Associations Between Urinary Phthalate Metabolites and Decreased Serum α-Klotho Level: A Cross-Sectional Study Among US Adults in Middle and Old Age
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Examinations of Urinary Phthalate Metabolites
2.3. Examinations of α-Klotho
2.4. Measurements of Confounders
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics
3.2. Associations Between Urinary Phthalate Metabolites and Serum α-Klotho
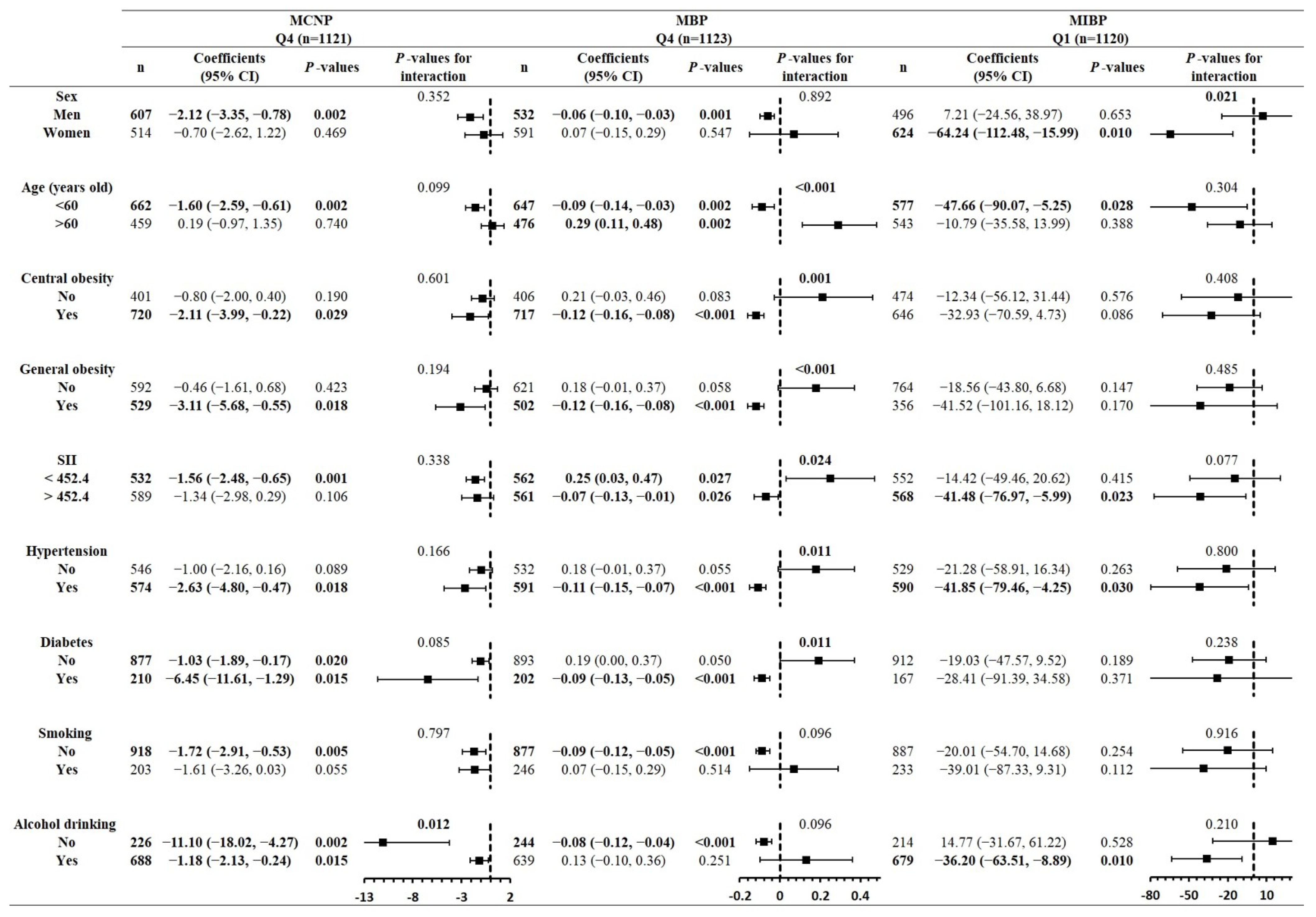
3.3. Findings of Stratified Analyses in Subgroups of Confounders
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heudorf, U.; Mersch-Sundermann, V.; Angerer, J. Phthalates: Toxicology and exposure. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2007, 210, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frery, N.; Santonen, T.; Porras, S.P.; Fucic, A.; Leso, V.; Bousoumah, R.; Duca, R.C.; El Yamani, M.; Kolossa-Gehring, M.; Ndaw, S.; et al. Biomonitoring of occupational exposure to phthalates: A systematic review. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2020, 229, 113548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.X.; Feng, N.X.; Zeng, L.J.; Chen, X.; Xiang, L.; Li, Y.W.; Cai, Q.Y.; Mo, C.H. Occurrence and human health risks of phthalates in indoor air of laboratories. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 135609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.Y.; Wei, Q.; Wang, L.Y.; Zhang, Z.M.; Zhang, X.Q.; Sun, A.L.; Chen, J.; Shi, X.Z. A comprehensive study of the effects of phthalates on marine mussels: Bioconcentration, enzymatic activities and metabolomics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 168, 112393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, L.J.; Huang, Y.H.; Chen, X.T.; Chen, X.H.; Mo, C.H.; Feng, Y.X.; Lu, H.; Xiang, L.; Li, Y.W.; Li, H.; et al. Prevalent phthalates in air-soil-vegetable systems of plastic greenhouses in a subtropical city and health risk assessments. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lind, P.M.; Lind, L. Circulating levels of bisphenol A and phthalates are related to carotid atherosclerosis in the elderly. Atherosclerosis 2011, 218, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, P.M.; Roos, V.; Ronn, M.; Johansson, L.; Ahlstrom, H.; Kullberg, J.; Lind, L. Serum concentrations of phthalate metabolites are related to abdominal fat distribution two years later in elderly women. Environ. Health 2012, 11, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lind, P.M.; Zethelius, B.; Lind, L. Circulating levels of phthalate metabolites are associated with prevalent diabetes in the elderly. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 1519–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.H.; Shen, Y.X.; Li, L.; Fan, T.T.; Wang, Y.; Wei, N. Phthalate exposure and high blood pressure in adults: A cross-sectional study in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 15934–15942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahlhut, R.W.; van Wijngaarden, E.; Dye, T.D.; Cook, S.; Swan, S.H. Concentrations of urinary phthalate metabolites are associated with increased waist circumference and insulin resistance in adult U.S. males. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 876–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trasande, L.; Liu, B.; Bao, W. Phthalates and attributable mortality: A population-based longitudinal cohort study and cost analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brassea-Pérez, E.; Hernández-Camacho, C.J.; Labrada-Martagón, V.; Vázquez-Medina, J.P.; Gaxiola-Robles, R.; Zenteno-Savín, T. Oxidative stress induced by phthalates in mammals: State of the art and potential biomarkers. Environ. Res. 2022, 206, 112636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Park, H.Y.; Bae, S.; Lim, Y.H.; Hong, Y.C. Diethylhexyl phthalates is associated with insulin resistance via oxidative stress in the elderly: A panel study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuro, O.M. The Klotho proteins in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Hwang, K.H.; Park, K.S.; Kong, I.D.; Cha, S.K. Biological Role of Anti-aging Protein Klotho. J. Lifestyle Med. 2015, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Sun, Z. Molecular basis of Klotho: From gene to function in aging. Endocr. Rev. 2015, 36, 174–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olauson, H.; Mencke, R.; Hillebrands, J.L.; Larsson, T.E. Tissue expression and source of circulating alphaKlotho. Bone 2017, 100, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.C.; Kuro-o, M.; Rosenblatt, K.P.; Brobey, R.; Papaconstantinou, J. The ASK1-Signalosome regulates p38 MAPK activity in response to levels of endogenous oxidative stress in the Klotho mouse models of aging. Aging 2010, 2, 597–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lee, S.; Choi, J.Y.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.J.; Min, J.Y.; Min, K.B. Association of alpha-klotho and lead and cadmium: A cross-sectional study. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 843, 156938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Ma, Y.; Cheng, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, W. Association between perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl internal exposure and serum alpha-Klotho levels in middle-old aged participants. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1136454. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Wei, Y. Exposure to p-dichlorobenzene and serum alpha-Klotho levels among US participants in their middle and late adulthood. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drew, D.A.; Katz, R.; Kritchevsky, S.; Ix, J.H.; Shlipak, M.G.; Newman, A.B.; Hoofnagle, A.N.; Fried, L.F.; Sarnak, M.; Gutierrez, O.M.; et al. Soluble Klotho and Incident Hypertension. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 16, 1502–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.; Chae, D.W.; Lee, K.B.; Sung, S.A.; Yoo, T.H.; Han, S.H.; Ahn, C.; Oh, K.H. Serum klotho is inversely associated with metabolic syndrome in chronic kidney disease: Results from the KNOW-CKD study. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charoenngam, N.; Ponvilawan, B.; Ungprasert, P. Lower circulating soluble Klotho level is associated with increased risk of all-cause mortality in chronic kidney disease patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2020, 52, 1543–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchanan, S.; Combet, E.; Stenvinkel, P.; Shiels, P.G. Klotho, Aging, and the Failing Kidney. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donate-Correa, J.; Martin-Nunez, E.; Mora-Fernandez, C.; Muros-de-Fuentes, M.; Perez-Delgado, N.; Navarro-Gonzalez, J.F. Klotho in cardiovascular disease: Current and future perspectives. World J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 6, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, T.; Duan, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Huang, X.; Bai, X.; Xie, L.; He, Y.; Ouyang, J.; Yang, Y.; et al. Human exposure to phthalate esters associated with e-waste dismantling: Exposure levels, sources, and risk assessment. Environ. Int. 2019, 124, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lyu, L.; Tao, Y.; Ju, H.; Chen, J. Health risks of phthalates: A review of immunotoxicity. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 313, 120173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicinska, P. Di-n-butyl phthalate, butylbenzyl phthalate and their metabolites induce haemolysis and eryptosis in human erythrocytes. Chemosphere 2018, 203, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, S.; Masai, E.; Kamimura, N.; Takahashi, K.; Anderson, R.C.; Faisal, P.A. Phthalates impact human health: Epidemiological evidences and plausible mechanism of action. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 340, 360–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikkam, M.; Tracey, R.; Guerrero-Bosagna, C.; Skinner, M.K. Plastics derived endocrine disruptors (BPA, DEHP and DBP) induce epigenetic transgenerational inheritance of obesity, reproductive disease and sperm epimutations. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhu, J.; Li, Y.; Lin, T.; Gan, L.; Yuan, X.; Xu, M.; Wei, G. Dynamic effect of di-2-(ethylhexyl) phthalate on testicular toxicity: Epigenetic changes and their impact on gene expression. Int. J. Toxicol. 2010, 29, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Chen, W.L. The relationship between polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons exposure and serum klotho among adult population. BMC Geriatr. 2022, 22, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; He, G.Y.; Wu, X.J.; Wang, C.P.; Luo, X.B.; Zhao, Y.; Long, Y. Association between environmental exposure to perchlorate, nitrate, and thiocyanate and serum alpha-Klotho levels among adults from the National Health and nutrition examination survey (2007–2014). BMC Geriatr. 2022, 22, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES): Laboratory Procedures Manual. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhanes/2007-2008/manuals/manual_lab.pdf (accessed on 8 November 2024).

| n for Examination | LOD | n of LLODs | (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2007–2008 | 2009–2010 | 2011–2012 | 2013–2014 | 2015–2016 | ||||
| MCNP | 13,502 | 0.500 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 190 | 1.4 |
| MCOP | 13,502 | 0.700 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.300 | 0.300 | 66 | 0.5 |
| MECP | 13,502 | 0.500 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.400 | 0.400 | 12 | 0.1 |
| MBP | 13,502 | 0.600 | 0.400 | 0.400 | 0.400 | 0.400 | 91 | 0.674 |
| MC1 | 13,502 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.400 | 0.400 | 409 | 3.0 |
| MCP | 5353 | 0.603 | 0.462 | N/G | N/G | N/G | 5111 | 95.5 |
| MEP | 13,502 | 0.462 | 0.462 | 0.600 | 1.200 | 1.200 | 6 | 0.1 |
| MHHP | 13,502 | 0.700 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.400 | 0.400 | 31 | 0.2 |
| MHP | 13,502 | 1.100 | 0.500 | 0.500 | 0.800 | 0.800 | 1241 | 9.2 |
| MNMP | 7842 | 1.100 | 0.500 | 0.500 | N/G | N/G | 3502 | 44.7 |
| MNP | 13,502 | 1.232 | 0.770 | 0.500 | 0.900 | 0.900 | 3189 | 23.6 |
| MOH | 13,502 | 0.600 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 50 | 0.4 |
| MOP | 5353 | 1.848 | 0.840 | N/G | N/G | N/G | 5270 | 98.5 |
| MZP | 13,502 | 0.216 | 0.216 | 0.300 | 0.300 | 0.300 | 116 | 0.9 |
| MIBP | 13,502 | 0.300 | 0.200 | 0.200 | 0.800 | 0.800 | 95 | 0.7 |
| MHNCP | 8149 | N/G | N/G | N/G | 0.400 | 0.400 | 2871 | 35.2 |
| HIBP | 2975 | N/G | N/G | N/G | N/G | 0.400 | 112 | 3.8 |
| MCOHP | 2975 | N/G | N/G | N/G | N/G | 0.500 | 1192 | 40.1 |
| MHBP | 2975 | N/G | N/G | N/G | N/G | 0.500 | 648 | 21.8 |
| Characteristics | Medians (P25, P75) or n (%) |
|---|---|
| Men (%) | 2192 (48.9) |
| Age (years) | 57.0 (48.0, 66.0) |
| Race (%) | |
| Mexican American | 709 (6.6) |
| Other Hispanic | 502 (4.9) |
| Non-Hispanic white | 1924 (72.8) |
| Non-Hispanic black | 899 (9.2) |
| Others | 448 (6.4) |
| Education level (%) | |
| Less than 9th grade | 592 (6.4) |
| 9–11th grade | 665 (10.7) |
| High school graduation | 1004 (22.1) |
| Some college graduation or AA degree | 1215 (29.9) |
| College graduation and above | 1004 (31.0) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 28.7 (25.2, 33.3) |
| WC (cm) | 100 (90.1, 110.3) |
| Urinary creatinine (mg/dL) | 103.0 (59.0, 156.0) |
| Count of lymphocytes (1000 cell/uL) | 2.0 (1.6, 2.5) |
| Count of segmented neutrophils (1000 cell/uL) | 3.9 (3.1, 5.0) |
| Count of platelets (1000 cell/uL) | 232 (197, 276) |
| SII | 452.4 (320.9, 643) |
| Current smoking (%) | 882 (18.8) |
| Alcohol drinking (%) | 2656 (80.0) |
| Hypertension (%) | 2071 (41.9) |
| T2DM (%) | 819 (14.5) |
| α-Klotho (pg/mL) | 804.4 (658.4, 997.6) |
| MCNP (ng/mL) | 2.0 (1.1, 4.1) |
| MCOP (ng/mL) | 8.8 (3.9, 24.4) |
| MECP (ng/mL) | 14.1 (7.0, 28.8) |
| MBP (ng/mL) | 12.3 (5.8, 25.1) |
| MC1 (ng/mL) | 1.9 (0.8, 4.2) |
| MEP (ng/mL) | 56.5 (20.4, 185.1) |
| MHHP (ng/mL) | 9.2 (4.3, 19.3) |
| MOH (ng/mL) | 5.6 (2.7, 11.5) |
| MZP (ng/mL) | 4.4 (1.9, 10.1) |
| MIBP (ng/mL) | 7.6 (3.6, 14.3) |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficients (95% CI) | p-Value | Coefficients (95% CI) | p-Value | Coefficients (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| MCNP | −0.99 (−1.85, −0.13) | 0.025 | −0.95 (−1.80, −0.10) | 0.029 | −1.14 (−2.00, −0.27) | 0.011 |
| MCOP | 0.08 (−0.12, 0.27) | 0.438 | 0.07 (−0.12, 0.26) | 0.483 | −0.01 (−0.12, 0.09) | 0.813 |
| MECP | 0.04 (−0.05, 0.14) | 0.367 | 0.04 (−0.06, 0.14) | 0.419 | 0.04 (−0.06, 0.14) | 0.403 |
| MBP | 0.02 (−0.00, 0.04) | 0.083 | 0.02 (−0.00, 0.04) | 0.101 | −0.08 (−0.14, −0.02) | 0.015 |
| MC1 | 0.07 (−0.26, 0.39) | 0.685 | 0.05 (−0.28, 0.39) | 0.747 | −0.06 (−0.28, 0.17) | 0.623 |
| MEP | 0.00 (−0.02, 0.01) | 0.622 | 0.00 (−0.02, 0.01) | 0.583 | −0.01 (−0.01, 0.01) | 0.846 |
| MHHP | 0.06 (−0.13, 0.25) | 0.509 | 0.06 (−0.13, 0.25) | 0.537 | 0.07 (−0.12, 0.26) | 0.494 |
| MOH | 0.13 (−0.23, 0.50) | 0.469 | 0.13 (−0.24, 0.50) | 0.494 | 0.15 (−0.23, 0.52) | 0.438 |
| MZP | 0.39 (−0.31, 1.09) | 0.266 | 0.25 (−0.40, 0.90) | 0.451 | 0.36 (−0.40, 0.12) | 0.347 |
| MIBP | 0.43 (−0.34, 1.21) | 0.271 | 0.37 (−0.35, 1.10) | 0.310 | 0.28 (−0.50, 1.06) | 0.473 |
| Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficients (95% CI) | p-Value | Coefficients (95% CI) | p-Value | Coefficients (95% CI) | p-Value | Coefficients (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| MCNP | −47.26 (−177.84, 83.31) | 0.473 | 81.35 (−70.87, 233.58) | 0.291 | 19.43 (−20, 58.85) | 0.330 | −1.66 (−2.58, −0.73) | 0.001 |
| MCOP | −29.08 (−58.97, 0.81) | 0.056 | 13.23 (−8.81, 35.28) | 0.236 | 0.45 (−7.16, 8.06) | 0.907 | −0.03 (−0.14, 0.07) | 0.532 |
| MECP | 7.46 (−9.39, 24.31) | 0.381 | 7.58 (−7.14, 22.30) | 0.309 | 3.46 (−3.43, 10.35) | 0.321 | 0.05 (−0.05, 0.15) | 0.303 |
| MBP | −8.54 (−22.91, 5.84) | 0.241 | 4.54 (−16.64, 25.72) | 0.671 | 4.00 (−4.61, 12.61) | 0.358 | −0.05 (−0.09, −0.01) | 0.030 |
| MC1 | −130.44 (−294.62, 33.73) | 0.118 | 62.26 (−32.86, 157.37) | 0.196 | −0.41 (−64.35, 63.54) | 0.990 | −0.06 (−0.26, 1.43) | 0.561 |
| MEP | −1.32 (−6.62, 3.98) | 0.621 | −4.13 (−9.21, 0.95) | 0.110 | −0.30 (−0.90, 0.29) | 0.311 | −0.01 (−0.03, 0.01) | 0.234 |
| MHHP | 17.81 (−12.06, 47.69) | 0.239 | 3.32 (−15.52, 22.17) | 0.727 | −2.47 (−13.45, 8.51) | 0.656 | 0.07 (−0.12, 0.26) | 0.487 |
| MOH | 47.52 (−20.04, 115.08) | 0.165 | 24.12 (−7.05, 55.29) | 0.127 | −7.84 (−25.04, 9.36) | 0.367 | 0.17 (−0.22, 0.55) | 0.387 |
| MZP | 15.79 (−68.17, 99.75) | 0.709 | 58.39 (−16.31, 133.09) | 0.124 | −9.60 (−26.22, 7.03) | 0.254 | 0.51 (−0.30, 1.31) | 0.214 |
| MIBP | −26.87 (−52.53, −1.21) | 0.040 | −19.3 (−48.77, 10.17) | 0.196 | 4.37 (−12.28, 21.02) | 0.603 | 0.32 (−0.43, 1.07) | 0.404 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Ma, S.; Li, Y. Associations Between Urinary Phthalate Metabolites and Decreased Serum α-Klotho Level: A Cross-Sectional Study Among US Adults in Middle and Old Age. Toxics 2024, 12, 817. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12110817
Liu Y, Zhao X, Ma S, Li Y. Associations Between Urinary Phthalate Metabolites and Decreased Serum α-Klotho Level: A Cross-Sectional Study Among US Adults in Middle and Old Age. Toxics. 2024; 12(11):817. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12110817
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yuyan, Xiaoyu Zhao, Shuxian Ma, and Yongfang Li. 2024. "Associations Between Urinary Phthalate Metabolites and Decreased Serum α-Klotho Level: A Cross-Sectional Study Among US Adults in Middle and Old Age" Toxics 12, no. 11: 817. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12110817
APA StyleLiu, Y., Zhao, X., Ma, S., & Li, Y. (2024). Associations Between Urinary Phthalate Metabolites and Decreased Serum α-Klotho Level: A Cross-Sectional Study Among US Adults in Middle and Old Age. Toxics, 12(11), 817. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12110817





