Measurement of Aerosol Particles from Vibrated Lab Coats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Experimental Results with Lab Coats (Used Lab Coat and New Lab Coat)
3.2. Experimental Results with the Suit
3.3. Experimental Results with the Shirt
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Friedlander, S.K. Smoke, Dust, and Haze: Fundamentals of Aerosol Dynamics, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hinds, W.C. Aerosol Technology: Properties, Behavior, and Measurement of Airborne Particles, 2nd ed.; A Wiley-Interscience Publication: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Geiser, M.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Kapp, N.; Schurch, S.; Kreyling, W.; Schulz, H.; Semmler, M.; Hof, V.I.; Heyder, J.; Gehr, P. Ultrafine particles cross cellular membranes by nonphagocytic mechanisms in lungs and in cultured cells. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 1555–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, C.; Chen, J.; Li, P.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Sang, B.; Li, R.; Shi, Y.; Cui, X.; Zhou, T. Respiratory Toxicology of Graphene-Based Nanomaterials: A Review. Toxics 2024, 12, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.U. Why does the SARS-CoV-2 Delta VOC spread so rapidly? Universal conditions for the rapid spread of respiratory viruses, minimum viral loads for viral aerosol generation, effects of vaccination on viral aerosol generation, and viral aerosol clouds. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Chen, Q.; Wu, B.; Rui, W.; Zheng, J.C.; Ding, W. Macrophages treated with particulate matter PM2.5 induce selective neurotoxicity through glutaminase-mediated glutamate generation. J. Neurochem. 2015, 134, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardo, M.; Li, C.; He, Q.; Levin-Zaidman, S.; Tsoory, M.; Yu, Q.; Wang, X.; Rudich, Y. Mechanisms of lung toxicity induced by biomass burning aerosols. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Sun, W.; Wei, L.; Ye, C.; Zhu, R. Association of Air Pollution with the Number of Common Respiratory Visits in Children in a Heavily Polluted Central City, China. Toxics 2023, 11, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Ambient Air Pollution: A Global Assessment of Exposure and Burden of Disease; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241511353 (accessed on 2 April 2024).
- Birgand, G.; Peiffer-Smadja, N.; Fournier, S.; Kerneis, S.; Lescure, F.X.; Lucet, J.C. Assessment of Air Contamination by SARS-CoV-2 in Hospital Settings. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2033232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, S.; Atkinson, B.; Onianwa, O.; Spencer, A.; Furneaux, J.; Grieves, J.; Taylor, C.; Milligan, I.; Bennett, A.; Fletcher, T.; et al. Air and surface sampling for monkeypox virus in a UK hospital: An observational study. Lancet Microbe 2022, 3, E904–E911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernaez, B.; Muñoz-Gómez, A.; Sanchiz, A.; Orviz, E.; Valls-Carbo, A.; Sagastagoitia, I.; Ayerdi, O.; Martín, R.; Puerta, T.; Vera, M.; et al. Monitoring monkeypox virus in saliva and air samples in Spain: A cross-sectional study. Lancet Microbe 2023, 10, E21–E28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.C.; Prather, K.A.; Sznitman, J.; Jimenez, J.L.; Lakdawala, S.S.; Tufekci, Z.; Marr, L.C. Airborne transmission of respiratory viruses. Science 2021, 373, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayana, T.B.; Wild, P.; Debatisse, A.; Jouannique, V.; Sakthithasan, K.; Suarez, G.; Canu, I.G. Job Exposure Matrix, a Solution for Retrospective Assessment of Particle Exposure in a Subway Network and Their Long-Term Effects. Toxics 2023, 11, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Li, Q.; Shang, X.; Liang, Y.; Ding, X.; Sun, H.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J. Commodity plastic burning as a source of inhaled toxic aerosols. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.U. Cryogenic Aerosol Generation: Airborne Mist Particles Surrounding Liquid Nitrogen. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreyszig, E. Advanced Engineering Mathematics, 8th ed.; John Wiley & Sons Publication: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Marsden, J.E.; Tromba, A.J. Vector Calculus, 3rd ed.; W.H. Freeman & Company: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
| Lab Coat A | Lab Coat B | Suit | Shirt (T-Shirt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensions | Length: 110 cm Width: 45 cm | Length: 110 cm Width: 45 cm | Length: 85 cm Width: 45 cm | Length: 70 cm Width: 45 cm |
| Material | Polyester (50%) + Cotton (50%) | Polyester (65%) + Cotton (35%) | Polyester (100%) | Polyester (40%) + Cotton (60%) |
| Used/New | Used (~10 years) | New (0 years) | Used (~3 years) | Used (~3 years) |
| Particle Concentration (Initial Condition, Cinitial) Particles/m3 | Particle Concentration (after Vibration of Lab Coat A for 10 s, Cvibration) Particles/m3 | Variation Ratio: Cvibration (average)/Cinitial (average) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Particle size | Average ± standard deviation | Average ± standard deviation | Ratio with [t-test p-value] |
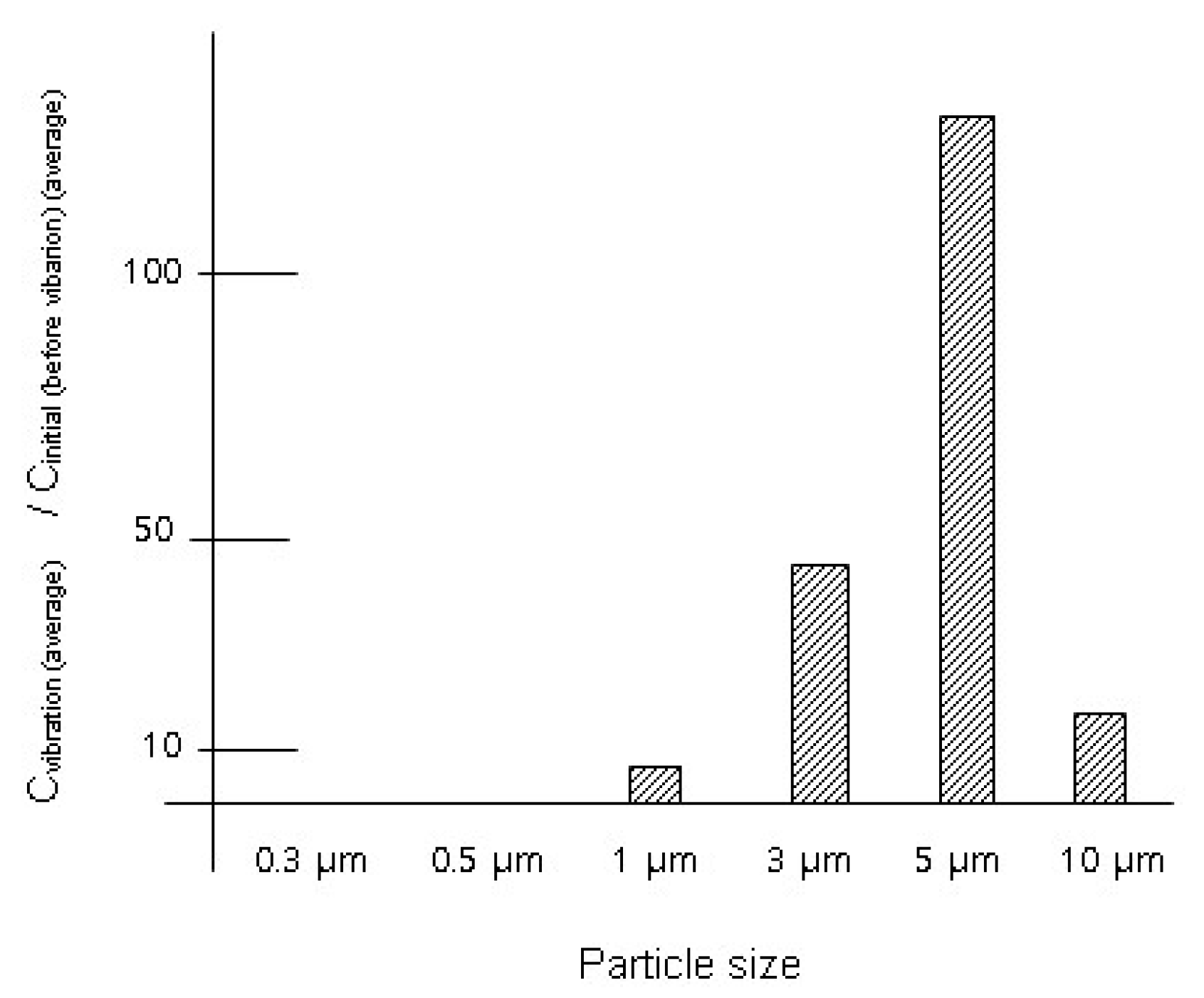
| 0.3 μm | 3.23 × 107 ± 5.28 × 105 | 1.80 × 104 ± 3.12 × 104 | 5.6 × 10−4 [4.9 × 10−5] |
| 0.5 μm | 3.40 × 106 ±1.68 × 105 | 0 × 104 ± 0 × 104 | 0 [4.1 × 10−4] |
| 1 μm | 7.15 × 105 ± 2.01 × 104 | 5.11 × 106 ± 7.54 × 105 | 7.1 [4.9 × 10−3] |
| 3 μm | 4.66 × 104 ± 1.98 × 104 | 2.11 × 106 ± 5.88 × 105 | 45 [0.014] |
| 5 μm | 2.93 × 104 ± 1.63 × 104 | 3.80 × 106 ± 9.01 × 105 | 130 [0.0096] |
| 10 μm | 6.83 × 103 ± 3.49 × 103 | 1.15 × 105 ± 1.17 × 105 | 17 [0.12] |
| Particle Concentration (Initial Condition, Cinitial) Particles/m3 | Particle Concentration (after Vibration of Lab Coat B for 10 s, Cvibration) Particles/m3 | Variation Ratio: Cvibration (average)/Cinitial(average) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Particle size | Average ± standard deviation | Average ± standard deviation | Ratio with [t-test p-value] |
| 0.3 μm | 3.09 × 107 ± 3.76 × 105 | 3.75 × 106 ± 1.49 × 106 | 0.12 [0.00065] |
| 0.5 μm | 3.50 × 106 ± 1.50 × 105 | 2.58 × 106 ± 4.82 × 105 | 0.74 [0.035] |
| 1 μm | 9.24 × 105 ± 2.04 × 104 | 6.95 × 106 ± 6.15 × 105 | 7.5 [0.0016] |
| 3 μm | 9.78 × 104 ± 7.90 × 103 | 1.57 × 106 ± 2.07 × 105 | 16 [0.0030] |
| 5 μm | 5.51 × 104 ± 1.62 × 103 | 1.45 × 106 ± 3.06 × 105 | 26 [0.0077] |
| 10 μm | 2.59 × 103 ± 8.89 × 102 | 1.11 × 105 ± 1.41 × 104 | 43 [0.0026] |
| Particle Concentration (Initial Condition, Cinitial) Particles/m3 | Particle Concentration (after Vibration of Suit for 10 s, Cvibration) Particles/m3 | Variation Ratio: Cvibration (average) /Cinitial (average) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Particle size | Average ± standard deviation | Average ± standard deviation | Ratio with [t-test p-value] |
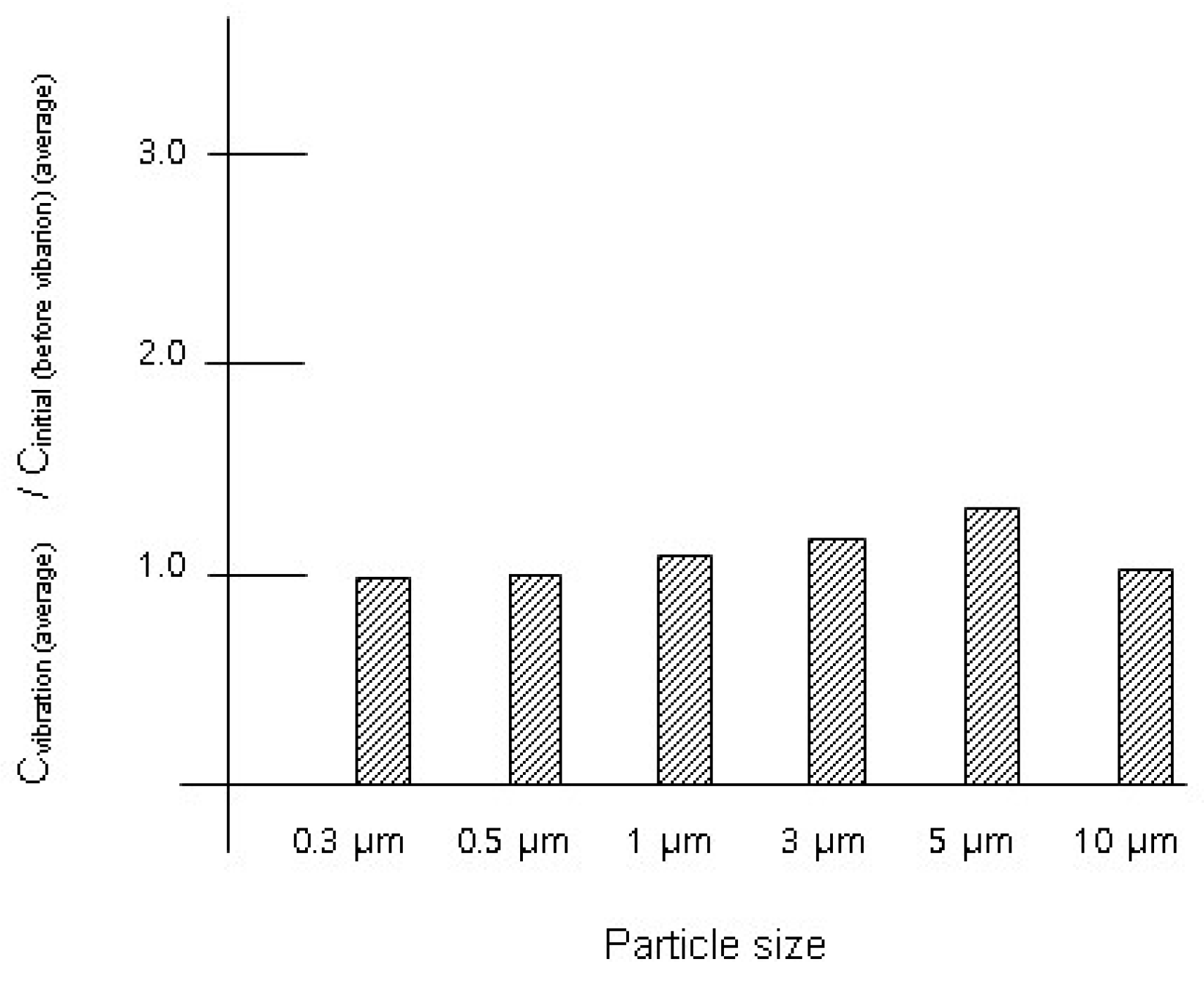
| 0.3 μm | 3.10 × 107 ± 1.72 × 105 | 3.03 × 107 ± 3.26 × 105 | 0.98 [0.043] |
| 0.5 μm | 3.34 × 106 ± 4.47 × 104 | 3.35 × 106 ± 3.17 × 104 | 1.00 [0.18] |
| 1 μm | 9.60 × 105 ± 2.42 × 104 | 1.05 × 106 ± 1.85 × 104 | 1.09 [0.032] |
| 3 μm | 1.21 × 105 ± 8.84 × 103 | 1.41 × 105 ± 5.93 × 103 | 1.17 [0.068] |
| 5 μm | 8.56 × 104 ± 8.97 × 103 | 1.12 × 105 ± 1.08 × 104 | 1.31 [0.072] |
| 10 μm | 1.22 × 104 ± 2.86 × 103 | 1.25 × 104 ± 3.61 × 103 | 1.02 [0.42] |
| Particle Concentration (Initial Condition, Cinitial) Particles/m3 | Particle Concentration (after Vibration of Shirt for 10 s, Cvibration) Particles/m3 | Variation Ratio: Cvibration (average) /Cinitial (average) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Particle size | Average ± standard deviation | Average ± standard deviation | Ratio with [t-test p-value] |
| 0.3 μm | 2.96 × 107 ± 3.83 × 105 | 2.86 × 106 ± 2.20 × 106 | 0.0970 [0.0015] |
| 0.5 μm | 3.50 × 106 ± 8.59 × 104 | 2.80 × 106 ± 2.66 × 105 | 0.799 [0.035] |
| 1 μm | 1.09 × 106 ± 4.77 × 104 | 8.53 × 106 ± 1.93 × 106 | 7.83 [0.011] |
| 3 μm | 1.24 × 105 ± 7.78 × 103 | 1.71 × 106 ± 4.40 × 105 | 13.8 [0.012] |
| 5 μm | 8.06 × 104 ± 3.24 × 103 | 1.84 × 106 ± 4.37 × 105 | 22.9 [0.0098] |
| 10 μm | 1.65 × 103 ± 5.40 × 102 | 2.41 × 104 ± 2.31 × 104 | 14.6 [0.12] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, B.U. Measurement of Aerosol Particles from Vibrated Lab Coats. Toxics 2024, 12, 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12080565
Lee BU. Measurement of Aerosol Particles from Vibrated Lab Coats. Toxics. 2024; 12(8):565. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12080565
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Byung Uk. 2024. "Measurement of Aerosol Particles from Vibrated Lab Coats" Toxics 12, no. 8: 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12080565
APA StyleLee, B. U. (2024). Measurement of Aerosol Particles from Vibrated Lab Coats. Toxics, 12(8), 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12080565







