Developmental Neurotoxicity of 3,3',4,4'-Tetrachloroazobenzene with Thyroxine Deficit: Sensitivity of Glia and Dentate Granule Neurons in the Absence of Behavioral Changes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Animals

2.2. Physical Parameters and Functional Observational Battery (FOB)
2.3. TH Analysis
2.4. Behavioral Assessments
2.4.1. Locomotor Activity
2.4.2. Startle Response and Pre-Pulse Startle Inhibition (PPI)
2.4.3. Forelimb and Hindlimb Grip Strength
2.4.4. Conditioned Avoidance
2.4.5. Morris Water Maze
2.4.6. Delayed Non-Matched to Position
2.5. Tissue Collection
2.6. Histology and Immunohistochemistry
2.7. Golgi Analysis
2.8. Hippocampal Stereology
2.9. Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Maternal and Pre-weaning Assessments
3.2. Serum TH Levels

3.3. Neurobehavioral Assessments
3.3.1. Functional Observational Battery
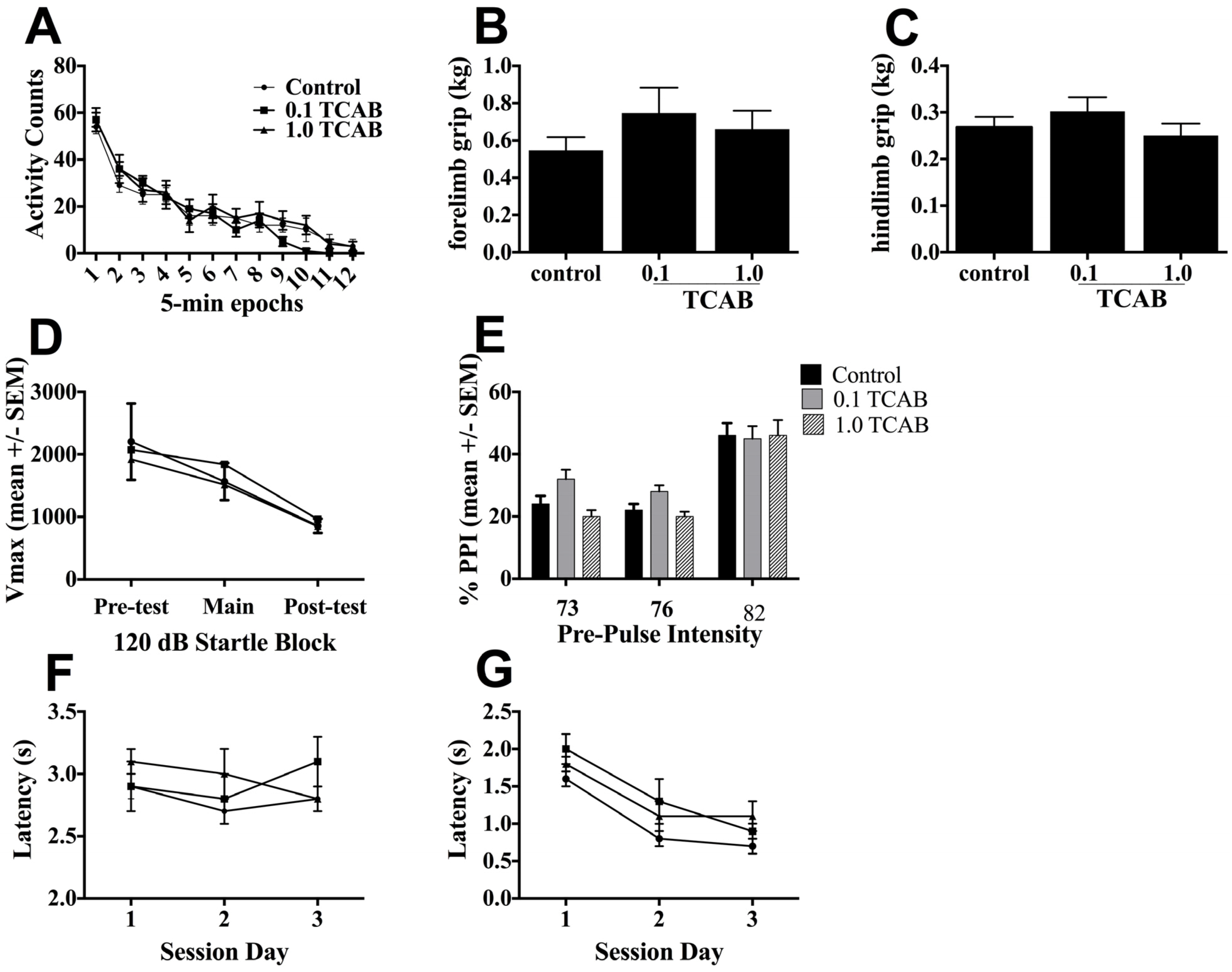
3.3.2. Locomotor Activity and Grip Strength
3.3.3. Pre-pulse Startle Inhibition
3.3.4. Conditioned Avoidance

3.3.5. Morris Water Maze

3.3.6. Delayed Non-matched to Position

3.4. Brain Histology and Immunohistochemistry
3.4.1. Minimal Effect of TCAB on Cortical Layering

3.4.2. Absence of Anatomical Effects of TCAB on Myelin

3.4.3. Morphological Features of Microglia and Astrocytes Related to Development rather than Gliosis
3.4.3.1. Astrocytes

3.4.3.2. Microglia
3.5. Computerized Stereology of Hippocampus


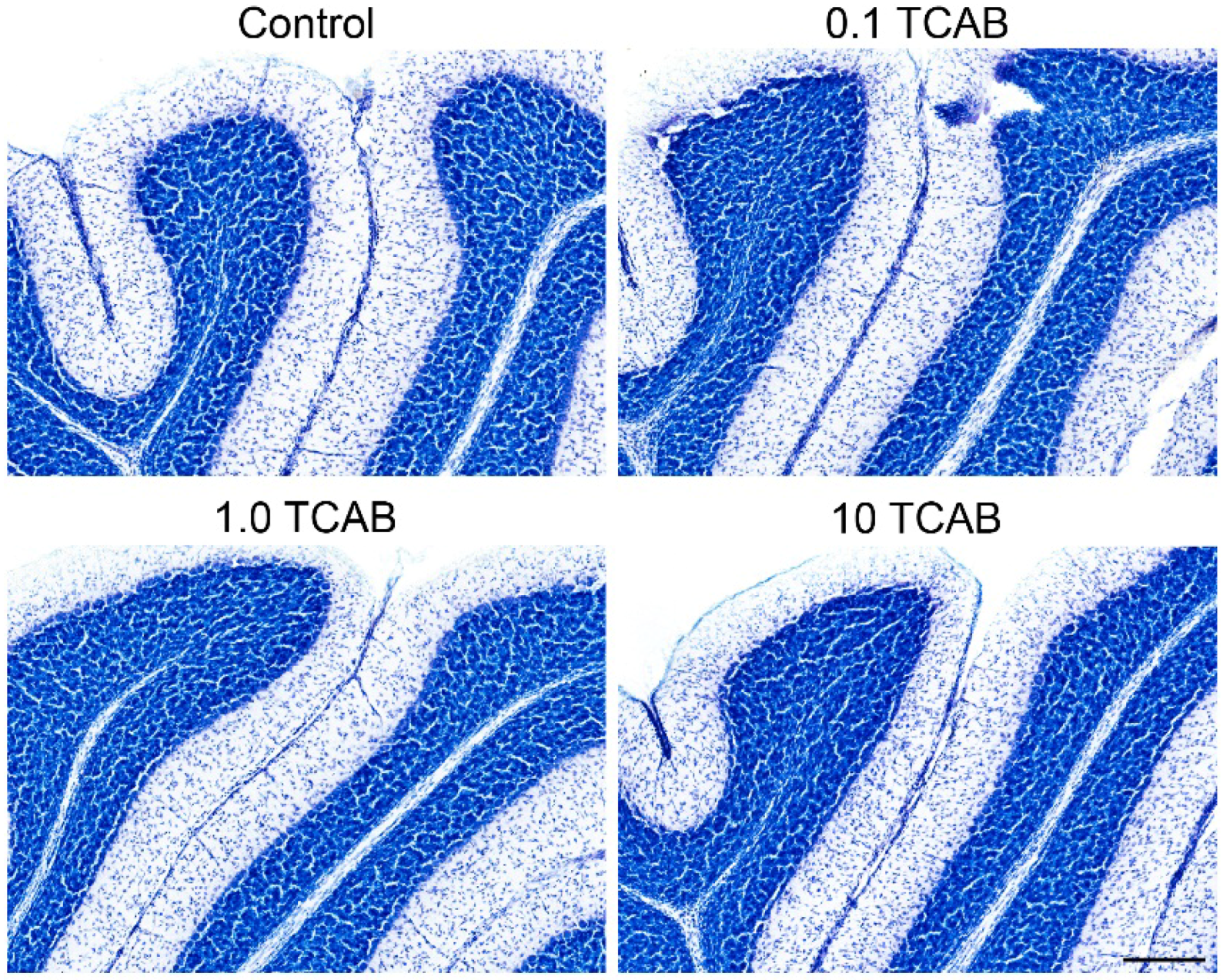
3.6. Cerebellar Morphology and Decreased Purkinje Cell Branching Area

4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thompson, C.C.; Potter, G.B. Thyroid hormone action in neural development. Cereb. Cortex 2000, 10, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, R.Z.; Sargent, J.D.; Larsen, P.R.; Waisbren, S.E.; Haddow, J.E.; Mitchell, M.L. Relation of severity of maternal hypothyroidism to cognitive development of offspring. J. Med. Screen 2001, 8, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunez, J.; Celi, F.S.; Ng, L.; Forrest, D. Multigenic control of thyroid hormone functions in the nervous system. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2008, 287, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenzel, D.; Huttner, W.B. Role of maternal thyroid hormones in the developing neocortex and during human evolution. Front. Neuroanat. 2013, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, L.; Kelley, M.W.; Forrest, D. Making sense with thyroid hormone—the role of T(3) in auditory development. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2013, 9, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G.W.; Schoonover, C.M.; Jones, S.A. Control of thyroid hormone action in the developing rat brain. Thyroid 2003, 13, 1039–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taurog, A. The mechanism of action of the thioureylene antithyroid drugs. Endocrinology 1976, 98, 1031–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barter, R.A.; Klaassen, C.D. UDP-glucuronosyltransferase inducers reduce thyroid hormone levels in rats by an extrathyroidal mechanism. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1992, 113, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, J.H.; Reivich, M.; Gordon, J.T.; Schoenhoff, M.B.; Patlak, C.S.; Dratman, M.B. Imaging triiodothyronine binding kinetics in rat brain; a model for studies in human subjects. Synapse 2006, 60, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakucska, I.; Rand, W.; Lechan, R.M. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone gene expression in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus is dependent upon feedback regulation by both triiodothyronine and thyroxine. Endocrinology 1992, 130, 2845–2850. [Google Scholar]
- Crantz, F.R.; Silva, J.E.; Larsen, P.R. An analysis of the sources and quantity of 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine specifically bound to nuclear receptors in rat cerebral cortex and cerebellum. Endocrinology 1982, 110, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadano-Ferraz, A.; Obregon, M.J.; St. Germain, D.L.; Bernal, J. The type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase is expressed primarily in glial cells in the neonatal rat brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 10391–10396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, R.; Fekete, C.; Goncalves, C.; Legradi, G.; Tu, H.M.; Harney, J.W.; Bianco, A.C.; Lechan, R.M.; Larsen, P.R. Regional physiological adaptation of the central nervous system deiodinases to iodine deficiency. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 281, e54–e61. [Google Scholar]
- Calvo, R.; Obregon, M.J.; Ruiz de Ona, C.; Escobar del Rey, F.; Morreale de Escobar, G. Congenital hypothyroidism, as studied in rats. Crucial role of maternal thyroxine but not of 3,5,3-triiodothyronine in the protection of the fetal brain. J. Clin. Invest. 1990, 86, 889–899. [Google Scholar]
- Grijota-Martinez, C.; Diez, D.; de Escobar, M.G.; Bernal, J.; Morte, B. Lack of action of exogenously administered T3 on the fetal rat brain despite expression of the monocarboxylate transporter 8. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 1713–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berbel, P.; Obrego, M.J.; Bernal, N.J.; Rey, F.E.D.; Escobar, G.M.D. Iodine supplementation during pregnancy: A public health challenge. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 18, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, A.; Morse, D.C.; Lans, M.C.; Schuur, A.G.; Murk, A.J.; Klasson-Wehler, E.; Bergman, A.; Visser, T.J. Interactions of persistent environmental organohalides with the thyroid hormone system: Mechanisms and possible consequences for animal and human health. Toxicol. Ind. Health 1998, 14, 59–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoeller, R.T.; Dowling, A.L.; Herzig, C.T.; Iannacone, E.A.; Gauger, K.J.; Bansal, R. Thyroid hormone, brain development, and the environment. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koibuchi, N.; Iwasaki, T. Regulation of brain development by thyroid hormone and its modulation by environmental chemicals. Endocr. J. 2006, 53, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, M.E.; Rovet, J.; Chen, Z.; Koibuchi, N. Developmental thyroid hormone disruption: Prevalence, environmental contaminants and neurodevelopmental consequences. Neurotoxicology 2012, 33, 842–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porterfield, S. Vulnerability of the developing brain to thyroid abnormalities: Environmental insults to the thyroid system. Environ. Health Perspect. 1994, 102, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brucker-Davis, F. Effects of environmental synthetic chemicals on thyroid function. Thyroid 1998, 6, 827–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.L.; Taylor, M.M.; Devito, M.J.; Crofton, K.M. Developmental exposure to brominated diphenyl ethers results in thyroid hormone disruption. Toxicol. Sci. 2002, 66, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crofton, K.M. Thyroid disrupting chemicals: Mechanisms and mixtures. Int. J. Androl. 2008, 3, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoeller, R.T.; Rovett, J. Timing of thyroid hormone action in the developing brain: Clinical observations and experimental findings. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2004, 16, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, M.E.; Zoeller, R.T. Thyroid hormone—Impact on the developing brain: Possible mechanisms of neurotoxicity. In Neurotoxicology: Target organ toxicology series, 3rd ed.; Harry, G.J., Tilson, H.A., Eds.; Informa Healthcare USA: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 79–111. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, M.E.; Hedge, J.M.; Valentin-Blasini, L.; Blount, B.C.; Kannan, K.; Tietge, J.; Zoeller, R.T.; Crofton, K.M.; Jarrett, J.M.; Fisher, J.W. An animal model of marginal iodine deficiency during development: The thyroid axis and neurodevelopmental outcome. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 132, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knipper, M.; Zinn, C.; Maier, H.; Praetorius, M.; Rohbock, K.; Köpschall, I.; Zimmerman, U. Thyroid hormone deficiency before the onset of hearing causes irreversible damage to peripheral and central auditory systems. J. Neurophysiol. 2000, 83, 3103–3112. [Google Scholar]
- Harry, G.J.; Lein, P.J. Developmental neurotoxicity of dioxins. In Dioxins and Persistent Organic Pollutants: Health and Toxicity, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 193–228. [Google Scholar]
- Poland, A.; Glover, E.; Kende, A.S.; DeCamp, M.; Giandomenico, C.M. 3,4,3N,4N-Tetrachloro azoxybenzene and azobenzene: Potent inducers of aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase. Science 1976, 194, 627–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, U.A.; Brown, M.M.; Logan, R.A.; Millar, L.C.; Bunce, N.J. Screening assay for dioxin-like compounds based on competitive binding to the murine hepatic Ah receptor. 1. Assay development. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 2595–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Birgelen, A.P.; Hébert, C.D.; Wenk, M.L.; Grimes, L.K.; Chapin, R.E.; Mahler, J.; Travlos, G.S.; Bucher, J.R. Toxicity of 3,3'4,4'-tetrachloroazobenzene in rats and mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1999, 156, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Toxicology Program. NTP technical report on the toxicity studies of 3,3'4,4'-tetrachloroazobenzene (CAS No. 14047-09-7) Administered by Gavage to F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice. Available online: http://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/ntp/htdocs/st_rpts/tox065.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2014).
- National Toxicology Program. Reproductive assessment by continuous breeding when 3,3'4,4'-tetrachloroazobenzene (TCAB) (CAS No. 14047-09-7) was administered to Sprague-Dawley rats by oral gavage. NTP Study Number RACB20101. NTP Technical Report 65. Available online: http://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/testing/types/repro/abstracts/racb/racb20101/index.html (accessed on 12 September 2014).
- National Toxicology Program. Toxicology and carcinogenesis studies of 3,3'4,4'-tetrachloroazobenzene (TCAB) (CAS No. 14047-09-07) in Harlan Sprague-Dawley rats and B6C3F1 mice (gavage studies). NTP Technical Report 558. Available online: http://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/ntp/htdocs/lt_rpts/tr558.pdf#search=racb20101 (accessed on 12 September 2014).
- Chatonnet, F.; Picou, F.; Fauquier, T.; Flamant, F. Thyroid Hormone Action in Cerebellum and Cerebral Cortex Development. J. Thyroid Res. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcana, T.; Einstein, E.R.; Csejtey, J. Influence of thyroid hormones on myelin proteins in the developing rat brain. J. Neurol. Sci. 1975, 25, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, M.D.; Cadete-Leite, A.; Andrade, J.P.; Paula-Barbosa, M.M. Effects of hypothyroidism upon the granular layer of the dentate gyrus in male and female adult rats: A morphometric study. J. Comp. Neurol. 1991, 314, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, M.D.; Sousa, N.; Lima-Andrade, M.T.; Calheiros, F.; Cadete-Leite, A.; Paula-Barbosa, M.M. Selective vulnerability of the hippocampal pyramidal neurons to hypothyroidism in male and female rats. J. Comp. Neurol. 1992, 322, 501–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.L.; Altman, J. The effects of early hypo- and hyperthyroidism on the development of the rat cerebellar cortex. II. Synaptogenesis in the molecular layer. Brain Res. 1972, 44, 25–36. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, F.R.; Goncalves, N.; Gomes, F.C.; de Freitas, M.S.; Moura Neto, V. Thyroid hormone action on astroglial cells from distinct brain regions during development. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 1998, 16, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, F.R.; Gervais, A.; Colin, C.; Izembart, M.; Neto, V.M.; Mallat, M. Regulation of microglial development: A novel role for thyroid hormone. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 2028–2038. [Google Scholar]
- National Toxicology Program. NTP range-finding report: Immunotoxicity of 3,3'4,4'-tetrachloroazobenzene in female Sprague Dawley rats (CASRN: 14047-09-07). Available online: http://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/testing/types/imm/abstract/i88486/_i88486/index.html (accessed on 15 September 2014).
- National Toxicology Program. National Toxicology Program specifications for the conduct of studies to evaluate the toxic and carcinogenic potential of chemical and biological and physical agents in laboratory animals for the National Toxicology Program. Available online: http://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/ntp/test_info/finalntp_toxcarspecsjan2011.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2014).
- Gilbert, M.E.; Sui, L. Dose-dependent reductions in spatial learning and synaptic function in the dentate gyrus of adult rats following developmental thyroid hormone insufficiency. Brain Res. 2006, 19, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wijk, N.; Rijntjes, E.; van de Heijning, B.J. Perinatal and chronic hypothyroidism impair behavioural development in male and female rats. Exp. Physiol. 2008, 93, 1199–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Olmos, J.S.; Beltramino, C.A.; de Olmos de Lorenzo, S. Use of an amino-cupric-silver technique for the detection of early and semiacute neuronal degeneration caused by neurotoxicants, hypoxia, and physical trauma. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 1994, 16, 545–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilms, H.; Hartmann, D.; Sievers, J. Ramification of microglia, monocytes and macrophages in vitro: Influences of various epithelial and mesenchymal cells and their conditioned media. Cell. Tissue Res. 1997, 287, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heppner, F.L.; Roth, K.; Nitsch, R.; Hailer, N.P. Vitamin E induces ramification and downregulation of adhesion molecules in cultured microglial cells. Glia 1998, 22, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlowski, D.; Slotys, Z.; Janeczko, K. Morphological development of microglia in the postnatal rat brain. A quantitative study. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2003, 21, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaan, N.M.; Kordower, J.H.; Collier, T.J. Age and region-specific responses of microglia, but not astrocytes, suggest a role in selective vulnerability of dopamine neurons after 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine exposure in monkeys. Glia 2008, 56, 1199–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundersen, H.J.; Jensen, E.B. The efficiency of systematic-sampling in stereology and its prediction. J. Microsc. 1987, 147, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouton, P.R.; Kelley-Bell, B.; Tweedie, D.; Spangler, E.L.; Perez, E.; Carlson, O.D.; Short, R.G.; deCabo, R.; Chang, J.; Ingram, D.K.; et al. The effects of age and lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-mediated peripheral inflammation on numbers of central catecholaminergic neurons. Neurobiol. Aging. 2012, 33, e427–e436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, M.J.; Slomianka, L.; Gundersen, H.J. Unbiased stereological estimation of the total number of neurons in the subdivisions of the rat hippocampus using the optical fractionator. Anat. Rec. 1991, 231, 482–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterio, D.C. The unbiased estimation of number and sizes of arbitrary particles using the dissector. J. Microsc. 1984, 134, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundersen, H.J. Stereology of arbitrary particles. A review of unbiased number and size estimators and the presentation of some new ones, in memory of William R. Thompson. J. Microsc. 1986, 143, 3–45. [Google Scholar]
- Galton, V.A.; Wood, E.T.; St Germain, E.A.; Withrow, C.A.; Aldrich, G.; St Germain, G.M.; Clark, A.S.; St Germain, D.L. Thyroid hormone homeostasis and action in the type 2 deiodinase-deficient rodent brain during development. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 3080–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsia, M.T.; Burant, C.F.; Kreamer, B.L.; Schrankel, K.R. Thymic atrophy induced by acute exposure of 3,3'4,4' tetrachloroazobenzene and 3,3',4,4'-tetrachloroazoxy-benzene in rats. Toxicology 1982, 24, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Kaneko, H.; Sato, K.; Yoshitake, A.; Yamada, H. Hepatic UDP glucuronyltransferase(s) activity toward thyroid hormones in rats: Induction and effects on serum thyroid hormone levels following treatment with various enzyme inducers. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1991, 111, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vansell, N.R.; Klaassen, C.D. Increase in rat liver UDP-glucuronosyltransferase mRNA by microsomal enzyme inducers that enhance thyroid hormone glucuronidation. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2002, 30, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelman, A.; Hill, J. Data Analysis Using Regression and Multilevel/Hierarchial Models; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Dudchenko, P.A. An overview of the tasks used to test working memory in rodents. Neurosci. Biobehavioral. Rev. 2004, 28, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunnett, S.B. Comparative effects of cholinergic drugs and lesions of nucleus basalis or fimbria–fornix on delayed matching in rats. Psychopharmacology 1985, 87, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampson, R.E.; Jarrard, L.E.; Deadwyler, S.A. Effects of ibotenatehippocampal and extrahippocampal destruction on delayed-matchand-nonmatch-to-sample behavior in rats. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 1492–1507. [Google Scholar]
- Wiig, K.A.; Burwell, R.D. Memory impairment on a delayed non-matching-to-position task after lesions of the perirhinal cortex in the rat. Behav. Neurosci. 1998, 112, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Peña, A. Oligodendrocyte development and thyroid hormone. J. Neurobiol. 1999, 40, 497–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strait, K.A.; Carlson, D.J.; Schwartz, H.L.; Oppenheimer, J.H. Transient stimulation of myelin basic protein gene expression in differentiating cultured oligodendrocytes: A model for 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine-induced brain development. Endocrinology 1997, 138, 635–641. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, S.A.; Jolson, D.M.; Cuta, K.K.; Mariash, C.N.; Anderson, G.W. Triiodothyronine is a survival factor for developing oligodendrocytes. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2003, 199, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barres, B.A.; Lazar, M.A.; Raff, M.C. A novel role for thyroid hormone, glucocorticoids and retinoic acid in timing oligodendrocyte development. Development 1994, 120, 1097–1108. [Google Scholar]
- Almazan, G.; Honegger, P.; Matthieu, J.M. Triiodothyronine stimulation of oligodendroglial differentiation and myelination. A developmental study. Dev. Neurosci. 1985, 7, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoonover, C.M.; Seibel, M.M.; Jolson, D.M.; Stack, M.J.; Rahman, R.J.; Jones, S.A.; Mariash, C.N.; Anderson, G.W. Thyroid hormone regulates oligodendrocyte accumulation in developing rat brain white matter tracts. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 5013–5020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarrola, N.; Rodríguez-Peña, A. Hypothyroidism coordinately and transiently affects myelin protein gene expression in most rat brain regions during postnatal development. Brain Res. 1997, 752, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Pena, A.; Ibarrola, N.; Iniguez, M.A.; Munoz, A.; Bernal, J. Neonatal hypothyroidism affects the timely expression of myelin-associated glycoprotein in the rat brain. J. Clin. Invest. 1993, 91, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, J.H.; Gilbert, M.E. Modest thyroid hormone insufficiency during development induces a cellular malformation in the corpus callosum: A model of cortical dysplasia. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 2593–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Callaghan, J.P.; Jensen, K.F.; Miller, D.B. Quantitative aspects of drug and toxicant-induced astrogliosis. Neurochem. Int. 1995, 26, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eng, L.F.; Ghimikar, R.S.; Lee, Y.L. Glial fibrillary acidic protein: GFAP-thirty-one years (1969–2000). Neurochem. Res. 2000, 25, 1439–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamoto, K.; Leblond, C.P. Radioautographic investigation of gliogenesis in the corpus callosum of young rats. II. Origin of microglial cells. J. Comp. Neurol. 1978, 180, 139–163. [Google Scholar]
- Eyo, U.B.; Dailey, M.E. Microglia: Key elements in neural development, plasticity, and pathology. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2011, 8, 494–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harry, G.J. Microglia during development and aging. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 139, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, T.; Betsholtz, C. The importance of microglia in the development of the vasculature in the central nervous system. Vasc. Cell 2013, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Paolicelli, R.C.; Sforazzini, F.; Weinhard, L.; Bolasco, G.; Pagani, F.; Vyssotski, A.L.; Bifone, A.; Gozzi, A.; Ragozzino, D.; et al. Deficient neuron-microglia signaling results in impaired functional brain connectivity and social behavior. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molofsky, A.V.; Krenick, R.; Ullian, E.; Tsai, H-h.; Deneen, B.; Richardson, W.D.; Barres, B.A.; Rowitch, D.H. Astrocytes and disease: A neurodevelopmental perspective. Gene. Dev. 2012, 26, 891–907. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Higashimori, H.; Morel, L. Developmental maturation of astrocytes and pathogenesis of neurodevelopmental disorders. J. Neurodevelop. Disord. 2013, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, R.; Gomes, F.C.A. Neuritogenesis induced by thyroid hormone-treated astrocytes is mediated by epidermal growth factor/mitogen-activated protein kinase-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathways and involves modulation of extracellular matrix proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 49311–49318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzano, J.; Bernal, J.; Morte, B. Influence of thyroid hormones on maturation of rat cerebellar astrocytes. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2007, 25, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohácsik, P.; Zeöld, A.; Bianco, A.C.; Gereben, B. Thyroid hormone and the neuroglia: Both source and target. J. Thyroid Res. 2011, 215718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trentin, A.G. Thyroid hormone and astrocyte morphogenesis. J. Endocrinol. 2006, 189, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, D.; Wirth, E.K.; Schweizer, U. Thyroid hormone transporters in the brain. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 21, 173–186. [Google Scholar]
- Mallat, M.; Lima, F.R.; Gervais, A.; Colin, C.; Moura Neto, V. New insights into the role of thyroid hormone in the CNS: The microglial track. Mol. Psych. 2002, 7, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekete, C.; Freitas, B.C.; Zeöld, A.; Wittmann, G.; Kádár, A.; Liposits, Z.; Christoffolete, M.A.; Singru, P.; Lechan, R.M.; Bianco, A.C.; et al. Expression patterns of WSB-1 and USP-33 underlie cell-specific posttranslational control of type 2 deiodinase in the rat brain. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 4865–4874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, B.C.; Gereben, B.; Castillo, M.; Kalló, I.; Zeöld, A.; Egri, P.; Liposits, Z.; Zavacki, A.M.; Maciel, R.M.; Jo, S.; et al. Paracrine signaling by glial cell-derived triiodothyronine activates neuronal gene expression in the rodent brain and human cells. J. Clin. Invest. 2010, 120, 2206–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, R.M. Adult rat brain astrocytes support survival of both NGF-dependent and NGF-insensitive neurons. Nature 1979, 282, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Dolado, M.; Iglesias, T.; Rodríguez-Peña, A.; Bernal, J.; Muñoz, A. Expression of neurotrophins and the trk family of neurotrophin receptors in normal and hypothyroid rat brain. Mol. Brain Res. 1994, 27, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Furukawa, S.; Omae, F.; Miyama, Y.; Hayashi, K. Correlative regulation of nerve growth factor level and choline acetyltransferase activity by thyroxine in particular regions of infant rat brain. J. Neurochem. 1994, 63, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trentin, A.G.; De Aguiar, C.B.; Garcez, R.C.; Alvarez-Silva, M. Thyroid hormone modulates the extracellular matrix organization and expression in cerebellar astrocyte: Effects on astrocyte adhesion. Glia 2003, 42, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegrist-Kaiser, C.A.; Juge-Aubry, C.; Tranter, M.P.; Ekenbarger, D.M.; Leonard, J.L. Thyroxine-dependent modulation of actin polymerization in cultured astrocytes. A novel, extranuclear action of thyroid hormone. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 5296–5302. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, S.; Das, S.; Poddar, R.; Sarkar, P.K. Role of thyroid hormone in the morphological differentiation and maturation of astrocytes: Temporal correlation with synthesis and organization of actin. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1996, 8, 2361–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, J.L.; Farwell, A.P. Thyroid hormone-regulated actin polymerization in brain. Thyroid 1997, 7, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, V.; Sinha, R.A.; Pathak, A.; Rastogi, L.; Kumar, P.; Pal, A.; Godbole, M.M. Maternal thyroid hormone deficiency affects the fetal neocorticogensis by reducing the proliferating pool, rate of neurogenesis and indirect neurogenesis. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 237, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, M.D.; Paula-Barbosa, M.M. Reorganization of mossy fiber synapses in male and female hypothyroid rats: A stereological study. J. Comp. Neurol. 1993, 337, 334–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, M.E.; Paczkowski, C. Propylthiouracil (PTU)-induced hypothyroidism in the developing rat impairs synaptic transmission and plasticity in the dentate gyrus of the adult hippocampus. Dev. Brain Res. 2003, 145, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, L.; Gilbert, M.E. Pre- and postnatal propylthiouracil-induced hypothyroidism impairs synaptic transmission and plasticity in area CA1 of the neonatal rat hippocampus. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 4195–4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Xu, H.; Gong, J.; Xi, Q.; Chen, J. Developmental iodine deficiency and hypothyroidism impair spatial memory in adolescent rat hippocampus: Involvement of CAMKII, calmodulin, and calcineurin. Neurotox. Res. 2011, 19, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, J. Effects of thyroid hormones on Central Nervous System. In Neurobehavioral Teratology; Yanai, J., Ed.; Elsevier Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1984; pp. 331–363. [Google Scholar]
- Hasebe, M.; Matsumoto, I.; Imagawa, T.; Uehara, M. Effects of an anti-thyroid drug, methimazole, administration to rat dams on the cerebellar cortex development in their pups. Int. J. Devl. Neurosci. 2008, 26, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; Eiraku, M.; Sato, M.; Takata, N.; Kiyohara, Y.; Mishina, M.; Hirase, H.; Hashikawa, T.; Kengaku, M. Remodeling of monoplanar purkinje cell dendrites during cerebellar circuit formation. PLoS One 2011, 6, e20108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morrison, M.E.; Mason, C.A. Granule neuron regulation of Purkinje cell development: Striking a balance between neurotrophin and glutamate signaling. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 3563–3573. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Harry, G.J.; Hooth, M.J.; Vallant, M.; Behl, M.; Travlos, G.S.; Howard, J.L.; Price, C.J.; McBride, S.; Mervis, R.; Mouton, P.R. Developmental Neurotoxicity of 3,3',4,4'-Tetrachloroazobenzene with Thyroxine Deficit: Sensitivity of Glia and Dentate Granule Neurons in the Absence of Behavioral Changes. Toxics 2014, 2, 496-532. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics2030496
Harry GJ, Hooth MJ, Vallant M, Behl M, Travlos GS, Howard JL, Price CJ, McBride S, Mervis R, Mouton PR. Developmental Neurotoxicity of 3,3',4,4'-Tetrachloroazobenzene with Thyroxine Deficit: Sensitivity of Glia and Dentate Granule Neurons in the Absence of Behavioral Changes. Toxics. 2014; 2(3):496-532. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics2030496
Chicago/Turabian StyleHarry, G. Jean, Michelle J. Hooth, Molly Vallant, Mamta Behl, Gregory S. Travlos, James L. Howard, Catherine J. Price, Sandra McBride, Ron Mervis, and Peter R. Mouton. 2014. "Developmental Neurotoxicity of 3,3',4,4'-Tetrachloroazobenzene with Thyroxine Deficit: Sensitivity of Glia and Dentate Granule Neurons in the Absence of Behavioral Changes" Toxics 2, no. 3: 496-532. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics2030496
APA StyleHarry, G. J., Hooth, M. J., Vallant, M., Behl, M., Travlos, G. S., Howard, J. L., Price, C. J., McBride, S., Mervis, R., & Mouton, P. R. (2014). Developmental Neurotoxicity of 3,3',4,4'-Tetrachloroazobenzene with Thyroxine Deficit: Sensitivity of Glia and Dentate Granule Neurons in the Absence of Behavioral Changes. Toxics, 2(3), 496-532. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics2030496




