The Impact of Agroecosystems on Nitrous Acid (HONO) Emissions during Spring and Autumn in the North China Plain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Measurements and Data
2.2. Data Processing and Definitions of Morning Peaks
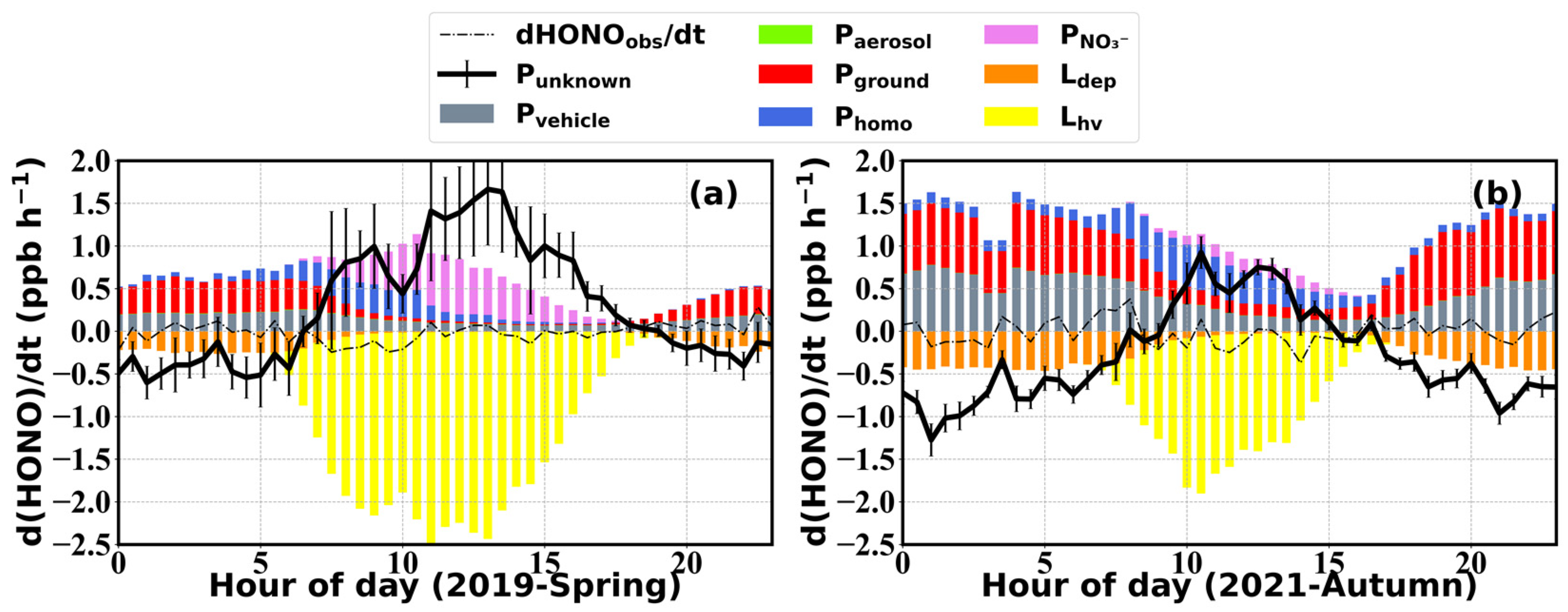
2.3. HONO Budget Analysis
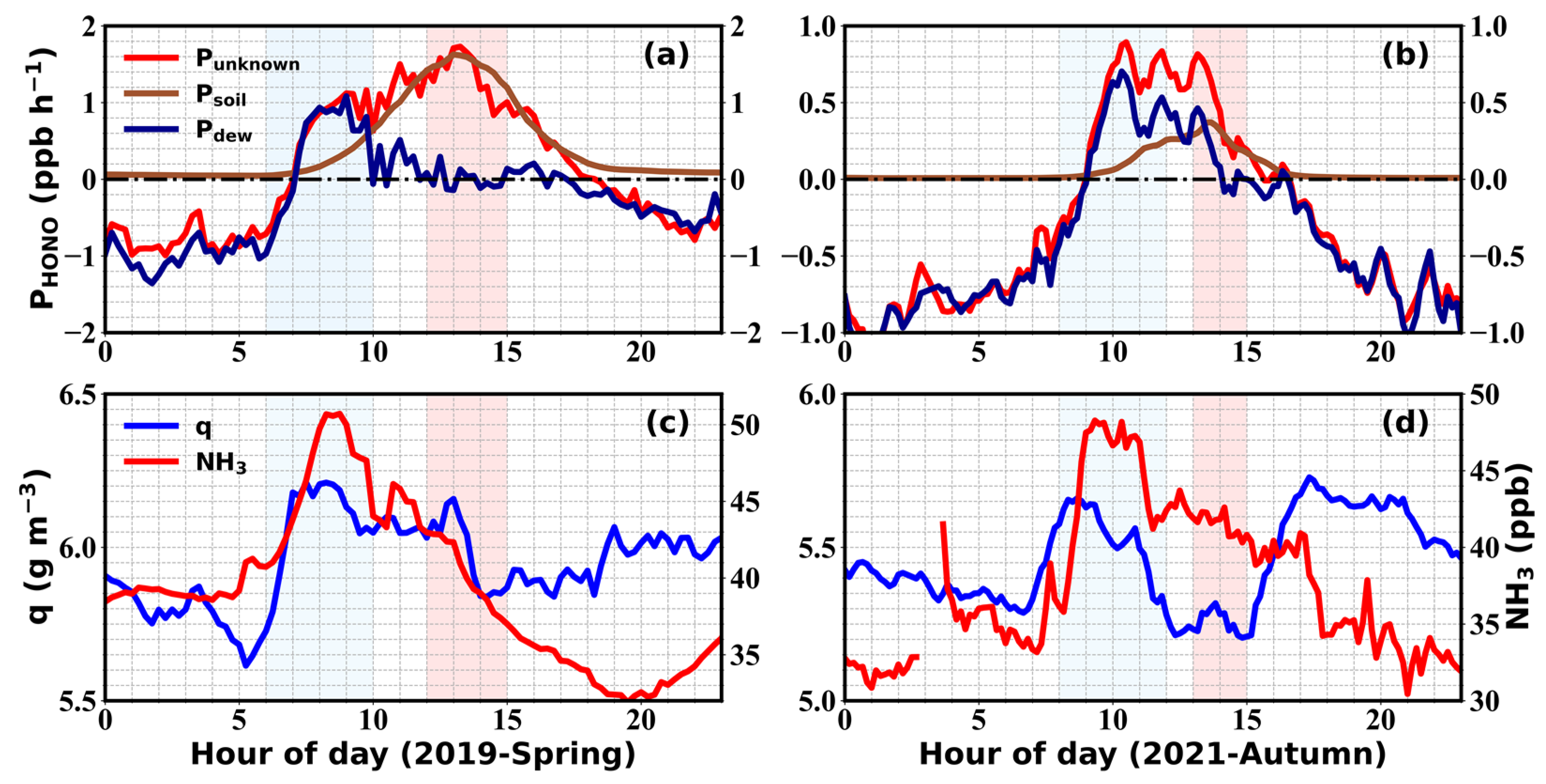
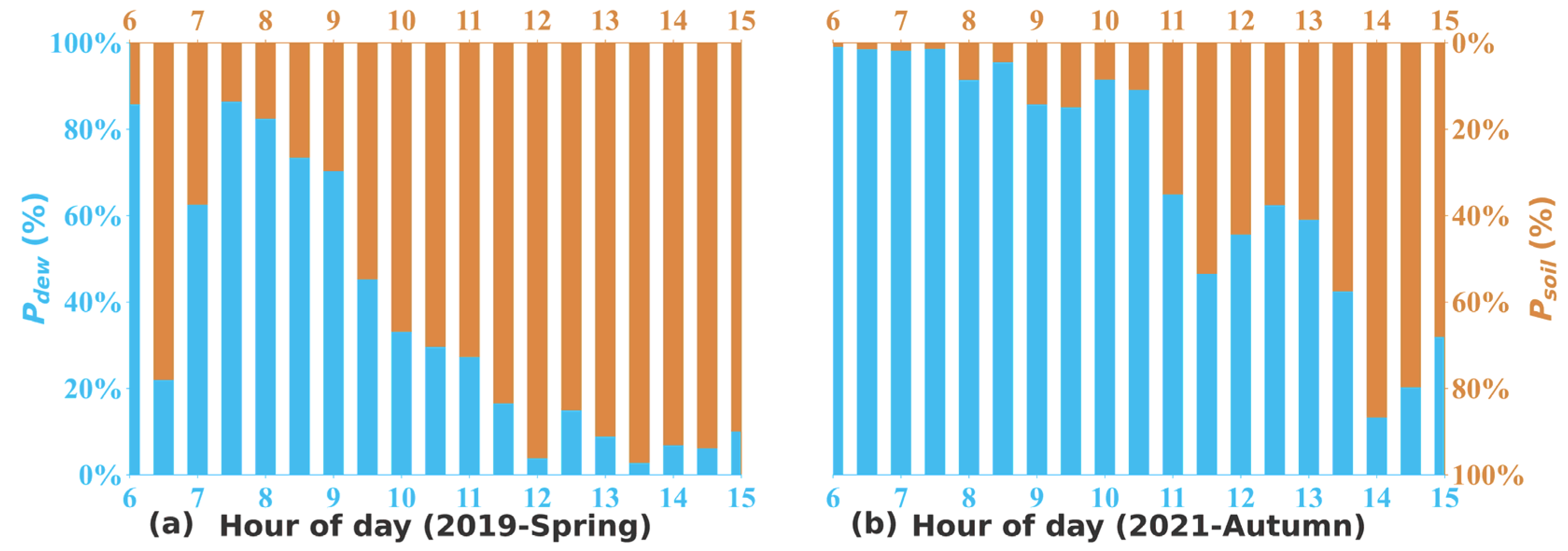
2.4. Derivation of Soil and Dew Water HONO Emissions
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Variations of HONO and NH3
3.2. Budget of HONO
3.3. Soil Emissions of HONO and NH3
4. Conclusions and Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Finlayson-Pitts, B.J.; Pitts, J.N., Jr. Tropospheric air pollution: Ozone, airborne toxics, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and particles. Science 1997, 276, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleffmann, J.; Gavriloaiei, T.; Hofzumahaus, A.; Holland, F.; Koppmann, R.; Rupp, L.; Schlosser, E.; Siese, M.; Wahner, A. Daytime formation of nitrous acid: A major source of OH radicals in a forest. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L05818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, H., 2nd. Normal atmosphere: Large radical and formaldehyde concentrations predicted. Science 1971, 173, 141–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Guo, S.; Tan, Z.; Wang, H.; Shang, D.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, Z.; Hu, M.; Zhang, Y. Exploring atmospheric free-radical chemistry in China: The self-cleansing capacity and the formation of secondary air pollution. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2019, 6, 579–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Shi, X.; Ma, Y.; Ren, X.; Jabbour, H.; Diao, Y.; Wang, W.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, W. Contribution of nitrous acid to the atmospheric oxidation capacity in an industrial zone in the Yangtze River Delta region of China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 5457–5475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tong, S.; Jia, C.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Wang, W.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Ji, D.; et al. The Levels and Sources of Nitrous Acid (HONO) in Winter of Beijing and Sanmenxia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2022, 127, e2021JD036278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Takeuchi, M.; Chen, C.; Qiu, Y.; Xie, C.; Xu, W.; Ma, N.; Worsnop, D.R.; Ng, N.L.; Sun, Y. Estimation of particulate organic nitrates from thermodenuder–aerosol mass spectrometer measurements in the North China Plain. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2021, 14, 3693–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Zu, K.; Lian, C.; Chen, S.; Dong, H.; Feng, M.; Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Lu, K.; et al. Elucidating the effect of HONO on O3 pollution by a case study in southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 144127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Hu, R.; Xie, P.; Lou, S.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Qin, M.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. Observation and simulation of HOx radicals in an urban area in Shanghai, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 810, 152275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, F.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhao, J. Photochemical Aging of Beijing Urban PM2.5: HONO Production. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 6309–6316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klosterköther, A.; Kurtenbach, R.; Wiesen, P.; Kleffmann, J. Determination of the emission indices for NO, NO2, HONO, HCHO, CO, and particles emitted from candles. Indoor Air 2021, 31, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, L.J.; Crilley, L.R.; Adams, T.J.; Ball, S.M.; Pope, F.D.; Bloss, W.J. Nitrous acid (HONO) emissions under real-world driving conditions from vehicles in a UK road tunnel. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 5231–5248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, K.; Ma, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, W.; Wu, Y.; Peng, J.; Shuai, S.; Hu, M.; Zhang, Y. Direct emission of nitrous acid (HONO) from gasoline cars in China determined by vehicle chassis dynamometer experiments. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 169, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, B.B.; Peng, Q.; Hall, S.R.; Ullmann, K.; Campos, T.L.; Weinheimer, A.; Montzka, D.; Tyndall, G.; Permar, W.; Hu, L.; et al. Spatially Resolved Photochemistry Impacts Emissions Estimates in Fresh Wildfire Plumes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL095443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, B.; Vogel, H.; Kleffmann, J.; Kurtenbach, R. Measured and simulated vertical profiles of nitrous acid—Part II. Model simulations and indications for a photolytic source. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 2957–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Ye, C.; Zhang, C.; Catoire, V.; Liu, P.; Gu, R.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Z.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, W.; et al. Evidence for Strong HONO Emission from Fertilized Agricultural Fields and its Remarkable Impact on Regional O3 Pollution in the Summer North China Plain. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2021, 5, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, N.; TerAvest, M.; Tang, D.; Hou, J.; Bertman, S.; Alaghmand, M.; Shepson, P.B.; Carroll, M.A.; Griffith, S.; et al. Nitric acid photolysis on forest canopy surface as a source for tropospheric nitrous acid. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 440–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhou, L.; Liu, S.; Lian, C.; Wang, W.; Liu, H.; Li, C.; Liu, Y.; Luo, L.; Xiao, K.; et al. Primary sources of HONO vary during the daytime: Insights based on a field campaign. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 903, 166605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; An, J.; Min, M.; Zhang, W.; Wang, F.; Xie, P. Impacts of HONO sources on the air quality in Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei Province of China. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 4735–4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, C.; Liu, P.; He, X.; Li, X.; Mu, Y. The seasonal variations and potential sources of nitrous acid (HONO) in the rural North China Plain. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 311, 119967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Su, H.; Li, X.; Cheng, Y.; Lu, K.; Cheng, P.; Gu, J.; Guo, S.; Hu, M.; Zeng, L.; et al. Daytime HONO formation in the suburban area of the megacity Beijing, China. Sci. China Chem. 2014, 57, 1032–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.A.; Huang, Z.; Bilal, M.; Assiri, M.E.; Mhawish, A.; Nichol, J.E.; de Leeuw, G.; Almazroui, M.; Wang, Y.; Alsubhi, Y. Long-term PM2.5 pollution over China: Identification of PM2.5 pollution hotspots and source contributions. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 893, 164871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, C.S.; Ma, N.; Liu, P.F.; Göbel, T.; Hallbauer, E.; Deng, Z.Z.; Ran, L.; Xu, W.Y.; Liang, Z.; et al. A parameterization of low visibilities for hazy days in the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 4935–4950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Liu, J.; Zhao, T.; Xu, X.; Han, H.; Wang, H.; Shu, Z. Atmospheric transport drives regional interactions of ozone pollution in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B. Analysis of the Vegetation Cover Change and the Relative Role of Its Influencing Factors in North China. J. Nat. Resour. 2015, 30, 12–23. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, W.; Tang, A.; Shen, J.; Cui, Z.; Vitousek, P.; Erisman, J.W.; Goulding, K.; Christie, P.; et al. Enhanced nitrogen deposition over China. Nature 2013, 494, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Reis, S.; Xu, J.; Gu, B. A high-resolution map of reactive nitrogen inputs to China. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Li, R.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, Y.; Fu, H.; Chen, J. An observational study of nitrous acid (HONO) in Shanghai, China: The aerosol impact on HONO formation during the haze episodes. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 630, 1057–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Bao, F.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, D.; Chen, C.; Zhao, J. Direct Formation of Electronic Excited NO2 Contributes to the High Yield of HONO during Photosensitized Renoxification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 11144–11151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monge, M.E.; D’Anna, B.; Mazri, L.; Giroir-Fendler, A.; Ammann, M.; Donaldson, D.J.; George, C. Light changes the atmospheric reactivity of soot. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6605–6609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricker, H.M.; Leonardi, A.; Navea, J.G. Reduction and Photoreduction of NO2 in Humic Acid Films as a Source of HONO, ClNO, N2O, NOx, and Organic Nitrogen. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2022, 6, 3066–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Ren, E.; Hu, M.; Fu, Q.; Duan, Y.; Huang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, S. Budget of atmospheric nitrous acid (HONO) during the haze and clean periods in Shanghai: Importance of heterogeneous reactions. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 900, 165717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, R.; Shen, H.; Xue, L.; Wang, T.; Gao, J.; Li, H.; Liang, Y.; Xia, M.; Yu, C.; Liu, Y.; et al. Investigating the sources of atmospheric nitrous acid (HONO) in the megacity of Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 812, 152270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.-J.; Yang, L.; Cao, J.; Wang, Q.; Tie, X.; Ho, K.-F.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, R.; Li, G.; Zhu, C.; et al. Concentration and sources of atmospheric nitrous acid (HONO) at an urban site in Western China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 593–594, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Brauers, T.; Häseler, R.; Bohn, B.; Fuchs, H.; Hofzumahaus, A.; Holland, F.; Lou, S.; Lu, K.D.; Rohrer, F.; et al. Exploring the atmospheric chemistry of nitrous acid (HONO) at a rural site in Southern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 1497–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Zhang, C.; Ye, C.; Liu, P.; Catoire, V.; Krysztofiak, G.; Chen, H.; Ren, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; et al. HONO Budget and Its Role in Nitrate Formation in the Rural North China Plain. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 11048–11057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oswald, R.; Behrendt, T.; Ermel, M.; Wu, D.; Su, H.; Cheng, Y.; Breuninger, C.; Moravek, A.; Mougin, E.; Delon, C.; et al. HONO emissions from soil bacteria as a major source of atmospheric reactive nitrogen. Science 2013, 341, 1233–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Horn, M.A.; Behrendt, T.; Müller, S.; Li, J.; Cole, J.A.; Xie, B.; Ju, X.; Li, G.; Ermel, M.; et al. Soil HONO emissions at high moisture content are driven by microbial nitrate reduction to nitrite: Tackling the HONO puzzle. ISME J. 2019, 13, 1688–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Kuang, Y.; Liu, C.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhai, M.; Zhang, G.; Xu, W.; Cheng, H.; Liu, Y.; et al. Severe photochemical pollution formation associated with strong HONO emissions from dew and guttation evaporation. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 913, 169309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, M.A.; Lissi, E.; Villena, G. Nitrite in rain and dew in Santiago city, Chile. Its possible impact on the early morning start of the photochemical smog. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhou, X.; Hou, J.; Gao, H.; Bertman, S.B. Importance of dew in controlling the air-surface exchange of HONO in rural forested environments. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L02813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Tang, J.; Lin, Y. Chemical Compositions of Dew and Scavenging of Particles in Changchun, China. Adv. Meteorol. 2015, 2015, 104048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Stieger, B.; Spindler, G.; Grosselin, B.; Mellouki, A.; Tuch, T.; Wiedensohler, A.; Herrmann, H. Role of the dew water on the ground surface in HONO distribution: A case measurement in Melpitz. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 13069–13089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, K. Observation and simulation of dew in rural and urban environments. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2004, 28, 76–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.N.; Brimblecombe, P. Dew and guttation: Formation and environmental significance. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1994, 67, 173–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; Xu, W.; Lin, W.; Meng, Z.; Zhao, H.; Ren, S.; Zhang, G.; Liang, L.; Xu, X. Explosive morning growth phenomena of NH3 on the North China Plain: Causes and potential impacts on aerosol formation. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 257, 113621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.X.; Zhao, C.S.; Ma, N.; Chen, J.; Xu, W.Y. A study of aerosol liquid water content based on hygroscopicity measurements at high relative humidity in the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 6417–6426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Kuang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Tao, J.; Zhao, G.; Bian, Y.; Yang, W.; Yu, Y.; Shen, C.; Liang, L.; et al. NH3-promoted hydrolysis of NO2 induces explosive growth in HONO. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 10557–10570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; He, Y.; Xu, W.; Yuan, B.; Zhang, G.; Ma, Z.; Wu, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S.; et al. Photochemical Aqueous-Phase Reactions Induce Rapid Daytime Formation of Oxygenated Organic Aerosol on the North China Plain. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3849–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Kuang, Y.; Liang, L.; He, Y.; Cheng, H.; Bian, Y.; Tao, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, P.; Ma, N.; et al. Dust-Dominated Coarse Particles as a Medium for Rapid Secondary Organic and Inorganic Aerosol Formation in Highly Polluted Air. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 15710–15721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; Xu, W.; Tao, J.; Luo, B.; Liu, L.; Xu, H.; Xu, W.; Xue, B.; Zhai, M.; Liu, P.; et al. Divergent Impacts of Biomass Burning and Fossil Fuel Combustion Aerosols on Fog-Cloud Microphysics and Chemistry: Novel Insights From Advanced Aerosol-Fog Sampling. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2024, 51, e2023GL107147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; Tao, J.; Xu, W.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, G.; Shen, C.; Bian, Y.; Zhao, C. Calculating ambient aerosol surface area concentrations using aerosol light scattering enhancement measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 216, 116919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Tao, J.; Bian, Y.; Ma, N.; Zhao, G. A novel method for deriving the aerosol hygroscopicity parameter based only on measurements from a humidified nephelometer system. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 6651–6662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Bozzetti, C.; Ho, K.-F.; Cao, J.-J.; Han, Y.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Slowik, J.G.; Platt, S.M.; Canonaco, F.; et al. High secondary aerosol contribution to particulate pollution during haze events in China. Nature 2014, 514, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, B.; Kuang, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhao, P. Joint increase of aerosol scattering efficiency and aerosol hygroscopicity aggravate visibility impairment in the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 839, 156279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinh, H.T.; Imanishi, K.; Morikawa, T.; Hagino, H.; Takenaka, N. Gaseous nitrous acid (HONO) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) emission from gasoline and diesel vehicles under real-world driving test cycles. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2017, 67, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Song, W.; Zhan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Tong, S.; Pei, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Contribution of Vehicle Emission and NO2 Surface Conversion to Nitrous Acid (HONO) in Urban Environments: Implications from Tests in a Tunnel. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 15616–15624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spataro, F.; Ianniello, A.; Esposito, G.; Allegrini, I.; Zhu, T.; Hu, M. Occurrence of atmospheric nitrous acid in the urban area of Beijing (China). Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 447, 210–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, G.; Ma, N.; He, Y.; Zhu, S.; Pan, X.; Dong, W.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, Q.; Ditas, J.; et al. Exploring HONO formation and its role in driving secondary pollutants formation during winter in the North China Plain. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 132, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Qin, M.; Fang, W.; Duan, J.; Tang, K.; Zhang, H.; Shao, D.; Liao, Z.; Feng, Y.; Huang, Y.; et al. Measurement of HONO flux using the aerodynamic gradient method over an agricultural field in the Huaihe River Basin, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 114, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Ye, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Liu, P.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, X.; Liu, J.; Mu, Y. Development and application of a twin open-top chambers method to measure soil HONO emission in the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, F.; Cheng, Y.; Kuhn, U.; Li, G.; Wang, W.; Kratz, A.M.; Weber, J.; Weber, B.; Pöschl, U.; Su, H. Key Role of Equilibrium HONO Concentration over Soil in Quantifying Soil–Atmosphere HONO Fluxes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 2204–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Xue, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, P.; Bao, F.; Li, X.; Mu, Y. Measurement report: Exchange fluxes of HONO over agricultural fields in the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 15733–15747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Fuchs, H.; Lu, K.; Hofzumahaus, A.; Bohn, B.; Broch, S.; Dong, H.; Gomm, S.; Häseler, R.; He, L.; et al. Radical chemistry at a rural site (Wangdu) in the North China Plain: Observation and model calculations of OH, HO2 and RO2 radicals. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 663–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Tan, Z.; Lu, K.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Chen, S.; Novelli, A.; Cho, C.; et al. Winter photochemistry in Beijing: Observation and model simulation of OH and HO2 radicals at an urban site. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VandenBoer, T.C.; Brown, S.S.; Murphy, J.G.; Keene, W.C.; Young, C.J.; Pszenny, A.A.P.; Kim, S.; Warneke, C.; de Gouw, J.A.; Maben, J.R.; et al. Understanding the role of the ground surface in HONO vertical structure: High resolution vertical profiles during NACHTT-11. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 10155–10171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Su, H.; Li, G.; Ma, N.; Pöschl, U.; Cheng, Y. Relative importance of gas uptake on aerosol and ground surfaces characterized by equivalent uptake coefficients. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 10981–11011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Han, C.; Zhang, T.; Tang, N.; Yang, H.; Xue, X. Heterogeneous photochemical uptake of NO2 on the soil surface as an important ground-level HONO source. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 271, 116289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, C.; Strekowski, R.S.; Kleffmann, J.; Stemmler, K.; Ammann, M. Photoenhanced uptake of gaseous NO2 on solid organic compounds: A photochemical source of HONO? Faraday Discuss. 2005, 130, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, S.; Mekic, M.; Jiang, H.; Zhou, W.; Loisel, G.; Song, W.; Wang, X.; Gligorovski, S. Photoenhanced Uptake of NO2 and HONO Formation on Real Urban Grime. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2019, 6, 413–417. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.; Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, Z.; Xia, M.; Yun, H.; Wang, W.; Yu, C.; Yue, D.; et al. The significant contribution of HONO to secondary pollutants during a severe winter pollution event in southern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Ma, Z.; Yang, S.; Yao, D.; Zhao, S.; Hu, B.; Tang, G.; Sun, J.; Cheng, M.; et al. Detailed budget analysis of HONO in Beijing, China: Implication on atmosphere oxidation capacity in polluted megacity. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 244, 117957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Cheng, P.; Yang, W. Aloft HONO measurement and its impact on atmospheric oxidation at the Canton Tower. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2023, 44, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michoud, V.; Colomb, A.; Borbon, A.; Miet, K.; Beekmann, M.; Camredon, M.; Aumont, B.; Perrier, S.; Zapf, P.; Siour, G.; et al. Study of the unknown HONO daytime source at a European suburban site during the MEGAPOLI summer and winter field campaigns. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 2805–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.; Spolaor, M.; Colosimo, S.F.; Pikelnaya, O.; Cheung, R.; Williams, E.; Gilman, J.B.; Lerner, B.M.; Zamora, R.J.; Warneke, C.; et al. Nitrous acid formation in a snow-free wintertime polluted rural area. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 1977–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shon, Z.H.; Lee, G.; Song, S.K.; Lee, M.; Han, J.; Lee, D. Characteristics of reactive nitrogen compounds and other relevant trace gases in the atmosphere at urban and rural areas of Korea during May–June, 2004. J. Atmos. Chem. 2007, 58, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, R.; Zheng, P.; Chen, T.; Dong, C.; Wang, Y.n.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Han, G.; Wang, X.; et al. Atmospheric nitrous acid (HONO) at a rural coastal site in North China: Seasonal variations and effects of biomass burning. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 229, 117429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Zhao, X.; Liu, P.; Mu, J.; He, G.; Zhang, C.; Tong, S.; Xue, C.; Zhao, X.; Ge, M.; et al. Atmospheric NOx oxidation as major sources for nitrous acid (HONO). NPJ Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2023, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, W.; Yan, C.; Huang, D.D.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Qiao, X.; Guo, Y.; Tian, L.; Zheng, P.; Xu, Z.; et al. Secondary organic aerosol formed by condensing anthropogenic vapours over China’s megacities. Nat. Geosci. 2022, 15, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fu, X.; Wu, D.; Wang, M.; Lu, K.; Mu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T. Agricultural Fertilization Aggravates Air Pollution by Stimulating Soil Nitrous Acid Emissions at High Soil Moisture. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 14556–14566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

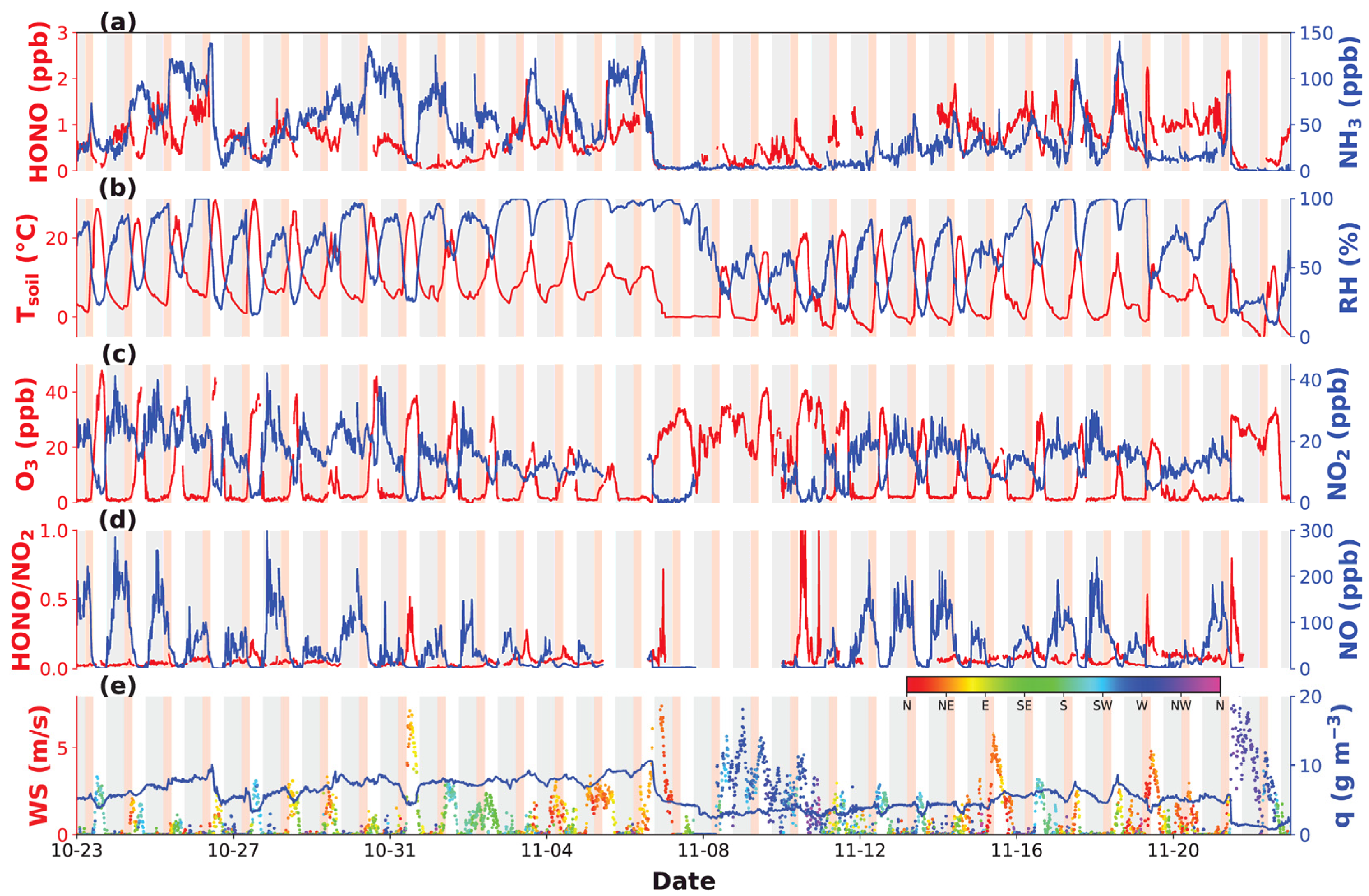
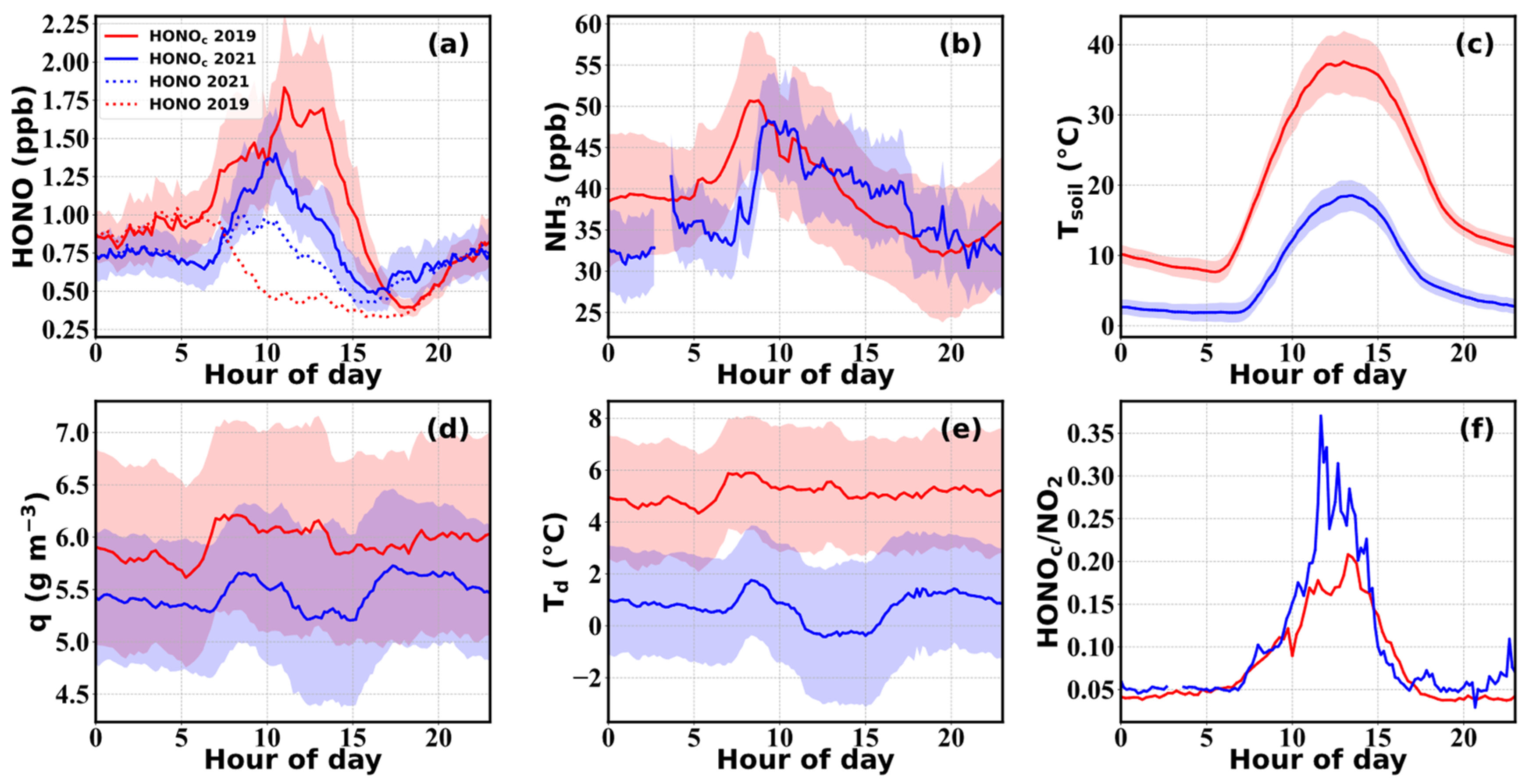
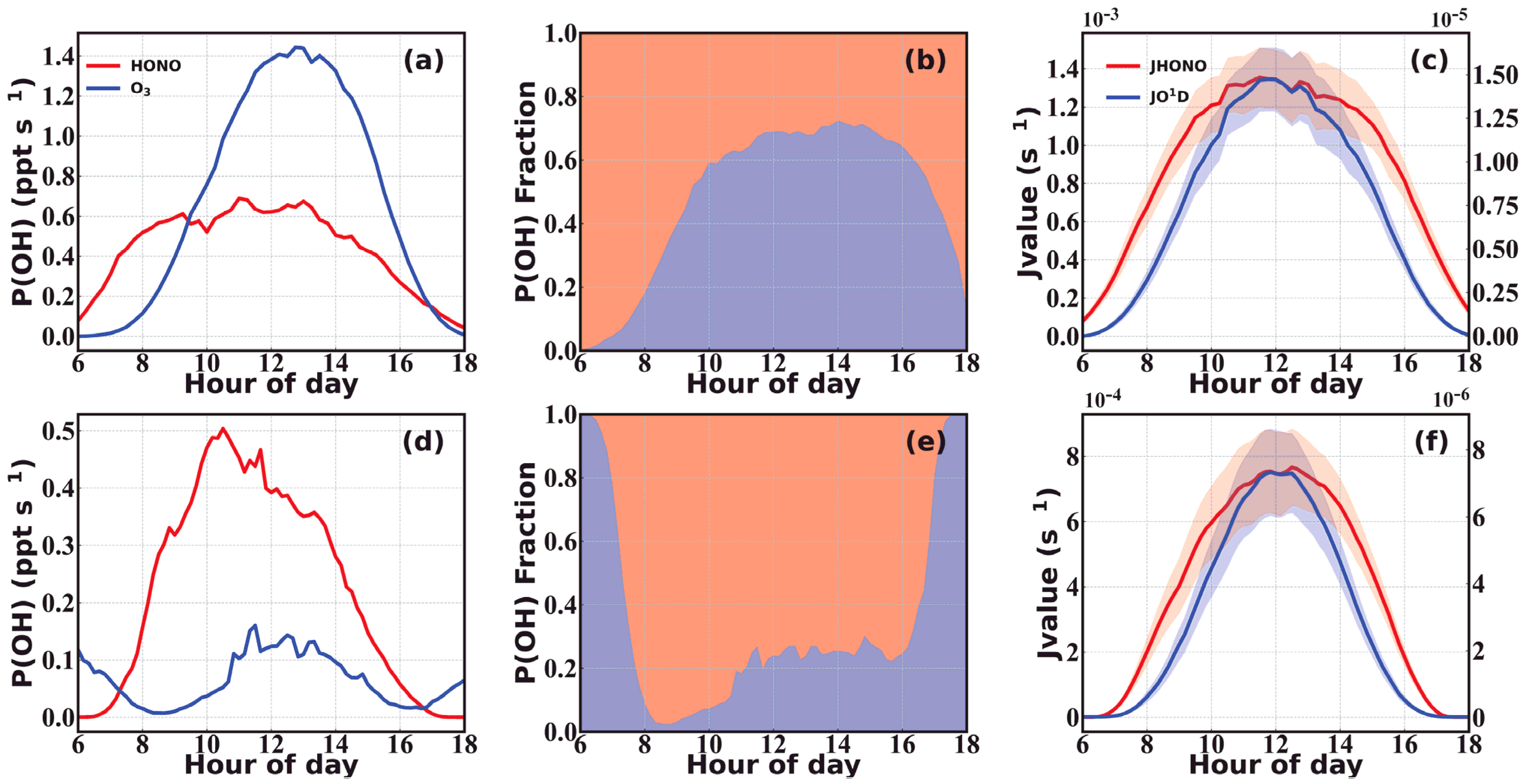
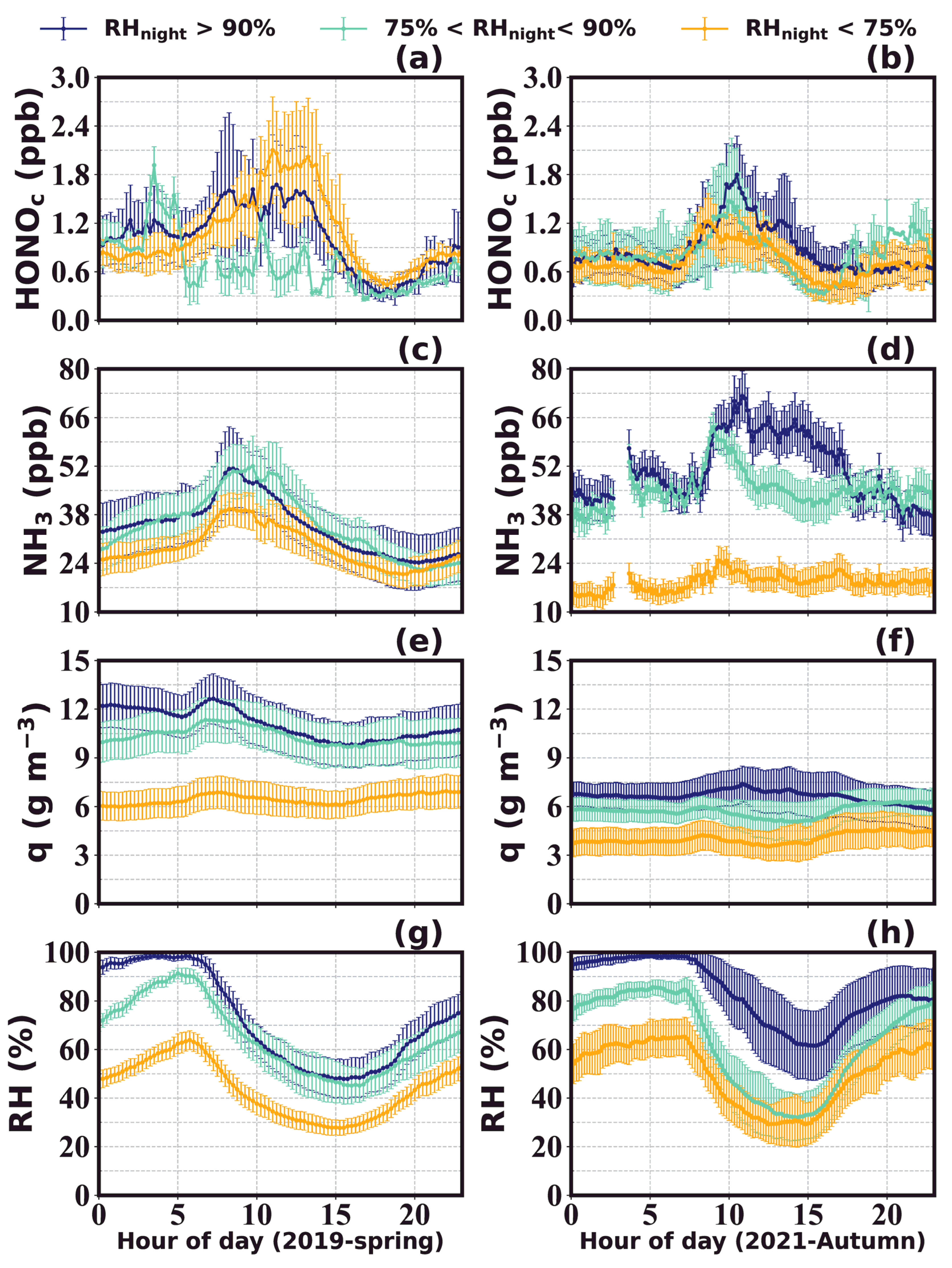

| Location | Period | HONO (ppbv) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Paris/France | July 2009 | 0.01–0.50 | [74] |
| Melpitz/Germany | April 2018 | 0.25 ± 0.11 | [43] |
| Utah/America | January–February 2012 | 0–0.27 | [75] |
| Seoul/Korea | June 2004 | 0.6 ± 0.8 | [76] |
| Dongying/China | June–July 2017 | 0.17 ± 0.20 | [77] |
| GC/China | October 2016 | 6.3 ± 4.6 | [48] |
| Wangdu/China | June 2017 | 1.1 ± 1.2 | [78] |
| Wangdu/China | December 2017 | 1.8 ± 1.4 | [20] |
| GC/China | April 2019 | 0.7 ± 0.4 | This study |
| Wangdu/China | June–August 2020 | 0.7 ± 0.5 | [20] |
| Wangdu/China | September 2020 | 0.8 ± 0.6 | [20] |
| GC/China | November 2021 | 0.7 ± 0.4 | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, J.; Xu, W.; Kuang, Y.; Xu, W.; Liu, C.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, H.; Ren, S.; Zhou, G.; Xu, X. The Impact of Agroecosystems on Nitrous Acid (HONO) Emissions during Spring and Autumn in the North China Plain. Toxics 2024, 12, 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12050331
Zeng J, Xu W, Kuang Y, Xu W, Liu C, Zhang G, Zhao H, Ren S, Zhou G, Xu X. The Impact of Agroecosystems on Nitrous Acid (HONO) Emissions during Spring and Autumn in the North China Plain. Toxics. 2024; 12(5):331. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12050331
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Jianhui, Wanyun Xu, Ye Kuang, Weiqi Xu, Chang Liu, Gen Zhang, Huarong Zhao, Sanxue Ren, Guangsheng Zhou, and Xiaobin Xu. 2024. "The Impact of Agroecosystems on Nitrous Acid (HONO) Emissions during Spring and Autumn in the North China Plain" Toxics 12, no. 5: 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12050331
APA StyleZeng, J., Xu, W., Kuang, Y., Xu, W., Liu, C., Zhang, G., Zhao, H., Ren, S., Zhou, G., & Xu, X. (2024). The Impact of Agroecosystems on Nitrous Acid (HONO) Emissions during Spring and Autumn in the North China Plain. Toxics, 12(5), 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12050331









