Intergenerational Effect of Early Life Exposure to Permethrin: Changes in Global DNA Methylation and in Nurr1 Gene Expression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Animals
2.3. Treatment and Experimental Design
2.4. Nucleic Acids Extraction
2.5. MeSAP-PCR
2.6. Gene Expression Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. General Findings
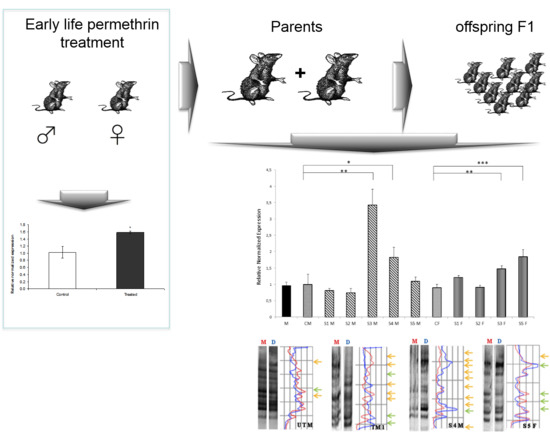
3.2. Nurr 1 Gene Expression in Young Rats

3.3. Nurr1 Gene Expression in F1 Offspring

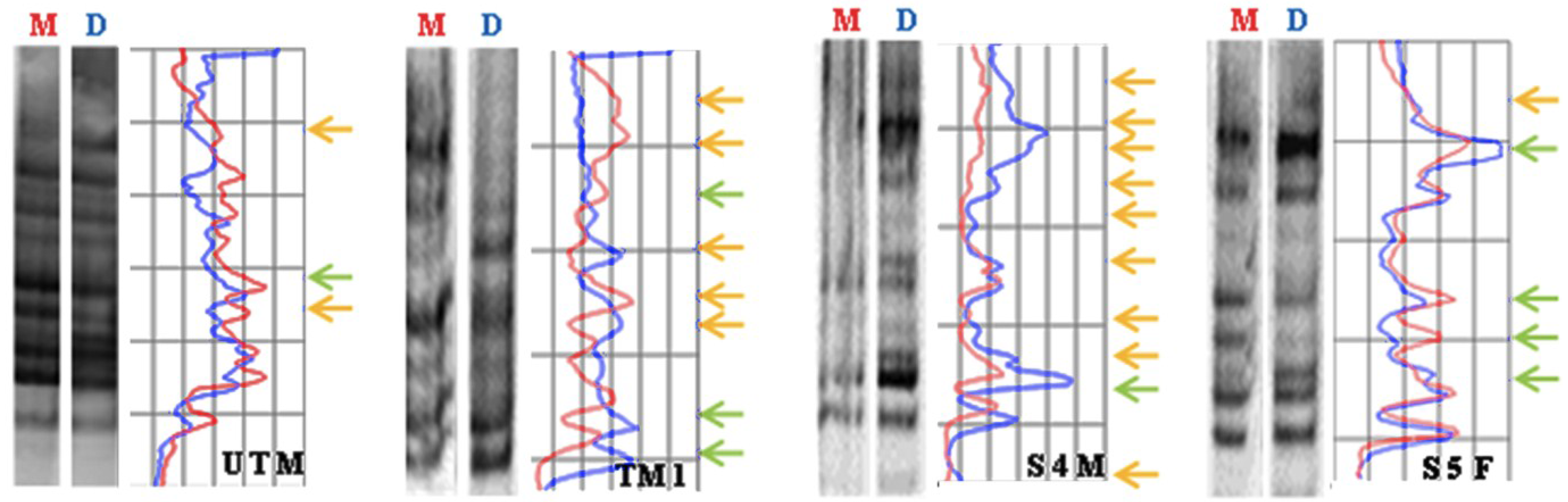
3.4. Global DNA Methylation Assessed by MeSAP-PCR
| Sample | Total of Variations | Mean Value ± SD |
|---|---|---|
| NTM (Untreated) | 3 | 3.5 ± 0.707 |
| NTF (Untreated) | 4 | |
| M1 (Mother) | 8 | 7 ± 1.732 |
| M2 (Mother) | 8 | |
| M3 (Mother) | 5 | |
| S1M | 4 | 7 ± 2.00 |
| S2M | 8 | |
| S3M | 6 | |
| S4M | 9 | |
| S5M | 8 | |
| S1F | 5 | 6.5 ± 2.38 |
| S2F | 10 | |
| S3F | 6 | |
| S5F | 5 |
3.5. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aumann, T.D.; Tomas, D.; Horne, M.K. Environmental and behavioural modulation of the number of substantia nigra dopamine neurons in adult mice. Brain Behav. 2013, 3, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moretto, A.; Colosio, C. Biochemical and toxicological evidence of neurological effects of pesticides: The example of Parkinson’s disease. Neurotoxicology 2011, 32, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.K.; Banerjee, B.D.; Bala, K.; Chhillar, M.; Chhillar, N. Gene-gene and gene-environment interaction on the risk of Parkinson’s disease. Curr. Aging Sci. 2014, 7, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baltazar, M.T.; Dinis-Oliveira, R.J.; de Lourdes Bastos, M.; Tsatsakis, A.M.; Duarte, J.A.; Carvalho, F. Pesticides exposure as etiological factors of Parkinson’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases—A mechanistic approach. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 230, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcioni, M.L.; Nasuti, C.; Bergamini, C.; Fato, R.; Lenaz, G.; Gabbianelli, R. The primary role of GSH against nuclear DNA damage of striatum induced by permethrin in rats. Neuroscience 2010, 168, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dardiotis, E.; Xiromerisiou, G.; Hadjichristodoulou, C.; Tsatsakis, A.M.; Wilks, M.F.; Hadjigeorgiou, G.M. The interplay between environmental and genetic factors in Parkinson’s disease susceptibility: The evidence for pesticides. Toxicology 2013, 307, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedeli, D.; Montani, M.; Galeazzi, R.; Nasuti, C.; Correia-Sá, L.; Domingues, V.F.; Massaccesi, L.; Gabbianelli, R. In vivo and in silico studies to identify mechanisms associated to Nurr1 downregulation following early life exposure to permethrin in rats. Neuroscience. submitted.
- Bradberry, S.M.; Cage, S.A.; Proudfoot, A.T.; Vale, J.A. Poisoning due to pyrethroids. Toxicol. Rev. 2005, 24, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carloni, M.; Nasuti, C.; Fedeli, D.; Montani, M.; Amici, A.; Vadhana, M.S.; Gabbianelli, R. The impact of early life permethrin exposure on development of neurodegeneration in adulthood. Exp. Gerontol. 2012, 47, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carloni, M.; Nasuti, C.; Fedeli, D.; Montani, M.; Amici, A.; Vadhana, M.S.; Gabbianelli, R. Early life permethrin exposure induces long-term brain changes in Nurr1, NF-kB and Nrf-2. Brain Res. 2013, 1515, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasuti, C.; Gabbianelli, R.; Falcioni, M.L.; di Stefano, A.; Sozio, P.; Cantalamessa, F. Dopaminergic system modulation, behavioural changes, and oxidative stress after neonatal administration of pyrethroids. Toxicology 2007, 229, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasuti, C.; Carloni, M.; Fedeli, D.; Gabbianelli, R.; di Stefano, A.; Cerasa, L.S.; Isabel, S.; Domingues, V.; Ciccocioppo, R. Effects of early life permethrin exposure on spatial working memory and on monoamine levels in different brain areas of pre-senescent rats. Toxicology 2013, 303, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedeli, G.; Carloni, D.; Nasuti, C.; Gambini, A.; Scocco, V.; Gabbianelli, R. Early life permethrin exposure leads to hypervitaminosis D, nitric oxide and catecholamines impairment. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2013, 107, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadhana, D.; Nasuti, C.; Carloni, M.; Fedeli, D.; Montani, M.; Amici, A.; Gabbianelli, R. Epigenetic regulation of Nurr1 in striatum of rats exposed to permethrin insecticide. Neurodegener. Dis. 2013, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedeli, D.; Montani, M.; Nasuti, C.; Gabbianelli, R. Early life permethrin treatment induces in striatum of older rats changes in α-synuclein content. J. Nutrigenet. Nutrigenom. 2014, 7, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calhji, C.; Hellstrom, I.C.; Zhang, T.Y.; Diorio, J.; Meaney, M.J. Environmental regulation of the neural epigenome. FEBS J. 2011, 13, 2049–2058. [Google Scholar]
- Naselli, F.; Catanzaro, I.; Bellavia, D.; Perez, A.; Sposito, L.; Caradonna, F. Role and importance of polymorphisms with respect to DNA methylation for the expression of CYP2E1 enzyme. Gene 2014, 15, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gene. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene (accessed on 17 November 2015).
- Kim, S.Y.; Choi, K.C.; Chang, M.S.; Kim, M.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Na, Y.S.; Lee, J.E.; Jin, B.K.; Lee, B.H.; Baik, J.H. The dopamine D2 receptor regulates the development of dopaminergic neurons via extracellular signal-regulated kinase and Nurr1 activation. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 4567–4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankovic, J.; Chen, S.; Le, W.D. The role of Nurr1 in the development of dopaminergic neurons and Parkinson’s disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2005, 77, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasuti, C.; Falcioni, M.L.; Nwankwo, I.E.; Cantalamessa, F.; Gabbianelli, R. Effect of permethrin plus antioxidants on locomotor activity and striatum in adolescent rats. Toxicology 2008, 251, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafalou, S.; Abdollahi, M. Pesticides and human chronic diseases: Evidences, mechanisms, and perspectives. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2013, 268, 157–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Baccarelli, A. Environmental chemical exposures and human epigenetics. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 41, 79–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collotta, M.; Bertazzi, P.A.; Bollati, V. Epigenetics and pesticides. Toxicology 2013, 307, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanthasamy, A.; Jin, H.; Anantharam, V.; Sondarva, G.; Rangasamy, V.; Rana, A.; Kanthasamy, A. Emerging neurotoxic mechanisms in environmental factors-induced neurodegeneration. Neurotoxicology 2012, 33, 833–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.; Li, L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, M. Enantioselective induction of oxidative stress by permethrin in rat adrenal pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2010, 29, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Ni, X. ROS-mediated DNA methylation pattern alterations in carcinogenesis. Curr. Drug Targets 2015, 16, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasuti, C.; Fattoretti, P.; Carloni, M.; Fedeli, D.; Ubaldi, M.; Ciccocioppo, R.; Gabbianelli, R. Neonatal exposure to permethrin pesticide causes lifelong fear and spatial learning deficits and alters hippocampal morphology of synapses. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2014, 6, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedeli, D.; Montani, M.; Carloni, M.; Nasuti, C.; Amici, A.; Gabbianelli, R. Leukocyte Nurr1 as peripheral biomarker of early-life environmental exposure to permethrin insecticide. Biomarkers 2012, 17, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.Y.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, S.K.; Lee, I.K.; Kang, J.H.; Chang, Y.S.; Jacobs, D.R.; Steffes, M.; Lee, D.H. Association of low-dose exposure to persistent organic pollutants with global DNA hypomethylation in healthy Koreans. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusiecki, J.A.; Baccarelli, A.; Bollati, V.; Tarantini, L.; Moore, L.E.; Bonefeld-Jorgensen, E.C. Global DNA hypomethylation is associated with high serum-persistent organic pollutants in Greenlandic Inuit. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 1547–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bordoni, L.; Nasuti, C.; Mirto, M.; Caradonna, F.; Gabbianelli, R. Intergenerational Effect of Early Life Exposure to Permethrin: Changes in Global DNA Methylation and in Nurr1 Gene Expression. Toxics 2015, 3, 451-461. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics3040451
Bordoni L, Nasuti C, Mirto M, Caradonna F, Gabbianelli R. Intergenerational Effect of Early Life Exposure to Permethrin: Changes in Global DNA Methylation and in Nurr1 Gene Expression. Toxics. 2015; 3(4):451-461. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics3040451
Chicago/Turabian StyleBordoni, Laura, Cinzia Nasuti, Maria Mirto, Fabio Caradonna, and Rosita Gabbianelli. 2015. "Intergenerational Effect of Early Life Exposure to Permethrin: Changes in Global DNA Methylation and in Nurr1 Gene Expression" Toxics 3, no. 4: 451-461. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics3040451
APA StyleBordoni, L., Nasuti, C., Mirto, M., Caradonna, F., & Gabbianelli, R. (2015). Intergenerational Effect of Early Life Exposure to Permethrin: Changes in Global DNA Methylation and in Nurr1 Gene Expression. Toxics, 3(4), 451-461. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics3040451