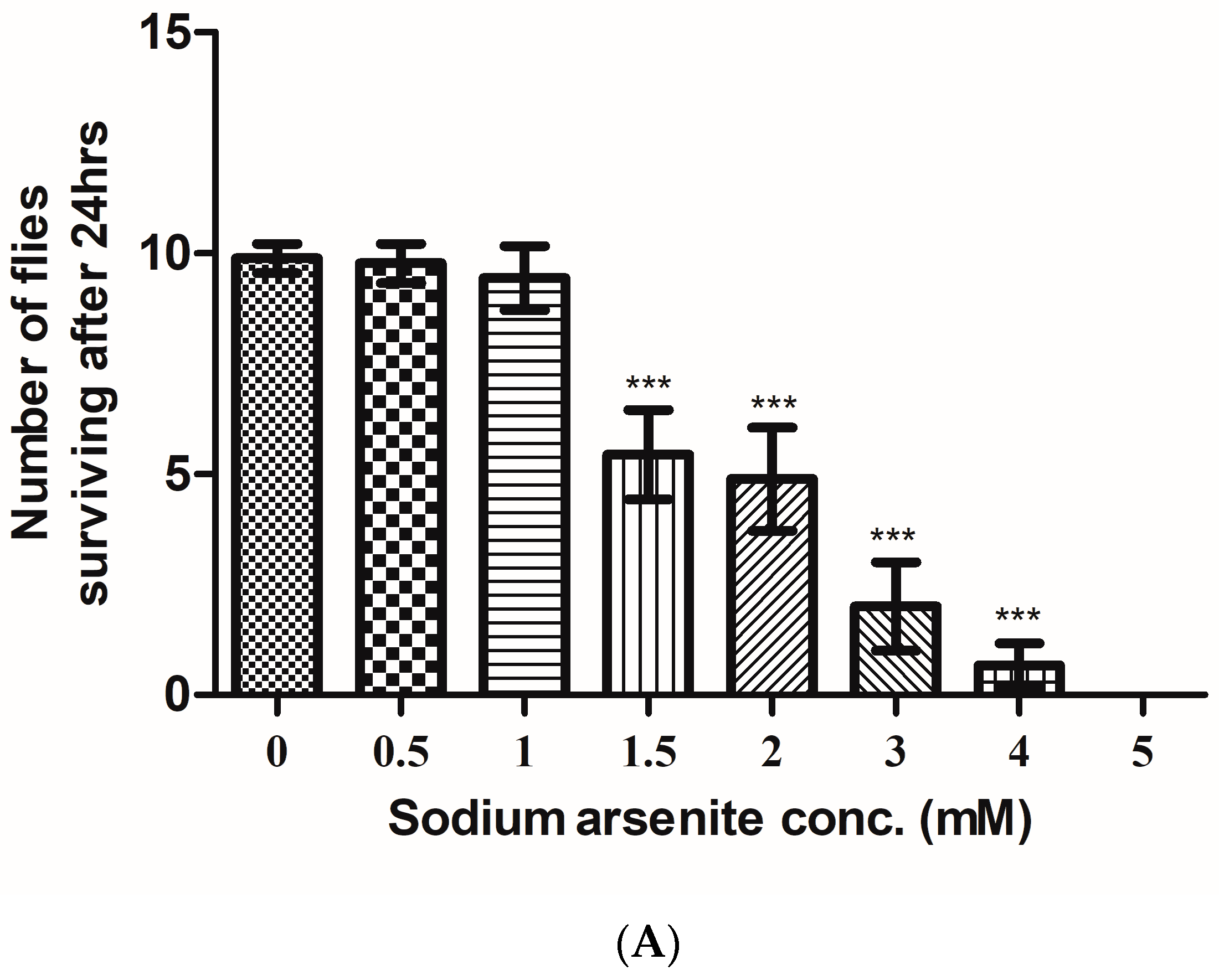
3.1. Estimation of LC50
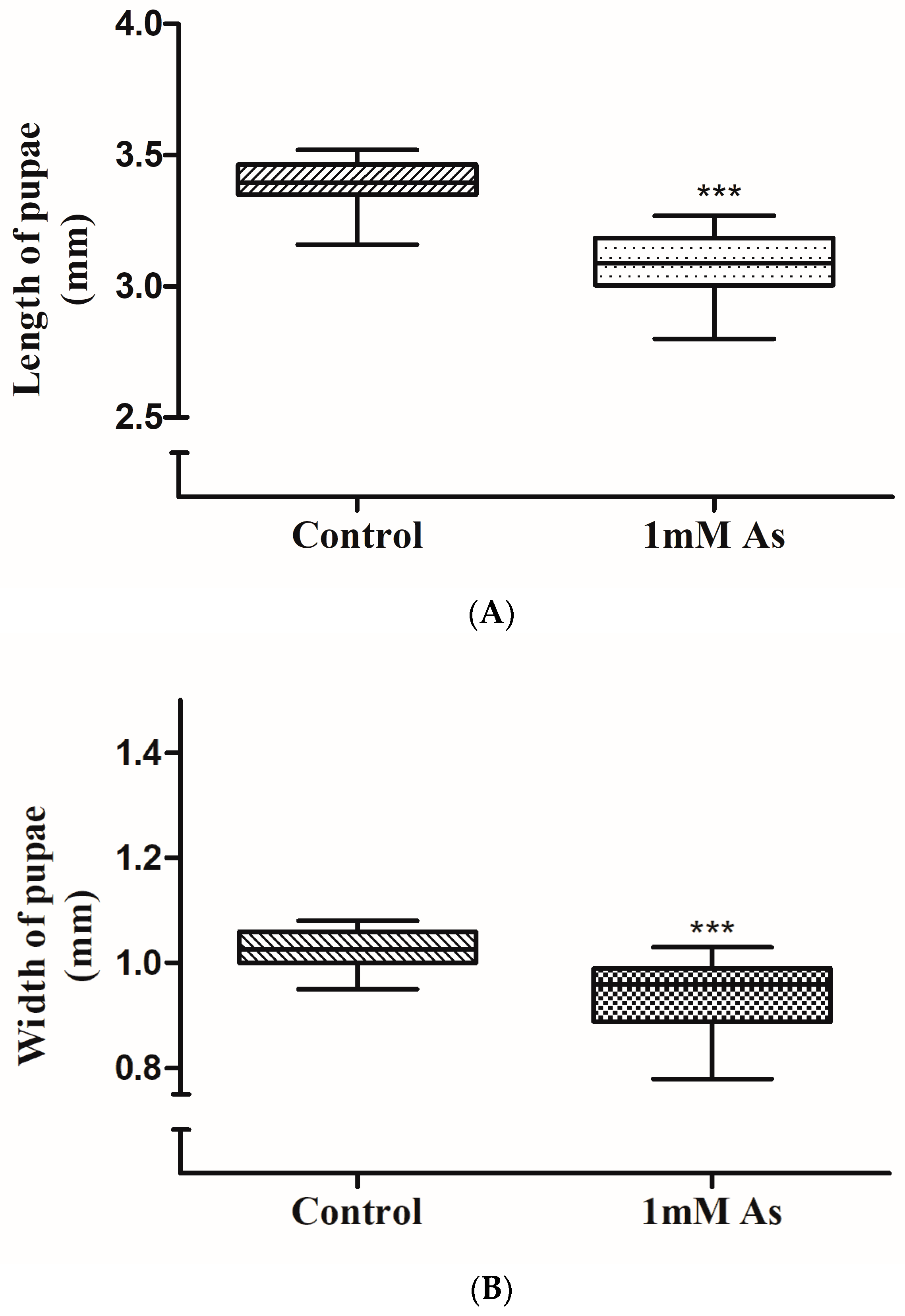
3.2. Pupae Size Measurement
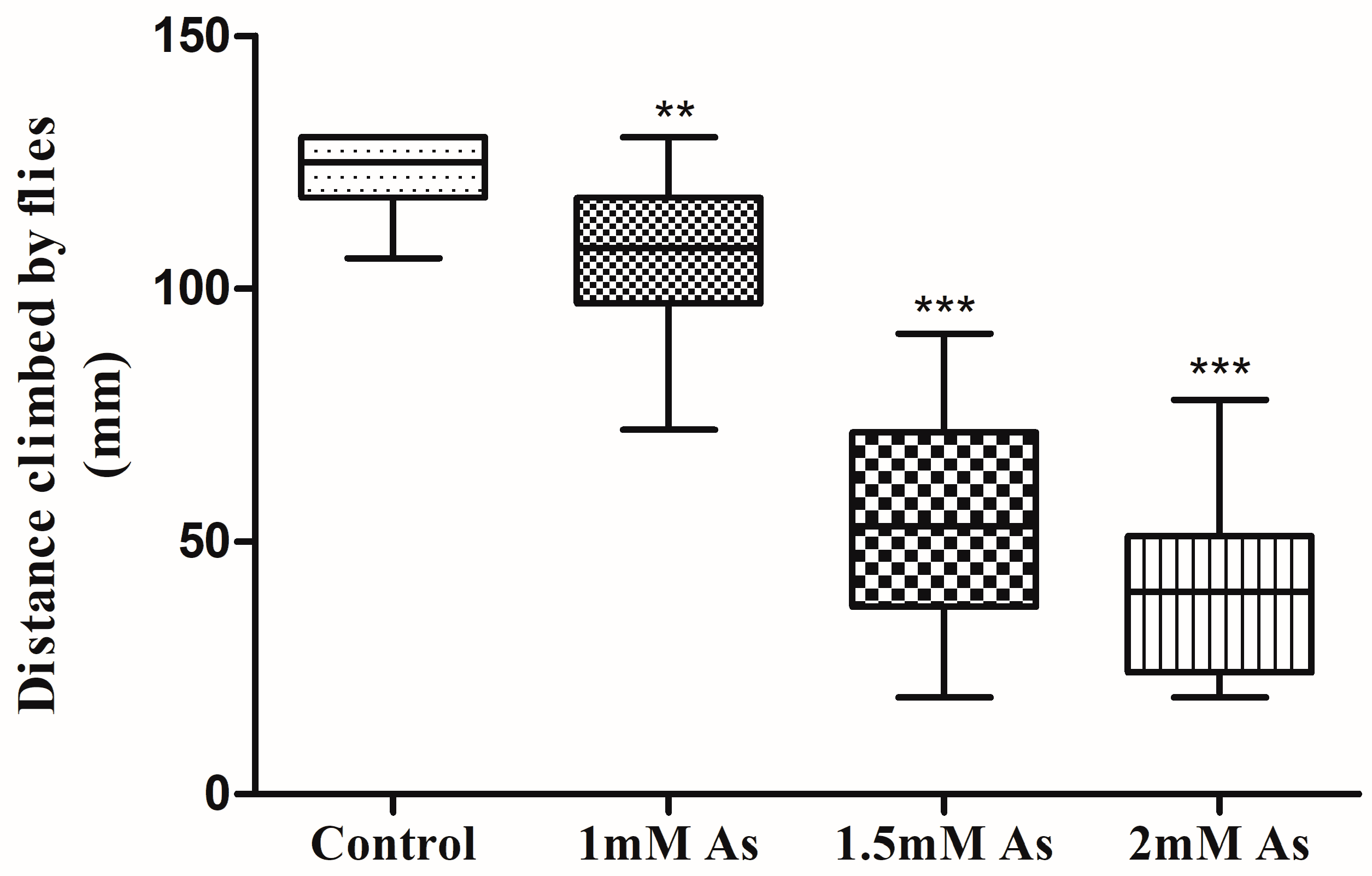
3.3. Climbing Assay
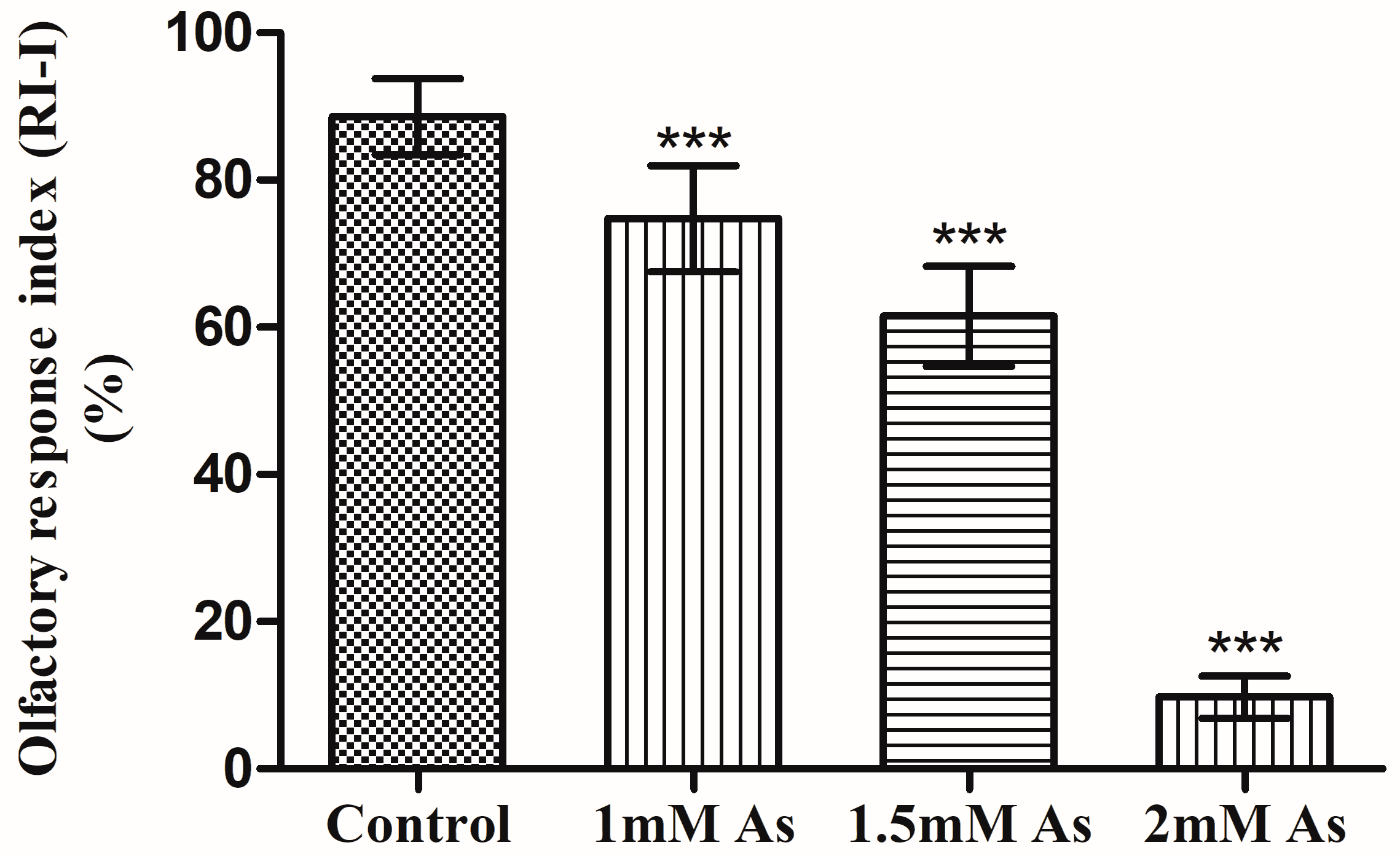
3.4. Olfactory Two-Choice Assay
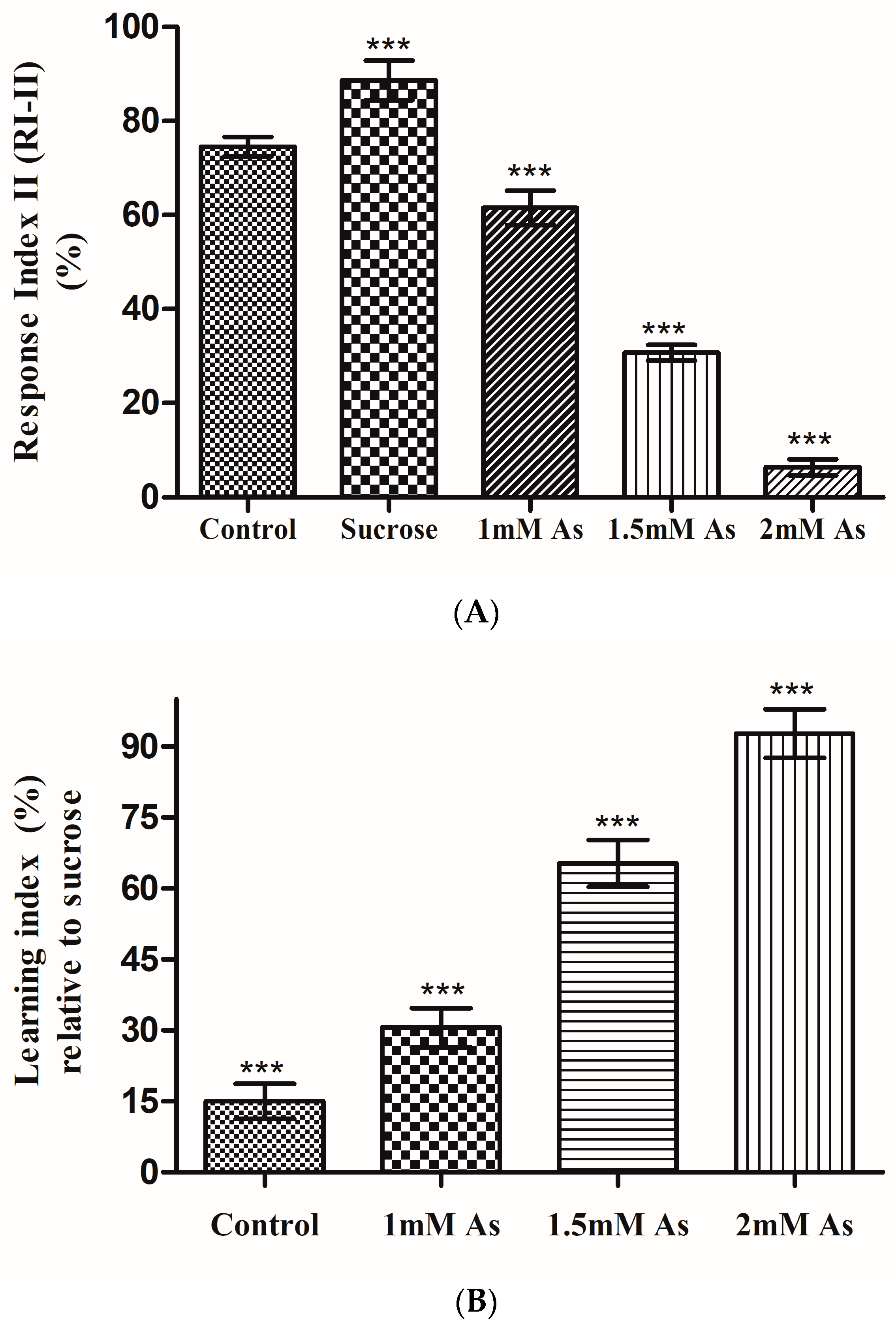
3.5. Learning Assay: T-Maze Assay
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Arsenic on Survivability
4.2. Effect of Arsenic on Development and Growth
4.3. Effect of Arsenic on the Locomotor Ability
4.4. Effect of Arsenic on the Cognitive Response of Olfaction
4.5. Effect of Arsenic on the Neurological Ability of Learning
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sarkar, A.; Paul, B. The global menace of Arsenic and its conventional remediation—A critical review. Chemosphere 2017, 173, 630–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y. Lessons Learned from Arsenic Mitigation among Private Well Households. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2017, 4, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravenscroft, P.; Brammer, H.; Richards, K.S. Arsenic Pollution: A Global Synthesis; RGS-IBG Book Series; A John Wiley and Sons Ltd.: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, J.M. Arsenic in groundwater. In Groundwater Development and Management; Sikdar, P.K., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 279–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Shen, J.; Carbrey, J.M.; Mukhopadhyay, R.; Agre, P.; Rosen, B.P. Arsenite transport by mammalian aquaglyceroporins AQP7 and AQP9. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 6053–6058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Torres-Avila, M.; Leal-Galicia, P.; Sánchez-Peña, L.C. Arsenite induces aquaglyceroporin 9 expression in murine livers. Environ. Res. 2010, 110, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calatayud, M.; Barrios, J.A.; Vélez, D.; Devesa, V. In vitro study of transporters involved in intestinal absorption of inorganic Arsenic. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ATSDR—Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. CAS ID#: 7440-38-2. 2013. Available online: http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/substances/toxsubstance.aspx?toxid=3 (accessed on 7 May 2019).
- WHO. Health Impacts of Chemicals: Arsenic. 2017. Available online: http://www.who.int/ipcs/assessment/public_health/Arsenic/en/ (accessed on 20 January 2019).
- Ahmad, S.A.; Khan, M.H.; Haque, M. Arsenic contamination in groundwater in Bangladesh: Implications and challenges for healthcare policy. Risk Manag. Healthc. Policy 2018, 11, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baker, B.A.; Cassano, V.A.; Murray, C.; ACOEM Task Force on Arsenic Exposure. Arsenic Exposure, Assessment, Toxicity, Diagnosis, and Management: Guidance for Occupational and Environmental Physicians. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2018, 60, e634–e639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.S.; Ye, B.J.; Kim, Y.M.; Kim, B.G.; Kang, G.H.; Kim, J.J.; Song, K.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Seo, J.W. Investigation of Health Effects According to the Exposure of Low Concentration Arsenic Contaminated Ground Water. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsuji, J.S.; Chang, E.T.; Gentry, P.R.; Clewell, H.J.; Boffetta, P.; Cohen, S.M. Dose-response for assessing the cancer risk of inorganic Arsenic in drinking water: The scientific basis for use of a threshold approach. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2019, 49, 36–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma-Lara, I.; Martínez-Castillo, M.; Quintana-Pérez, J.C. Arsenic exposure: A public health problem leading to several cancers. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 110, 104539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Rahman, A.; Khan, M.; Renzaho, A. Human health risks and socio-economic perspectives of Arsenic exposure in Bangladesh: A scoping review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 150, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Rahaman, H. Contamination of Arsenic, manganese and coliform bacteria in groundwater at Kushtia District, Bangladesh: Human health vulnerabilities. J. Water Health 2018, 16, 782–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, W.; Rasool, A.; Junaid, M.; Zhang, H. A comprehensive review on current status, mechanism, and possible sources of Arsenic contamination in groundwater: A global perspective with prominence of Pakistan scenario. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 737–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NRC (National Research Council); U.S. Subcommittee on Arsenic in Drinking Water. Arsenic in Drinking Water; National Academies Press (U.S.): Washington, DC, USA, 2000. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK230893/ (accessed on 7 May 2019).
- Akakuru, O.C.; Akudinobi, B.E.B.; Usman, A.O. Organic and heavy metal assessment of groundwater sources around Nigeria national petroleum cooperation oil depot Aba, South-Eastern Nigeria. J. Nat. Sci. Res. 2017, 7, 48–58. [Google Scholar]
- Le, X.C.; Cullen, W.R.; Reimer, K.J. Human urinary Arsenic excretion after one-time ingestion of seaweed, crab, and shrimp. Clin. Chem. 1994, 40, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.J. Blackfoot disease: Arsenic or humic acid? Lancet 1990, 336, 115–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igharo, G.O.; Anetor, J.I.; Osibanjo, O.O.; Osadolor, H.B.; Dike, K.C. Toxic metal levels in Nigerian electronic waste workers indicate occupational metal toxicity associated with crude electronic waste management practices. Biokemistry 2014, 26, 107–113. [Google Scholar]
- Morales, K.H.; Ryan, L.; Kuo, T.L.; Wu, M.M.; Chen, C.J. Risk of internal cancers from Arsenic in drinking water. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, R.; Saxena, P.; Johnson, S.; Mathur, H.; Agarwal, H. Heavy Metals in Cosmetics. Centre for Science and Environment. 2014. Available online: https://cdn.cseindia.org/userfiles/Heavy_Metals_in_Cosmetics_Report.pdf (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Yadav, M.K.; Saidulu, D.; Gupta, A.K.; Ghosal, P.S.; Mukherjee, A. Status and management of Arsenic pollution in groundwater: A comprehensive appraisal of recent global scenario, human health impacts, sustainable field-scale treatment technologies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-Jacques, N.; Parker, L.; Brown, P.; Dummer, T.J. Arsenic in drinking water and urinary tract cancers: A systematic review of 30 years of epidemiological evidence. Environ. Health Glob. Access Sci. Source 2014, 13, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beckett, W.S.; Moore, J.L.; Keogh, J.P.; Bleecker, M.L. Acute encephalopathy due to occupational exposure to Arsenic. Br. J. Ind. Med. 1986, 43, 66–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnson, A.A.; Stolzing, A. The role of lipid metabolism in aging, lifespan regulation, and age-related disease. Aging Cell 2019, 18, e13048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ugur, B.; Chen, K.; Bellen, H.J. Drosophila tools and assays for the study of human diseases. Dis. Model. Mech. 2016, 9, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buck, L.; Axel, R. A novel multigene family may encode odorant receptors: A molecular basis for odor recognition. Cell 1991, 65, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chess, A.; Buck, L.; Dowling, M.M.; Axel, R.; Ngai, J. Molecular biology of smell: Expression of the multigene family encoding putative odorant receptors. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 1992, 57, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vosshall, L.B.; Wong, A.M.; Axel, R. An olfactory sensory map in the fly brain. Cell 2000, 102, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carlson, J.R. Functional expression of a Drosophila odor receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 8936–8937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laissue, P.P.; Vosshall, L.B. The olfactory sensory map in Drosophila. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2008, 628, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolins, M.; Ruchirawat, M.; Landrigan, P. The developmental neurotoxicity of Arsenic: Cognitive and behavioral consequences of early life exposure. Ann. Glob. Health 2014, 80, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza-Lombó, C.; Pappa, A.; Panayiotidis, M.I.; Gonsebatt, M.E.; Franco, R. Arsenic-induced neurotoxicity: A mechanistic appraisal. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 24, 1305–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlin, D.J.; Naujokas, M.F.; Bradham, K.D.; Cowden, J.; Heacock, M.; Henry, H.F.; Lee, J.S.; Thomas, D.J.; Thompson, C.; Tokar, E.J.; et al. Arsenic and Environmental Health: State of the Science and Future Research Opportunities. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 890–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rizki, M.; Kossatz, E.; Velázquez, A.; Creus, A.; Farina, M.; Fortaner, S.; Sabbioni, E.; Marcos, R. Metabolism of Arsenic in Drosophila melanogaster and the genotoxicity of dimethylarsinic acid in the Drosophila wing spot test. Environ. Mol. Mutagen 2006, 47, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finney, D.J. Probit analysis; a statistical treatment of the sigmoid response curve. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1952, 110, 263. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Xu, A.Q.; Giraud, J.; Poppinga, H.; Riemensperger, T.; Fiala, A.; Birman, S. Neural Control of Startle-Induced Locomotion by the Mushroom Bodies and Associated Neurons in Drosophila. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klimaczewski, C.V.; Ecker, A.; Piccoli, B.; Aschner, M.; Barbosa, N.V.; Rocha, J.B.T. Peumus boldus attenuates copper-induced toxicity in Drosophila melanogaster. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekker, T.; Ibba, I.; Siju, K.P.; Stensmyr, M.C.; Hansson, B.S. Olfactory shifts parallel superspecialism for toxic fruit in Drosophila melanogaster sibling, D. sechellia. Curr. Biol. 2006, 16, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruebenbauer, A.; Schlyter, F.; Hansson, B.S.; Löfstedt, C.; Larsson, M.C. Genetic variability and robustness of host odor preference in Drosophila melanogaster. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, 1438–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farhadian, S.F.; Suárez-Fariñas, M.; Cho, C.E.; Pellegrino, M.; Vosshall, L.B. Post-fasting olfactory, transcriptional, and feeding responses in Drosophila. Physiol. Behav. 2012, 105, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwaerzel, M.; Monastirioti, M.; Scholz, H.; Friggi-Grelin, F.; Birman, S.; Heisenberg, M. Dopamine and octopamine differentiate between aversive and appetitive olfactory memories in Drosophila. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 10495–10502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chakraborty, T.S.; Goswami, S.P.; Siddiqi, O. Sensory correlates of imaginal conditioning in Drosophila melanogaster. J. Neurogenet. 2009, 23, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamberlan, D.C.; Halmenschelager, P.T.; Silva, L.F.O.; da Rocha, J.B.T. Copper decreases associative learning and memory in Drosophila melanogaster. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 135306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vittoria, M.; Tilmann, A.; Claudia, B.; Alexandros, K. Kanellopoulos, Modelling Learning and Memory in Drosophila to Understand Intellectual Disabilities. Neuroscience 2020, 445, 12–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duker, A.A.; Carranza, E.J.; Hale, M. Arsenic geochemistry and health. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, V.M.; Jiménez-Capdeville, M.E.; Giordano, M. The effects of Arsenic exposure on the nervous system. Toxicol. Lett. 2003, 145, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadorani, S.; Bahadorani, P.; Marcon, E.; Walker, D.W.; Hilliker, A.J.A. Drosophila model of Menkes disease reveals a role for DmATP7 in copper absorption and neurodevelopment. Dis. Models Mech. 2010, 3, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bonilla-Ramirez, L.; Jimenez-Del-Rio, M.; Velez-Pardo, C. Acute and chronic metal exposure impairs locomotion activity in Drosophila melanogaster: A model to study Parkinsonism. Biometals 2011, 24, 1045–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Sohel, N.; Yunus, F.M.; Alam, N.; Nahar, Q.; Streatfield, P.K.; Yunus, M. Arsenic exposure and young adult’s mortality risk: A 13-year follow-up study in Matlab, Bangladesh. Environ. Int. 2019, 123, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niño, S.A.; Martel-Gallegos, G.; Castro-Zavala, A.; Ortega-Berlanga, B.; Delgado, J.M.; Hernández-Mendoza, H.; Romero-Guzmán, E.; Ríos-Lugo, J.; Rosales-Mendoza, S.; Jiménez-Capdeville, M.E.; et al. Chronic Arsenic Exposure Increases Aβ(1-42) Production and Receptor for Advanced GlyCation End Products Expression in Rat Brain. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2018, 31, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.C.; Ho, I.C. Modulation of cellular antioxidant defense activities by sodium arsenite in human fibroblasts. Arch. Toxicol. 1995, 69, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Lin-Shiau, S.Y.; Lin, J.K. Involvement of reactive oxygen species and caspase 3 activation in arsenite-induced apoptosis. J. Cell. Physiol. 1998, 177, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchowsky, A.; Klei, L.R.; Dudek, E.J.; Swartz, H.M.; James, P.E. Stimulation of reactive oxygen, but not reactive nitrogen species, in vascular endothelial cells exposed to low levels of arsenite. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 27, 1405–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynn, S.; Gurr, J.R.; Lai, H.T.; Jan, K.Y. NADH oxidase activation is involved in arsenite-induced oxidative DNA damage in human vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ. Res. 2000, 86, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tabacova, S.; Baird, D.D.; Balabaeva, L.; Lolova, D.; Petrov, I. Placental Arsenic and cadmium in relation to lipid peroxides and glutathione levels in maternal-infant pairs from a copper smelter area. Placenta 1994, 15, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golub, M.S.; Macintosh, M.S.; Baumrind, N. Developmental and reproductive toxicity of inorganic Arsenic: Animal studies and human concerns. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B Crit. Rev. 1998, 1, 199–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beamish, C.R.; Love, T.M.; Rand, M.D. Developmental Toxicology of Metal Mixtures in Drosophila: Unique Properties of Potency and Interactions of Mercury Isoforms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marie, V. Effects of Arsenic on maternal and fetal health. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2009, 29, 381–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaszczak, J.S.; Wolpe, J.B.; Bhandari, R.; Jaszczak, R.G.; Halme, A. Growth Coordination During Drosophila melanogaster Imaginal Disc Regeneration Is Mediated by Signaling Through the Relaxin Receptor Lgr3 in the Prothoracic Gland. Genetics 2016, 204, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riddiford, L.M. Hormone receptors and the regulation of insect metamorphosis. Receptor 1993, 3, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Polak, M.; Opoka, R.; Cartwright, I.L. Response of fluctuating asymmetry to Arsenic toxicity: Support for the developmental selection hypothesis. Environ. Pollut. 2002, 118, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handel, S.E.; Stickland, N.C. The growth and differentiation of porcine skeletal muscle fibre types and the influence of birthweight. J. Anat. 1987, 152, 107–119. [Google Scholar]
- Hopenhayn, C.; Ferreccio, C.; Browning, S.R.; Huang, B.; Peralta, C.; Gibb, H.; Hertz-Picciotto, I. Arsenic exposure from drinking water and birth weight. Epidemiology 2003, 14, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, A.; Vahter, M.; Smith, A.H.; Nermell, B.; Yunus, M.; El Arifeen, S.; Persson, L.A.; Ekström, E.C. Arsenic exposure during pregnancy and size at birth: A prospective cohort study in Bangladesh. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2009, 169, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McMichael, B.D.; Perego, M.C.; Darling, C.L. Long-term Arsenic exposure impairs differentiation in mouse embryonal stem cells. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2021, 41, 1089–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, J.K.; Kowalski, S.; Rogina, B. Determination of the spontaneous locomotor activity in Drosophila melanogaster. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 51449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coulom, H.; Birman, S. Chronic exposure to rotenone models sporadic Parkinson’s disease in Drosophila melanogaster. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 10993–10998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaudhuri, A.; Bowling, K.; Funderburk, C.; Lawal, H.; Inamdar, A.; Wang, Z.; O’Donnell, J.M. Interaction of genetic and environmental factors in a Drosophila parkinsonism model. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 2457–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meenakshi-Sundaram, S.; Mahadevan, A.; Taly, A.B. Wilson’s disease: A clinico-neuropathological autopsy study. J. Clin. Neurosci. Off. J. Neurosurg. Soc. Australas. 2008, 15, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilarte, T.R. Manganese and Parkinson’s disease: A critical review and new findings. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barone, M.C.; Bohmann, D. Assessing neurodegenerative phenotypes in Drosophila dopaminergic neurons by climbing assays and whole brain immunostaining. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 74, e50339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, A.Y.; Wilburn, P.; Hao, X.; Tully, T. Walking deficits and centrophobism in an α-synuclein fly model of Parkinson’s disease. Genes Brain Behav. 2014, 13, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.; Lazopulo, S.; Syed, S.; Zhai, R.G. Encyclopedia of Behavioral Neuroscience, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul, K.S.M.; Jayasinghe, S.S.; Chandana, E.P.; Jayasumana, C.; De Silva, P.M.C. Arsenic and human health effects: A review. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 40, 828–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, J.M.; Beach, M.G.; Porpiglia, E. The Drosophila cell corpse engulfment receptor Draper mediates glial clearance of severed axons. Neuron 2006, 50, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiang, A.; Priya, R.; Ramaswami, M.; Vijayraghavan, K.; Rodrigues, V. Neuronal activity and Wnt signaling act through Gsk3-beta to regulate axonal integrity in mature Drosophila olfactory sensory neurons. Development 2009, 136, 1273–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kazama, H.; Yaksi, E.; Wilson, R.I. Cell death triggers olfactory circuit plasticity via glial signaling in Drosophila. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 7619–7630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hueston, C.E.; Olsen, D.; Li, Q.; Okuwa, S.; Peng, B.; Wu, J.; Volkan, P.C. Chromatin Modulatory Proteins and Olfactory Receptor Signaling in the Refinement and Maintenance of Fruitless Expression in Olfactory Receptor Neurons. PLoS Biol. 2016, 14, e1002443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muñiz-Ortiz, J.G.; Shang, J.; Catron, B.; Landero, J.; Caruso, J.A.; Cartwright, I.L. A transgenic Drosophila model for Arsenic methylation suggests a metabolic rationale for differential dose-dependent toxicity endpoints. Toxicol Sci. 2011, 121, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niño, S.A.; Chi-Ahumada, E.; Ortíz, J.; Zarazua, S.; Concha, L.; Jiménez-Capdeville, M.E. Demyelination associated with chronic Arsenic exposure in Wistar rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 393, 114955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral Pinto, M.M.; Marinho-Reis, A.P.; Almeida, A.; Ordens, C.M.; Silva, M.M.; Freitas, S.; Simões, M.R.; Moreira, P.I.; Dinis, P.A.; Diniz, M.L.; et al. Human predisposition to cognitive impairment and its relation with environmental exposure to potentially toxic elements. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 1767–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.C.; Chang, F.C.; Hong, Y.H.; Li, J.C.; Chen, P.L.; Chen, C.H.; Chiu, T.W.; Lu, T.T.; Wang, Y.M.; Kao, C.F. Assessing the cognitive status of Drosophila by the value-based feeding decision. NPJ Aging Mech. Dis. 2021, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundey, M.K.; Roy, M.; Roy, S.; Awasthi, M.K.; Sharma, R. Antioxidant potential of Ocimum sanctum in Arsenic-induced nervous tissue damage. Braz. J. Vet. Pathol. 2013, 6, 95–101. [Google Scholar]
- Tyler, C.R.; Allan, A.M. The Effects of Arsenic Exposure on Neurological and Cognitive Dysfunction in Human and Rodent Studies: A Review. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2014, 1, 132–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chandravanshi, L.P.; Yadav, R.S.; Shukla, R.K.; Singh, A.; Sultana, S.; Pant, A.B.; Parmar, D.; Khanna, V.K. Reversibility of changes in brain cholinergic receptors and acetylcholinesterase activity in rats following early life Arsenic exposure. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. Off. J. Int. Soc. Dev. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoyama, K.; Watabe, M.; Nakaki, T. Regulation of neuronal glutathione synthesis. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2008, 108, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anushree, A.; Ali, M.Z.; Ahsan, J. Acute Exposure to Arsenic Affects Cognition in Drosophila melanogaster Larvae. Entomol. Appl. Sci. Lett. 2022, 9, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anushree; Ali, M.Z.; Bilgrami, A.L.; Ahsan, J. Acute Exposure to Arsenic Affects Pupal Development and Neurological Functions in Drosophila melanogaster. Toxics 2023, 11, 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11040327
Anushree, Ali MZ, Bilgrami AL, Ahsan J. Acute Exposure to Arsenic Affects Pupal Development and Neurological Functions in Drosophila melanogaster. Toxics. 2023; 11(4):327. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11040327
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnushree, Md Zeeshan Ali, Anwar L. Bilgrami, and Jawaid Ahsan. 2023. "Acute Exposure to Arsenic Affects Pupal Development and Neurological Functions in Drosophila melanogaster" Toxics 11, no. 4: 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11040327
APA StyleAnushree, Ali, M. Z., Bilgrami, A. L., & Ahsan, J. (2023). Acute Exposure to Arsenic Affects Pupal Development and Neurological Functions in Drosophila melanogaster. Toxics, 11(4), 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11040327









