Emerging Links between Cadmium Exposure and Insulin Resistance: Human, Animal, and Cell Study Data
Abstract
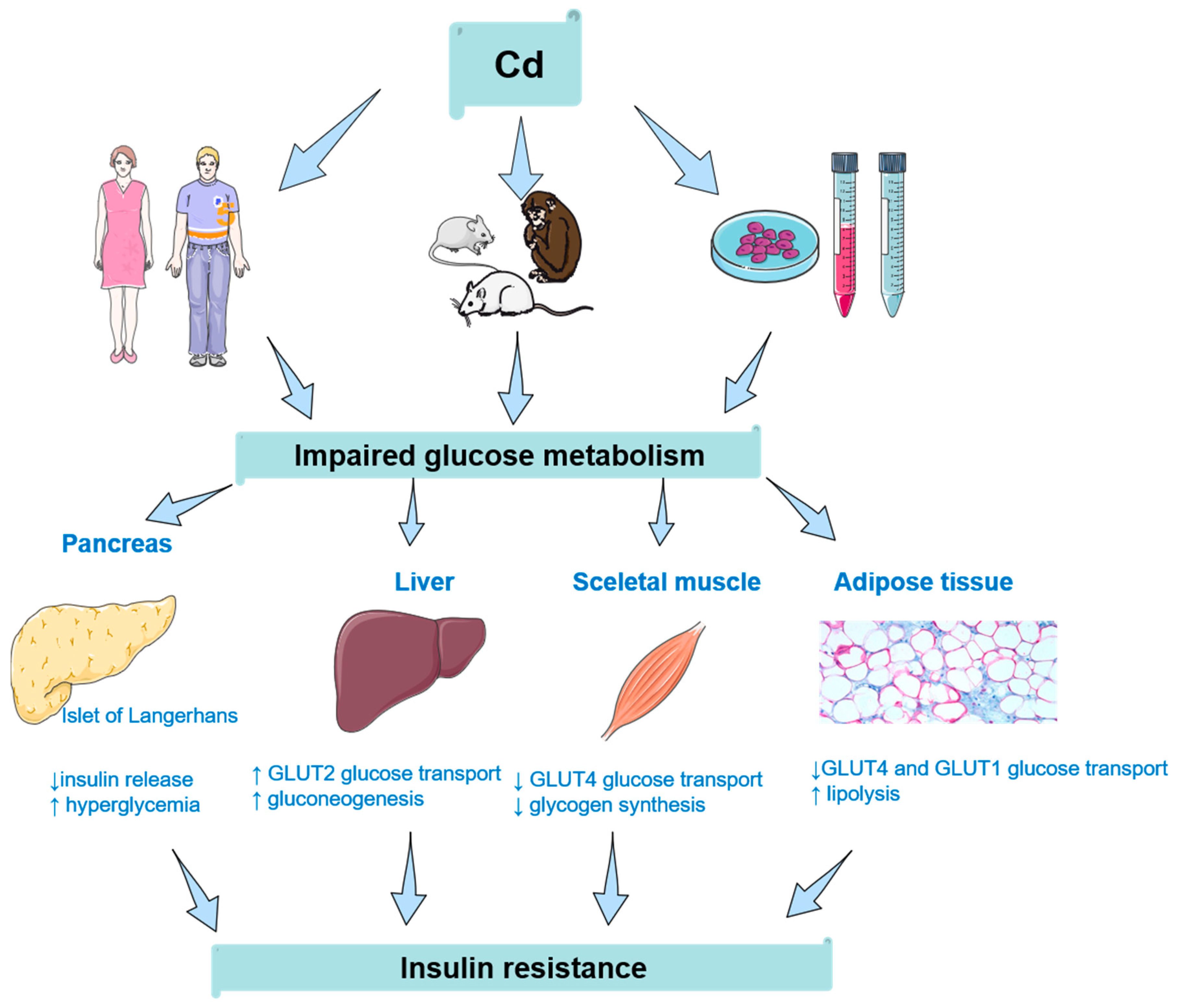
:1. Introduction
2. Insulin Resistance and Cadmium: Human Studies
3. Insulin Resistance and Cadmium: Animal Studies
4. Insulin Resistance and Cadmium: Cellular Studies
4.1. Non-Pancreatic Cells
4.2. Pancreatic Cells
5. Insulin Resistance and Cadmium: Is There a Threshold?
6. Conclusions and Remarks for Future
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yeni-Komshian, H.; Carantoni, M.; Abbasi, F.; Reaven, G.M. Relationship between several surrogate estimates of insulin resistance and quantification of insulin-mediated glucose disposal in 490 healthy nondiabetic volunteers. Diabetes Care 2000, 23, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reaven, G. The metabolic syndrome or the insulin resistance syndrome? Different names, different concepts, and different goals. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2004, 33, 283–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronald Kahn, C. Insulin resistance, insulin insensitivity, and insulin unresponsiveness: A necessary distinction. Metabolism 1978, 27, 1893–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reaven, G.M. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes 1988, 37, 1595–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, C.K.; Hevener, A.L.; Barnard, R.J. Metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance: Underlying causes and modification by exercise training. Compr. Physiol. 2013, 3, 1–58. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.M.; Okumura, M.J.; Davis, M.M.; Herman, W.H.; Gurney, J.G. Prevalence and determinants of insulin resistance among U.S. adolescents: A population-based study. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 2427–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hectors, T.L.M.; Vanparys, C.; Van Gaal, L.F.; Jorens, P.G.; Covaci, A.; Blust, R. Insulin resistance and environmental pollutants: Experimental evidence and future perspectives. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dixit, P.K.; Lazarow, A. Effects of metal ions and sulfhydryl inhibitors on glucose metabolism by adipose tissue. Am. J. Physiol. 1967, 213, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dover, E.N.N.; Patel, N.Y.; Stýblo, M. Impact of in vitro heavy metal exposure on pancreatic β-cell function. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 299, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yang, X. The Essential Element Manganese, Oxidative Stress, and Metabolic Diseases: Links and Interactions. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tripathi, D.; Mani, V.; Pal, R.P. Vanadium in Biosphere and Its Role in Biological Processes. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018, 186, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldwaser, I.; Gefel, D.; Gershonov, E.; Fridkin, M.; Shechter, Y. Insulin-like effects of vanadium: Basic and clinical implications. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2000, 80, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Villalva, A.; Colín-Barenque, L.; Bizarro-Nevares, P.; Rojas-Lemus, M.; Rodríguez-Lara, V.; García-Pelaez, I.; Ustarroz-Cano, M.; López-Valdez, N.; Albarrán-Alonso, J.C.; Fortoul, T.I. Pollution by metals: Is there a relationship in glycemic control? Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 46, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satarug, S. Dietary Cadmium Intake and Its Effects on Kidneys. Toxics 2018, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Satarug, S.; Vesey, D.A.; Gobe, G.C. Current health risk assessment practice for dietary cadmium: Data from different countries. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 106, 430–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repić, A.; Bulat, P.; Antonijević, B.; Antunović, M.; Džudović, J.; Buha, A.; Bulat, Z. The influence of smoking habits on cadmium and lead blood levels in the Serbian adult people. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fransson, M.N.; Barregard, L.; Sallsten, G.; Akerstrom, M.; Johanson, G. Physiologically-based toxicokinetic model for cadmium using markov-chain monte carlo analysis of concentrations in blood, urine, and kidney cortex from living kidney donors. Toxicol. Sci. 2014, 141, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nordberg, G.F.; Nogawa, K.; Nordberg, M.; Friberg, L.T. Cadmium. In Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals, 3rd ed.; Nordberg, G., Fowler, B., Nordberg, M., Nordberg, G., Fowler, L., Friberg, L., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007; pp. 445–486. [Google Scholar]
- Satarug, S.; Garrett, S.H.; Sens, M.A.; Sens, D.A. Cadmium, Environmental Exposure, and Health Outcomes. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 118, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezynska, M.; Brzóska, M.M. Environmental exposure to cadmium—A risk for health of the general population in industrialized countries and preventive strategies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 3211–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buha, A.; Jugdaohsingh, R.; Matovic, V.; Bulat, Z.; Antonijevic, B.; Kerns, J.G.; Goodship, A.; Hart, A.; Powell, J.J. Bone mineral health is sensitively related to environmental cadmium exposure- experimental and human data. Environ. Res. 2019, 176, 108539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djordjevic, V.R.; Wallace, D.R.; Schweitzer, A.; Boricic, N.; Knezevic, D.; Matic, S.; Grubor, N.; Kerkez, M.; Radenkovic, D.; Bulat, Z.; et al. Environmental cadmium exposure and pancreatic cancer: Evidence from case control, animal and in vitro studies. Environ. Int. 2019, 128, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buha, A.; Wallace, D.; Matovic, V.; Schweitzer, A.; Oluic, B.; Micic, D.; Djordjevic, V. Cadmium Exposure as a Putative Risk Factor for the Development of Pancreatic Cancer: Three Different Lines of Evidence. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, D.R.; Buha Djordjevic, A. Heavy metal and pesticide exposure: A mixture of potential toxicity and carcinogenicity. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2020, 19, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browar, A.; Koufos, E.; Wei, Y.; Leavitt, L.; Prozialeck, W.; Edwards, J. Cadmium Exposure Disrupts Periodontal Bone in Experimental Animals: Implications for Periodontal Disease in Humans. Toxics 2018, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronchetti, S.A.; Miler, E.A.; Duvilanski, B.H.; Cabilla, J.P. Cadmium Mimics Estrogen-Driven Cell Proliferation and Prolactin Secretion from Anterior Pituitary Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, N.; Peiris-John, R.; Wickremasinghe, R.; Senanayake, H.; Sathiakumar, N. Cadmium a metalloestrogen: Are we convinced? J. Appl. Toxicol. 2012, 32, 318–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollack, A.Z.; Schisterman, E.F.; Goldman, L.R.; Mumford, S.L.; Albert, P.S.; Jones, R.L.; Wactawski-Wende, J. Cadmium, lead, and mercury in relation to reproductive hormones and anovulation in premenopausal women. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1156–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Zhu, G.; Jin, T. Effects of Cadmium Exposure on Age of Menarche and Menopause. Toxics 2017, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.X.; Wang, P.; Feng, W.; Liu, C.; Yang, P.; Chen, Y.J.; Sun, L.; Sun, Y.; Yue, J.; Gu, L.J.; et al. Relationships between seminal plasma metals/metalloids and semen quality, sperm apoptosis and DNA integrity. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 224, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Angelis, C.; Galdiero, M.; Pivonello, C.; Salzano, C.; Gianfrilli, D.; Piscitelli, P.; Lenzi, A.; Colao, A.; Pivonello, R. The environment and male reproduction: The effect of cadmium exposure on reproductive functions and its implication in fertility. Reprod. Toxicol. 2017, 73, 105–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariba Lovaković, B. Cadmium, arsenic, and lead: Elements affecting male reproductive health. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2020, 19, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buha, A.; Matovic, V.; Antonijevic, B.; Bulat, Z.; Curcic, M.; Renieri, E.A.; Tsatsakis, A.M.; Schweitzer, A.; Wallace, D. Overview of cadmium thyroid disrupting effects and mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buha, A.; Antonijević, B.; Bulat, Z.; Jaćević, V.; Milovanović, V.; Matović, V. The impact of prolonged cadmium exposure and co-exposure with polychlorinated biphenyls on thyroid function in rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 221, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojsavljević, A.; Rovčanin, B.; Krstić, Đ.; Jagodić, J.; Borković-Mitić, S.; Paunović, I.; Živaljević, V.; Mitić, B.; Gavrović-Jankulović, M.; Manojlović, D. Cadmium as main endocrine disruptor in papillary thyroid carcinoma and the significance of Cd/Se ratio for thyroid tissue pathophysiology. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2019, 55, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Đukić-Ćosić, D.; Baralić, K.; Javorac, D.; Djordjevic, A.B.; Bulat, Z. An overview of molecular mechanisms in cadmium toxicity. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2020, 19, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, D.R.; Taalab, Y.M.; Heinze, S.; Tariba Lovaković, B.; Pizent, A.; Renieri, E.; Tsatsakis, A.; Farooqi, A.A.; Javorac, D.; Andjelkovic, M.; et al. Toxic-Metal-Induced Alteration in miRNA Expression Profile as a Proposed Mechanism for Disease Development. Cells 2020, 9, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amaral, A.F.S.; Porta, M.; Silverman, D.T.; Milne, R.L.; Kogevinas, M.; Rothman, N.; Cantor, K.P.; Jackson, B.P.; Pumarega, J.A.; López, T.; et al. Pancreatic cancer risk and levels of trace elements. Gut 2012, 61, 1583–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luckett, B.G.; Su, L.J.; Rood, J.C.; Fontham, E.T.H. Cadmium Exposure and Pancreatic Cancer in South Louisiana. J. Environ. Public Health 2012, 2012, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uetani, M.; Kobayashi, E.; Suwazono, Y.; Honda, R.; Nishijo, M.; Nakagawa, H.; Kido, T.; Nogawa, K. Tissue cadmium (Cd) concentrations of people living in a Cd polluted area. Jpn. Biometals 2006, 19, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, N.; Manoharan, V.; Miltonprabu, S. Grape seed proanthocyanidins protects against cadmium induced oxidative pancreatitis in rats by attenuating oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis via Nrf-2/HO-1 signaling. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2016, 32, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulat, Z.P.; Djukić-Ćosić, D.; Maličević, Ž.; Bulat, P.; Matović, V. Zinc or Magnesium Supplementation Modulates Cd Intoxication in Blood, Kidney, Spleen, and Bone of Rabbits. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2008, 124, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Muayed, M.; Raja, M.R.; Zhang, X.; MacRenaris, K.W.; Bhatt, S.; Chen, X.; Urbanek, M.; O’Halloran, T.V.; Lowe, W.L., Jr. Accumulation of cadmium in insulin-producing β cells. Islets 2012, 4, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mather, A.; Pollock, C. Glucose handling by the kidney. Kidney Int. 2011, 79, S1–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Merali, Z.; Singhal, R.L. Diabetogenic Effects of Chronic Oral Cadmium Administration To Neonatal Rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1980, 69, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, G.G.; Il’Yasova, D.; Ivanova, A. Urinary cadmium, impaired fasting glucose, and diabetes in the NHANES III. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 468–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallia, A.; Allen, N.B.; Badon, S.; El Muayed, M. Association between urinary cadmium levels and prediabetes in the NHANES 2005–2010 population. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2014, 217, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Afridi, H.I.; Kazi, T.G.; Kazi, N.; Jamali, M.K.; Arain, M.B.; Jalbani, N.; Baig, J.A.; Sarfraz, R.A. Evaluation of status of toxic metals in biological samples of diabetes mellitus patients. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2008, 80, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzino, G.; Irrera, N.; Bitto, A.; Pallio, G.; Mannino, F.; Arcoraci, V.; Aliquò, F.; Minutoli, L.; De Ponte, C.; D’Andrea, P.; et al. Cadmium-induced oxidative stress impairs glycemic control in adolescents. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro, E.M.; da Rosa Franchi Santos, L.F.; Scavuzzi, B.M.; Iriyoda, T.M.V.; Peixe, T.S.; Lozovoy, M.A.B.; Reiche, E.M.V.; Dichi, I.; Simão, A.N.C.; Santos, M.J. Trace Elements Associated with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Insulin Resistance. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 191, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugabo, Y.; Li, L.; Renier, G. The Connection Between C-Reactive Protein (CRP) and Diabetic Vasculopathy. Focus on Preclinical Findings. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2010, 6, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquet, A.; Ounnas, F.; Lénon, M.; Arnaud, J.; Demeilliers, C.; Moulis, J.-M. Chronic Exposure to Low-Level Cadmium in Diabetes: Role of Oxidative Stress and Comparison with Polychlorinated Biphenyls. Curr. Drug Targets 2016, 17, 1385–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barregard, L.; Bergström, G.; Fagerberg, B. Cadmium exposure in relation to insulin production, insulin sensitivity and type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional and prospective study in women. Environ. Res. 2013, 121, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Song, J.; Zhu, C.; Wang, Y.; Yin, X.; Huang, G.; Zhao, K.; Zhu, J.; Duan, Z.; Su, L. Association between cadmium exposure and diabetes mellitus risk: A prisma-compliant systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 113129–113141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anetor, J.I.; Uche, C.Z.; Ayita, E.B.; Adedapo, S.K.; Adeleye, J.O.; Anetor, G.O.; Akinlade, S.K. Cadmium Level, Glycemic Control, and Indices of Renal Function in Treated Type II Diabetics: Implications for Polluted Environments. Front. Public Heal. 2016, 4, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maret, W.; Moulis, J.-M. The Bioinorganic Chemistry of Cadmium in the Context of Its Toxicity. In Cadmium: From Toxicity to Essentialit; Sigel, A., Sigel, H., Sigel, R.K.O., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherland, 2013; pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Moulis, J.M. Cellular mechanisms of cadmium toxicity related to the homeostasis of essential metals. BioMetals 2010, 23, 877–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matović, V.; Buha, A.; Bulat, Z.; Đukić-Ćosić, D. Cadmium Toxicity Revisited: Focus on Oxidative Stress Induction and Interactions with Zinc and Magnesium. Arch. Ind. Hyg. Toxicol. 2011, 62, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bulat, Z.; Dukić-Ćosić, D.; Antonijević, B.; Buha, A.; Bulat, P.; Pavlović, Z.; Matović, V. Can zinc supplementation ameliorate cadmium-induced alterations in the bioelement content in rabbits? Arh. Hig. Rada Toksikol. 2017, 68, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moulis, J.-M.; Bourguignon, J.; Catty, P. CHAPTER 23. cadmium. In Metallobiology; Maret, W., Wedd, A., Eds.; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 695–746. ISBN 978-1-84973-599-5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.V. Zinc and insulin in pancreatic beta-cells. Endocrine 2014, 45, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L. Zinc and Its Transporters, Pancreatic β-Cells, and Insulin Metabolism. Vitam. Horm. 2014, 95, 365–390. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz, K.J.C.; De Oliveira, A.R.S.; Morais, J.B.S.; Severo, J.S.; Mendes, P.M.V.; De Sousa Melo, S.R.; De Sousa, G.S.; Do Nascimento Marreiro, D. Zinc and insulin resistance: Biochemical and molecular aspects. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018, 186, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaddiwudhipong, W.; Mahasakpan, P.; Limpatanachote, P.; Krintratun, S. Correlations of urinary cadmium with hypertension and diabetes in persons living in cadmium-contaminated villages in in northwestern Thailand: A population study. Environ. Res. 2010, 110, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swaddiwudhipong, W.; Mahasakpan, P.; Funkhiew, T.; Limpatanachote, P. Changes in cadmium exposure among persons living in cadmium-contaminated areas in Northwestern Thailand: A five-year follow-up. J. Med. Assoc. Thail. 2010, 93, 1217–1222. [Google Scholar]
- Swaddiwudhipong, W.; Limpatanachote, P.; Mahasakpan, P.; Krintratun, S.; Punta, B.; Funkhiew, T. Progress in cadmium-related health effects in persons with high environmental exposure in northwestern Thailand: A five-year follow-up. Environ. Res. 2012, 112, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spoto, B.; Pisano, A.; Zoccali, C. Insulin resistance in chronic kidney disease: A systematic review. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2016, 311, F1087–F1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Satarug, S.; Ruangyuttikarn, W.; Nishijo, M.; Ruiz, P. Urinary Cadmium Threshold to Prevent Kidney Disease Development. Toxics 2018, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edwards, J.R.; Prozialeck, W.C. Cadmium, diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 238, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghafghazi, T.; Mennear, J.H. Effects of acute and subacute cadmium administration on carbohydrate metabolism in mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1973, 26, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ithakissios, D.S.; Ghafghazi, T.; Mennear, J.H.; Kessler, W.V. Effect of multiple doses of cadmium on glucose metabolism and insulin secretion in the rat. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1975, 31, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, R.R.; Early, J.L.; Nonavinakere, V.K.; Mallory, Z. Effect of cadmium on blood glucose level in the rat. Toxicol. Lett. 1990, 54, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapatwala, K.D.; Rajanna, E.; Desaiah, D. Cadmium Induced Changes in Gluconeogenic Enzymes in Rat Kidney and Liver. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 1980, 3, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.J.; Jin, T.Y.; Zhou, Y.F. Insulin expression in rats exposed to cadmium. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2007, 20, 295–301. [Google Scholar]
- Jacquet, A.; Arnaud, J.; Hininger-Favier, I.; Hazane-Puch, F.; Couturier, K.; Lénon, M.; Lamarche, F.; Ounnas, F.; Fontaine, E.; Moulis, J.M.; et al. Impact of chronic and low cadmium exposure of rats: Sex specific disruption of glucose metabolism. Chemosphere 2018, 207, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacquet, A.; Barbeau, D.; Arnaud, J.; Hijazi, S.; Hazane-Puch, F.; Lamarche, F.; Quiclet, C.; Couturier, K.; Fontaine, E.; Moulis, J.M.; et al. Impact of maternal low-level cadmium exposure on glucose and lipid metabolism of the litter at different ages after weaning. Chemosphere 2019, 219, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeFronzo, R.A. Pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2004, 88, 787–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoluci, M.C.; Quadros, A.S.; Sarmento-Leite, R.; Schaan, B.D. Insulin resistance and triglyceride/HDLcindex are associated with coronary artery disease. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2010, 2, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, J.C.; Park, S.Y.; Hah, B.G.; Choi, G.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Kwon, T.H.; Kim, E.K.; Lachaal, M.; Jung, C.Y.; Lee, W. Cadmium induces impaired glucose tolerance in rat by down-regulating GLUT4 expression in adipocytes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2003, 413, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, M.C.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms of insulin action and insulin resistance. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 2133–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olson, A.L. Regulation of GLUT4 and Insulin-Dependent Glucose Flux. ISRN Mol. Biol. 2012, 2012, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, S.; Czech, M.P. The GLUT4 Glucose Transporter. Cell Metab. 2007, 5, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turgut, S.; Kaptanoǧlu, B.; Turgut, G.; Emmungil, G.; Genç, O. Effects of cadmium and zinc on plasma levels of growth hormone, insulin-like growth factor I, and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2005, 108, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinkov, A.A.; Filippini, T.; Ajsuvakova, O.P.; Aaseth, J.; Gluhcheva, Y.G.; Ivanova, J.M.; Bjørklund, G.; Skalnaya, M.G.; Gatiatulina, E.R.; Popova, E.V.; et al. The role of cadmium in obesity and diabetes. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 741–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Jin, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, Z.; Fu, Z. Subchronic Exposure of Mice to Cadmium Perturbs Their Hepatic Energy Metabolism and Gut Microbiome. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2015, 28, 2000–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czech, M.P. Mechanisms of insulin resistance related to white, beige, and brown adipocytes. Mol. Metab. 2020, 34, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belani, M.; Purohit, N.; Pillai, P.; Gupta, S.; Gupta, S. Modulation of steroidogenic pathway in rat granulosa cells with subclinical Cd exposure and insulin resistance: An impact on female fertility. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, A.; Wada, O.; Ono, T.; Ono, H.; Manabe, S.; Ishikawa, S. Cadmium-induced stimulation of lipogenesis from glucose in rat adipocytes. Biochem. J. 1984, 219, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrison, S.A.; Buxton, J.M.; Clancy, B.M.; Czech, M.P. Evidence that erythroid-type glucose transporter intrinsic activity is modulated by cadmium treatment of mouse 3T3-L1 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 19438–19449. [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami, T.; Nishiyama, K.; Kadota, Y.; Sato, M.; Inoue, M.; Suzuki, S. Cadmium modulates adipocyte functions in metallothionein-null mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2013, 272, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, T.; Sugimoto, H.; Furuichi, R.; Kadota, Y.; Inoue, M.; Setsu, K.; Suzuki, S.; Sato, M. Cadmium reduces adipocyte size and expression levels of adiponectin and Peg1/Mest in adipose tissue. Toxicology 2010, 267, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; Moon, J.Y.; Yoo, B.S. Cadmium inhibits the differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocyte through the C/EBPα and PPARγ pathways. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 35, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.K.; Spielmann, M.; Bork, U.; Thévenod, F. Cd2+-induced swelling-contraction dynamics in isolated kidney cortex mitochondria: Role of Ca2+ uniporter, K+ cycling, and protonmotive force. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2005, 289, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nebert, D.W.; Liu, Z. SLC39A8 gene encoding a metal ion transporter: Discovery and bench to bedside. Hum. Genom. 2019, 13, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, R.; Chandi, M.; Kanke, M.; Stýblo, M.; Sethupathy, P. Arsenic is more potent than cadmium or manganese in disrupting the INS-1 beta cell microRNA landscape. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 3099–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghagghazi, T.; Mennear, J.H. The inhibitory effect of cadmium on the secretory activity of the isolated perfused rat pancreas. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1975, 31, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plasman, P.O.; Hermann, M.; Herchuelz, A.; Lebrun, P. Sensitivity to Cd2+ but resistance to Ni2+ of Ca2+ inflow into rat pancreatic islets. Am. J. Physiol. 1990, 258, E529–E533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jijakli, H.; Malaisse, W.J. Verapamil- and cadmium-resistant stimulation of calcium uptake and insulin release by D-glucose in depolarised pancreatic islets exposed to diazoxide. Cell. Signal. 1998, 10, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, T.; Rorsman, F.; Berggren, P.O.; Hellman, B. Accumulation of cadmium in pancreatic beta cells is similar to that of calcium in being stimulated by both glucose and high potassium. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1986, 888, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, T.; Berggren, P.O.; Hellman, B. Cadmium-induced insulin release does not involve changes in intracellular handling of calcium. BBA-Mol. Cell Res. 1987, 929, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasimenko, T.N.; Senyavina, N.V.; Anisimov, N.U.; Tonevitskaya, S.A. A Model of Cadmium Uptake and Transport in Caco-2 Cells. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2016, 161, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquet, A.; Cottet-Rousselle, C.; Arnaud, J.; Julien Saint Amand, K.; Ben Messaoud, R.; Lénon, M.; Demeilliers, C.; Moulis, J.M. Mitochondrial morphology and function of the pancreatic β-cells INS-1 model upon chronic exposure to sub-lethal cadmium doses. Toxics 2018, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallace, D.; Spandidos, D.; Tsatsakis, A.; Schweitzer, A.; Djordjevic, V.; Djordjevic, A. Potential interaction of cadmium chloride with pancreatic mitochondria: Implications for pancreatic cancer. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 44, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.-C.C.; Hsu, C.-C.C.; Liu, S.-H.H.; Su, C.-C.C.; Yen, C.-C.C.; Lee, M.-J.J.; Chen, K.-L.L.; Ho, T.-J.J.; Hung, D.-Z.Z.; Wu, C.-C.C.; et al. Cadmium Induces Apoptosis in Pancreatic β-Cells through a Mitochondria-Dependent Pathway: The Role of Oxidative Stress-Mediated c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase Activation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.C.; Kuo, C.Y.; Yang, C.Y.; Liu, J.M.; Hsu, R.J.; Lee, K.I.; Su, C.C.; Wu, C.C.; Lin, C.T.; Liu, S.H.; et al. Cadmium exposure induces pancreatic β-cell death via a Ca2+-triggered JNK/CHOP-related apoptotic signaling pathway. Toxicology 2019, 425, 152252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paniagua, L.; Diaz-Cueto, L.; Huerta-Reyes, M.; Arechavaleta-Velasco, F. Cadmium exposure induces interleukin-6 production via ROS-dependent activation of the ERK1/2 but independent of JNK signaling pathway in human placental JEG-3 trophoblast cells. Reprod. Toxicol. 2019, 89, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, I.; Damdimopoulou, P.; Stenius, U.; Adamsson, A.; Mäkelä, S.I.; Åkesson, A.; Berglund, M.; Håkansson, H.; Halldin, K. Cadmium-induced effects on cellular signaling pathways in the liver of transgenic estrogen reporter mice. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 127, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dasgupta, P.; Kulkarni, P.; Bhat, N.S.; Majid, S.; Shiina, M.; Shahryari, V.; Yamamura, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Gupta, R.K.; Dahiya, R.; et al. Activation of the Erk/MAPK signaling pathway is a driver for cadmium induced prostate cancer. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 401, 115102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, I.; Damdimopoulou, P.; Stenius, U.; Halldin, K. Cadmium at nanomolar concentrations activates Raf-MEK-ERK1/2 MAPKs signaling via EGFR in human cancer cell lines. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2015, 231, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulis, J.M.; Bulat, Z.; BuhaDjordjevic, A. Threshold in the toxicology of metals: Challenges and pitfalls of the concept. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2020, 19, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munn, S.; Goumenou, M. Thresholds for endocrine disrupters and related uncertainties report of the endocrine disrupters expert advisory group. JRC Sci. Policy Rep. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamanti-Kandarakis, E.; Bourguignon, J.P.; Giudice, L.C.; Hauser, R.; Prins, G.S.; Soto, A.M.; Zoeller, R.T.; Gore, A.C. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals: An Endocrine Society scientific statement. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 293–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, L.N.; Colborn, T.; Hayes, T.B.; Heindel, J.J.; Jacobs, D.R.; Lee, D.H.; Shioda, T.; Soto, A.M.; vom Saal, F.S.; Welshons, W.V.; et al. Hormones and endocrine-disrupting chemicals: Low-dose effects and nonmonotonic dose responses. Endocr. Rev. 2012, 33, 378–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hass, U.; Christiansen, S.; Axelstad, M.; Boberg, J.; Andersson, A.; Skakkebæk, N.E.; Bay, K.; Holbech, H.; Kinnberg, K.L.; Bjerregaard, P. Evaluation of 22 SIN List 2.0 Substances According to the Danish Proposal on Criteria for Endocrine Disrupters; DTU Food: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zoeller, R.T.; Vandenberg, L.N. Assessing dose-response relationships for endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs): A focus on non-monotonicity. Environ. Heal. A Glob. Access Sci. Source 2015, 14, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- European Commission. Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH). Off. J. Eur. Union 2006, 49, 396. [Google Scholar]
- Brescia, S. Thresholds of adversity and their applicability to endocrine disrupting chemicals. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2020, 50, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrott, J.L.; Bjerregaard, P.; Brugger, K.E.; Gray, L.E.; Iguchi, T.; Kadlec, S.M.; Weltje, L.; Wheeler, J.R. Uncertainties in biological responses that influence hazard and risk approaches to the regulation of endocrine active substances. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2017, 13, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- OCDE. OECD Conceptual Framework for Testing and Assessment of Endocrine Disrupters (as revised in 2012). OECD Ser. Test. Assess. 2012, 8, 1829. [Google Scholar]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Farrokhi, F.R.; Butler, A.E.; Sahebkar, A. Insulin resistance: Review of the underlying molecular mechanisms. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 8152–8161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesti, G. Pathophysiology of insulin resistance. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 20, 665–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Hyperglycemic | Hypoglycemic |
|---|---|
| Arsenic | Zinc |
| Mercury | Vanadium |
| Iron | Chromium |
| Lead | Magnesium |
| Nickel | |
| Cadmium |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buha, A.; Đukić-Ćosić, D.; Ćurčić, M.; Bulat, Z.; Antonijević, B.; Moulis, J.-M.; Goumenou, M.; Wallace, D. Emerging Links between Cadmium Exposure and Insulin Resistance: Human, Animal, and Cell Study Data. Toxics 2020, 8, 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics8030063
Buha A, Đukić-Ćosić D, Ćurčić M, Bulat Z, Antonijević B, Moulis J-M, Goumenou M, Wallace D. Emerging Links between Cadmium Exposure and Insulin Resistance: Human, Animal, and Cell Study Data. Toxics. 2020; 8(3):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics8030063
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuha, Aleksandra, Danijela Đukić-Ćosić, Marijana Ćurčić, Zorica Bulat, Biljana Antonijević, Jean-Marc Moulis, Marina Goumenou, and David Wallace. 2020. "Emerging Links between Cadmium Exposure and Insulin Resistance: Human, Animal, and Cell Study Data" Toxics 8, no. 3: 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics8030063
APA StyleBuha, A., Đukić-Ćosić, D., Ćurčić, M., Bulat, Z., Antonijević, B., Moulis, J. -M., Goumenou, M., & Wallace, D. (2020). Emerging Links between Cadmium Exposure and Insulin Resistance: Human, Animal, and Cell Study Data. Toxics, 8(3), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics8030063








