Association Between Urinary Metal Levels and Chronic Kidney Dysfunction in Rural China: A Study on Sex-Specific Differences
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Urinary Metal Determination
2.3. Kidney Outcomes Measurement
2.4. Determination of Other Variables
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.5.1. Single-Exposure Models
2.5.2. Quantile G-Computation (QGC) and Weighted Quantile Sum (WQS) Regression Model
2.5.3. Bayesian Kernel Machine Regression (BKMR) Model
2.5.4. Sensitivity Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics
3.2. Urinary Metal Concentration
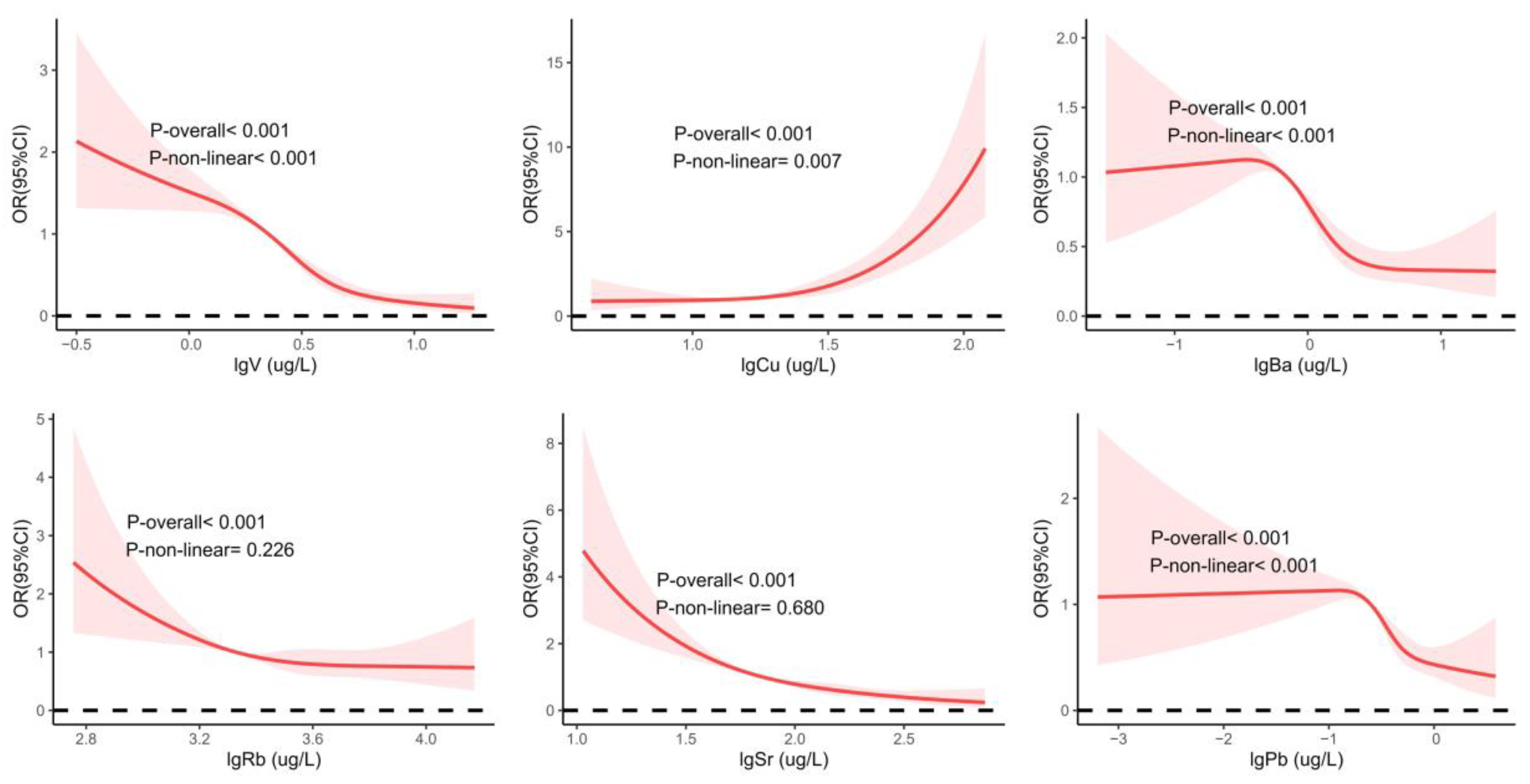
3.3. Single-Metal Model of Urine Metal and CKD
3.4. Multi-Metals Model of Urine Metal and CKD
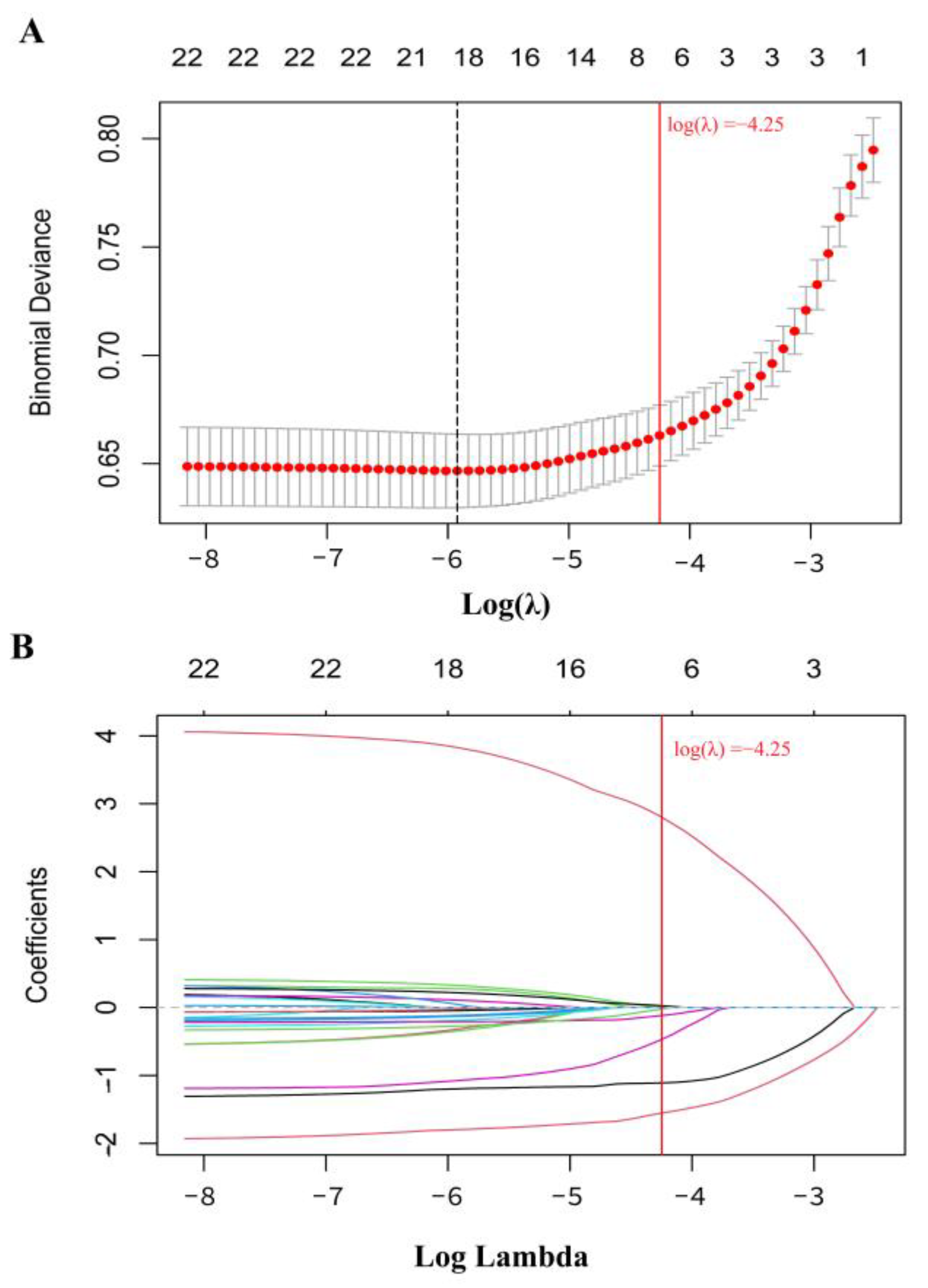
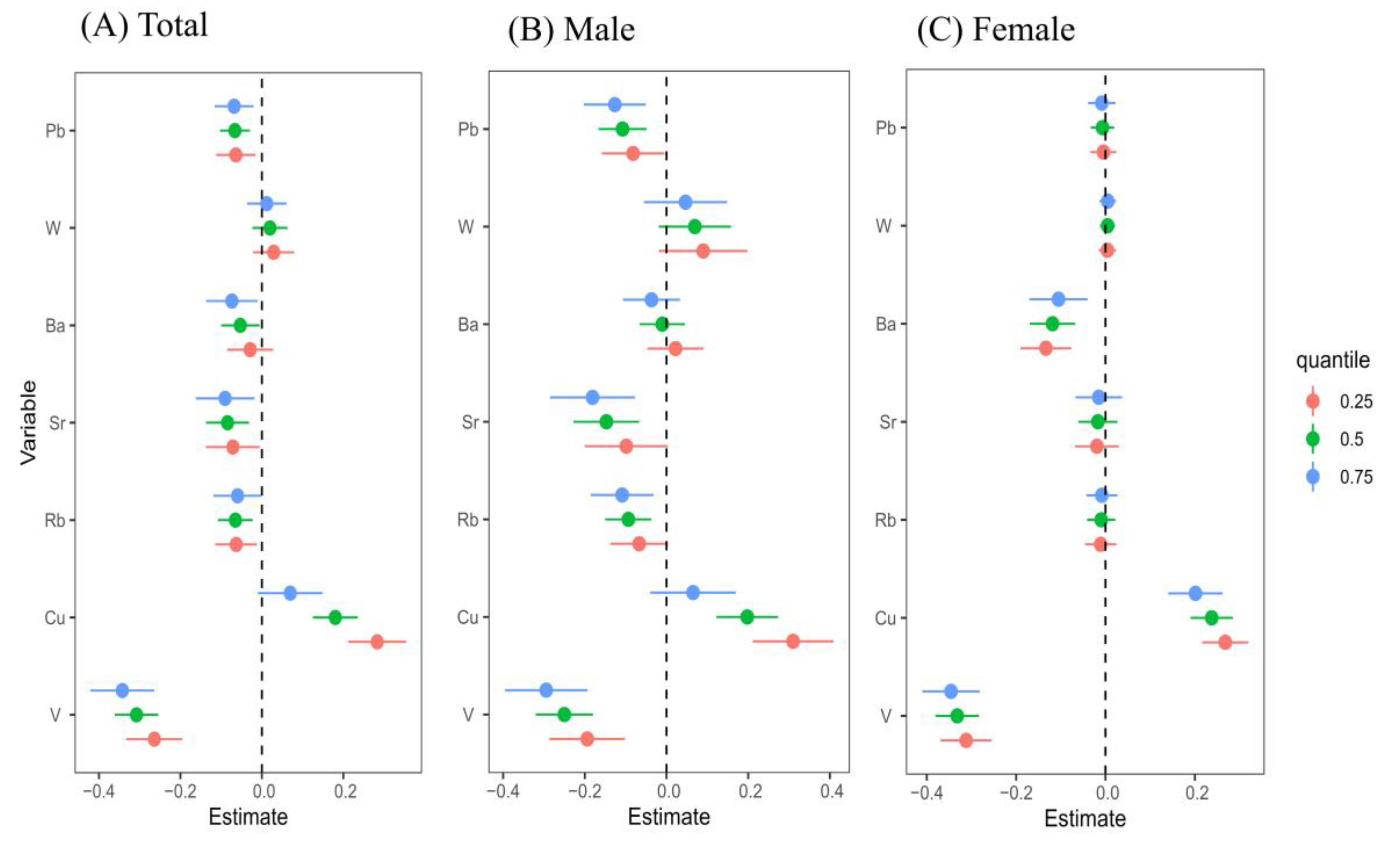
3.4.1. QGC Model Assessment of the Association Between Urinary Metals and CKD, Verified by WQS
3.4.2. BKMR Model Assessment of the Association Between Urinary Metals and CKD
3.5. Sensitivity Analysis Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kotwal, S.S.; Perkovic, V.; Jardine, M.J.; Kim, D.; Shah, N.A.; Lin, E.; Coggan, S.; Billot, L.; Vart, P.; Wheeler, D.C.; et al. The Global Kidney Patient Trials Network and the CAPTIVATE Platform Clinical Trial Design: A Trial Protocol. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2449998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, K.; Qing, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y. Epidemiological shifts in chronic kidney disease: A 30-year global and regional assessment. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coresh, J.; Selvin, E.; Stevens, L.A.; Manzi, J.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Levey, A.S. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA 2007, 298, 2038–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.W.; Li, Y.L.; Li, S.X.; Yang, Y.P.; Li, F.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Deng, P.Z.; Wu, J.J.; Wang, W.; et al. Association of Long-term Ambient Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) and Incident CKD: A Prospective Cohort Study in China. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2022, 80, 638–647.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Fang, X.; Ji, X.; Tang, Z.; Wang, C.; Guan, S.; Wu, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Z. Kidney dysfunction is associated with risk of cardiovascular events in middle-aged and elderly population with hypertension: A 5-year community-based cohort study in China. Clin. Nephrol. 2020, 93, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, X.; Yang, L.; He, M.; Zhang, H.; Wei, X.; Qin, J.; Li, X.; Lu, G.; et al. Relation between cadmium body burden and cognitive function in older men: A cross-sectional study in China. Chemosphere 2020, 250, 126535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelii, M.; Senatore, L.; Paglialonga, F.; Consolo, S.; Montini, G.; Rocchi, A.; Marchisio, P.; Patria, M.F. Respiratory complications and sleep disorders in children with chronic kidney disease: A correlation often underestimated. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2023, 45, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Wu, T.; You, Y.; Liu, F.; Hou, Q.; Mo, C.; Zhou, L.; Yang, J. Correlation between the triglyceride-glucose index and chronic kidney disease among adults with metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: Fourteen-year follow-up. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1400448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adejumo, O.A.; Edeki, I.R.; Sunday Oyedepo, D.; Falade, J.; Yisau, O.E.; Ige, O.O.; Adesida, A.O.; Daniel Palencia, H.; Sabri Moussa, A.; Abdulmalik, J.; et al. Global prevalence of depression in chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Nephrol. 2024, 37, 2455–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, X.; Zhang, M.; Hu, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Nie, S.; Huang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Hou, F.F.; et al. Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease in China: Results From the Sixth China Chronic Disease and Risk Factor Surveillance. JAMA Intern. Med. 2023, 183, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlassara, L.; Zanoni, F.; Gharavi, A.G. Familial Aggregation of CKD: Gene or Environment? Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 77, 861–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Oh, S.; Kang, H.; Kim, S.; Lee, G.; Li, L.; Kim, C.T.; An, J.N.; Oh, Y.K.; Lim, C.S.; et al. Environment-Wide Association Study of CKD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 15, 766–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewchalermvong, K.; Rangkadilok, N.; Nookabkaew, S.; Suriyo, T.; Satayavivad, J. Arsenic Speciation and Accumulation in Selected Organs after Oral Administration of Rice Extracts in Wistar Rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 3199–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozak, K.; Antosiewicz, D.M. Tobacco as an efficient metal accumulator. Biometals 2023, 36, 351–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, H.S.; Kang, I.G.; Lee, S.G.; Eom, S.Y.; Kim, Y.D.; Oh, S.Y.; Kwon, H.J.; Park, K.S.; Kim, H.; Choi, B.S.; et al. Arsenic exposure and seafood intake in Korean adults. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2017, 36, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowan, J.; Kordas, K.; Queirolo, E.I.; Vahter, M.; Mañay, N.; Peregalli, F.; Desai, G. Contribution of household drinking water intake to arsenic and lead exposure among Uruguayan schoolchildren. Chemosphere 2022, 292, 133525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Dang, Y.; Ouyang, C.; Pan, J.; Yang, A.; Hu, X. Associations of mixed metal exposure with chronic kidney disease from NHANES 2011–2018. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gong, X.; Li, R.; Gao, W.; Hu, D.; Yi, X.; Liu, Y.; Fang, J.; Shao, J.; Ma, Y.; et al. Exposure to cadmium and lead is associated with diabetic kidney disease in diabetic patients. Environ. Health 2024, 23, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Morata, I.; Sobel, M.; Tellez-Plaza, M.; Navas-Acien, A.; Howe, C.G.; Sanchez, T.R. A State-of-the-Science Review on Metal Biomarkers. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2023, 10, 215–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, O.; Scholze, M.; Ermler, S.; McPhie, J.; Bopp, S.K.; Kienzler, A.; Parissis, N.; Kortenkamp, A. Ten years of research on synergisms and antagonisms in chemical mixtures: A systematic review and quantitative reappraisal of mixture studies. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasten-Jolly, J.; Lawrence, D.A. The cationic (calcium and lead) and enzyme conundrum. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B Crit. Rev. 2018, 21, 400–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gromadzka, G.; Tarnacka, B.; Flaga, A.; Adamczyk, A. Copper Dyshomeostasis in Neurodegenerative Diseases-Therapeutic Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ma, J.; Wang, R.; Luo, Y.; Zheng, S.; Wang, X. Zinc transporter 1 functions in copper uptake and cuproptosis. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 2118–2129.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, X.; Cai, J.; Lin, Y.; Liu, Q.; Xu, M.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Wei, C.; Wei, Y.; Huang, S.; et al. Correlation between urinary contents of some metals and fasting plasma glucose levels: A cross-sectional study in China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 228, 112976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Wang, R.; He, P.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, Z.; Yang, H.; Guan, S.; Sun, J. Association between urinary metal concentrations and abnormal estimated glomerular filtration rate in Chinese community-dwelling elderly: Exploring the mediating effect of triglycerides. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 259, 114966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michels, W.M.; Grootendorst, D.C.; Verduijn, M.; Elliott, E.G.; Dekker, F.W.; Krediet, R.T. Performance of the Cockcroft-Gault, MDRD, and new CKD-EPI formulas in relation to GFR, age, and body size. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 5, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brück, K.; Jager, K.J.; Dounousi, E.; Kainz, A.; Nitsch, D.; Ärnlöv, J.; Rothenbacher, D.; Browne, G.; Capuano, V.; Ferraro, P.M.; et al. Methodology used in studies reporting chronic kidney disease prevalence: A systematic literature review. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 31, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KDIGO 2024 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2024, 105, S117–S314. [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Fu, Y.; Huang, F.; Wen, L.; Weng, X.; Yao, H.; Liang, H.; Kuang, M.; Jing, C. Association between blood metal exposures and hyperuricemia in the U.S. general adult: A subgroup analysis from NHANES. Chemosphere 2023, 318, 137873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keil, A.P.; Buckley, J.P.; O’Brien, K.M.; Ferguson, K.K.; Zhao, S.; White, A.J. A Quantile-Based g-Computation Approach to Addressing the Effects of Exposure Mixtures. Environ. Health Perspect. 2020, 128, 47004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gao, D.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Gao, Q.; Chen, R.; Xu, S.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Exposure to multiple metals in early pregnancy and gestational diabetes mellitus: A prospective cohort study. Environ. Int. 2020, 135, 105370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, M.; Trombetta, L.D. Low level mancozeb exposure causes copper bioaccumulation in the renal cortex of rats leading to tubular injury. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 100, 104148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Wan, Z.; Zhang, M.; Hu, L.; Song, L.; Wang, Y.; Lv, Y.; Wang, L. The association between urinary metals/metalloids and chronic kidney disease among general adults in Wuhan, China. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Meng, W.; Kuang, H.; Chen, X.; Zhu, X.; Wang, L.; Tan, H.; Xu, Y.; Ding, P.; Xiang, M.; et al. Association of urinary exposure to multiple metal(loid)s with kidney function from a national cross-sectional study. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 882, 163100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Lin, Y.; Meng, L.; Peng, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Jin, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, M.; et al. Association of copper exposure with prevalence of chronic kidney disease in older adults. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 2720–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiayi, H.; Ziyuan, T.; Tianhua, X.; Mingyu, Z.; Yutong, M.; Jingyu, W.; Hongli, Z.; Li, S. Copper homeostasis in chronic kidney disease and its crosstalk with ferroptosis. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 202, 107139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Wang, L.; Huang, M.; Xu, G.; Yang, M. Metabolic changes induced by heavy metal copper exposure in human ovarian granulosa cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 285, 117078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Kalita, J.; Bora, H.K.; Misra, U.K. Relationship of antioxidant and oxidative stress markers in different organs following copper toxicity in a rat model. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2016, 293, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolt, A.M.; Mann, K.K. Tungsten: An Emerging Toxicant, Alone or in Combination. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2016, 3, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menke, A.; Guallar, E.; Cowie, C.C. Metals in Urine Diabetes in, U.S. Adults. Diabetes 2016, 65, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.; Macaluso, F.; Moore, C.; Mesenbring, E.; Johnson, R.J.; Hamman, R.F.; James, K.A. Urine tungsten and chronic kidney disease in rural Colorado. Environ. Res. 2021, 195, 110710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, R.; Zhu, X.; Shrubsole, M.J.; Yu, C.; Xia, Z.; Dai, Q. Associations of renal function with urinary excretion of metals: Evidence from NHANES 2003–2012. Environ. Int. 2018, 121 Pt 2, 1355–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Fan, L.; Wang, Y.; Dong, S.; Han, M.; Qin, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, A. Combined exposure to multiple metals on hypertension in NHANES under four statistical models. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 92937–92949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.; He, J.; Zhou, S.; Dong, H.; Rinklebe, J.; Ok, Y.S. Vanadium in the Environment: Biogeochemistry and Bioremediation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 14770–14786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ścibior, A.; Pietrzyk, Ł.; Plewa, Z.; Skiba, A. Vanadium: Risks and possible benefits in the light of a comprehensive overview of its pharmacotoxicological mechanisms and multi-applications with a summary of further research trends. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2020, 61, 126508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Li, Y.; Yu, Y.; Mo, T.; Jiang, H.; Li, X.; Yang, H.; Xu, C.; et al. Associations of plasma metal concentrations with the decline in kidney function: A longitudinal study of Chinese adults. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 189, 110006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Taehwan Kim, A.; Liu, X.; Yan, L.; Moo Kim, S. Antioxidant and antidiabetic activities of vanadium-binding protein and trifuhalol A. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo-Relloso, A.; Grau-Perez, M.; Galan-Chilet, I.; Garrido-Martinez, M.J.; Tormos, C.; Navas-Acien, A.; Gomez-Ariza, J.L.; Monzo-Beltran, L.; Saez-Tormo, G.; Garcia-Barrera, T.; et al. Urinary metals and metal mixtures and oxidative stress biomarkers in an adult population from Spain: The Hortega Study. Environ. Int. 2019, 123, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waidyanatha, S.; Weber, F.X.; Fallacara, D.M.; Harrington, J.M.; Levine, K.; Robinson, V.G.; Sparrow, B.R.; Stout, M.D.; Fernando, R.; Hooth, M.J.; et al. Systemic exposure and urinary excretion of vanadium following perinatal subchronic exposure to vanadyl sulfate and sodium metavanadate via drinking water. Toxicol. Lett. 2022, 360, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azay, J.; Brès, J.; Krosniak, M.; Teissedre, P.L.; Cabanis, J.C.; Serrano, J.J.; Cros, G. Vanadium pharmacokinetics and oral bioavailability upon single-dose administration of vanadyl sulfate to rats. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2001, 15, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoroddu, M.A.; Aaseth, J.; Crisponi, G.; Medici, S.; Peana, M.; Nurchi, V.M. The essential metals for humans: A brief overview. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2019, 195, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Huang, D.; Xiao, S.; Lei, L.; Wu, K.; Yang, Y.; Liu, M.; Qiu, X.; Liu, S.; Zeng, X. Associations between co-exposure to multiple metals and renal function: A cross-sectional study in Guangxi, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 2637–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdivielso, J.M.; Jacobs-Cachá, C.; Soler, M.J. Sex hormones and their influence on chronic kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2019, 28, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrap, P.; Sánchez, B.N.; Téllez-Rojo, M.M.; Basu, N.; Tamayo-Ortiz, M.; Peterson, K.E.; Meeker, J.D.; Watkins, D.J. In utero and peripubertal metals exposure in relation to reproductive hormones and sexual maturation and progression among girls in Mexico City. Environ. Res. 2019, 177, 108630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Solal, M. Strontium overload and toxicity: Impact on renal osteodystrophy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2002, 17 (Suppl. S2), 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Hu, N.; Li, J.; Pu, M.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Liao, D. The correlation of urinary strontium with the risk of chronic kidney disease among the general United States population. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1251232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Zeeshan, M.; Xiong, L.H.; Lv, J.Y.; Wu, Y.; Tang, X.J.; Zhou, Y.; Ou, Y.Q.; Huang, W.Z.; Feng, W.R.; et al. Co-exposure to perfluoroalkyl acids and heavy metals mixtures associated with impaired kidney function in adults: A community-based population study in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 839, 156299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, N.; Hotta, Y.; Ito, H.; Naiki-Ito, A.; Matsuta, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Ohashi, K.; Hayakawa, T.; Sanagawa, A.; Horita, Y.; et al. High preoperative serum strontium levels increase the risk of acute kidney injury after cardiopulmonary bypass. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2023, 27, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Yi, X.; Guo, J.; Xu, S.; Xiao, Y.; Huang, X.; Duan, Y.; Luo, D.; Xiao, S.; Huang, Z.; et al. Association of plasma and urine metals levels with kidney function: A population-based cross-sectional study in China. Chemosphere 2019, 226, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheshmedzhieva, D.; Ilieva, S.; Permyakov, E.A.; Permyakov, S.E.; Dudev, T. Ca2+/Sr2+ Selectivity in Calcium-Sensing Receptor (CaSR): Implications for Strontium’s Anti-Osteoporosis Effect. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosiba, A.A.; Wang, Y.; Chen, D.; Wong, C.K.C.; Gu, J.; Shi, H. The roles of calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) in heavy metals-induced nephrotoxicity. Life Sci. 2020, 242, 117183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnawi, E.A.; Doherty, J.E.; Ferreira, P.G.; Wilson, J.M. Extra-gastric expression of the proton pump H+/K+-ATPase in the gills and kidney of the teleost Oreochromis niloticus. J. Exp. Biol. 2020, 223 Pt 16, jeb214890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danziger, J.; Dodge, L.E.; Hu, H.; Mukamal, K.J. Susceptibility to Environmental Heavy Metal Toxicity among Americans with Kidney Disease. Kidney360 2022, 3, 1191–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Tang, P.; Jiao, B.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Yi, M.; Dai, Y. Association between blood metals mixture and chronic kidney disease in adults: NHANES 2013–2016. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2024, 83, 127395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrero, J.J.; Hecking, M.; Chesnaye, N.C.; Jager, K.J. Sex and gender disparities in the epidemiology and outcomes of chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gade, M.; Comfort, N.; Re, D.B. Sex-specific neurotoxic effects of heavy metal pollutants: Epidemiological, experimental evidence and candidate mechanisms. Environ. Res. 2021, 201, 111558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarneau, J.M.; Beach, J.; Cherry, N. Urinary Metals as a Marker of Exposure in Men and Women in the Welding and Electrical Trades: A Canadian Cohort Study. Ann. Work Expo. Health 2022, 66, 1111–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, C.; Li, Z.; Fan, Y.; Li, X.; Qian, H.; Yu, H.; Xu, Q.; Lu, C. Independent and combined associations of urinary heavy metals exposure and serum sex hormones among adults in NHANES 2013–2016. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 281, 117097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Variables | Total | Chronic Kidney Disease | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | |||
| Subjects, n (%) | 2919 | 397 (13.60) | 2522 (86.40) | |
| Sex, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Man | 1070 (36.66) | 190 (47.86) | 880 (34.89) | |
| Woman | 1849 (63.34) | 207 (52.14) | 1642 (65.11) | |
| Age, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| <60 | 1490 (51.04) | 149 (37.53) | 1341 (53.17) | |
| ≥60 | 1429 (48.96) | 248 (62.47) | 1181 (46.83) | |
| BMI, n (%) | 0.003 | |||
| <18.5 | 224 (7.67) | 41 (10.33) | 183 (7.26) | |
| 18.5–24 | 1764 (60.43) | 210 (52.90) | 1554 (61.62) | |
| ≥24 | 931 (31.89) | 146 (36.77) | 785 (31.12) | |
| Ethnicity, n (%) | 0.243 | |||
| Han | 579 (19.84) | 91 (22.93) | 488 (19.35) | |
| Yao | 2194 (75.16) | 288 (72.54) | 1906 (75.57) | |
| Other | 146 (5.00) | 18 (4.53) | 128 (5.08) | |
| Smoking status, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Yes | 518 (17.75) | 94 (23.68) | 424 (16.81) | |
| No | 2401 (82.25) | 303 (76.32) | 2098 (83.19) | |
| Drinking status, n (%) | 0.718 | |||
| Yes | 911 (31.21) | 127 (31.99) | 784 (31.09) | |
| No | 2008 (68.79) | 270 (68.01) | 1738 (68.91) | |
| Education level, n (%) | 0.014 | |||
| ≤6 years | 1846 (63.24) | 273 (68.77) | 1573 (62.37) | |
| >6 years | 1073 (36.76) | 124 (31.23) | 949 (37.63) | |
| Physical work, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Yes | 1026 (35.15) | 217 (54.66) | 1676 (66.46) | |
| No | 1893 (64.85) | 180 (45.34) | 846 (33.54) | |
| Hypertension, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Yes | 1300 (44.54) | 94 (39.66) | 1063 (42.15) | |
| No | 1619 (55.46) | 143 (60.34) | 1459 (57.85) | |
| Diabetes, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Yes | 337 (11.55) | 237 (59.70) | 260 (10.31) | |
| No | 2582 (88.45) | 160 (40.30) | 2262 (89.69) | |
| Hyperuricemia, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Yes | 478 (16.38) | 117 (29.47) | 361 (14.31) | |
| No | 2441 (83.62) | 280 (70.53) | 2161 (85.69) | |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 91.64 ± 19.35 | 78.89 ± 22.49 | 93.63 ± 18.03 | |
| UACR, mg/g, n (%) | ||||
| ≥30 | 347 (11.89) | 347 (87.41) | 0 (0.00) | |
| <30 | 2572 (88.11) | 50 (12.59) | 2522 (100.00) | |
| Variable | V | Cu | Rb | Sr | Ba | W | Pb | OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QGC | |||||||||
| Total | −0.448 | 0.768 | −0.107 | −0.119 | −0.164 | 0.232 | −0.162 | −0.430 (−0.656, −0.204) | <0.001 |
| Male | −0.588 | 0.656 | −0.061 | −0.064 | −0.139 | 0.344 | 0.149 | −0.394 (−0.883, 0.096) | 0.115 |
| Female | −0.358 | 0.854 | −0.145 | −0.174 | −0.170 | 0.146 | −0.152 | −0.557 (−0.834, −0.280) | <0.001 |
| WQS | |||||||||
| Total | −0.508 | - | −0.028 | −0.189 | −0.213 | - | −0.061 | −0.885 (−1.083, −0.899) | <0.001 |
| Male | −0.492 | - | −0.108 | −0.093 | −0.035 | - | −0.271 | −0.753 (−1.051, −0.454) | <0.001 |
| Female | −0.574 | - | −0.014 | −0.147 | −0.167 | - | −0.098 | −0.793 (−1.050, −0.536) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teng, K.; Guan, Q.; Liu, Q.; Mo, X.; Luo, L.; Rong, J.; Zhang, T.; Jin, W.; Zhao, L.; Wu, S.; et al. Association Between Urinary Metal Levels and Chronic Kidney Dysfunction in Rural China: A Study on Sex-Specific Differences. Toxics 2025, 13, 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13010055
Teng K, Guan Q, Liu Q, Mo X, Luo L, Rong J, Zhang T, Jin W, Zhao L, Wu S, et al. Association Between Urinary Metal Levels and Chronic Kidney Dysfunction in Rural China: A Study on Sex-Specific Differences. Toxics. 2025; 13(1):55. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13010055
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeng, Kaisheng, Qinyi Guan, Qiumei Liu, Xiaoting Mo, Lei Luo, Jiahui Rong, Tiantian Zhang, Wenjia Jin, Linhai Zhao, Songju Wu, and et al. 2025. "Association Between Urinary Metal Levels and Chronic Kidney Dysfunction in Rural China: A Study on Sex-Specific Differences" Toxics 13, no. 1: 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13010055
APA StyleTeng, K., Guan, Q., Liu, Q., Mo, X., Luo, L., Rong, J., Zhang, T., Jin, W., Zhao, L., Wu, S., Zhang, Z., & Qin, J. (2025). Association Between Urinary Metal Levels and Chronic Kidney Dysfunction in Rural China: A Study on Sex-Specific Differences. Toxics, 13(1), 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13010055







