A Study on Dust Storm Pollution and Source Identification in Northwestern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
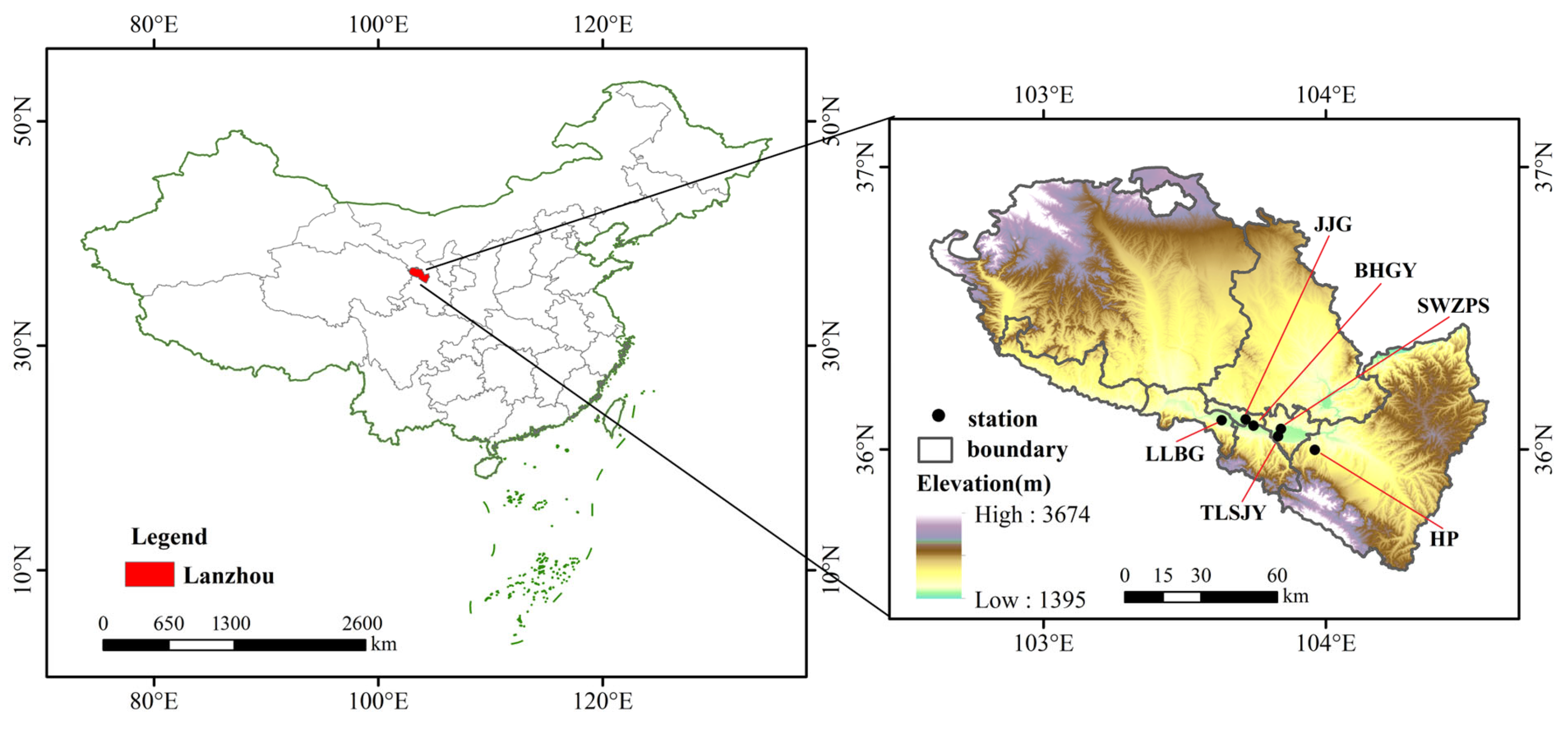
2.1. Area Overview
2.2. Research Data
2.2.1. Station Data
2.2.2. Aerosol Data
2.2.3. Meteorological Data
2.2.4. Dust Data
2.3. Research Methods
2.3.1. Backward Trajectory Clustering Analysis
2.3.2. Concentration-Weighted Trajectory Analysis
2.3.3. GEE
3. Results and Analysis
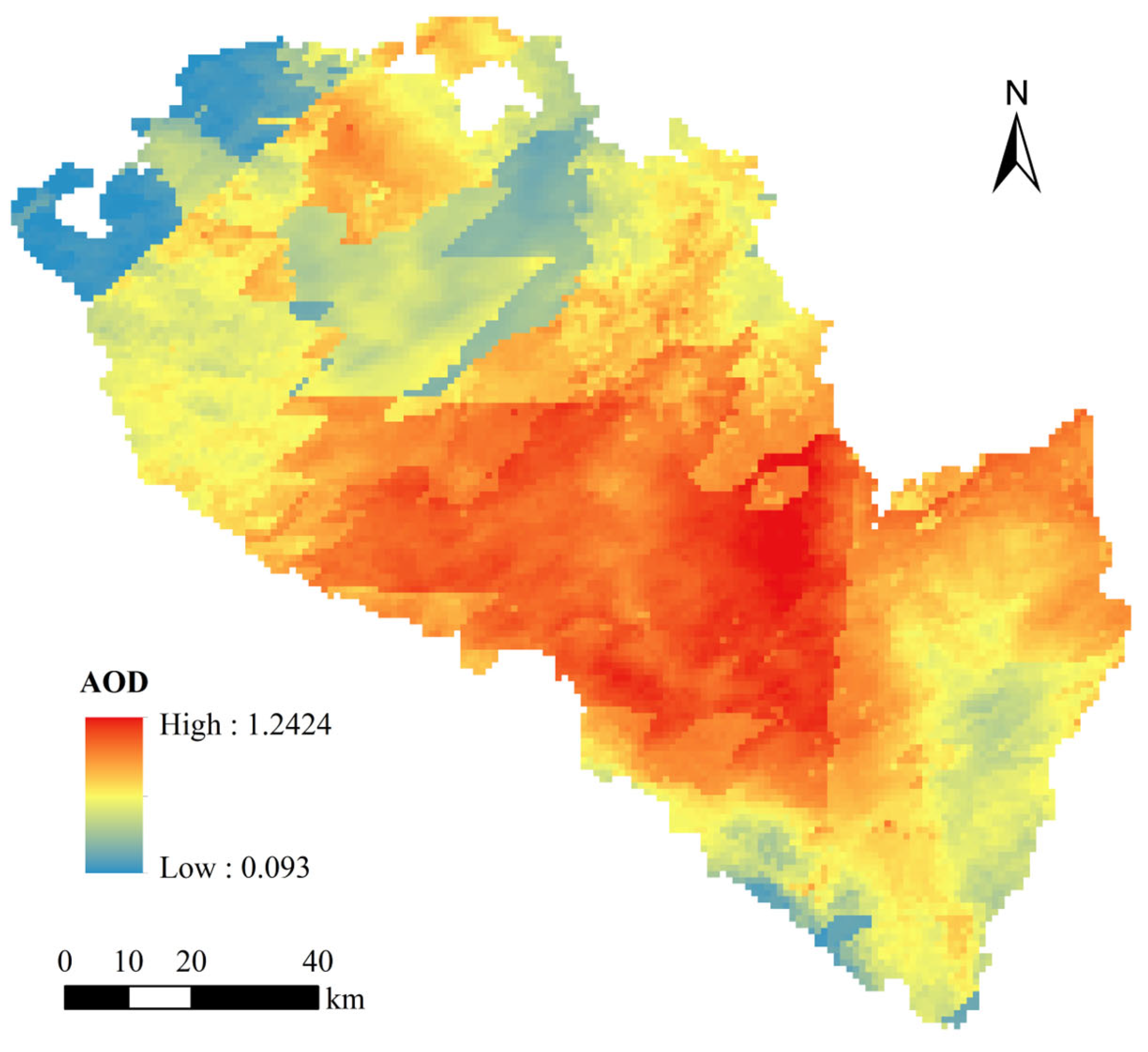
3.1. AOD Spatial Distribution During Severe Pollution in Lanzhou
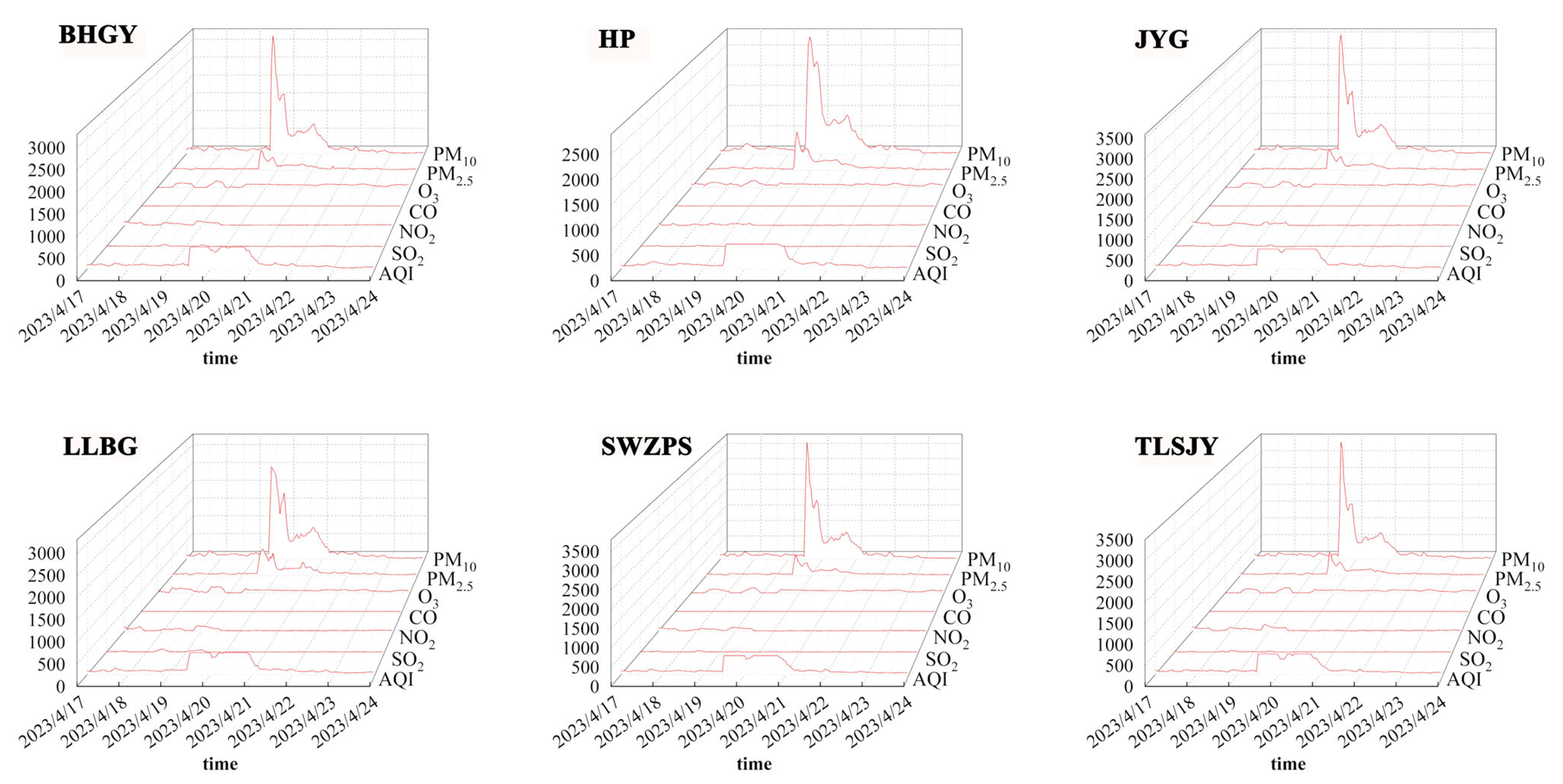
3.2. Air Quality Changes During a Dust Storm in Lanzhou
3.3. Backward Trajectory of the Dust Storm
3.4. Potential Pollution Sources During the Dust Storm
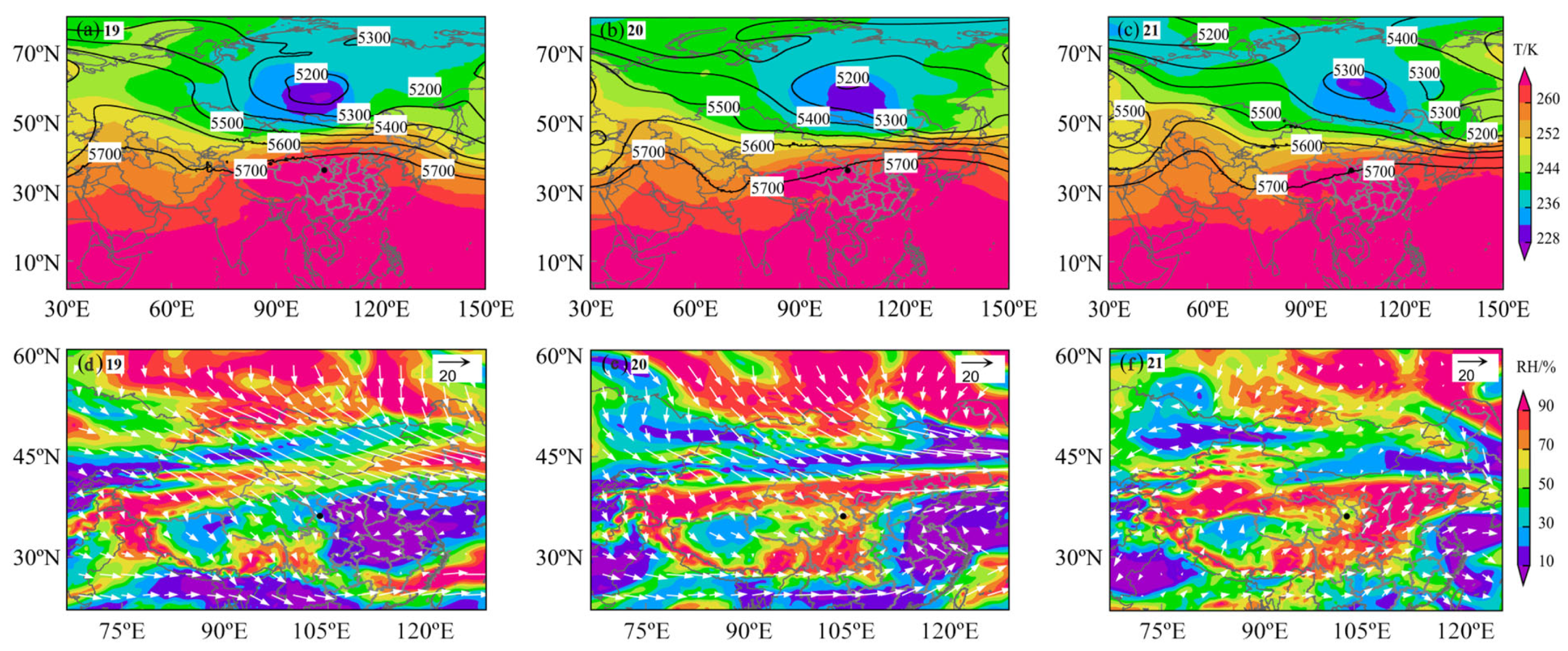
3.5. Meteorological Conditions During the Dust Storm
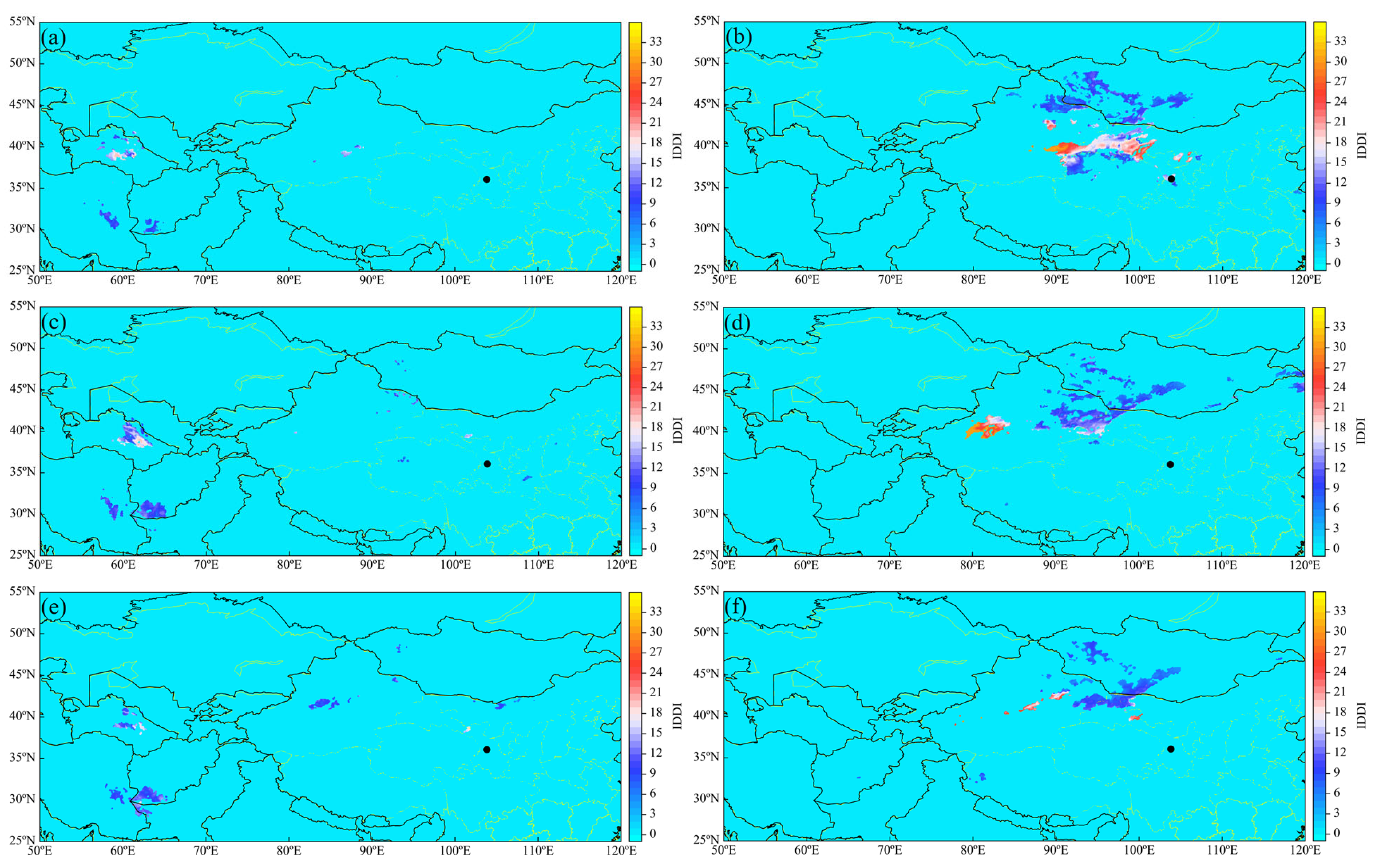
3.6. Dust Conditions During the Dust Storm
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ummenhofer, C.C.; Meehl, G.A. Extreme weather and climate events with ecological relevance: A review. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372, 20160135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgakopoulou, V.E.; Taskou, C.; Diamanti, A.; Beka, D.; Papalexis, P.; Trakas, N.; Spandidos, D.A. Saharan dust and respiratory health: Understanding the link between airborne particulate matter and chronic lung diseases (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2024, 28, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpinar-Elci, M.; Berumen-Flucker, B.; Bayram, H.; Al-Taiar, A. Climate Change, Dust Storms, Vulnerable Populations, and Health in the Middle East: A Review. J. Environ. Health 2021, 84, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Q.Y.; Sun, X.Z.; Yang, J.; Pan, B.T.; Zhao, S.L.; Wang, L. Dust Storms in Northern China: Long-Term Spatiotemporal Characteristics and Climate Controls. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 6683–6700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.H.; Quan, L.S.; Shi, S.Y. Variations of the dust storm in China and its climatic control. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 1216–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour, K.; Sciortino, M.; Kaskaoutis, D.G. Classification of weather clusters over the Middle East associated with high atmospheric dust-AODs in West Iran. Atmos. Res. 2021, 259, 105682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Zhu, X.; Pan, H.; Ai, W.; Song, W.; Pan, Y. Changes of the relationship between spring sand dust frequency and large-scale atmospheric circulation. Atmos. Res. 2019, 226, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Jia, X.; Li, K.; Li, Y. Horizontal wind erosion flux and potential dust emission in arid and semiarid regions of China: A major source area for East Asia dust storms. Catena 2015, 133, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Huang, J.; Li, J.; Jia, R.; Jiang, N.; Kang, L.; Ma, X.; Xie, T. Comparison of dust emissions, transport, and deposition between the Taklimakan Desert and Gobi Desert from 2007 to 2011. Sci. China-Earth Sci. 2017, 60, 1338–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Yan, H. Climate effects of dust aerosols over East Asian arid and semiarid regions. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 11398–11416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Zhuang, G.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Lin, Y.; Fu, J.S. Mixing of Asian dust with pollution aerosol and the transformation of aerosol components during the dust storm over China in spring 2007. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D00K13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Amiraslani, F.; Liu, J.; Zhou, N. Identification of dust storm source areas in West Asia using multiple environmental datasets. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 502, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.L.; Gong, S.L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Blanchet, J.-P.; McKendry, I.G.; Zhou, Z.J. A simulated climatology of Asian dust aerosol and its trans-Pacific transport. Part I: Mean climate and validation. J. Clim. 2016, 19, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.-C.; Li, J.; Che, H.; Chen, B.; Wang, H. Transport of East Asian dust storms to the marginal seas of China and the southern North Pacific in spring 2010. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 148, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.-C.; Wang, H. The transport and deposition of dust and its impact on phytoplankton growth in the Yellow Sea. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 99, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desouza, N.D.; Simon, B.; Qureshi, M.S. Evolutionary characteristics of a dust storm over Oman on 2 February 2008. Meteorol. Atmos. Physics 2011, 114, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Tao, S. Changes in wind speed over China during 1956–2004. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2010, 99, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurosaki, Y.; Mikami, M. Threshold wind speed for dust emission in east Asia and its seasonal variations. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2007, 112, D17202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezazadeh, M.; Irannejad, P.; Shao, Y. Climatology of the Middle East dust events. Aeolian Res. 2013, 10, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Sun, Y.B.; Ma, L.; Long, X. A multidisciplinary approach to trace Asian dust storms from source to sink. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 105, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.Y.; Luo, H.P.; Pan, N.H.; Zhao, R.; Yang, L.Q.; Yang, Y.Y.; Tian, J. Contribution of dust in northern China to PM Concentrations over the Hexi corridor. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 947–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandakji, T.; Gill, T.E.; Lee, J.A. Identifying and characterizing dust point sources in the southwestern United States using remote sensing and GIS. Geomorphology 2020, 353, 107019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar-Mohajer, N.; Shaban, M. Source Tracing of PM2.5 in a Metropolitan Area Using a Low-Cost Air Quality Monitoring Network: Case Study of Denver, Colorado, USA. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opp, C.; Groll, M.; Abbasi, H.; Foroushani, M.A. Causes and Effects of Sand and Dust Storms: What Has Past Research Taught Us? A Survey. J. Risk Financ. Manag. 2021, 14, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ding, J.L.; Chen, X.Y.; Wang, J.J. Aerosols characteristics, sources, and drive factors analysis in typical megacities, NW China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 403, 136879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, V.S.; Lyapustin, A.; de Carvalho, L.A.; Barbosa, C.C.F.; Novo, E.M.L.M. Validation of high-resolution MAIAC aerosol product over South America. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 7537–7559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhawish, A.; Banerjee, T.; Sorek-Hamer, M.; Lyapustin, A.; Broday, D.M.; Chatfield, R. Comparison and evaluation of MODIS Multi-angle Implementation of Atmospheric Correction (MAIAC) aerosol product over South Asia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 224, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Wang, J.; Li, R.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L. Performance of MODIS high-resolution MAIAC aerosol algorithm in China: Characterization and limitation. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 213, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ding, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Ge, X.; Wang, R.; Zuo, H. Validation and comparison of high-resolution MAIAC aerosol products over Central Asia. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 251, 118273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Korkin, S.; Huang, D. MODIS collection 6 MAIAC algorithm. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 5741–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Su, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Cao, M.; Wang, L.; Yang, L. Evaluation and analysis of long-term MODIS MAIAC aerosol products in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 948, 174983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.Y.; Draxler, R.R. TrajStat: GIS-based software that uses various trajectory statistical analysis methods to identify potential sources from long-term air pollution measurement data. Environ. Model. Softw. 2009, 24, 938–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draxler, R.R.; Hess, G.D. An overview of the HYSPLIT_4 modelling system for trajectories, dispersion and deposition. Aust. Meteorol. Mag. 1998, 47, 295–308. [Google Scholar]
- Napi, N.N.L.M.; Ooi, M.C.G.; Talib, M.L.; Juneng, L.; Nadzir, M.S.M.; Chan, A.; Li, L.; Abdullah, S. Contribution of aerosol species to the 2019 smoke episodes over the east coast of peninsular Malaysia. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2022, 22, 210393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Fan, Z.; Xia, J.; Chen, S.; Chen, X. Temporal distribution, influencing factors and pollution sources of urban ambient air quality in Nanchong, China. Environ. Eng. Res. 2015, 20, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammoudi, N.; Kovács, J.; Gresina, F.; Varga, G. Combined use of HYSPLIT model and MODIS aerosols optical depth to study the spatiotemporal circulation patterns of Saharan dust events over Central Europe. Aeolian Res. 2024, 67, 100899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, I.; Zhang, L.; Blanchard, P.; Dalziel, J.; Tordon, R. Concentration-weighted trajectory approach to identifying potential sources of speciated atmospheric mercury at an urban coastal site in Nova Scotia, Canada. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 6031–6048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.F.; Bai, G.Z.; Wang, L.W. Analysis of the spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of AOD in typical industrial cities in northwest China and the influence of meteorological factors. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2024, 15, 101957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.Y.; Gao, X.Q.; Chang, Y.; Zhao, S.P.; Li, P.D. The pattern and mechanism of an unhealthy air pollution event in Lanzhou, China. Urban Clim. 2023, 48, 101409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| AQI Values | Air Quality Level | Levels of Health Concern | Colors |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0–50 | I | Good | Green |
| 51–100 | II | Moderate | Yellow |
| 101–150 | III | Unhealthy for Sensitive Groups | Orange |
| 151–200 | IV | Unhealthy | Red |
| 201–300 | V | Very Unhealthy | Purple |
| 301–500 | VI | Hazardous | Maroon |
| Date | AQI | PM2.5 | PM10 | CO | NO2 | SO2 | O3 | Temperature | Humidity | Wind Speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 04.17 | 97 | 44 | 144 | 0.6 | 40 | 10 | 114 | 18.22 | 21.47 | 1.88 |
| 04.18 | 93 | 46 | 136 | 0.6 | 53 | 16 | 140 | 18.68 | 24.91 | 1.76 |
| 04.19 | 500 | 238 | 1042 | 0.5 | 38 | 10 | 89 | 16.01 | 27.93 | 3.84 |
| 04.20 | 500 | 167 | 654 | 0.3 | 12 | 6 | 80 | 10.10 | 24.42 | 2.88 |
| 04.21 | 122 | 68 | 193 | 0.4 | 12 | 5 | 85 | 7.54 | 53.25 | 2.58 |
| 04.22 | 69 | 46 | 87 | 0.4 | 14 | 6 | 86 | 6.93 | 59.38 | 2.02 |
| 04.23 | 42 | 29 | 32 | 0.6 | 18 | 6 | 76 | 6.31 | 70.95 | 1.60 |
| Cluster | Number | PM2.5 | PM10 | Transit Area | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Sd | Mean | Sd | |||
| 1 | 14 | 62.9 | 49.65 | 179.63 | 219.81 | Mongolia, the central and western regions of Inner Mongolia, and northern Ningxia |
| 2 | 9 | 152.48 | 125.09 | 681.3 | 686.46 | Gansu and Inner Mongolia border area and north-central Xinjiang |
| 3 | 5 | 44.11 | 5.74 | 129.03 | 18.25 | Border regions between Gansu and Inner Mongolia |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, H.; Wang, F.; Bai, G.; Li, H. A Study on Dust Storm Pollution and Source Identification in Northwestern China. Toxics 2025, 13, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13010033
Meng H, Wang F, Bai G, Li H. A Study on Dust Storm Pollution and Source Identification in Northwestern China. Toxics. 2025; 13(1):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13010033
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Hongfei, Feiteng Wang, Guangzu Bai, and Huilin Li. 2025. "A Study on Dust Storm Pollution and Source Identification in Northwestern China" Toxics 13, no. 1: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13010033
APA StyleMeng, H., Wang, F., Bai, G., & Li, H. (2025). A Study on Dust Storm Pollution and Source Identification in Northwestern China. Toxics, 13(1), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13010033






