Developmental Neurotoxicity of Difenoconazole in Zebrafish Embryos
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Test Organisms
2.3. Locomotor Behavior Assay
2.4. Enzymatic Activity and Neurotransmitter Assay
2.5. Gene Expression Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
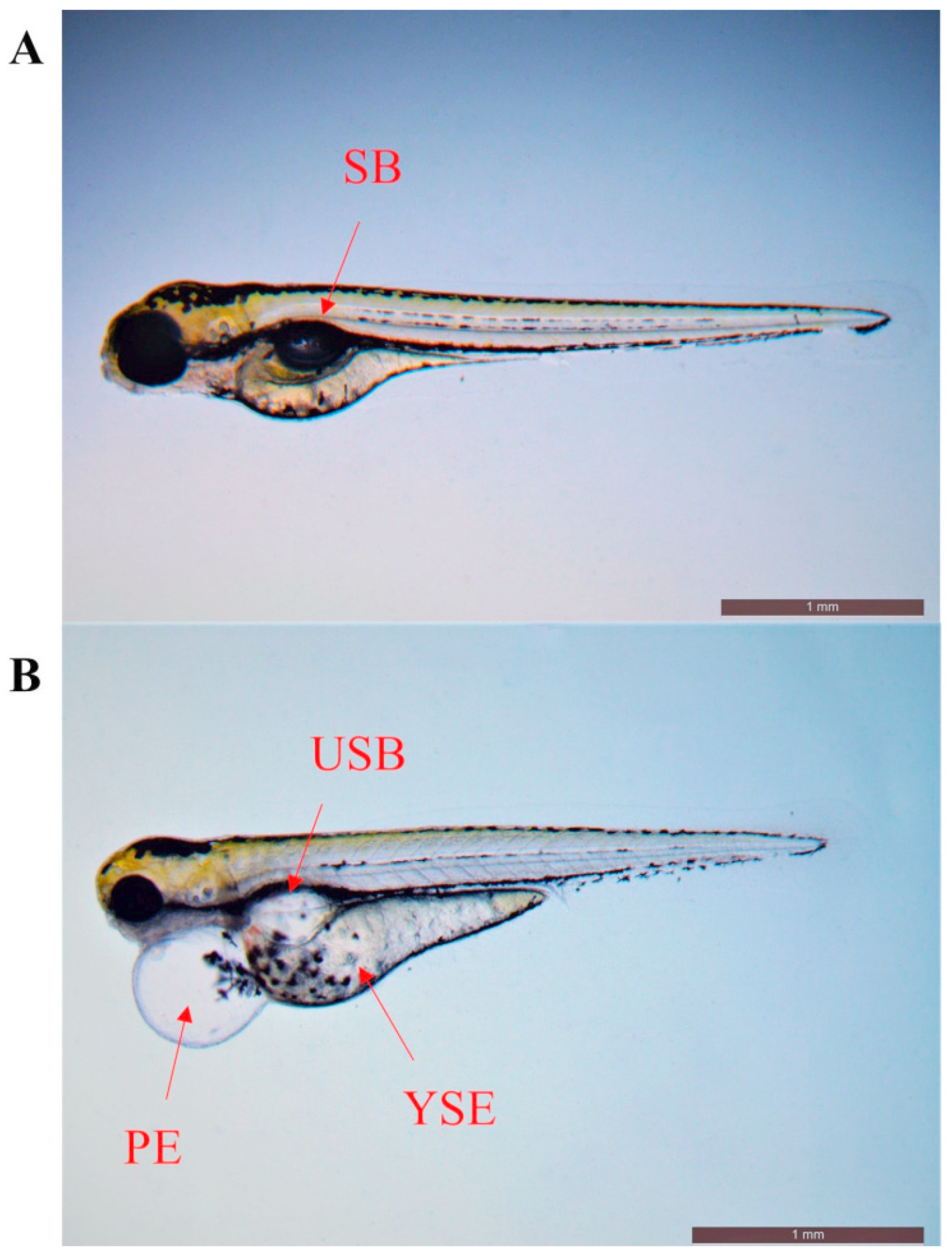
3.1. Developmental Toxicity
3.2. Alterations in Behavior
3.3. Neurotransmitter Content
3.4. AChE Activity
3.5. Gene Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shalini, K.; Kumar, N.; Drabu, S.; Sharma, P.K. Advances in Synthetic approach to and Antifungal Activity of Triazoles. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2011, 7, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefrancq, M.; Jadas-Hécart, A.; La Jeunesse, I.; Landry, D.; Payraudeau, S. High Frequency Monitoring of Pesticides in Runoff Water to Improve Understanding of their Transport and Environmental Impacts. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 587–588, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanden Bossche, H.; Marichal, P.; Gorrens, J.; Coene, M.C. Biochemical Basis for the Activity and Selectivity of Oral Antifungal Drugs. Br. J. Clin. Pract. Suppl. 1990, 71, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Hamada, M.S.; Yin, Y.; Ma, Z. Sensitivity to Iprodione, Difenoconazole and Fludioxonil of Rhizoctonia cerealis Isolates Collected from Wheat in China. Crop. Prot. 2011, 30, 1028–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yao, S.; Cao, D.; Ju, C.; Yu, S.; Xu, S.; Fang, H.; Yu, Y. Increased Triazole-resistance and cyp51A Mutations in Aspergillus fumigatus after Selection with a Combination of the Triazole Fungicides Difenoconazole and Propiconazole. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, S. Dynamics of Difenoconazole and Propiconazole Residues on Pomegranate over 2 years under Field Conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 5795–5806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, Y.; Stenrød, M.; Wu, C.; Almvik, M.; Holten, R.; Clarke, J.L.; Yuan, S.; Wu, X.; Xu, J.; Dong, F.; et al. Degradation of Difenoconazole in Water and Soil: Kinetics, Degradation Pathways, Transformation Products Identification and Ecotoxicity Assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 418, 126303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teló, G.M.; Marchesan, E.; Zanella, R.; Limberger de Oliveira, M.; Coelho, L.L.; Martins, M.L. Residues of Fungicides and Insecticides in Rice Field. Agron. J. 2015, 107, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latiff, K.A.; Bakar, N.K.A.; Isa, N.M. Preliminary Study of Difenoconazole Residues in Rice Paddy Watersheds. Malays. J. Sci. 2010, 29, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhang, C.; Wu, C.; Liu, X. Difenoconazole Residues in Rice and Paddy System. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2011, 25, 339–342. [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer, R.B.; Pettigrove, V.; Rose, G.; Allinson, G.; Wightwick, A.; von der Ohe, P.C.; Shimeta, J.; Kühne, R.; Kefford, B.J. Effects of Pesticides Monitored with Three Sampling Methods in 24 Sites on Macroinvertebrates and Microorganisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1665–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Chai, T.; Wang, K.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, L.; Li, X.; Wang, C. Occurrence and Origin of Sensitivity toward Difenoconazole in Zebrafish (Danio reio) during different Life Stages. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 160, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Chen, L.; Wu, S.; Lv, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, X. Effects of Difenoconazole on Hepatotoxicity, Lipid Metabolism and Gut Microbiota in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265 Pt A, 114844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Zuo, Z.; Guo, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, M.; Yang, Z.; Wang, C. Reproductive Effects of Life-cycle Exposure to Difenoconazole on Female Marine Medaka (Oryzias melastigma). Ecotoxicology 2017, 26, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, M.; Qi, S.; Zhu, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Dong, K.; Wang, C. Effects of the Bioconcentration and Parental Transfer of Environmentally Relevant Concentrations of Difenoconazole on Endocrine Disruption in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, X.; Pang, S.; Sun, X.; Gao, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Wang, C. Evaluation of Acute and Developmental Effects of Difenoconazole via Multiple Stage Zebrafish Assays. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 175, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Liang, Y.; Gong, X.; You, L.; Ji, C.; Wang, S.L.; Wang, C.; Chi, X. Difenoconazole Induces Cardiovascular Toxicity through Oxidative Stress-mediated Apoptosis in Early Life Stages of Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 216, 112227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, B.; Nunes, B. Reliability of Behavioral Test with Fish: How Neurotransmitters may Exert Neuromodulatory Effects and Alter the Biological Responses to Neuroactive Agents. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 734, 139372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Rinwa, P.; Kaur, G.; Machawal, L. Stress: Neurobiology, Consequences and Management. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2013, 5, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altenhofen, S.; Nabinger, D.D.; Wiprich, M.T.; Pereira, T.C.B.; Bogo, M.R.; Bonan, C.D. Tebuconazole Alters Morphological, Behavioral and Neurochemical Parameters in Larvae and Adult Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 2017, 180, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, A.J.; Planchart, A. The Neurological Toxicity of Heavy Metals: A Fish Perspective. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 208, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Song, S.; Hu, C.; Tang, L.; Lam, J.C.W.; Lam, P.K.S.; Chen, L. Dietary administration of probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus modulates the neurological toxicities of perfluorobutanesulfonate in zebrafish. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265 Pt B, 114832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, D.A.; Grandjean, P.; de Groot, D.; Paule, M.G. Developmental Origins of Adult Diseases and Neurotoxicity: Epidemiological and Experimental Studies. Neurotoxicology 2012, 33, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, C.; Bai, Y.; Sun, B.; Zhou, X.; Chen, L. Exposure to methylparaben at environmentally realistic concentrations significantly impairs neuronal health in adult zebrafish. J. Environ. Sci. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Rinkwitz, S.; Mourrain, P.; Becker, T.S. Zebrafish: An Integrative System for Neurogenomics and Neurosciences. Prog. Neurobiol. 2011, 93, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Liu, M.; Wan, T.; Tang, L.; Sun, B.; Zhou, B.; Lam, J.; Lam, P.; Chen, L. Disturbances in Microbial and Metabolic Communication across the Gut-Liver Axis Induced by a Dioxin-like Pollutant: An Integrated Metagenomics and Metabolomics Analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, K.; Fu, W.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, S.; Ye, Q.; Gui, W. QSAR Models for the Acute Toxicity of 1,2,4-triazole Fungicides to Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Yu, L.; Gui, W.; Zhu, G. Exposure to Difenoconazole Causes Changes of Thyroid Hormone and Gene Expression Levels in Zebrafish Larvae. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 40, 983–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Yan, W.; Liu, C.; Li, L.; Yu, L.; Zhao, S.; Li, G. Microcystin-LR Exposure Induces Developmental Neurotoxicity in Zebrafish Embryo. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 213, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallare, A.; Nagel, K.; Köhler, H.R.; Triebskorn, R. Comparative Embryotoxicity and Proteotoxicity of Three Carrier Solvents to Zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2006, 63, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christou, M.; Kavaliauskis, A.; Ropstad, E.; Fraser, T.W.K. DMSO Effects Larval Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Behavior, with Additive and Interaction Effects when Combined with Positive Controls. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 134490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogungbemi, A.O.; Teixido, E.; Massei, R.; Scholz, S.; Küster, E. Optimization of the Spontaneous Tail Coiling Test for Fast Assessment of Neurotoxic Effects in the Zebrafish Embryo Using an Automated Workflow in KNIME®. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2020, 81, 106918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, B.; Dai, L.; Liu, C.; Sun, Q.; Yu, L. Nano-TiO2 Aggravates Bioaccumulation and Developmental Neurotoxicity of Triphenyl Phosphate in Zebrafish Larvae. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stainier, D.Y. Zebrafish genetics and vertebrate heart formation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2001, 2, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, X.; Chai, T.; Wang, K.; Zhu, L.; Huang, Y.; Shen, G.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, C. The developmental effect of difenoconazole on zebrafish embryos: A mechanism research. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 212, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ren, Y.; Ning, X.; Li, G.; Sang, N. Environmental exposure to triazole fungicide causes left-right asymmetry defects and contributes to abnormal heart development in zebrafish embryos by activating PPARγ-coupled Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 859, 160286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Cao, Y.; Tong, L.; Tao, F.; Wang, X.; Wu, H.; Wang, M. Exposure to prothioconazole induces developmental toxicity and cardiovascular effects on zebrafish embryo. Chemosphere 2020, 251, 126418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Souders, C.L.; Li, P.; Pang, S.; Qiu, L.; Martyniuk, C.J. Developmental toxicity of the triazole fungicide cyproconazole in embryo-larval stages of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 4913–4923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, M.; Chen, X.; Wang, C.; Song, M.; Zhang, J.; Bi, S.; Wang, C. Life cycle exposure to propiconazole reduces fecundity by disrupting the steroidogenic pathway and altering DNA methylation in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Int. 2020, 135, 105384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoupa, M.; Machera, K. Zebrafish as an alternative vertebrate model for investigating developmental toxicity-the triadimefon example. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Little, E.E.; Finger, S.E. Swimming Behavior as an Indicator of Sublethal Toxicity in Fish. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1990, 9, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, J.; Oliveri, A.; Levin, E.D. Zebrafish Model Systems for Developmental Neurobehavioral Toxicology. Birth Defects Res. C 2013, 99, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drapeau, P.; Saint-Amant, L.; Buss, R.R.; Chong, M.; McDearmid, J.R.; Brustein, E. Development of the Locomotor Network in Zebrafish. Prog. Neurobiol. 2002, 68, 85–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, M.; Zhu, W.; Wang, D.; Qi, S.; Wang, Y.; Yan, J.; Dong, K.; Zheng, M.; Wang, C. Metabolomics and transcriptomics reveal the toxicity of difenoconazole to the early life stages of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 194, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, M.; Teng, M.; Tian, S.; Yan, J.; Meng, Z.; Yan, S.; Li, R.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, W. Developmental Toxicity and Neurotoxicity of Penconazole Enantiomers Exposure on Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, M.; Zhao, F.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, S.; Tian, S.; Yan, J.; Meng, Z.; Bi, S.; Wang, C. Effect of Propiconazole on the Lipid Metabolism of Zebrafish Embryos (Danio rerio). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 4623–4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basnet, R.M.; Guarienti, M.; Memo, M. Zebrafish Embryo as an In Vivo Model for Behavioral and Pharmacological Characterization of Methylxanthine Drugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baraban, S.C.; Taylor, M.R.; Castro, P.A.; Baier, H. Pentylenetetrazole Induced Changes in Zebrafish Behavior, Neural Activity and c-fos Expression. Neuroscience 2005, 131, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montiglio, P.O.; Royauté, R. Contaminants as a Neglected Source of Behavioural Variation. Anim. Behaviour. 2014, 88, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basnet, R.M.; Zizioli, D.; Taweedet, S.; Finazzi, D.; Memo, M. Zebrafish Larvae as a Behavioral Model in Neuropharmacology. Biomedicines 2019, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kusch, R.C.; Krone, P.H.; Chivers, D.P. Chronic exposure to low concentrations of waterborne cadmium during embryonic and larval development results in the long-term hindrance of antipredator behavior in zebrafish. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2008, 27, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitzer, J.; Driever, W. Development of the Dopamine Systems in Zebrafish. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2009, 651, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- JavadiEsfahani, R.; Kwong, R.W.M. The Sensory-motor Responses to Environmental Acidosis in Larval Zebrafish: Influences of Neurotransmitter and Water Chemistry. Chemosphere 2019, 235, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heusinkveld, H.J.; Molendijk, J.; van den Berg, M.; Westerink, R.H.S. Azole Fungicides Disturb Intracellular Ca2+ in an Additive Manner in Dopaminergic PC12 Cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 134, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, C.Y.; Cowden, J.; Simmons, S.O.; Padilla, S.; Ramabhadran, R. Gene Expression Changes in Developing Zebrafish as Potential Markers for Rapid Developmental Neurotoxicity Screening. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2010, 32, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, S.; Jahangeer, M.; Maknoon Razia, D.; Ashiq, M.; Ghaffar, A.; Akram, M.; El Allam, A.; Bouyahya, A.; Garipova, L.; Ali Shariati, M.; et al. Dopamine in Parkinson’s disease. Clin. Chim. Acta 2021, 522, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irons, T.D.; Kelly, P.E.; Hunter, D.L.; MacPhail, R.C.; Padilla, S. Acute Administration of Dopaminergic Drugs has Differential Effects on Locomotion in Larval Zebrafish. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2013, 103, 792–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kung, T.S.; Richardson, J.R.; Cooper, K.R.; White, L.A. Developmental Deltamethrin Exposure Causes Persistent Changes in Dopaminergic Gene Expression, Neurochemistry, and Locomotor Activity in Zebrafish. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 146, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, G.R.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.P.; Liu, T.X.; Le, W.D. Nr4a2 is essential for the differentiation of dopaminergic neurons during zebrafish embryogenesis. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2008, 39, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panula, P.; Chen, Y.C.; Priyadarshini, M.; Kudo, H.; Semenova, S.; Sundvik, M.; Sallinen, V. The Comparative Neuroanatomy and Neurochemistry of Zebrafish CNS Systems of Relevance to Human Neuropsychiatric Diseases. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 40, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, C.; Karanth, S.; Liu, J. Pharmacology and Toxicology of Cholinesterase Inhibitors: Uses and Misuses of a Common Mechanism of Action. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2005, 19, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Tao, L.; Song, D.; Li, Y.; Gao, F. Bimetallic Pd@ Au Nanorods Based Ultrasensitive Acetylcholinesterase Biosensor for Determination of Organophosphate Pesticides. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 255, 2575–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Huang, C.; Hu, C.; Yu, K.; Yang, L.; Zhou, B. Acute Exposure to DE-71: Effects on Locomotor Behavior and Developmental Neurotoxicity in Zebrafish Larvae. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 2338–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rima, M.; Lattouf, Y.; Abi Younes, M.; Bullier, E.; Legendre, P.; Mangin, J.M.; Hong, E. Dynamic Regulation of the Cholinergic System in the Spinal Central Nervous System. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Ueshima, E.; Muraoka, O.; Tanaka, H.; Yeo, S.Y.; Huh, T.L.; Miki, N. Zebrafish elav/HuC Homologue as a very Early Neuronal Marker. Neurosci. Lett. 1996, 216, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, M.; Heinrich, G. Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor Gene Expression in the Developing Zebrafish. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 1997, 15, 983–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshii, A.; Constantine-Paton, M. Postsynaptic BDNF-TrkB Signaling in Synapse Maturation, Plasticity, and Disease. Dev. Neurobiol. 2010, 70, 304–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nielsen, A.L.; Jørgensen, A.L. Structural and Functional Characterization of the Zebrafish Gene for Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein, GFAP. Gene 2003, 310, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middeldorp, J.; Hol, E.M. GFAP in Health and Disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2011, 93, 421–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brösamle, C.; Halpern, M.E. Characterization of Myelination in the Developing Zebrafish. Glia 2002, 39, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajmone-Cat, M.A.; D’Urso, M.C.; di Blasio, G.; Brignone, M.S.; De Simone, R.; Minghetti, L. Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 is Part of the Molecular Machinery Regulating the Adaptive Response to LPS Stimulation in Microglial Cells. Brain Behav. Immun. 2016, 55, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udvadia, A.J.; Koster, R.W.; Skene, J.H. GAP-43 Promoter Elements in Transgenic Zebrafish Reveal a Difference in Signals for Axon Growth during CNS Development and Regeneration. Development 2001, 128, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benowitz, L.I.; Routtenberg, A. GAP-43: An Intrinsic Determinant of Neuronal Development and Plasticity. Trends Neurosci. 1997, 20, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Yu, K.; Huang, C.; Yu, L.; Zhu, B.; Lam, P.K.; Lam, J.C.; Zhou, B. Prenatal Transfer of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDEs) Results in Developmental Neurotoxicity in Zebrafish Larvae. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 9727–9734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Gene Name | Sequence of the Primer (5′–3′) | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|
| β−actin | Forward: ATGGATGAGGAAATCGCTGCC Reverse: CTCCCTGATGTCTGGGTCGTC | NM_181601.5 |
| mbp | Forward: AATCAGCAGGTTCTTCGGAGGAGA Reverse: AAGAAATGCACGACAGGGTTGACG | AY860977 |
| α1−tubulin | Forward: AATCACCAATGCTTGCTTCGAGCC Reverse: TTCACGTCTTTGGGTACCACGTCA | NM_194388 |
| ngn1 | Forward: AAGCAGGGCAAGTCAAGAGA Reverse: ACGTCGGTTTGCAAGTATCC | AF024535 |
| syn2a | Forward: GTGACCATGCCAGCATTTC Reverse: TGGTTCTCCACTTTCACCTT | NM_001002597.2 |
| elavl3 | Forward: AGACAAGATCACAGGCCAGAGCTT Reverse: TGGTCTGCAGTTTGAGACCGTTGA | NM_131449 |
| gap43 | Forward: TGCTGCATCAGAAGAACTAA Reverse: CCTCCGGTTTGATTCCATC | NM_131341 |
| bdnf | Forward: ATAGTAACGAACAGGATGG Reverse: GCTCAGTCATGGGAGTCC | NM_131595.2 |
| manf | Forward: AGATGGAGAGTGTGAAGTCTGTGTG Reverse: CAATTGAGTCGCTGTCAAAACTTG | NM_001076629 |
| gafp | Forward: GGATGCAGCCAATCGTAAT Reverse: TTCCAGGTCACAGGTCAG | NM_131373 |
| chrna7 | Forward: TCAGTATTTTGCCACCACCA Reverse: CTTTGTCTTCGCCAGGTCTC | NM_201219.2 |
| ache | Forward: CCCTCCAGTGGGTACAAGAA Reverse: GGGCCTCATCAAAGGTAACA | NM_131846.2 |
| nr4a2b | Forward: GAAGACGGCGAAATCGATGC Reverse: CTGGCGGTTCTGACAACTTCC | NM_001002406.1 |
| drd1 | Forward: TGGTTCCTTTCTGCAACCCA Reverse: AGTGATGAGTTCGCCCAACC | NM_001135976.2 |
| drd2 | Forward: TCCACAAAATCAGGAAAAGCGT Reverse: CAGCCAATGTAAACCGGCAA | XM_005157501.4 |
| shha | Forward: GCAAGATAACGCGCAATTCGGAGA Reverse: TGCATCTCTGTGTCATGAGCCTGT | NM_131063.3 |
| Control (0 mg/L) | 0.25 mg/L | 0.5 mg/L | 1 mg/L | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Survival rate (%) | 90.00 ± 3.85 | 85.56 ± 2.22 | 84.44 ± 2.22 | 83.33 ± 1.92 |
| Hatching rate (%) | 94.99 ± 0.74 | 92.40 ± 0.56 | 93.40 ± 1.58 | 91.79 ± 1.50 |
| Heart rate (times/60 s) | 176.60 ± 3.40 | 174.30 ± 2.56 | 169.20 ± 3.08 | 164.20 ± 2.74 * |
| Malformation rate (%) | 1.00 ± 0.86 | 2.09 ± 1.05 | 5.55 ± 1.94 | 18.28 ± 2.51 * |
| Body length (mm) | 4.03 ± 0.03 | 3.96 ± 0.03 | 3.92 ± 0.03 | 3.91 ± 0.03 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Q.; Deng, P.; Xing, D.; Liu, H.; Shi, F.; Hu, L.; Zou, X.; Nie, H.; Zuo, J.; Zhuang, Z.; et al. Developmental Neurotoxicity of Difenoconazole in Zebrafish Embryos. Toxics 2023, 11, 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11040353
Yang Q, Deng P, Xing D, Liu H, Shi F, Hu L, Zou X, Nie H, Zuo J, Zhuang Z, et al. Developmental Neurotoxicity of Difenoconazole in Zebrafish Embryos. Toxics. 2023; 11(4):353. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11040353
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Qing, Ping Deng, Dan Xing, Haoling Liu, Fang Shi, Lian Hu, Xi Zou, Hongyan Nie, Junli Zuo, Zimeng Zhuang, and et al. 2023. "Developmental Neurotoxicity of Difenoconazole in Zebrafish Embryos" Toxics 11, no. 4: 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11040353
APA StyleYang, Q., Deng, P., Xing, D., Liu, H., Shi, F., Hu, L., Zou, X., Nie, H., Zuo, J., Zhuang, Z., Pan, M., Chen, J., & Li, G. (2023). Developmental Neurotoxicity of Difenoconazole in Zebrafish Embryos. Toxics, 11(4), 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11040353





