Characterizing Aircraft Exhaust Emissions and Impact Factors at Tianjin Binhai International Airport via Open-Path Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectrometer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Measurements and Methods
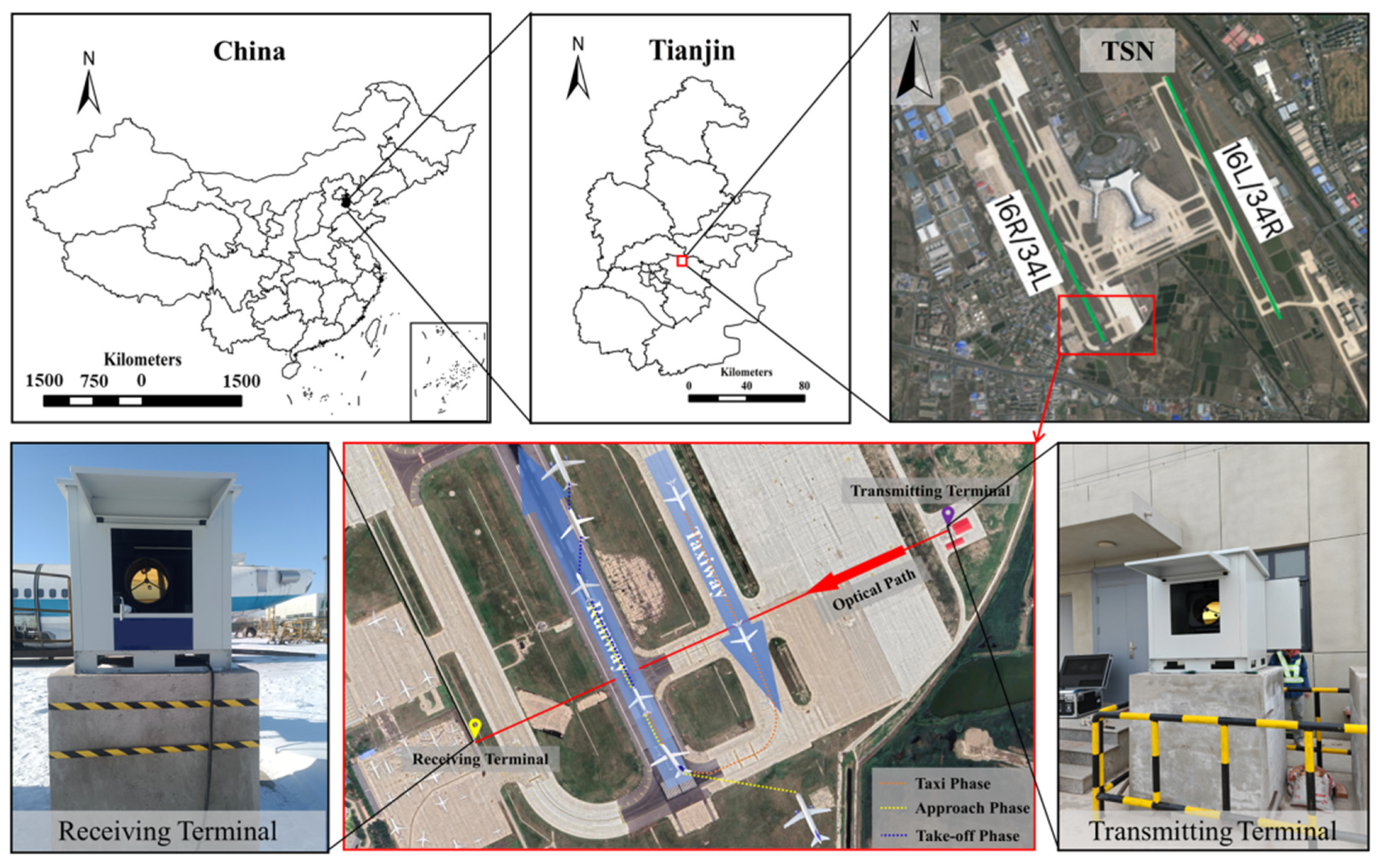
2.1. Test Airport
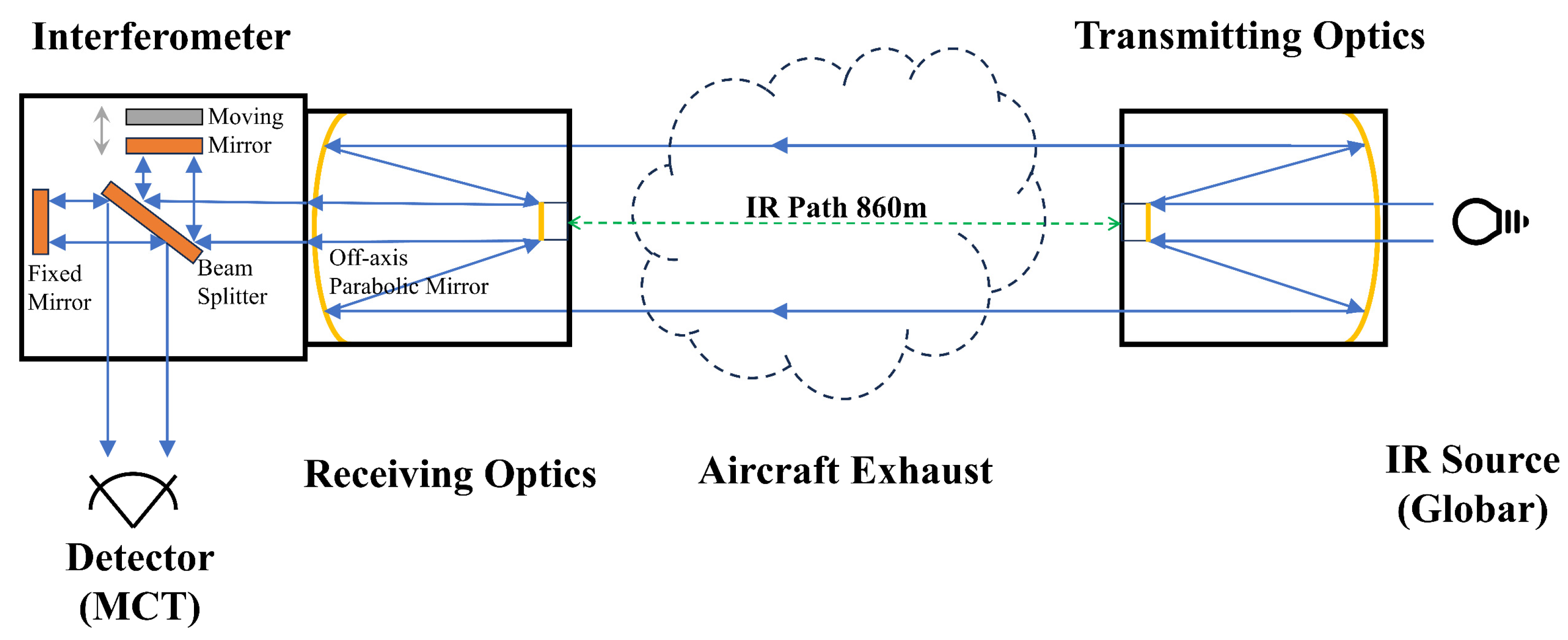
2.2. Emission Measurement System
2.3. Data Processing Methods and Quality Control
3. Result and Discussion
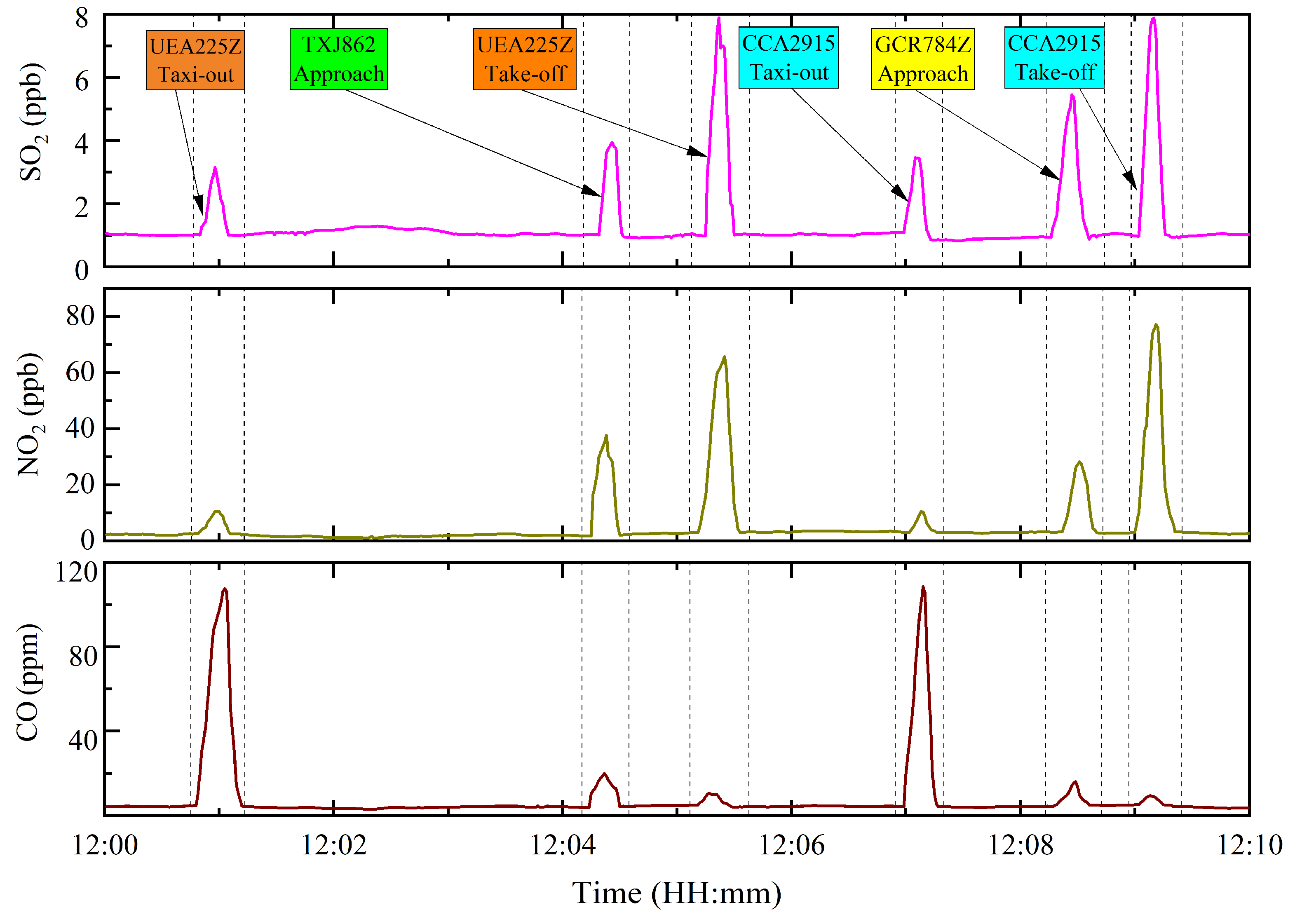
3.1. Airport Air Quality
3.2. Emission Index
3.3. Impact Factors
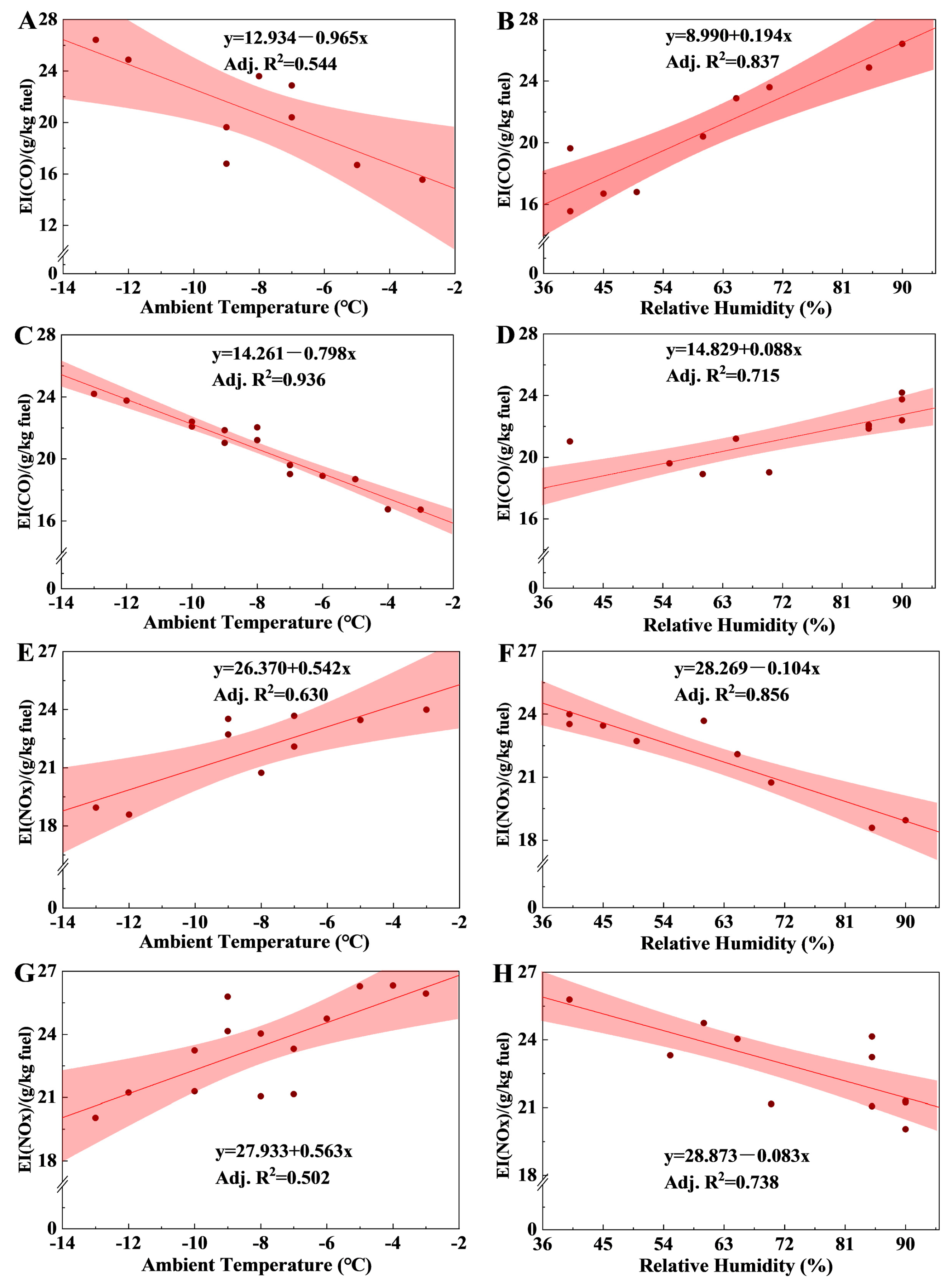
3.3.1. Meteorological Conditions
3.3.2. Aircraft Age Conditions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agarwal, A.; Speth, R.L.; Fritz, T.M.; Jacob, S.D.; Rindlisbacher, T.; Iovinelli, R.; Owen, B.; Miake-Lye, R.C.; Sabnis, J.S.; Barrett, S.R.H. SCOPE11 Method for Estimating Aircraft Black Carbon Mass and Particle Number Emissions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 1364–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masiol, M.; Harrison, R.M. Aircraft engine exhaust emissions and other airport-related contributions to ambient air pollution: A review. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 95, 409–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgut, E.T.; Usanmaz, O. An assessment of cruise NOX emissions of short-haul commercial flights. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 171, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudda, N.; Durant, L.W.; Fruin, S.A.; Durant, J.L. Impacts of Aviation Emissions on Near-Airport Residential Air Quality. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 8580–8588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.H.; Saunois, M.; Bousquet, P.; Lin, X.; Berchet, A.; Hegglin, M.I.; Canadell, J.G.; Jackson, R.B.; Deushi, M.; Jöckel, P.; et al. On the role of trend and variability in the hydroxyl radical (OH) in the global methane budget. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 13011–13022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ossola, R.; Gruseck, R.; Houska, J.; Manfrin, A.; Vallieres, M.; McNeill, K. Photochemical Production of Carbon Monoxide from Dissolved Organic Matter: Role of Lignin Methoxyarene Functional Groups. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 13449–13460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.X.; Huang, X.; Song, Y.; Tang, J.; Cao, J.J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.X.; Xu, T.T.; Kang, L.; et al. Ammonia emission control in China would mitigate haze pollution and nitrogen deposition, but worsen acid rain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 7760–7765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grennfelt, P.; Engleryd, A.; Forsius, M.; Hov, O.; Rodhe, H.; Cowling, E. Acid rain and air pollution: 50 years of progress in environmental science and policy. Ambio 2020, 49, 849–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapadia, Z.Z.; Spracklen, D.V.; Arnold, S.R.; Borman, D.J.; Mann, G.W.; Pringle, K.J.; Monks, S.A.; Reddington, C.L.; Benduhn, F.; Rap, A.; et al. Impacts of aviation fuel sulfur content on climate and human health. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 10521–10541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Ahn, J.W.; Kim, K.H.; Son, Y.S. Historic and futuristic review of electron beam technology for the treatment of SO2 and NOX in flue gas. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 355, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prashanth, P.; Speth, R.L.; Eastham, S.D.; Sabnis, J.S.; Barrett, S.R.H. Post-combustion emissions control in aero-gas turbine engines. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 916–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.Y.; Abbatt, J.P.D. Oxidation of sulfur dioxide by nitrogen dioxide accelerated at the interface of deliquesced aerosol particles. Nat. Chem. 2021, 13, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokuslu, A. Estimation of aircraft emissions at Georgian international airport. Energy 2020, 206, 118219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoh, R.; Engberg, Z.; Shapiro, M.; Dray, L.; Stettler, M.E.J. The high-resolution Global Aviation emissions Inventory based on ADS-B (GAIA) for 2019–2021. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2024, 24, 725–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Wang, X.; Han, B.; Zhao, J.; Guan, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.; Yu, J.; Feng, Y.; et al. Exploring emission spatiotemporal pattern and potential reduction capacity in China’s aviation sector: Flight trajectory optimization perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahnke, C.; Gomes, R.; Bundke, U.; Berg, M.; Ziereis, H.; Sharma, M.; Righi, M.; Hendricks, J.; Zahn, A.; Wahner, A.; et al. Properties and Processing of Aviation Exhaust Aerosol at Cruise Altitude Observed from the IAGOS-CARIBIC Flying Laboratory. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 6945–6953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, S.; Kiliç, D.; Flynn, M.; Williams, P.; Allan, J. International airport emissions and their impact on local air quality: Chemical speciation of ambient aerosols at Madrid-Barajas Airport during the AVIATOR campaign. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2024, 24, 9045–9058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.W.; Zhu, M.Y.; Zhou, L.M.; Gao, M.Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhong, S.H.; Pan, K.; Chen, L.F. Evaluating high-resolution aviation emissions using real-time flight data. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Jiao, Y.F.; Lang, J.L.; Chen, D.S.; Huang, C.; Wei, P.; Li, S.Y.; Cheng, S.Y. Improved estimation of air pollutant emissions from landing and takeoff cycles of civil aircraft in China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.J.; Tian, H.Z.; Hao, Y.; Liu, S.H.; Liu, X.Y.; Zhu, C.Y.; Wu, Y.M.; Liu, W.; Bai, X.X.; Wu, B.B. Atmospheric emission inventory of multiple pollutants from civil aviation in China: Temporal trend, spatial distribution characteristics and emission features analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujovic, D.; Todorovic, N. An assessment of pollutant emissions due to air traffic at Nikola Tesla International Airport, Belgrade, and the link between local air quality and weather types. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2017, 56, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.R.; Yu, Z.H.; Zhang, C.; Chen, L.F. IVOC/SVOC and size distribution characteristics of particulate matter emissions from a modern aero-engine combustor in different operational modes. Fuel 2022, 314, 112781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgut, E.T.; Cavcar, M.; Usanmaz, O.; Yay, O.D.; Dogeroglu, T.; Armutlu, K. Investigating actual landing and takeoff operations for time-in-mode, fuel and emissions parameters on domestic routes in Turkey. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2017, 53, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Fu, Q.Y.; Yu, Y.M.; Liu, Q.Z.; Pan, J.; Cheng, J.P.; Wang, Z.W.; Liu, L.Q. Quantifying aircraft emissions of Shanghai Pudong International Airport with aircraft ground operational data. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.N.; Zou, C.; Fang, T.G.; Sun, N.X.; Liang, X.Y.; Wu, L.; Mao, H.J. Emissions from international airport and its impact on air quality: A case study of beijing daxing international airport (PKX), China. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 336, 112472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heland, J.; Schafer, K. Determination of major combustion products in aircraft exhausts by FTIR emission spectroscopy. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 3067–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klapmeyer, M.E.; Marr, L.C. CO2, NOX, and Particle Emissions from Aircraft and Support Activities at a Regional Airport. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 10974–10981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, K.; Jahn, C.; Sturm, P.; Lechner, B.; Bacher, M. Aircraft emission measurements by remote sensing methodologies at airports. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 5261–5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgut, E.T.; Cavcar, M.; Yay, O.D.; Ucarsu, M.; Yilmaz, E.; Usanmaz, O.; Armutlu, K.; Dogeroglu, T. A gaseous emissions analysis of commercial aircraft engines during test-cell run. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 116, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinsey, J.S.; Hays, M.D.; Dong, Y.; Williams, D.C.; Logan, R. Chemical Characterization of the Fine Particle Emissions from Commercial Aircraft Engines during the Aircraft Particle Emissions eXperiment (APEX) 1 to 3. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 3415–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.R.; Liu, H.Y.; Han, Z.L.; Fan, Y.K.; Lei, L. Combustion and particulate I/SVOC characteristics of an aero-engine combustor with dual-stage under operational power and injection pressure. Energy 2024, 302, 131796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carslaw, D.C.; Ropkins, K.; Laxen, D.; Moorcroft, S.; Marner, B.; Williams, M.L. Near-field commercial aircraft contribution to nitrogen oxides by engine, aircraft type, and airline by individual plume sampling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 1871–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Qin, M.; Fang, W.; Liao, Z.T.; Gui, H.Q.; Shi, Z.; Yang, H.N.; Meng, F.H.; Shao, D.; Hu, J.Q.; et al. Detection of Aircraft Emissions Using Long-Path Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy at Hefei Xinqiao International Airport. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaporozhets, O.; Synylo, K. Improvements on aircraft engine emission and emission inventory asesessment inside the airport area. Energy 2017, 140, 1350–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Wang, L.J.; Deng, Z.Q.; Shi, Y.L.; Yu, J. Source emission and attribution of a large airport in Central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schürmann, G.; Schäfer, K.; Jahn, C.; Hoffmann, H.; Bauerfeind, M.; Fleuti, E.; Rappenglück, B. The impact of NOX, CO and VOC emissions on the air quality of Zurich airport. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmis, C.G.; Sgouros, G.; Flocas, H.; Schäfer, K.; Jahn, C.; Hoffmann, M.; Heyder, C.; Kurtenbach, R.; Niedojadlo, A.; Wiesen, P.; et al. The role of meteorology on the background air quality at the Athens International Airport. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 5561–5571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valotto, G.; Varin, C. Characterization of hourly NOX atmospheric concentrations near the Venice International Airport with additive semi-parametric statistical models. Atmos. Res. 2016, 167, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyprianidis, K.G.; Dahlquist, E. On the trade-off between aviation NOX and energy efficiency. Appl. Energy 2017, 185, 1506–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Z.; Sun, X.X.; Sethi, V.; Nalianda, D.; Li, Y.G.; Wang, L. Review of modern low emissions combustion technologies for aero gas turbine engines. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2017, 94, 12–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroyan, Y.; Wojcieszyk, M.L.; Kaario, O.; Larmi, M. Modeling the impact of sustainable aviation fuel properties on end-use performance and emissions in aircraft jet engines. Energy 2022, 255, 124470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aygun, H.; Turan, O. Analysis of cruise conditions on energy, exergy and NOX emission parameters of a turbofan engine for middle-range aircraft. Energy 2023, 267, 126468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.L.; Anderson, D.C.; Martin, C.R.; Ren, X.R.; Salawitch, R.J.; He, H.; Canty, T.P.; Hains, J.C.; Dickerson, R.R. Using near-road observations of CO, NOy, and CO2 to investigate emissions from vehicles: Evidence for an impact of ambient temperature and specific humidity. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 232, 117558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Yao, C.D.; Han, G.P.; Wei, H.Y.; Wang, Q.G. The impact of intake air temperature on performance and exhaust emissions of a diesel methanol dual fuel engine. Fuel 2015, 162, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Huang, J.C. An oxygenating additive for improving the performance and emission characteristics of marine diesel engines. Ocean Eng. 2003, 30, 1699–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weilenmann, M.; Favez, J.Y.; Alvarez, R. Cold-start emissions of modern passenger cars at different low ambient temperatures and their evolution over vehicle legislation categories. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 2419–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirola, C.; Galli, F.; Rinaldini, C.A.; Manenti, F.; Milani, M.; Montorsi, L. Effects of humidified enriched air on combustion and emissions of a diesel engine. Renew. Energy 2020, 155, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Xiao, K.; Cheng, J.P.; Yu, Y.M.; Liu, Q.Z.; Pan, J.; Chen, J.J.; Chen, F.T.; Fu, Q.Y. Characterizing aircraft engine fuel and emission parameters of taxi phase for Shanghai Hongqiao International Airport with aircraft operational data. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogut, M.Z.; Yalcin, E.; Karakoc, T.H. Assessment of degradation effects for an aircraft engine considering exergy analysis. Energy 2017, 140, 1417–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, D.; Singh, S.K.; Agarwal, A.K. Effect of Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) on performance, emissions, deposits and durability of a constant speed compression ignition engine. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 2900–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Author | Instrument/Method | Sampling Point | Meteorological Condition | Pollutant Concentration | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO | NO | NO2 | SO2 | ||||
| Duan et al. (2022) [33] | Long-path DOAS instrument | Hefei Xinqiao International Airport | - | - | - | 4.0–16.1 ppb (Median: 8.2 ppb) | 1.4–3.6 ppb (Median: 2.1 ppb) |
| Schürmann et al. (2007) [36] | Long-path FTIR and DOAS instruments | Pier A (designated for parking and simultaneous handling of up to four aircrafts) | - | - | Bdl*–61.1 µg/m3 (Median: 3.1 µg/m3) | 3.6–103.8 µg/m3 (Median: 19.6 µg/m3) | - |
| Pier B (designated for long-term parking of aircrafts with no handling taking place) | - | - | Bdl*–76.3 µg/m3 (Median: 6.6 µg/m3) | 3.0–98.3 µg/m3 (Median: 17.5 µg/m3) | - | ||
| Taxiway | - | 0.06–0.49 mg/m3 (Median: 0.19 mg/m3) | 0.07–132.0 µg/m3 (Median: 15.4 µg/m3) | 0.04–274.0 µg/m3 (Median: 22.6 µg/m3) | - | ||
| Handling (airport apron area mainly impacted by ground support vehicle emissions) | - | 0.00–1.91 mg/m3 (Median: 0.22 mg/m3) | 0.8–636.0 µg/m3 (Median: 25.2 µg/m3) | 0.3–131.0 µg/m3 (Median: 29.6 µg/m3) | - | ||
| Helmis et al. (2011) [37] | Mobile monitoring stations | Athens International Airport | Moderate surface flow (wind speed: 7–9 m/s at 10 m height) | 0.06–0.68 mg/m3 (Median: 0.18 mg/m3) | 1.0–42.0 µg/m3 (Median: 92.0 µg/m3) | 5.0–78.0 µg/m3 (Median: 21.0 µg/m3) | 1.0–18.0 µg/m3 (Median: 10.0 µg/m3) |
| Strong surface flows (wind speed: 9–15 m/s at 10 m height) | 0.06–0.15 mg/m3 (Median: 0.09 mg/m3) | 0.06–56.0 µg/m3 (Median: 22.1 µg/m3) | 2.0–21.5 µg/m3 (Median: 5.0 µg/m3) | 1.0–16.0 µg/m3 (Median: 8.5 µg/m3) | |||
| This study | Long-path FTIR instrument | Tianjin Binhai International Airport | Wind speed: 1–4 m/s; dominant direction: 330° | 1.01–6.89 ppm (Median: 3.24 ppm) | - | 2.94–15.96 ppb (Median: 7.60 ppb) | 0.63–3.98 ppb (Median: 1.54 ppb) |
| Combinations | Phase | EI (NOX) (g/kg Fuel) | EI (CO) (g/kg Fuel) | Sample Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A320-214/CFM56-5B4 | Taxi | 3.06 ± 1.66 | 33.23 ± 5.48 | 104 |
| Approach | 8.14 ± 1.60 | 3.66 ± 1.75 | 65 | |
| Take-off | 22.77 ± 3.67 | 1.00 ± 0.72 | 104 | |
| B737-700/CFM56-7B26 | Taxi | 2.59 ± 1.36 | 20.44 ± 5.97 | 46 |
| Approach | 9.34 ± 1.11 | 3.59 ± 1.00 | 17 | |
| Take-off | 21.94 ± 4.11 | 0.97 ± 0.64 | 46 | |
| B737-800/CFM56-7B27 | Taxi | 2.81 ± 1.69 | 20.01 ± 4.44 | 567 |
| Approach | 9.31 ± 1.95 | 2.26 ± 1.18 | 188 | |
| Take-off | 23.48 ± 4.02 | 1.14 ± 0.90 | 567 | |
| A320-232/V2527-A5 | Taxi | 2.66 ± 1.50 | 16.19 ± 5.86 | 74 |
| Approach | 9.48 ± 1.57 | 2.85 ± 0.94 | 30 | |
| Take-off | 22.84 ± 3.77 | 1.05 ± 0.74 | 74 | |
| CRJ900/CF34-8C5 | Taxi | 2.94 ± 1.58 | 17.90 ± 3.32 | 19 |
| Approach | 9.34 ± 0.82 | 5.09 ± 1.97 | 8 | |
| Take-off | 11.35 ± 5.37 | 0.94 ± 0.59 | 19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, J.; Mao, Z.; Han, B.; Fan, Z.; Ma, S.; Li, J.; Wang, R.; Yu, J. Characterizing Aircraft Exhaust Emissions and Impact Factors at Tianjin Binhai International Airport via Open-Path Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectrometer. Toxics 2024, 12, 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12110782
Zhao J, Mao Z, Han B, Fan Z, Ma S, Li J, Wang R, Yu J. Characterizing Aircraft Exhaust Emissions and Impact Factors at Tianjin Binhai International Airport via Open-Path Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectrometer. Toxics. 2024; 12(11):782. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12110782
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Jingbo, Zixiang Mao, Bo Han, Zhiyong Fan, Simeng Ma, Jingxin Li, Rui Wang, and Jian Yu. 2024. "Characterizing Aircraft Exhaust Emissions and Impact Factors at Tianjin Binhai International Airport via Open-Path Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectrometer" Toxics 12, no. 11: 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12110782
APA StyleZhao, J., Mao, Z., Han, B., Fan, Z., Ma, S., Li, J., Wang, R., & Yu, J. (2024). Characterizing Aircraft Exhaust Emissions and Impact Factors at Tianjin Binhai International Airport via Open-Path Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectrometer. Toxics, 12(11), 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12110782





