Orally Administered 6:2 Chlorinated Polyfluorinated Ether Sulfonate (F-53B) Causes Thyroid Dysfunction in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
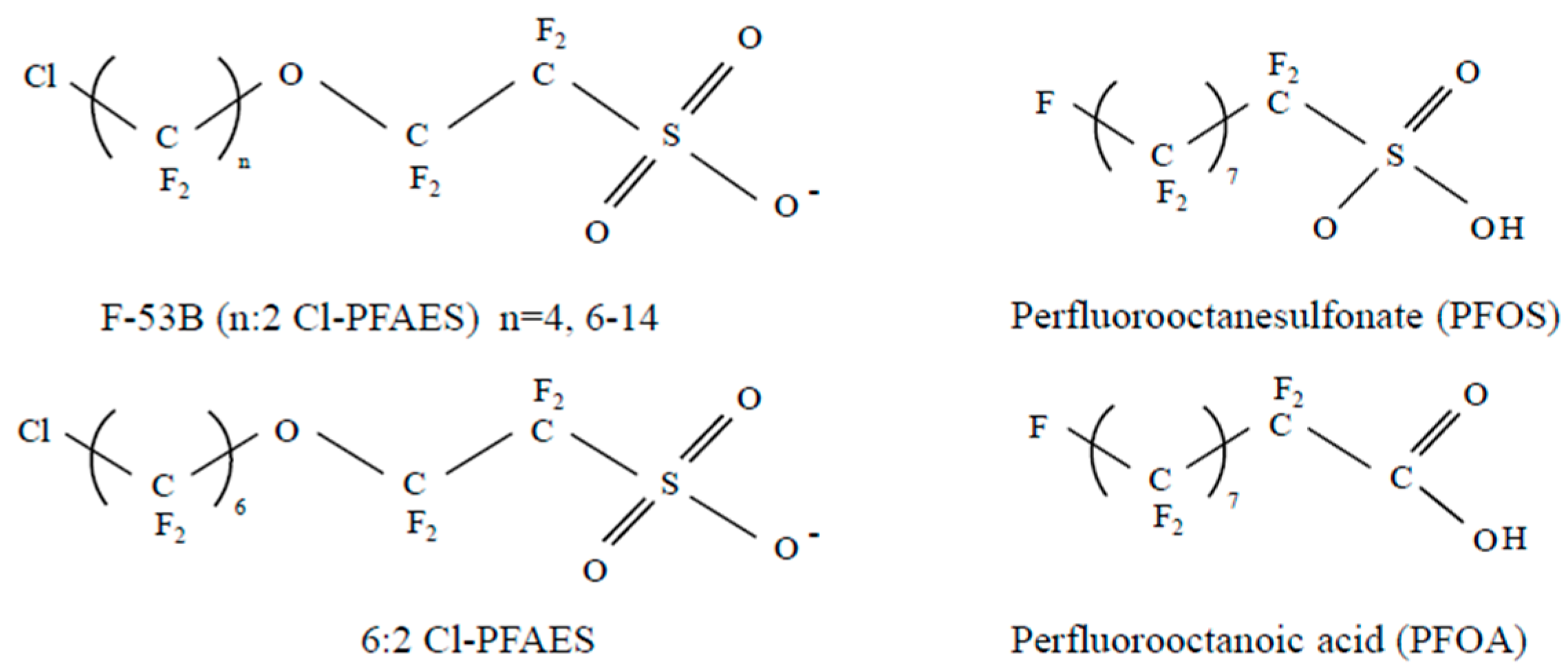
2.1. Test Substance
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Clinical Pathology and Hormone Measurement
2.4. Necropsy and Measurement of Organ Weight
2.5. Histological Analysis and Protein Expression
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
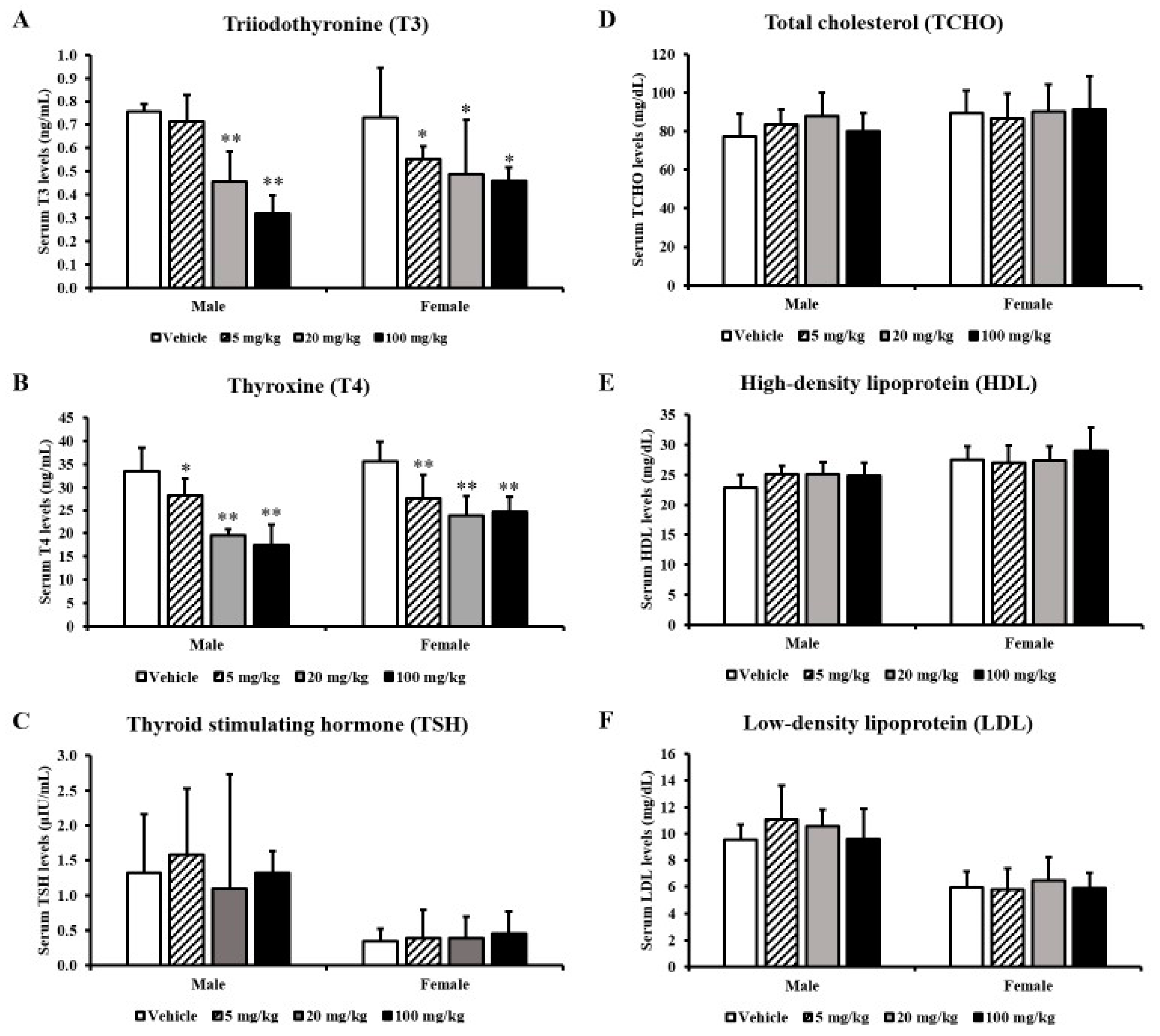
3.1. Thyroid Hormones and Thyroid Hormone-Related Parameters
3.2. Body and Organ Weights
3.3. Histopathology
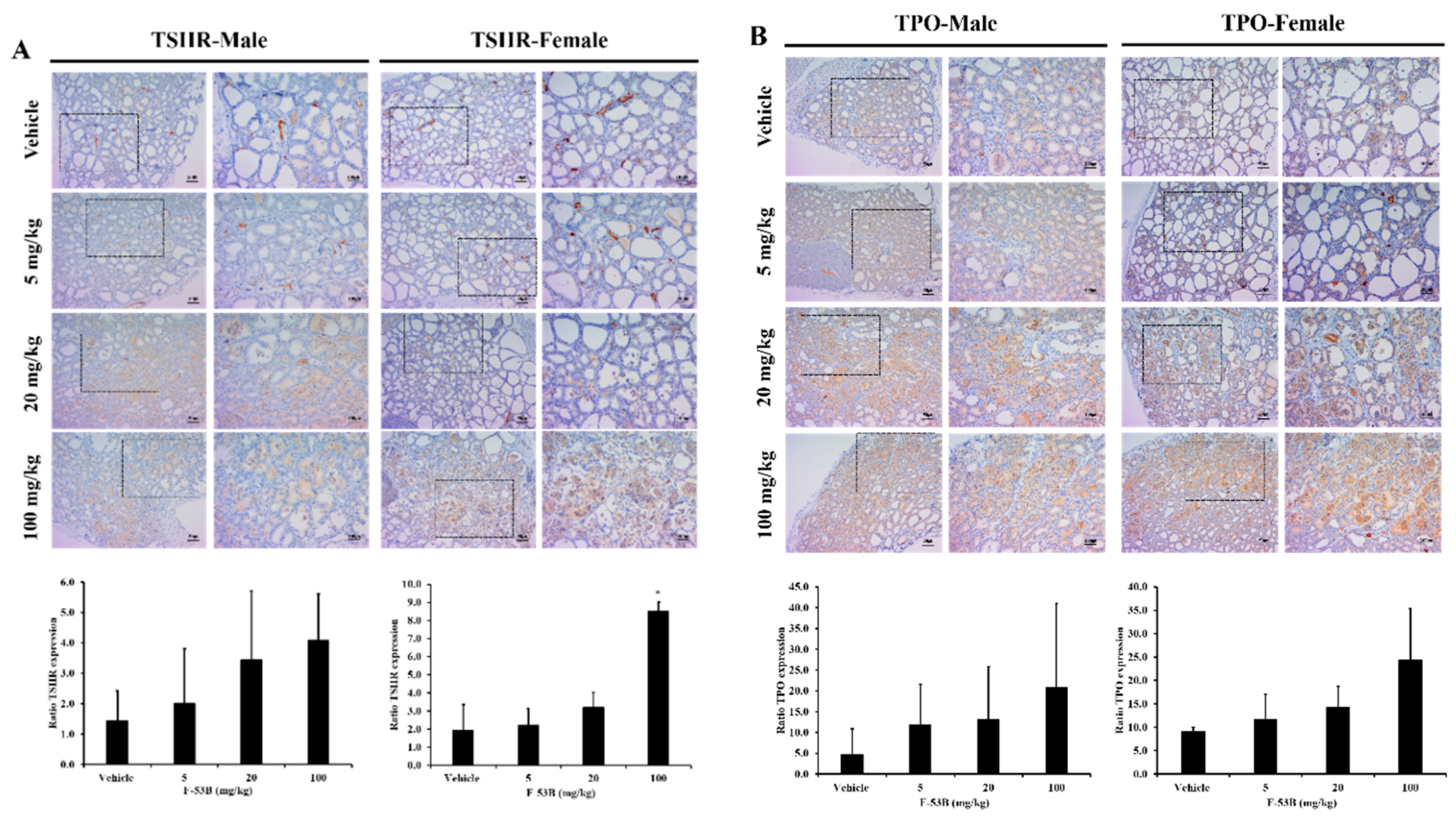
3.4. Thyroid Hormone Biosynthesis-Related Protein Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gebbink, W.A.; Bossi, R.; Rigét, F.F.; Rosing-Asvid, A.; Sonne, C.; Dietz, R. Observation of emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in Greenland marine mammals. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 2384–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buck, R.C.; Franklin, J.; Berger, U.; Conder, J.M.; Cousins, I.T.; de Voogt, P.; Jensen, A.A.; Kannan, K.; Mabury, S.A.; van Leeuwen, S.P. Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluroalkyl substances in the environment: Terminology, classification, and origins. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2011, 7, 513–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, C.; Anitole, K.; Hodes, C.; Lai, D.; Pfahles-Hutchens, A.; Seed, J. Perfluoroalkyl acids: A review of monitoring and toxicological findings. Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 99, 366–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, H.; Quan, X. Effect of developmental perfluorooctane sulfonate exposure on spatial learning and memory ability of rats and mechanism associated with synaptic plasticity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 76, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.Y.; Wong, C.K.C.; Oger, C.; Durand, T.; Galano, J.M.; Lee, J.C.Y. Prenatal exposure to the contaminant perfluorooctane sulfonate elevates lipid peroxidation during mouse fetal development but not in the pregnant dam. Free Radic. Res. 2015, 49, 1015–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coperchini, F.; Awwad, O.; Rotondi, M.; Santini, F.; Imbriani, M.; Chiovato, L. Thyroid disruption by perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluoroocanate (PFOA). J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2017, 40, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Song, B.; Xiao, R.; Zheng, G.; Gong, J.; Chen, M.; Xu, P.; Zhang, P.; Shen, M.; Yi, H. Assessing the human health risks of perfluorooctane sulfonate by in vivo and in vitro studies. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 598–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Environment Program (2009) SC-4/17: Listing of perfluorooctane sulfonic acid its salts and perfluorooctane sulfonyl fluoride, COP-4; Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants, United Nations Environment Program. Available online: http://www.pops.int/TheConvention/ThePOPs/TheNewPOPs/tabid/2511/Default.aspx (accessed on 7 August 2020).
- Kim, M.J.; Moon, S.; Oh, B.C.; Jung, D.; Ji, K.; Choi, K.; Park, Y.J. Association between perfluoroalkyl substances exposure and thyroid function in adults: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.W.; Asher, B.J.; Besoon, S.; Benskin, J.P.; Ross, M.S. PFOS or PreFOS? Are perfluorooctane sulfonate precursor (PreFOS) important determinants of human and environmental perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) exposure? J. Environ. Monit. 2010, 12, 1974–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, J.S. Fluorotechnology is critical to modern life: The FluoroCouncil counterpoint to the Madrid statement. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, A112–A113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; DeWitt, J.C.; Higgins, C.P.; Cousins, I.T. A Never-ending story of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs)? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2508–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Vestergren, R.; Zhou, Z.; Song, X.; Xu, L.; Liang, Y.; Cai, Y. Tissue distribution and whole body burden of the chlorinated polyfluoroalkyl ether sulfonic acid F-53B in crucian carp (Carassius carassius): Evidence for a highly bioaccumulative contaminant of emerging concern. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 14156–14165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Li, J.; Gao, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, J.; He, X.; Zhang, X. Bioaccumulation and effects of novel chlorinated polyfluorinated ether sulfonate in freshwater alga Scenedesmus obliquus. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, G.; Liu, J.; Duy, S.V.; Sauvé, S. Analysis of F-53B, Gen X, ADONA, and emerging fluoroalkylether substances in environmental and biomonitoring samples: A review. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2019, 23, e00066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.L.; Vestergren, R.; Xu, L.; Zhou, Z.; Li, C.X.; Liang, Y.; Cai, Y.Q. Human exposure and elimination kinetic of chlorinated polyfluoroalkyl ether sulfonic acids (Cl-PFESAs). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 2396–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Toxicology Program Public Health Service, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NTP TOX 97: NTP Technical Report on the Toxicity Studies of Perfluoroalkyl Carboxylates (Perfluorohexanoic Acid, Perfluorooctanoic acid, Perfluorononanoic Acid, and Perfluorodecanoic Acid) Administered by Gavage to Sprague Dawley (Hsd: Sprague Dawley SD) Rats; National Toxicology Program Public Health Service, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Research Triangle Park, NC, USA, 2019; ISSN 2378-8992.
- National Toxicology Program Public Health Service, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NTP TOX 96: NTP Technical Report on the Toxicity Studies of Perfluoroalkyl Sulfonates (Perfluorobutane Sulfonic Acid, Perfluorohexane Sulfonate Potassium Salt, and Perfluorooctane Sulfonic Acid) Administered by Gavage to Sprague Dawley (Hsd: Sprague Dawley SD) Rats; National Toxicology Program Public Health Service, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Research Triangle Park, NC, USA, 2019; ISSN 2378-8992.
- Shi, G.; Wang, J.; Guo, H.; Sheng, N.; Cui, Q.; Pan, Y.; Guo, Y.; Sun, Y.; Dai, J. Parental exposure to 6:2 chlorinated polyfluorinated ether sulfonate (F-53B) induced transgenerational thyroid hormone disruption in zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 665, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Ren, X.M.; Ruan, T.; Li, C.H.; Guo, L.H.; Jiang, G. Chlorinated polyfluoroalkylether sulfonates exhibit similar binding potency and activity to thyroid hormone transport proteins and nuclear receptors as perfluorooctanesulfonate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 9412–9418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Cui, Q.; Wang, J.; Guo, H.; Pan, Y.; Sheng, N.; Guo, Y.; Dai, J. Chronic exposure to 6:2 chlorinated polyfluorinated ether sulfonate acid (F-53B) induced hepatotoxic effects in adult zebrafish and disrupted the PPAR signaling pathway in their offspring. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, P.M. Physiological and molecular basis of thyroid hormone action. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 1097–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biebermann, H.; Schöneberg, T.; Krude, H.; Schultz, G.; Gudermann, T.; Grüters, A. Mutations of the human thyrotropin receptor gene causing thyroid hypoplasia and persistent congenital hypothyroidism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 3471–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowicz, M.J.; Targovnik, H.M.; Varela, V.; Cochaux, P.; Krawiec, L.; Pisarev, M.A.; Propato, F.V.; Juvenal, G.; Chester, H.A.; Vassart, G. Identification of a mutation in the coding sequence of the human thyroid peroxidase gene causing congenital goiter. J. Clin. Investig. 1992, 90, 1200–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujiwara, H.; Tatsumi, K.; Miki, K.; Harada, T.; Miyai, K.; Takai, S.; Amino, N. Congenital hypothyroidism caused by a mutation in the Na+/I- symporter. Nat. Genet. 1997, 16, 124–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD Guideline for the Testing (OECD TG) of Chemicals: OECD TG 408 Repeated Dose 90-day Oral Toxicity Study in Rodents. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/env/ehs/testing/oecdguidelinesforthetestingofchemicals.htm (accessed on 25 June 2018).
- Chang, S.C.; Thibodeaux, J.R.; Eastvold, M.L.; Ehresman, D.J.; Bjork, J.A.; Froehlich, J.W.; Lau, C.; Singh, R.J.; Wallace, K.B.; Butenhoff, J.L. Thyroid hormone status and pituitary function in adult rats given oral doses of perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS). Toxicology 2008, 243, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briels, N.; Ciesielski, T.M.; Herzke, D.; Jaspers, V.B. Developmental toxicity of perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) and its chlorinated polyfluoroalkyl ether sulfonate alternative F-53B in the domestic chicken. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12859–12867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.C.; Ehresman, D.J.; Bjork, J.A.; Wallace, K.B.; Parker, G.A.; Stump, D.G.; Butenhoff, J.L. Gestational and lactational exposure to potassium perfluorooctane sulfonate (K+ PFOS) in rats, toxicokinetics, thyroid hormone status, and related gene expression. Reprod. Toxicol. 2009, 27, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, G.; Hensch, T.K. Critical period regulation by thyroid hormones: Potential mechanisms and sex-specific aspects. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Organs | Groups (mg/kg/day) a | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle | 5 | 20 | 100 | |
| Male | ||||
| Thyroid gland | ||||
| Hyperplasia | 0 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| Female | ||||
| Thyroid gland | ||||
| Hyperplasia | 0 | 0 | 4 | 5 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, S.-H.; Lee, S.H.; Yang, J.-Y.; Lee, J.H.; Jung, K.K.; Seok, J.H.; Kim, S.-H.; Nam, K.T.; Jeong, J.; Lee, J.K.; et al. Orally Administered 6:2 Chlorinated Polyfluorinated Ether Sulfonate (F-53B) Causes Thyroid Dysfunction in Rats. Toxics 2020, 8, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics8030054
Hong S-H, Lee SH, Yang J-Y, Lee JH, Jung KK, Seok JH, Kim S-H, Nam KT, Jeong J, Lee JK, et al. Orally Administered 6:2 Chlorinated Polyfluorinated Ether Sulfonate (F-53B) Causes Thyroid Dysfunction in Rats. Toxics. 2020; 8(3):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics8030054
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, So-Hye, Seung Hee Lee, Jun-Young Yang, Jin Hee Lee, Ki Kyung Jung, Ji Hyun Seok, Sung-Hee Kim, Ki Taek Nam, Jayoung Jeong, Jong Kwon Lee, and et al. 2020. "Orally Administered 6:2 Chlorinated Polyfluorinated Ether Sulfonate (F-53B) Causes Thyroid Dysfunction in Rats" Toxics 8, no. 3: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics8030054
APA StyleHong, S.-H., Lee, S. H., Yang, J.-Y., Lee, J. H., Jung, K. K., Seok, J. H., Kim, S.-H., Nam, K. T., Jeong, J., Lee, J. K., & Oh, J.-H. (2020). Orally Administered 6:2 Chlorinated Polyfluorinated Ether Sulfonate (F-53B) Causes Thyroid Dysfunction in Rats. Toxics, 8(3), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics8030054





