MicroRNA in the Exosomes Mediated by Resveratrol to Activate Neuronal Cells
Abstract
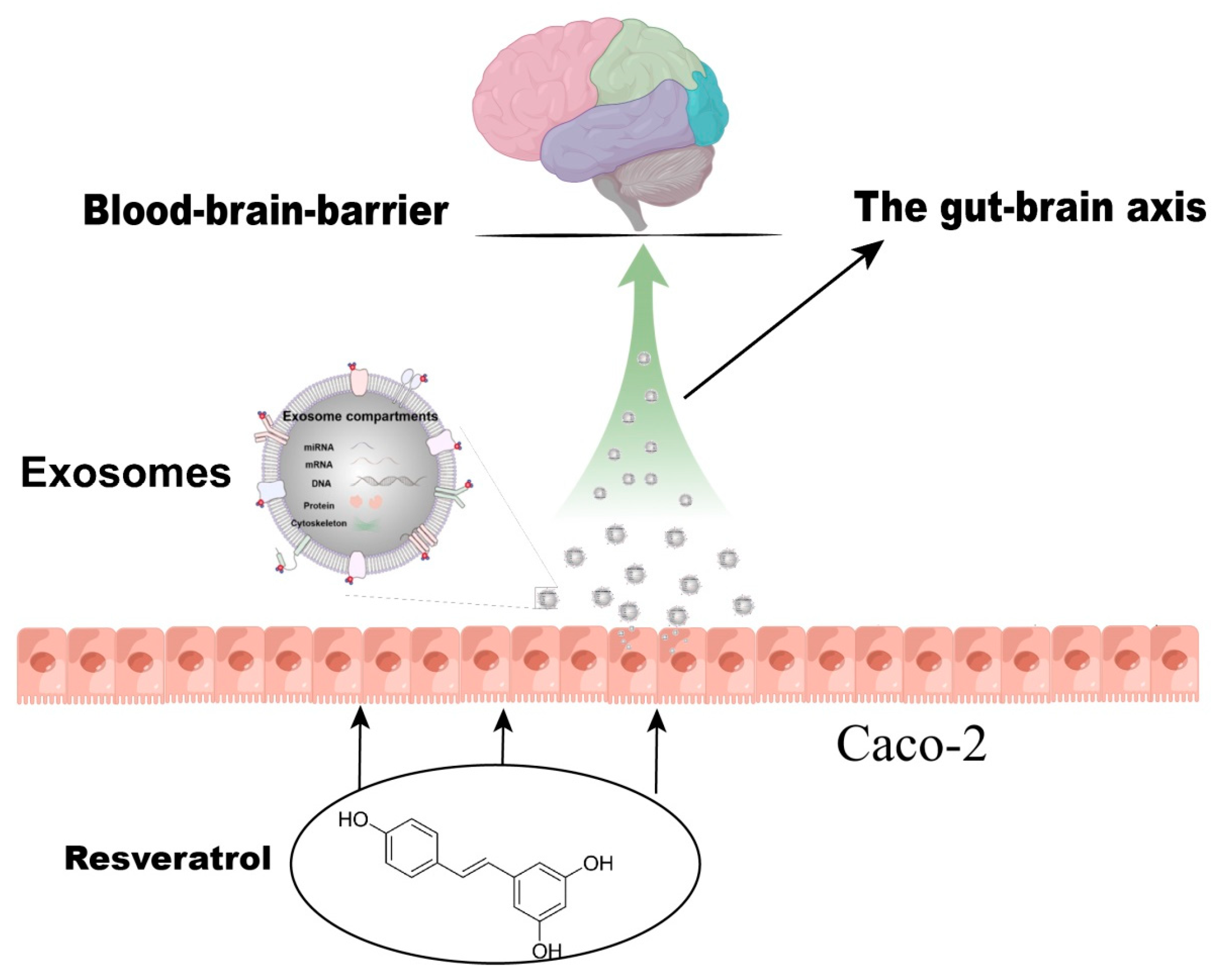
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Cell Culture
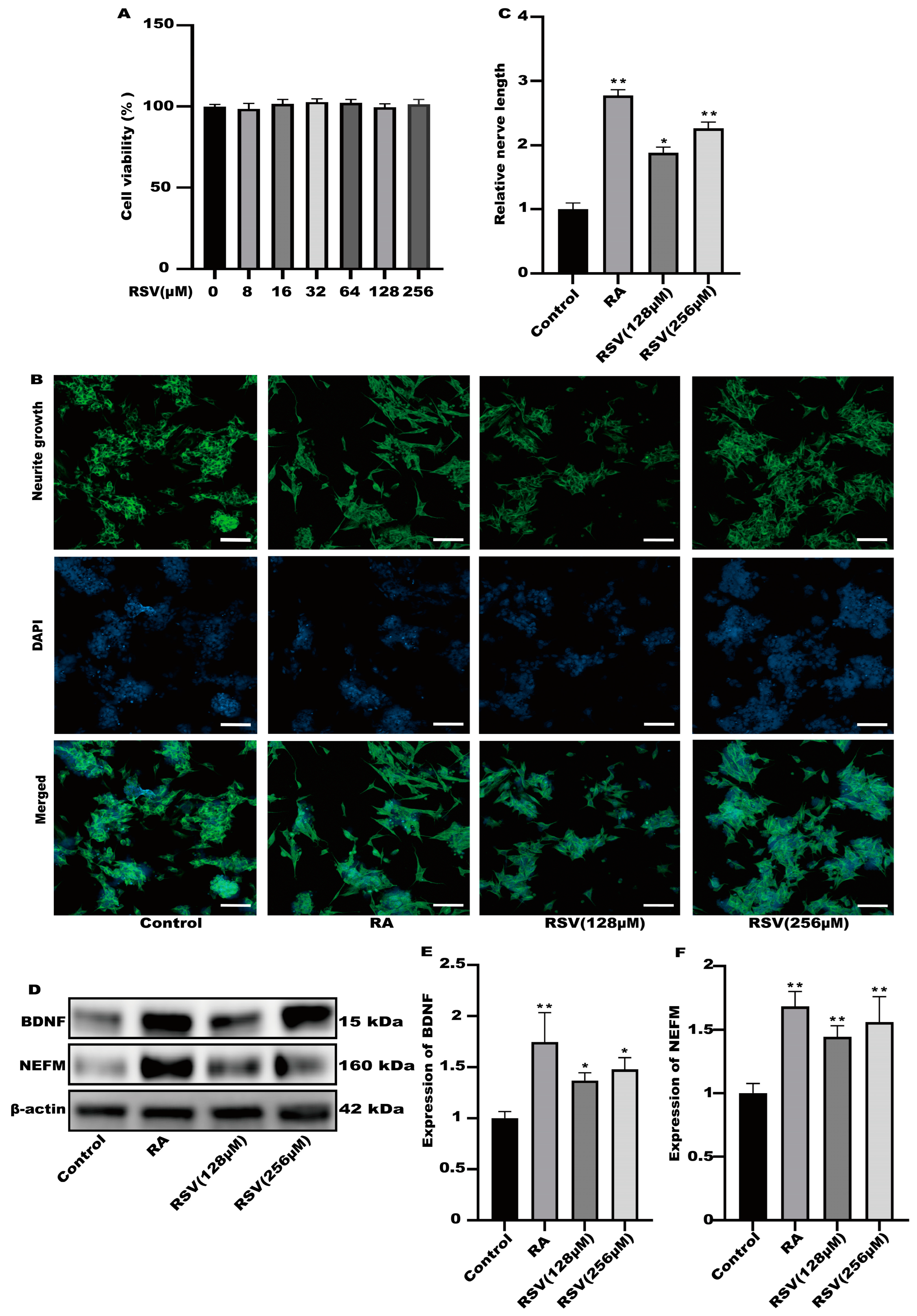
2.3. Cell Viability
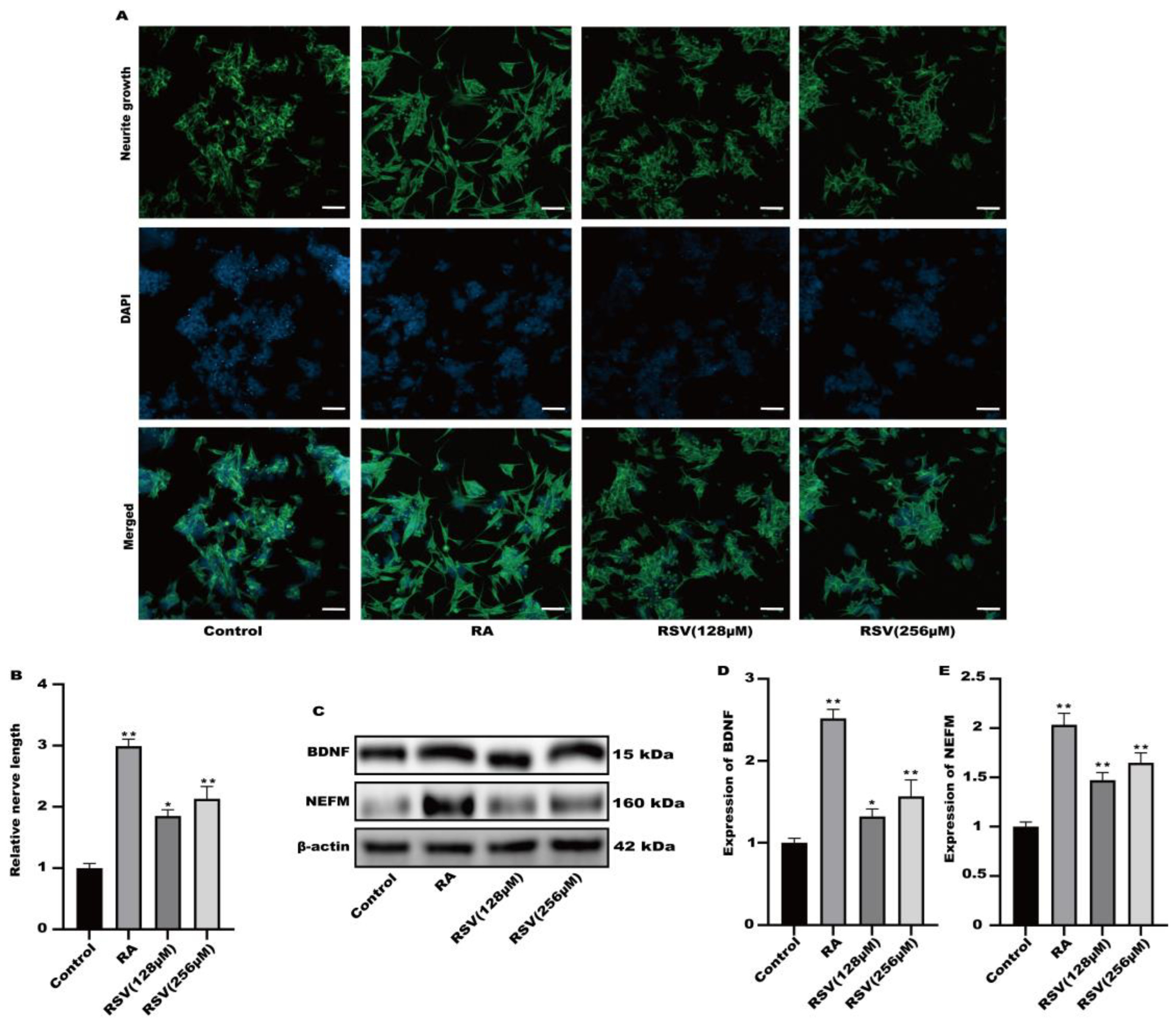
2.4. Measurement of Neurite Growth on SH-SY5Y Cells
2.5. Protein Expression Analysis
2.6. Establishment of Caco-2 Cells Model
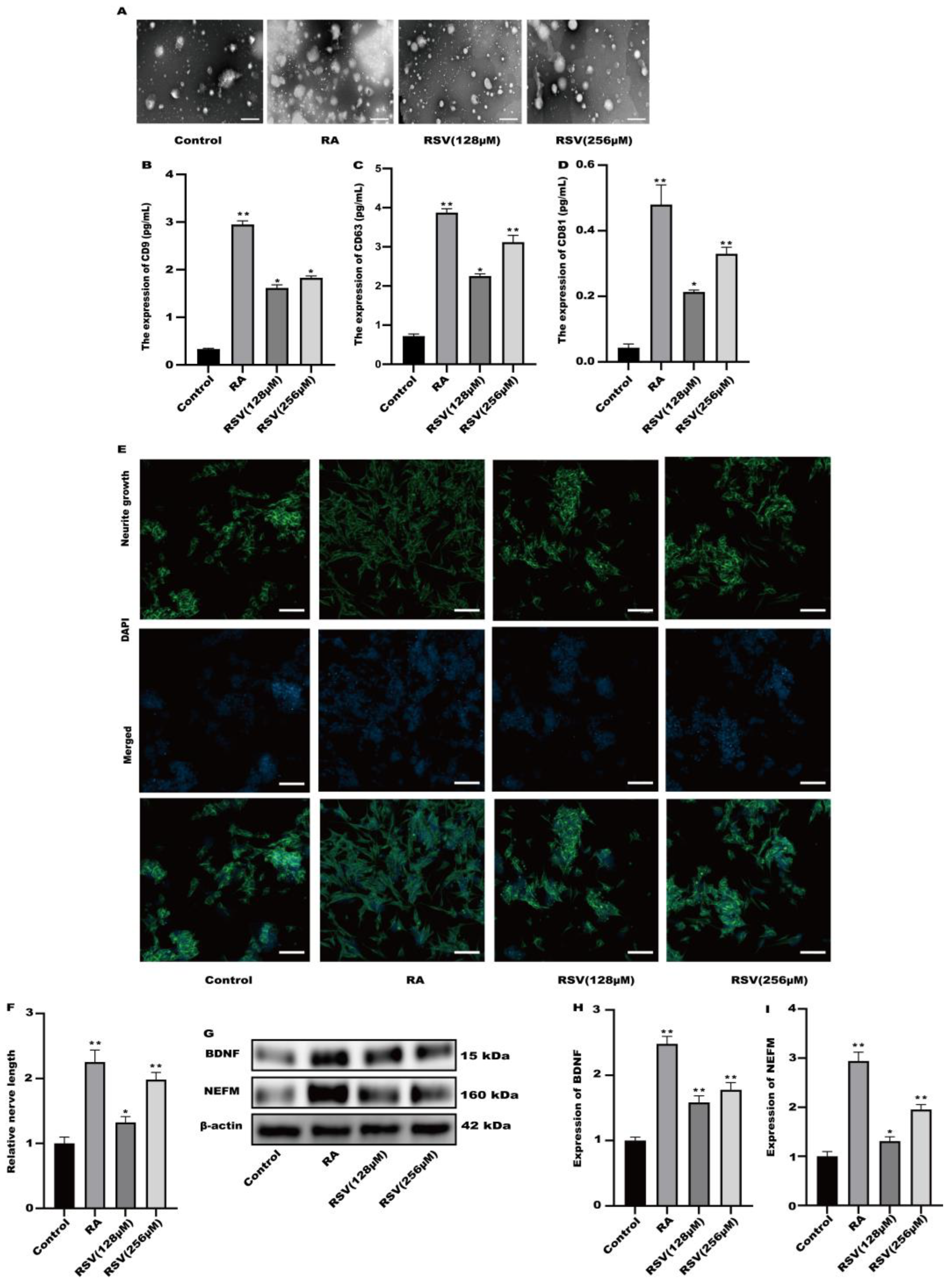
2.7. Exosome Isolation
2.8. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
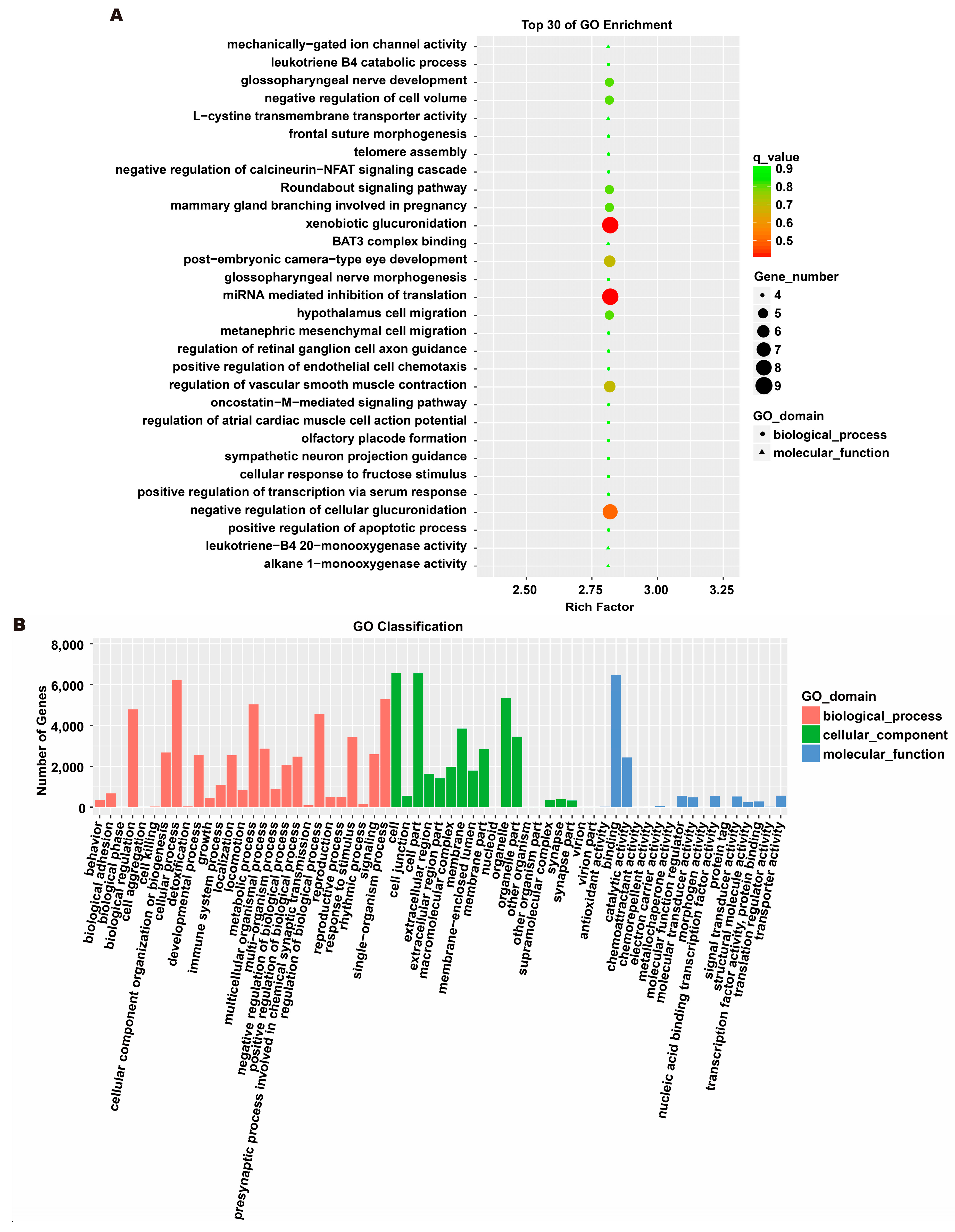
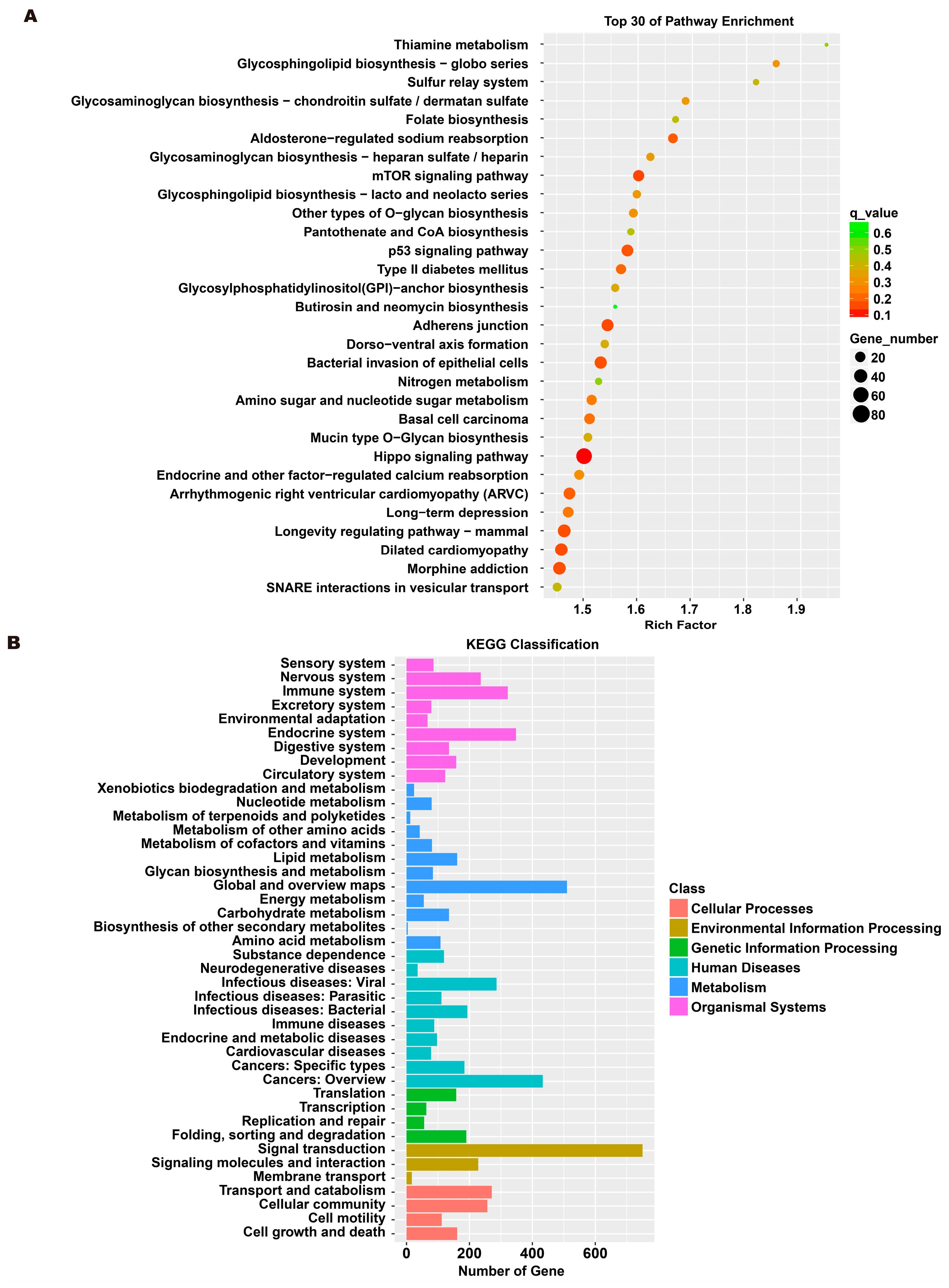
2.9. RNA Sequencing (RNA-seq) and Bioinformatic Analysis
2.10. Preparation of miRNA Mimics
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Medium of Caco-2 Cells Treated with Resveratrol (RSV) Could Induce Neurite Outgrowth in SH-SY5Y Cells
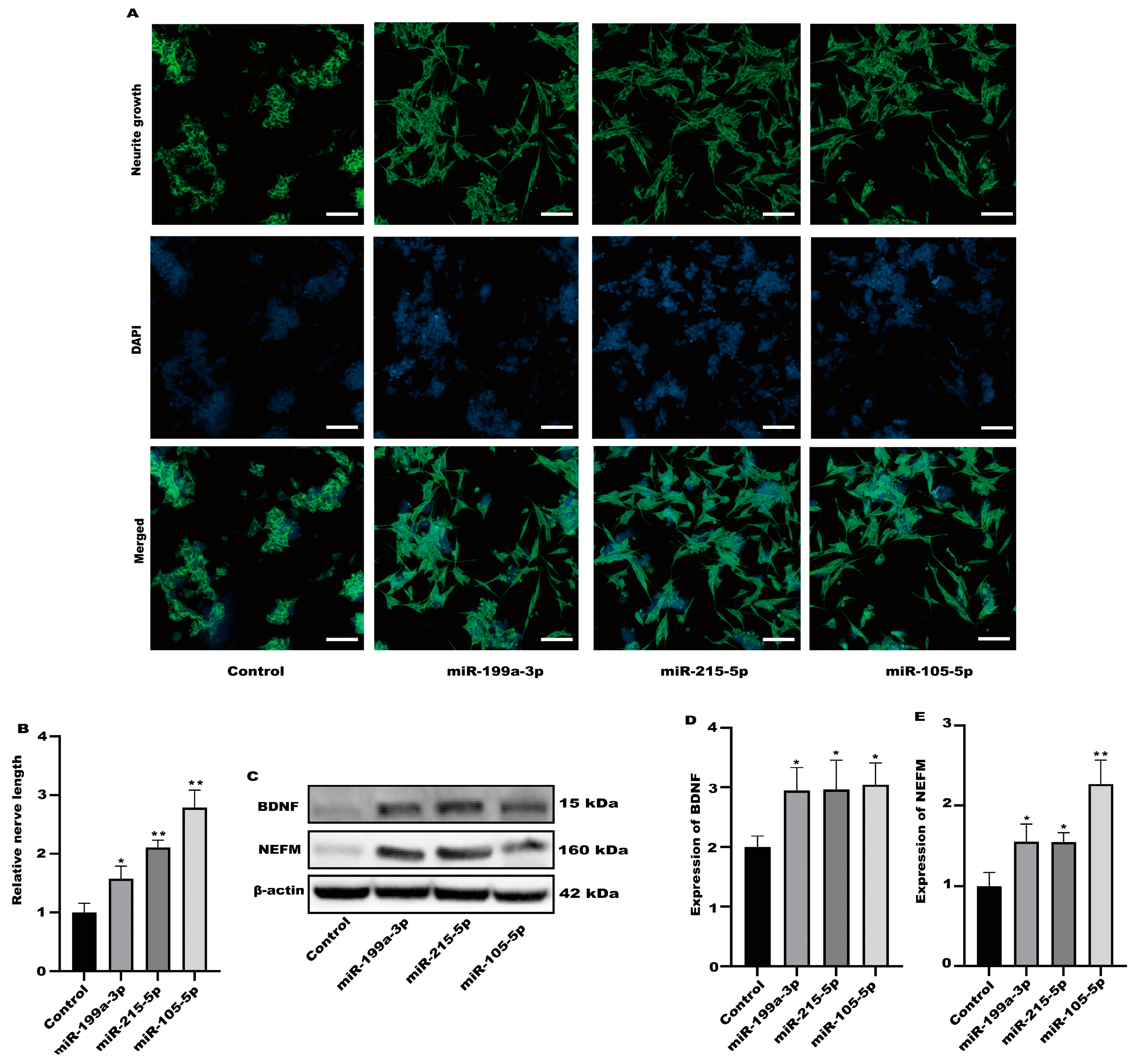
3.2. Neurite Growth Was Induced in SH-SY5Y Cells by Factors Released from RSV-Treated Caco-2 Cells
3.3. SH-SY5Y Cell Neuritis Was Induced by Exosomes Produced from RSV-Treated Caco-2 Cells
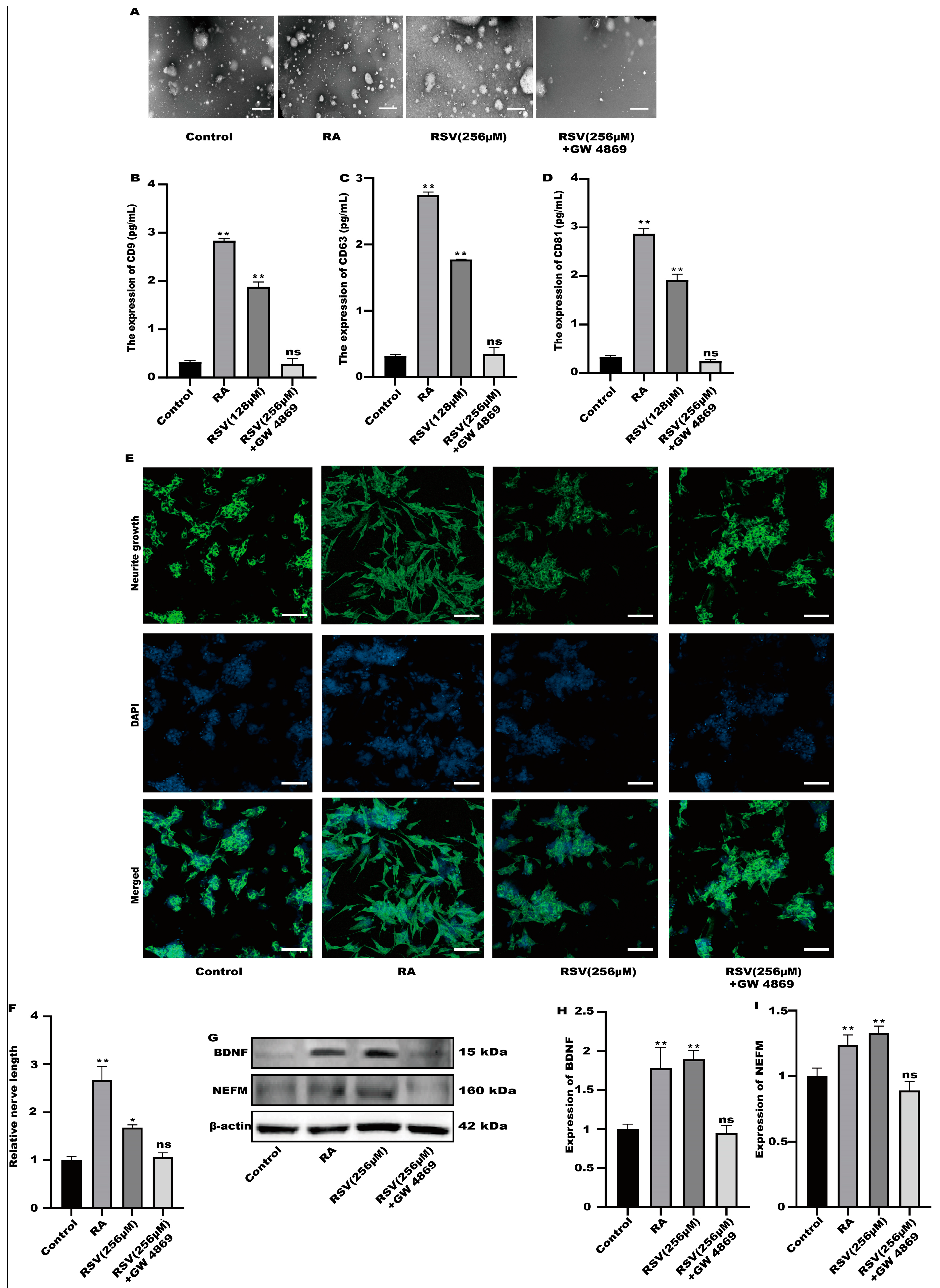
3.4. SH-SY5Y Cells Could Not Be Activated after the Production of Exosomes Was Inhibited
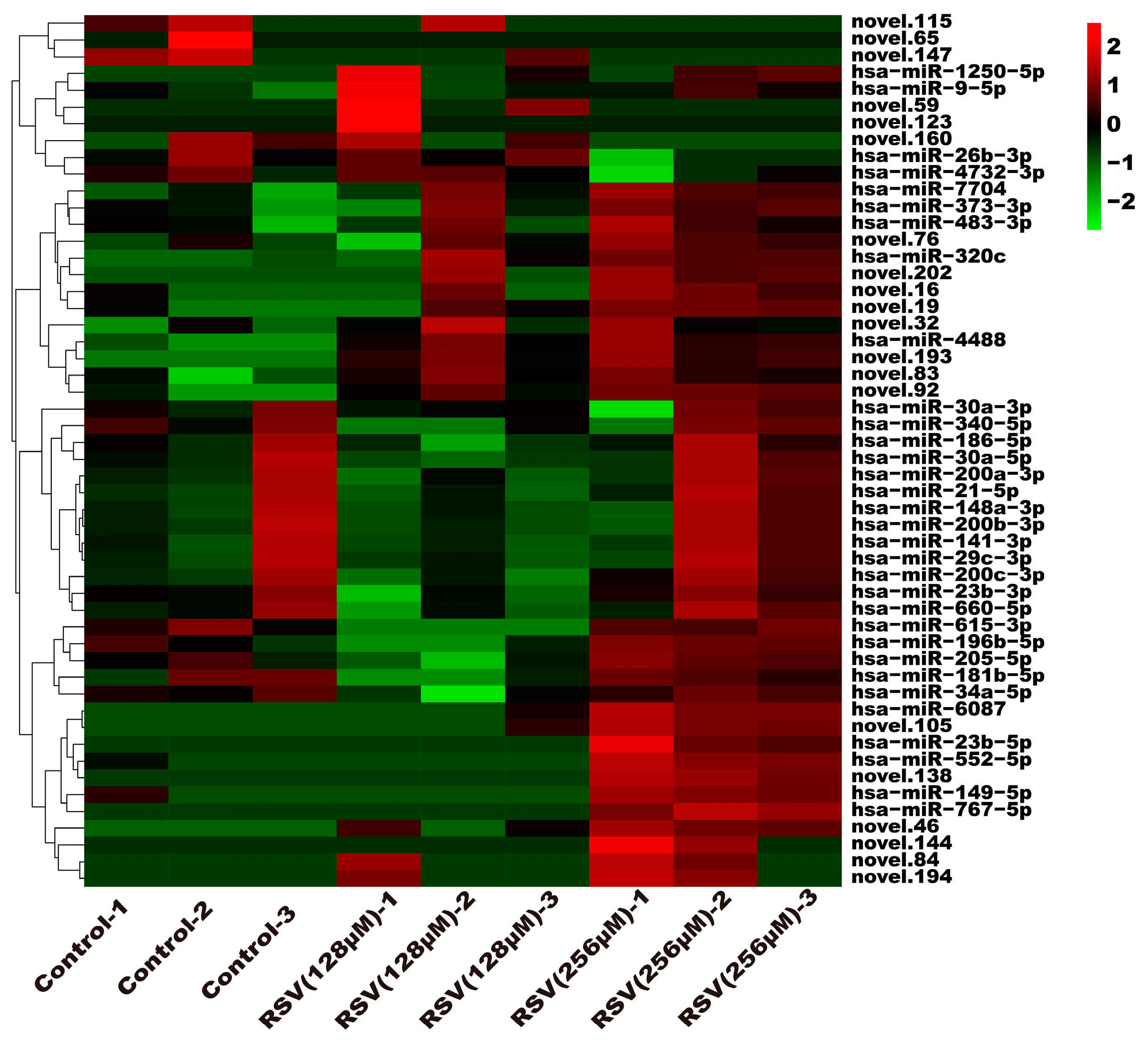
3.5. Analysis of Exosome miRNA Expression Profiles
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RSV | Resveratrol |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| NEAA | Nonessential amino acids |
| MEM | Modified Eagle Medium |
| NEFM | Neurofilament medium polypeptide |
| BDNF | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| RNA-seq | RNA sequencing |
| GO | Gene ontology |
| KEGG | Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes |
References
- Xiao, Y.; Qin, T.; Sun, L.; Qian, W.; Li, J.; Duan, W.; Lei, J.; Wang, Z.; Ma, J.; Li, X.; et al. Resveratrol Ameliorates the Malignant Progression of Pancreatic Cancer by Inhibiting Hypoxia-induced Pancreatic Stellate Cell Activation. Cell Transplant. 2020, 29, 963689720929987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.S.; Li, Y.S.; Kuo, Y.C.; Tsai, S.J.; Lin, C.C. Preparation and Evaluation of Novel Transfersomes Combined with the Natural Antioxidant Resveratrol. Molecules 2019, 24, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motlagh Scholle, L.; Schieffers, H.; Al-Robaiy, S.; Thaele, A.; Dehghani, F.; Lehmann Urban, D.; Zierz, S. The Effect of Resveratrol on Mitochondrial Function in Myoblasts of Patients with the Common m.3243A>G Mutation. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, N.D.; Gutierrez, G.; Matos, M.; Fernandez, M.A. Preservation of the Antioxidant Capacity of Resveratrol via Encapsulation in Niosomes. Foods 2021, 10, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Huang, H.; Zheng, F.; Liu, H.; Qiu, F.; Chen, Y.; Liang, C.L.; Dai, Z. Resveratrol exerts antitumor effects by downregulating CD8+CD122+ Tregs in murine hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncoimmunology 2020, 9, 1829346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yon, J.M.; Kim, Y.B.; Park, D. The Ethanol Fraction of White Rose Petal Extract Abrogates Excitotoxicity-Induced Neuronal Damage In Vivo and In Vitro through Inhibition of Oxidative Stress and Proinflammation. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penumathsa, S.V.; Thirunavukkarasu, M.; Koneru, S.; Juhasz, B.; Zhan, L.; Pant, R.; Menon, V.P.; Otani, H.; Maulik, N. Statin and resveratrol in combination induces cardioprotection against myocardial infarction in hypercholesterolemic rat. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2007, 42, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Xu, J.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wu, D.; Zhang, H.; Qin, J. Molecular Analysis of UV-C Induced Resveratrol Accumulation in Polygonum cuspidatum Leaves. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, H.; Kim, Y.S.; Koehler, R.C.; Doré, S. Potential mechanism by which resveratrol, a red wine constituent, protects neurons. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 993, 276–286, discussion 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ates, O.; Cayli, S.R.; Yucel, N.; Altinoz, E.; Kocak, A.; Durak, M.A.; Turkoz, Y.; Yologlu, S. Central nervous system protection by resveratrol in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2007, 14, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.S.; Zheng, W.H.; Bastianetto, S.; Chabot, J.G.; Quirion, R. Neuroprotective effects of resveratrol against beta-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity in rat hippocampal neurons: Involvement of protein kinase C. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 141, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Yu, S.; Simonyi, A.; Rottinghaus, G.; Sun, G.Y.; Sun, A.Y. Resveratrol protects against neurotoxicity induced by kainic acid. Neurochem. Res. 2004, 29, 2105–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Xu, J.; Rottinghaus, G.E.; Simonyi, A.; Lubahn, D.; Sun, G.Y.; Sun, A.Y. Resveratrol protects against global cerebral ischemic injury in gerbils. Brain Res. 2002, 958, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.T.; Chiou, R.Y.; Chen, L.G.; Chen, M.H.; Tseng, W.T.; Hsieh, H.T.; Yang, Y.L. Neuroprotective effects of resveratrol on cerebral ischemia-induced neuron loss mediated by free radical scavenging and cerebral blood flow elevation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 3126–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Q.; Zhang, Z.D.; Lu, X.R.; Qin, Z.; Liu, X.W.; Li, S.H.; Bai, L.X.; Ge, B.W.; Li, J.Y.; Yang, Y.J. Multi-omics reveals aspirin eugenol ester alleviates neurological disease. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 166, 115311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Wang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Feng, S.; Fu, Y.; Luo, Y. Metformin Inhibits Tumor Metastasis through Suppressing Hsp90α Secretion in an AMPKα1-PKCγ Dependent Manner. Cells 2020, 9, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisatsune, T.; Kaneko, J.; Kurashige, H.; Cao, Y.; Satsu, H.; Totsuka, M.; Katakura, Y.; Imabayashi, E.; Matsuda, H. Effect of Anserine/Carnosine Supplementation on Verbal Episodic Memory in Elderly People. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2016, 50, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Pinilla, F. Brain foods: The effects of nutrients on brain function. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo de Sa, F.D.; Heimesaat, M.M.; Bereswill, S.; Nattramilarasu, P.K.; Schulzke, J.D.; Bucker, R. Resveratrol Prevents Campylobacter jejuni-Induced Leaky gut by Restoring Occludin and Claudin-5 in the Paracellular Leak Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 640572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro, M.D.; Nowomiejska, K.; Avitabile, T.; Rejdak, R.; Tripodi, S.; Porta, A.; Reibaldi, M.; Figus, M.; Posarelli, C.; Fiedorowicz, M. Effect of Resveratrol on In Vitro and In Vivo Models of Diabetic Retinophathy: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ano, Y.; Takaichi, Y.; Uchida, K.; Kondo, K.; Nakayama, H.; Takashima, A. Iso-alpha-Acids, the Bitter Components of Beer, Suppress Microglial Inflammation in rTg4510 Tauopathy. Molecules 2018, 23, 3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iturri, J.; Weber, A.; Moreno-Cencerrado, A.; Vivanco, M.D.; Benitez, R.; Leporatti, S.; Toca-Herrera, J.L. Resveratrol-Induced Temporal Variation in the Mechanical Properties of MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells Investigated by Atomic Force Microscopy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zang, N.; Zhou, N.; Li, W.; Xie, X.; Deng, Y.; Ren, L.; Long, X.; Li, S.; Zhou, L.; et al. Resveratrol inhibits the TRIF-dependent pathway by upregulating sterile alpha and armadillo motif protein, contributing to anti-inflammatory effects after respiratory syncytial virus infection. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 4229–4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.; Wang, W. A Systemic Review on the Regulatory Roles of miR-34a in Gastrointestinal Cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 2855–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zempleni, J.; Sukreet, S.; Zhou, F.; Wu, D.; Mutai, E. Milk-Derived Exosomes and Metabolic Regulation. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2019, 7, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugihara, Y.; Onoue, S.; Tashiro, K.; Sato, M.; Hasegawa, T.; Katakura, Y. Carnosine induces intestinal cells to secrete exosomes that activate neuronal cells. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inotsuka, R.; Uchimura, K.; Yamatsu, A.; Kim, M.; Katakura, Y. gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) activates neuronal cells by inducing the secretion of exosomes from intestinal cells. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 9285–9290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Erviti, L.; Seow, Y.; Yin, H.; Betts, C.; Lakhal, S.; Wood, M.J. Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by systemic injection of targeted exosomes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Record, M.; Subra, C.; Silvente-Poirot, S.; Poirot, M. Exosomes as intercellular signalosomes and pharmacological effectors. Biochem. Pharmacology. 2011, 81, 1171–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Li, G.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, J.; Yang, L.; Huang, J. miR-199a decreases Neuritin expression involved in the development of Alzheimer’s disease in APP/PS1 mice. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 46, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Parker Kerrigan, B.C.; Yang, D.; Hu, L.; Shmulevich, I.; Sood, A.K.; Xue, F.; Zhang, W. Post-transcriptional regulatory network of epithelial-to-mesenchymal and mesenchymal-to-epithelial transitions. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2014, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, A.U.; Khan, P.; Maurya, S.K.; Siddiqui, J.A.; Santamaria-Barria, J.A.; Batra, S.K.; Nasser, M.W. Liquid biopsies to occult brain metastasis. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| miRNA | Function of Target Genes |
|---|---|
| miR-122-5p | Transduction of nerve signals |
| miR-199a-3p | Parkinson’s disease |
| miR-199b-3p | Role in development of nervous system |
| miR-320c | Neurodegeneration |
| miR-215-5p | The neurexin family |
| miR-146b-3p | AMPK signaling pathway |
| miR-199a-5p | Ras signaling pathway |
| miR-432-5p | Function in synaptic vesicle exocytosis |
| miR-105-5p | Neurodegenerative disorder |
| miR-199b-5p | Alzheimer’s disease |
| miR-411-5p | Axon guidance |
| miR-483-3p | Phospholipase D signaling pathway |
| miR-6808-3p | Cholinergic synapse |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Tao, Q.; Bai, L.; Qin, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; Yang, Y.; Ge, W.; Li, J. MicroRNA in the Exosomes Mediated by Resveratrol to Activate Neuronal Cells. Toxics 2024, 12, 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12020122
Zhang Z, Tao Q, Bai L, Qin Z, Liu X, Li S, Yang Y, Ge W, Li J. MicroRNA in the Exosomes Mediated by Resveratrol to Activate Neuronal Cells. Toxics. 2024; 12(2):122. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12020122
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhendong, Qi Tao, Lixia Bai, Zhe Qin, Xiwang Liu, Shihong Li, Yajun Yang, Wenbo Ge, and Jianyong Li. 2024. "MicroRNA in the Exosomes Mediated by Resveratrol to Activate Neuronal Cells" Toxics 12, no. 2: 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12020122
APA StyleZhang, Z., Tao, Q., Bai, L., Qin, Z., Liu, X., Li, S., Yang, Y., Ge, W., & Li, J. (2024). MicroRNA in the Exosomes Mediated by Resveratrol to Activate Neuronal Cells. Toxics, 12(2), 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12020122







