Collection of Anthropogenic Litter from the Shores of Lake Malawi: Characterization of Plastic Debris and the Implications of Public Involvement in the African Great Lakes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites
2.2. Beach Clean-Up Methodology
2.3. Data Handling
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Collection of Anthropogenic Litter
3.2. Plastic Litter
3.3. Implications for Public Involvement and Plastic Pollution in the African Great Lakes
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Derraik, J.G.B. The pollution of the marine environment by plastic debris: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2002, 44, 842–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do Sul, J.A.I.; Costa, M.F. Marine debris review for Latin America and the Wider Caribbean Region: From the 1970s until now, and where do we go from here? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 54, 1087–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo, M.; De losÁngeles Gallardo, M.; Luna-Jorquera, G.; Núñez, P.; Vásquez, N.; Thiel, M. Anthropogenic debris on beaches in the SE Pacific (Chile): Results from a national survey supported by volunteers. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1718–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, M.C.; Silva-Cavalcanti, J.S.; Costa, M.F. Anthropogenic litter on beaches with different levels of development and use: A snapshot of a coast in Pernambuco (Brazil). Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballance, A.; Ryan, P.G.; Turpie, J.K. How much is a clean beach worth? The impact of litter on beach users in the Cape Peninsula, South Africa. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2000, 96, 210–213. [Google Scholar]
- Gregory, M.R.; Andrady, A.L. Plastics in the marine environment. In Plastics and the Environment; Andrady, A.L., Ed.; John Wiley and Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 379–401. [Google Scholar]
- Gregory, M.R. The hazards of persistent marine pollution: Drift plastics and conservation islands. J. R. Soc. New Zealand 1991, 21, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syberg, K.; Khan, F.R.; Selck, H.; Palmqvist, A.; Banta, G.T.; Daley, J.; Sano, L.; Duhaime, M.B. Microplastics: Addressing ecological risk through lessons learned. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordella, S.; Geraga, M.; Papatheodorou, G.; Fakiris, E.; Mitropoulou, I.M. Litter composition and source contribution for 80 beaches in Greece, eastern Mediterranean: A nationwide voluntary clean-up campaign. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2013, 16, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S.L.; Gregorio, D.; Carreon, M.; Weisberg, S.B.; Leecaster, M.K. Composition and distribution of beach debris in Orange County, California. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2001, 42, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelms, S.E.; Coombes, C.; Foster, L.C.; Galloway, T.S.; Godley, B.J.; Lindeque, P.K.; Witt, M.J. Marine anthropogenic litter on British beaches: A 10-year nationwide assessment using citizen science data. Sci. Tot. Environ. 2017, 579, 1399–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ocean Conservancy. Trassh Travels, International Coastal Cleanup 2010 Report; The Ocean Conservancy: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ocean Conservancy. The Beach and Beyond, International Coastal Cleanup 2019 Report; The Ocean Conservancy: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rees, G.; Pond, K. Marine litter monitoring programmes – a review of methods with special reference to national surveys. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1995, 30, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudor, D.T.; Williams, A.T. Some threshold levels in beach litter measurement. Shore Beach 2001, 69, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Storrier, K.L.; McGlashan, D.J. Development and management of a coastal litter campaign: The voluntary coastal partnership approach. Mar. Pol. 2006, 30, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syberg, K.; Hansen, S.F.; Christensen, T.B.; Khan, F.R. Risk perception of plastic pollution: Importance of stakeholder involvement and citizen science. In Freshwater Microplastics the Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Wagner, M., Lambert, S., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; Volume 58, pp. 203–221. [Google Scholar]
- Driedger, A.G.; Dürr, H.H.; Mitchell, K.; Van Cappellen, P. Plastic debris in the Laurentian Great Lakes: A review. J. Gt. Lakes Res. 2015, 41, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bootsma, H.A.; Hecky, R.E. A comparative introduction to the biology and limnology of the African Great Lakes. J. Gt. Lakes Res. 2003, 29, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusher, A.L.; McHugh, M.; Thompson, R.C. Occurrence of microplastics in the gastrointestinal tract of pelagic and demersal fish from the English Channel. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 67, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, W.; Bender, C.; Porcher, J.M. Wild gudgeons (Gobiogobio) from French rivers are contaminated by microplastics: Preliminary study and first evidence. Environ. Res. 2014, 128, 98–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güven, O.; Gökdağ, K.; Jovanović, B.; Kıdeyş, A.E. Microplastic litter composition of the Turkish territorial waters of the Mediterranean Sea, and its occurrence in the gastrointestinal tract of fish. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderon, E.A.; Hansen, P.; Rodríguez, A.; Blettler, M.C.; Syberg, K.; Khan, F.R. Microplastics in the digestive tracts of four fish species from the Ciénaga Grande de Santa Marta Estuary in Colombia. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biginagwa, F.; Mayoma, B.; Shashoua, Y.; Syberg, K.; Khan, F.R. First evidence of microplastics in the African Great Lakes: Recovery from Lake Victoria Nile perch and Nile tilapia. J. Gt. Lakes Res. 2016, 42, 1146–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.R.; Mayoma, B.S.; Biginagwa, F.J.; Syberg, K. Microplastics in Inland African Waters: Presence, Sources, and Fate. In Freshwater Microplastics the Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Wagner, M., Lambert, S., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; Volume 58, pp. 101–124. [Google Scholar]
- Ngupula, G.W.; Kayanda, R.J.; Mashafi, C.A. Abundance, composition and distribution of solid wastes in the Tanzanian waters of Lake Victoria. Afr. J. Aquat. Sci. 2014, 39, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J. Application of Environment Agency’s Aesthetic Assessment Protocol (Beach Survey).R, D Technical Summary E1-117/TR; Environment Agency: Bristol, UK, 2002; p. 3.
- Silva-Iniguez, L.; Fisher, D.W. Quantification and classification of marine litter on the municipal beach of Ensenada, Baja California, Mexico. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2003, 46, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujieda, S.; Sasaki, K. Stranded debris of foamed plastic on the coast of ETA Island and Kurahashi Island in Hiroshima Bay. Nippon. Suisan Gakkaishi 2005, 71, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Browne, M.A.; Galloway, T.S.; Thompson, R.C. Spatial patterns of plastic debris along estuarine shorelines. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3404–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Free, C.M.; Jensen, O.P.; Mason, S.A.; Eriksen, M.; Williamson, N.J.; Boldgiv, B. High-levels of microplastic pollution in a large, remote, mountain lake. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 85, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njeru, J. The urban political ecology of plastic bag waste problem in Nairobi, Kenya. Geoforum 2006, 37, 1046–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapp, J.; Swanston, L. Doing away with plastic shopping bags: International patterns of norm emergence and policy implementation. Environ. Polit. 2009, 18, 315–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikgang, J.; Leiman, A.; Visser, M. Resources, conservation and recycling analysis of the plastic-bag levy in South Africa. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2012, 66, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanzania Bans Tourists From Bringing Plastic Bags Into the Country. Available online: https://www.globalcitizen.org/en/content/tanzania-plastic-bag-ban-travelers/ (accessed on 22 November 2019).
- NOAA Marine Debris Tracker. Available online: https://marinedebris.noaa.gov/partnerships/marine-debris-tracker (accessed on 22 November 2019).
- Marine LitterWatch in a Nutshell. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/themes/water/europes-seas-and-coasts/assessments/marine-litterwatch/at-a-glance/marine-litterwatch-in-a-nutshell (accessed on 24 November 2019).
- Ruiz-Mallén, I.; Riboli-Sasco, L.; Ribrault, C.; Heras, M.; Laguna, D.; Perié, L. Citizen science: Toward transformative learning. Sci. Commun. 2016, 38, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beat Plastic Pollution. Available online: www.unenvironment.org/interactive/beat-plastic-pollution (accessed on 22 November 2019).
- Adebiyi-Abiola, B.; Assefa, S.; Sheikh, K.; García, J.M. Cleaning up plastic pollution in Africa. Science 2019, 365, 1249–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
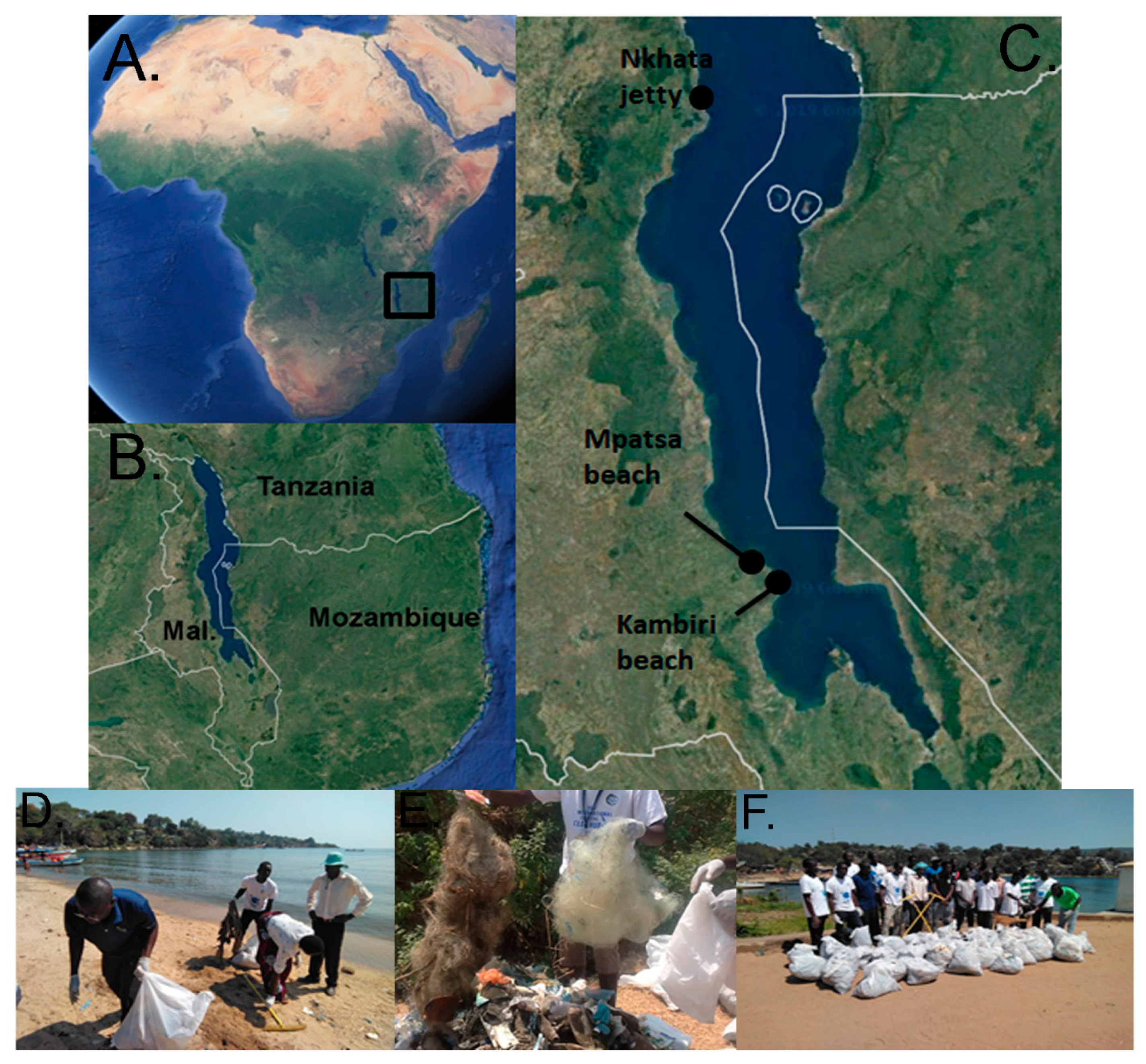


| Site | Location (Longitude, Latitude) | Description and Main Anthropogenic Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Kambiri beach | 34.617952°, −13.781318° | Sandy beach with relatively gentle slope and scattered human settlements Tourism, maize farming, fishing, open market, livestock present, transportation mostly by wooden boats |
| Mpatsa beach | 34.602600°, −13.762000° | Sandy beach with relatively gentle slope and scattered human settlements Tourism, fishing, maize farming, transportation mostly by wooden boats |
| Nkhata jetty | 34.290731°, −11.606589° | Port area which forms a transportation hub linking Malawi, Tanzania, Mozambique and inland islands; historical memorial site which attracts tourists, recreation, cassava farming, fishing and market. Beach with minimal sand accumulation. Has various infrastructure developments including warehouse to cater for imports and exports services. |
| Site | Years | Approximated Area Covered (m2) | No. of Volunteers | Total No. of Items Collected | Total No. of Plastic Items Collected |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kambiri beach | 2015 | 100,000 | 350 | 89,442 | 68,836 |
| 2016 | 160,000 | 821 | 177,087 | 132,666 | |
| Mpatsa beach | 2017 | 20,000 | 64 | 19,238 | 16,361 |
| Nkhata jetty | 2018 | 40,000 | 904 | 204,297 | 171,092 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mayoma, B.S.; Mjumira, I.S.; Efudala, A.; Syberg, K.; Khan, F.R. Collection of Anthropogenic Litter from the Shores of Lake Malawi: Characterization of Plastic Debris and the Implications of Public Involvement in the African Great Lakes. Toxics 2019, 7, 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics7040064
Mayoma BS, Mjumira IS, Efudala A, Syberg K, Khan FR. Collection of Anthropogenic Litter from the Shores of Lake Malawi: Characterization of Plastic Debris and the Implications of Public Involvement in the African Great Lakes. Toxics. 2019; 7(4):64. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics7040064
Chicago/Turabian StyleMayoma, Bahati S., Innocent S. Mjumira, Aubrery Efudala, Kristian Syberg, and Farhan R. Khan. 2019. "Collection of Anthropogenic Litter from the Shores of Lake Malawi: Characterization of Plastic Debris and the Implications of Public Involvement in the African Great Lakes" Toxics 7, no. 4: 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics7040064






