Lethal and Sublethal Toxicity of Beta-Carboline Alkaloids from Peganum harmala (L.) against Aedes albopictus Larvae (Diptera: Culicidae)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material, Standards, and Reagents
2.2. Total Alkaloid Extracts of P. harmala Seeds
2.3. Insect
2.4. Evaluation of Bioefficacy
2.4.1. Individual Toxicity of the Tested Alkaloids
2.4.2. Synergistic Toxicity of Binary Mixtures of Four Isolated Alkaloids
2.5. Sublethal Effects of the Tested Alkaloids on Larval Growth
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
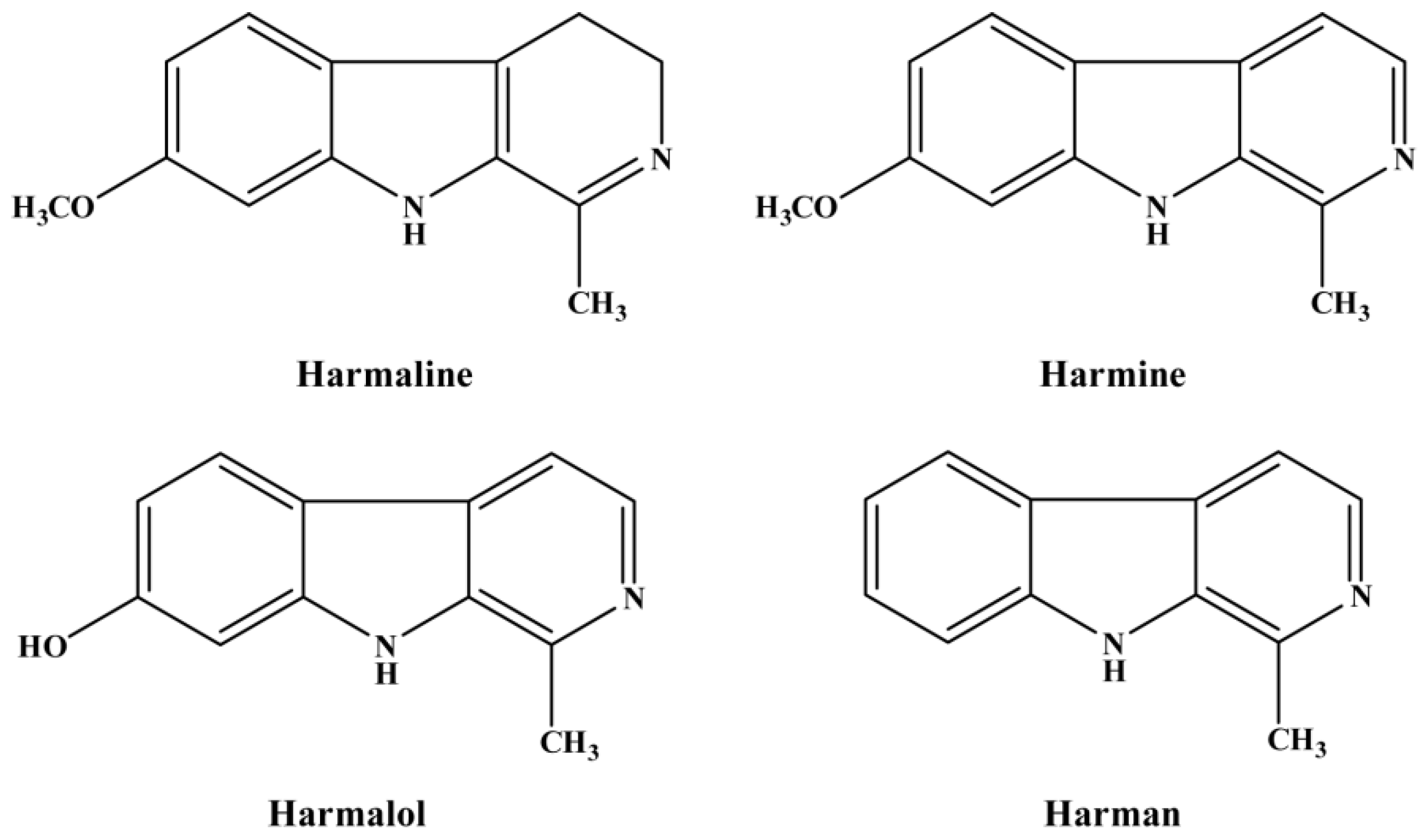
3.1. Contents of the Isolated Alkaloids of P. harmala
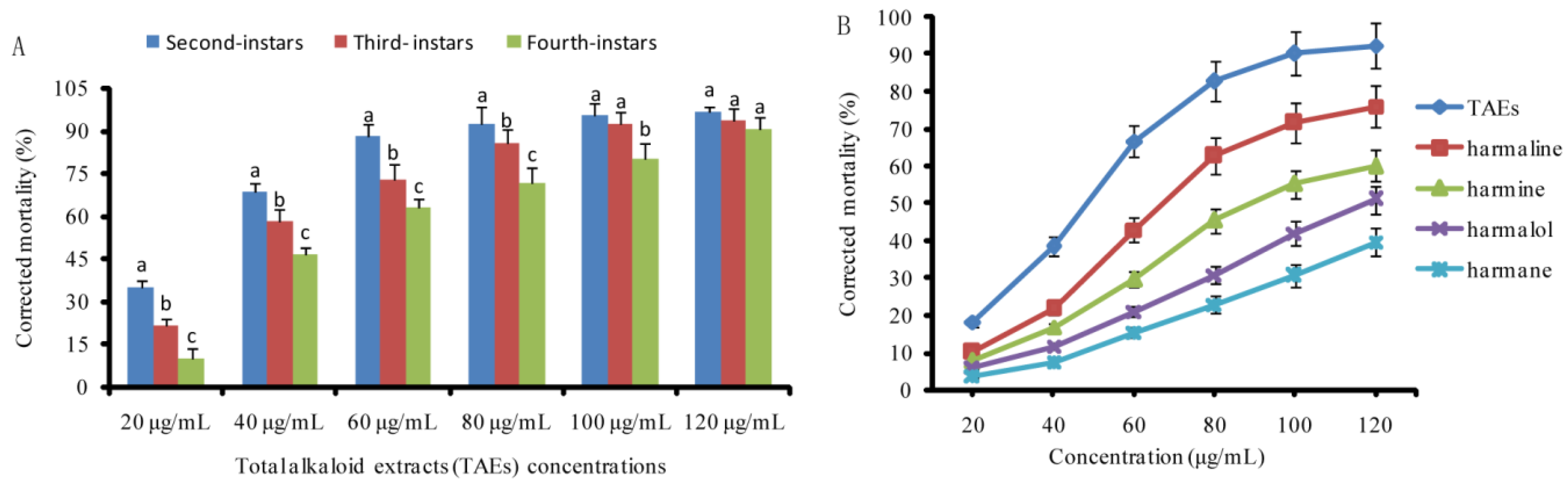
3.2. Larvicidal Activity of the Tested Alkaloids
3.3. Comparison of the Lethal Concentration (LC50) of Third-Instar Larvae
3.4. Synergistic Toxicity of Binary Mixtures
3.5. Sublethal Effects of Total Alkaloid Extracts (TAEs) on Larval Development
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Bhatt, S.; Gething, P.W.; Brady, O.J.; Messina, J.P.; Farlow, A.W.; Moyes, C.L.; Drake, J.M.; Brownstein, J.S.; Hoen, A.G.; Sankoh, O.; et al. The global distribution and burden of dengue. Nature 2013, 496, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manni, M.; Guglielmino, C.R.; Scolari, F.; Vega, R.A.; Failloux, A.B.; Somboon, P.; Lisa, A.; Savini, G.; Bonizzoni, M.; Gomulski, L.M.; et al. Genetic evidence for a worldwide chaotic dispersion pattern of the arbovirus vector, Aedes albopictus. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jourdain, F.; Roiz, D.; de Valk, H.; Noël, H.; L’Ambert, G.; Franke, F.; Paty, M.-C.; Guinard, A.; Desenclos, J.-C.; Roche, B. From importation to autochthonous transmission: Drivers of chikungunya and dengue emergence in a temperate area. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, C.J. The role of Aedes albopictus as an arbovirus vector. Parassitologia 2020, 37, 108–113. [Google Scholar]
- Ishak, I.H.; Jaal, Z.; Ranson, H.; Wondji, C.S. Contrasting patterns of insecticide resistance andknockdown resistance (kdr) in the dengue vectors Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus from Malaysia. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.C.; Zhu, C.Y.; Jia, Q.C.; Yan, D.M.; Liu, G.J.; Wu, H.X.; Song, X.P.; Liu, Q.Y.; Wang, J.; Meng, F.X. Resistance of Aedes albopictus to commonly used insecticides in different areas of China, 2017–2018. Chin. J. Vector Biol. Control 2017, 31, 126–132. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N. Insecticide resistance in mosquitoes: Impact, mechanisms, and research directions. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2015, 60, 537–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinesh, D.S.; Kumari, S.; Kumar, V.; Das, P. The potentiality of botanicals and their products as an alternative to chemical insecticides to sandflies (Diptera: Psychodidae): A review. J. Vector Borne Dis. 2014, 51, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Shaalan, E.A.; Canyon, D.; Younes, M.W.; Abdel-Wahab, H.; Mansour, A.H. A review of botanical phytochemicals with mosquitocidal potential. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 1149–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.P.; Cheng, X.M.; Wang, C.H. A review on traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and toxicology of the genus Peganum. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 203, 127–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mina, C.N.; Mohammad, H.F.; Gholamreza, A. Medicinal properties of Peganum harmala L. in traditional Iranian medicine and modern phytotherapy: A review. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2015, 35, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moloudizargari, M.; Mikaili, P.; Aghajanshakeri, S.; Asghari, M.H.; Shayegh, J. Pharmacological and therapeutic effects of Peganum harmala and its main alkaloids. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2013, 7, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Committee (CPC). Drug Standards of the Ministry of Public Health of the People’s 587 Republic of China (Uygur Pharmaceutical Section); Chinese Pharmacopoeia Committee: Beijing, China, 1998; p. 80.
- Liu, L.; Cheng, X.M.; Wang, C.H.; Wang, Z.T. Quality standard for alkaliod extract of Peganum harmala L. Chin. J. Pharm. 2010, 41, 420–423. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.H.; Liu, J.; Zheng, L.M. Analysis of harmine and harmaline of Peganum harmala in different parts and different localities. Chin. Pharm. J. 2002, 37, 211–215. [Google Scholar]
- Haarmann-Stemmann, T.; Sendker, J.; Götz, C.; Krug, N.; Bothe, H.; Fritsche, E.; Proksch, P.; Abel, J. Regulation of dioxin receptor function by different beta-carboline alkaloids. Arch. Toxicol. 2010, 84, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.A.; Maalik, A.; Iqbal, Z.; Malik, I. Recent pharmacological developments in β-carboline alkaloid “harmaline”. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 721, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.L.; Jiang, S.L.; Xue, L.G. A preliminary report on the field control effect of the extract of Peganum harmala to phytophagy spider mites. J. Northwest Sci.-Tech. Univ. Agric. For. 1997, 25, 111–114. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.L.; Guo, X.Q.; Zhan, G.L.; Liu, B. A preliminary study on the resources of botanical insecticides in East Gansu province. Acta Bot. Bor-Occid Sin. 1999, 19, 209–211. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.M.; Mu, K.; Jiang, S.L.; Li, D.K.; Li, W.Y.; Ma, T.F.; Li, Y.M. Toxicity effects of total alkaloids of Peganum harmala against Spodoptera frugiperda larvae blood corpuscles and in vitro cultured Sf9 cells. J. Northwest A. F. Univ. 2016, 44, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Abbassi, K.; Atay-Kadiri, Z.; Ghaout, S. Biological effects of alkaloids extracted from three plants of Moroccan arid areas on the desert locust. Physiol. Entomol. 2003, 26, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Xiao, H.; Guo, X.; Li, B.; Pan, H.; Zhang, J.; Miao, X. Microwave-assisted extraction of three bioactive alkaloids from Peganum harmala L. and their acaricidal activity against Psoroptes cuniculi in vitro. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 192, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moazeni, M.; Ardakani, Z.S.S.; Saharkhiz, M.J.; Jalaei, J.; Khademolhoseini, A.A.; Abad, S.S.E.; Alavi, A.M. In vitro ovicidal activity of Peganum harmala seeds extract on the eggs of Fasciola hepatica. J. Parasit. Dis. 2017, 41, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, X.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, J.; Kang, N.; Liu, X.; Wu, J.; Liu, Y.; Tan, P. The toxicity assessment of extract of Peganum harmala L. seeds in Caenorhabditis elegans. BMC Complement. Med. 2020, 20, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, Q.F.; Zhong, G.L.; Hu, M.Y.; Luo, J.J.; Li, X.G. Bioactivities and physiological effects of extracts of Peganum harmala against Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2005, 8, 2014–2022. [Google Scholar]
- Jbilou, R.; Amri, H.; Bouayad, N.; Ghailani, N.; Ennabili, A.; Sayah, F. Insecticidal effects of extracts of seven plant species on larval development, a-amylase activity and offspring production of Tribolium castaneum (Herbst) (Insecta: Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-mazra’awi, M.S.; Ateyyat, M. Insecticidal and repellent activities of medicinal plant extracts against the sweet potato whitefly, Bemisia tabaci (Hom.:Aleyrodidae) and its parasitoid Eretmocerus mundus (Hym.: Aphelinidae). J. Pest Sci. 2009, 82, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rharrabe, K.; Bakrim, A.; Ghailani, N.; Sayah, F. Bioinsecticidal effect of harmaline on Plodia interpunctella development (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 2007, 89, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, C.A.; Zangerl, A.R.; Berenbaum, M.R. Effects of natural and synthetic neuroactive substances on the growth and feeding of cabbage looper, Trichoplusia ni. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1996, 80, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjannet, H.; Skhiri, F.; Mighri, Z.; Simmonds, M.S.J.; Blaney, W.M. Antifeedant activity of plant extracts and of new natural diglyceride compounds isolated from Ajuga pseudoiva leaves against Spodoptera littoralis larvae. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2001, 4, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stermitz, F.; Lorenz, P.; Tawara, J.; Zenewicz, L.; Lewis, K. Synergy in a medicinal plant: Antimicrobial action of berberine potentiated by 50-methoxyhydnocarpin, a multidrug pump inhibitor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 1433–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nenaah, G. Antibacterial and antifungal activities of (beta)-carboline alkaloids of Peganum harmala (L.) seeds and their combination effects. Fitoterapia 2010, 81, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan-ul-Haq, M.; Hu, Q.B.; Hu, M.Y.; Lin, Q.S.; Zhang, W.L. Biological impact of harmaline, ricinine and their combined effects with Bacillus thuringiensis on Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Pest Sci. 2009, 82, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartal, M.; Altun, M.L.; Kurucu, S. HPLC method for the analysis of harmol, harmalol, harmine and harmaline in the seeds of Peganum harmala L. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. 2003, 31, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Guidelines for Laboratory and Field Testing of Mosquito Larvicides World Health Organization Communicable Disease Control, Prevention and Eradication; WHO Pesticide Evaluation Scheme (WHOPES): Geneva, Switzerland, 2005; pp. 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- Finney, D.J. Probit Analysis; Cambridge University Press: London, UK, 1971; pp. 68–72. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso-Amelot, M.; Calcagno, M. Modeling synergistic and antagonistic interactions in xenobiotic compounds. J. Chem. Ecol. 2000, 26, 513–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.; Firn, R. On the evolution of plant secondary chemical diversity. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1991, 333, 273–280. [Google Scholar]
- O’Hearn, E.; Molliver, M.E. Degeneration of Purkinje cells in parasagittal zones of the cerebellar vermis after treatment with ibogaine or harmaline. Neuroscience 1993, 55, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieczorek, H.; Putzenlechner, M.; Zeiske, W.; Klein, U. A vacuolartype proton pump energizes H+/K+ antiport in an animal plasma membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 15340–15347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Treatments | Mean Mortality (%) ± SE | Co-Toxicity Coefficient | Type of Effect | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 48 h | 24 h | 48 h | 24 h | 48 h | |
| Harmaline (A) | 22.3 ± 1.1 d | 29.7 ± 1.3 d | - | - | - | - |
| Harmine (B) | 19.8 ± 0.9 d | 23.6 ± 1.1 d | - | - | - | - |
| Harmalol (C) | 18.6 ± 1.2 d | 22.3 ± 1.4 d | - | - | - | - |
| Harmane (D) | 17.9 ± 1.3 d | 21.5 ± 1.2 d | - | - | - | - |
| A + B | 59.2 ± 2.1 b | 79.3 ± 2.1 a | +141 | +149 | Synergism | Synergism |
| A + C | 56.1 ± 1.9 b | 72.5 ± 2.4 b | +137 | +139 | Synergism | Synergism |
| A + D | 55.6 ± 2.2 b | 69.5 ± 1.9 b | +138 | +136 | Synergism | Synergism |
| B + C | 52.3 ± 1.8 c | 60.2 ± 2.1 c | +136 | +131 | Synergism | Synergism |
| B + D | 50.4 ± 2.0 c | 54.9 ± 1.7 c | +134 | +122 | Synergism | Synergism |
| C + D | 48.3 ± 1.6 c | 51.9 ± 1.9 c | +132 | +119 | Synergism | Synergism |
| TAEs | 65.2 ± 2.4 a | 83.1 ± 2.6 a | - | - | Synergism | Synergism |
| Treatment | Number of Larvae Tested | Larvae Grow Time/h(Mean ± SE) | Pupa Time/h (Mean ± SE) | Pupation Rate/% (Mean ± SE) | Emergence Rate/% (Mean ± SE) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 210 | 156.8 ± 6.2 c | 55.3 ± 6.5 c | 96.8 ± 2.1 a | 94.1 ± 3.9 a |
| LC10 | 210 | 183.9 ± 8.2 b | 67.2 ± 7.3 b | 89.4 ± 5.6 a | 87.3 ± 6.3 a |
| LC30 | 240 | 201.3 ± 9.3 a | 83.5 ± 8.1 a | 74.5 ± 6.2 b | 65.4 ± 5.1 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, N.; Chen, L.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Jiang, S. Lethal and Sublethal Toxicity of Beta-Carboline Alkaloids from Peganum harmala (L.) against Aedes albopictus Larvae (Diptera: Culicidae). Toxics 2023, 11, 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11040341
Jiang N, Chen L, Li J, Li W, Jiang S. Lethal and Sublethal Toxicity of Beta-Carboline Alkaloids from Peganum harmala (L.) against Aedes albopictus Larvae (Diptera: Culicidae). Toxics. 2023; 11(4):341. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11040341
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Nan, Li Chen, Jinmei Li, Wenyong Li, and Shuanglin Jiang. 2023. "Lethal and Sublethal Toxicity of Beta-Carboline Alkaloids from Peganum harmala (L.) against Aedes albopictus Larvae (Diptera: Culicidae)" Toxics 11, no. 4: 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11040341
APA StyleJiang, N., Chen, L., Li, J., Li, W., & Jiang, S. (2023). Lethal and Sublethal Toxicity of Beta-Carboline Alkaloids from Peganum harmala (L.) against Aedes albopictus Larvae (Diptera: Culicidae). Toxics, 11(4), 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11040341






