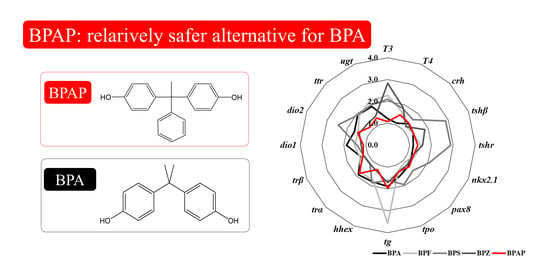
Zebrafish Embryonic Exposure to BPAP and Its Relatively Weak Thyroid Hormone-Disrupting Effects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Chemicals and Chemical Analysis
2.2. Zebrafish Culture and Exposure Design
2.3. TH Measurement
2.4. RNA Isolation and Quantitative RT-PCR
2.5. RNA-Sequencing and Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA)
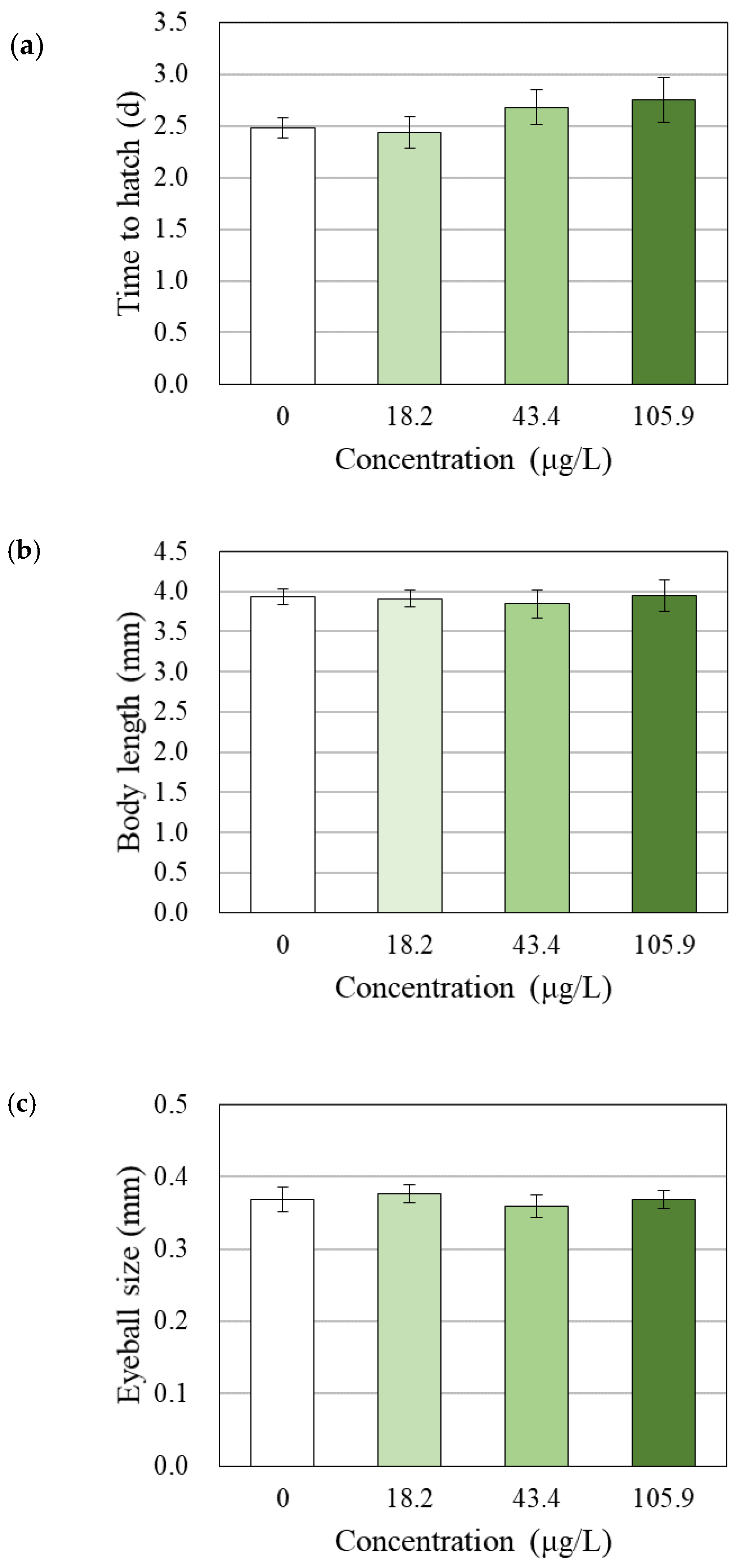
2.6. Hatchability, Growth, and Morphological Observations
2.7. Behavior Analysis (Locomotor Activity)
2.8. Statistical Analysis
2.9. Integrated Comparison with Other Bisphenols
3. Results
3.1. Changes in the TH and TSHβ Levels
3.2. Transcriptional Changes in TH-Related Genes
3.3. RNA Sequencing and IPA
3.4. Changes in Survival, Hatchability, Growth and Morphology
3.5. Behavioral Changes
3.6. Integrated Comparison with Other Bisphenols
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of BPAP on the TH Levels
4.2. Effects of BPAP on Gene Transcription and the Transcriptome
4.3. Effects of BPAP on Hatching, Growth and Behavior
4.4. Disruption Potency of BPAP in Comparison with that of Other Bisphenols
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, D.H.; Zhou, E.X.; Yang, Z.L. Waterborne exposure to BPS causes thyroid endocrine disruption in zebrafish larvae. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Ren, X.M.; Li, Y.Y.; Yao, X.F.; Li, C.H.; Qin, Z.F.; Guo, L.H. Bisphenol A alternatives bisphenol S and bisphenol F interfere with thyroid hormone signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 1072–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Kim, C.; Shin, H.; Kho, Y.; Choi, K. Comparison of thyroid hormone disruption potentials by bisphenols A, S, F, and Z in embryo-larval zebrafish. Chemosphere 2019, 221, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.M.; Tian, X.F.; Fang, X.D.; Ji, F.J. Waterborne exposure to bisphenol F causes thyroid endocrine disruption in zebrafish larvae. Chemosphere 2016, 147, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, T.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tang, W.; Wang, F.; Diao, X. Thyroid Disruption in Zebrafish Larvae by Short-Term Exposure to Bisphenol AF. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 13069–13084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Fang, P.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X. Rapid method for the separation and recovery of endocrine-disrupting compound bisphenol AP from wastewater. Langmuir 2013, 29, 3968–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Li, J.; Yu, T.; Zhou, L.; Fan, X.; Xiao, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Lv, J.; Jia, X.; et al. Bisphenol AP is anti-estrogenic and may cause adverse effects at low doses relevant to human exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 1625–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Kannan, K. A survey of alkylphenols, bisphenols, and triclosan in personal care products from China and the United States. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014, 67, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Kannan, K. A survey of bisphenol A and other bisphenol analogues in foodstuffs from nine cities in China. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo Risk Assess. 2014, 31, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asimakopoulos, A.G.; Xue, J.; De Carvalho, B.P.; Iyer, A.; Abualnaja, K.O.; Yaghmoor, S.S.; Kumosani, T.A.; Kannan, K. Urinary biomarkers of exposure to 57 xenobiotics and its association with oxidative stress in a population in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Environ. Res. 2016, 150, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Xue, J.; Gao, C.Z.; Qiu, R.L.; Li, Y.X.; Li, X.; Huang, M.Z.; Kannan, K. Urinary Concentrations of bisphenols and their association with biomarkers of oxidative stress in people living near E-waste recycling facilities in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4045–4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Fang, J.; Ren, L.; Fan, R.; Zhang, J.; Liu, G.; Zhou, L.; Chen, D.; Yu, Y.; Lu, S. Urinary bisphenol analogues and triclosan in children from south China and implications for human exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 238, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Liu, Q.; Yan, K.; Wu, S.; Han, Z.; Guo, R.; Chen, M.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J. Bisphenol analogues in surface water and sediment from the shallow Chinese freshwater lakes: Occurrence, distribution, source apportionment, and ecological and human health risk. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Liao, C.; Song, G.J.; Ra, K.; Kannan, K.; Moon, H.B. Emission of bisphenol analogues including bisphenol A and bisphenol F from wastewater treatment plants in Korea. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 1000–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, C.; Youn, H.; Choi, K. Thyroid hormone disrupting potentials of bisphenol A and its analogues—In vitro comparison study employing rat pituitary (GH3) and thyroid follicular (FRTL-5) cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2017, 40, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Choi, K.; Ji, K. Effects of bisphenol analogs on thyroid endocrine system and possible interaction with 17beta-estradiol using GH3 cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2018, 53, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament and the Council of the European Union. Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2010 on the Protection of Animals Used for Scientific Purposes. Off. J. Eur. Union 2010, 53, 33–79. [Google Scholar]
- Elsalini, O.S.; Gartzen, J.; Cramer, M.; Rohr, K.B. Zebrafish hhex, nk2.1a, and pax2.1 regulate thyroid growth and differentiation downstream of Nodel-dependent transcription factors. Dev. Biol. 2003, 263, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spaan, K.; Haigis, A.C.; Weiss, J.; Legradi, J. Effects of 25 thyroid hormone disruptors on zebrafish embryos: A literature review of potential biomarkers. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 656, 1238–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Optiz, R.; Antonica, F.; Costagliola, S. New model system to illuminate thyroid organogenesis. Part I: An update on the zebrafish toolbox. Eur. Thyroid J. 2013, 2, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Percie du Sert, N.; Ahluwalia, A.; Alam, S.; Avey, M.T.; Baker, M.; Browne, W.J.; Clark, A.; Cuthill, I.C.; Dirnagl, U.; Emerson, M.; et al. Reporting animal research: Explanation and elaboration for the ARRIVE guidelines 2.0. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Deng, J.; Shi, X.; Liu, C.; Yu, K.; Zhou, B. Exposure to DE-71 alters thyroid hormone levels and gene transcription in the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis of zebrafish larvae. Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 97, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCurley, A.T.; Callard, G.V. Characterization of housekeeping genes in zebrafish: Male-female differences and effects of tissue type, developmental stage and chemical treatment. BMC Mol. Biol. 2008, 9, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Chun, H.S.; Lee, J.; Park, H.J.; Kim, K.T.; Kim, C.H.; Yoon, S.; Kim, W.K. Plausibility of the zebrafish embryos/larvae as an alternative animal model for autism: A comparison study of transcriptome changes. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Qiu, X.; Meng, S.; Xu, H.; Wu, X.; Yang, M. Proteomic profile and toxicity pathway analysis in zebrafish embryos exposed to bisphenol A and di-n-butyl phthalate at environmentally relevant levels. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, W.B.; Mole, R.A.; Brooks, B.W. Experimental Protocol for Examining Behavioral Response Profiles in Larval Fish: Application to the Neuro-stimulant Caffeine. JoVE J. Vis. Exp. 2018, e57938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, W.K.; Lee, S.K.; Choi, K.; Jung, J. Integrative assessment of biomarker responses in pale chub (Zacco platypus) exposed to copper and benzo[a]pyrene. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 92, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.Q.; Zhao, G.F.; Feng, M.; Wen, W.; Li, K.; Zhang, P.W.; Peng, X.; Huo, W.J.; Zhou, H.D. Chronic exposure to pentachlorophenol alters thyroid hormones and thyroid hormone pathway mRNAs in zebrafish. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boas, M.; Feldt-Rasmussen, U.; Main, K.M. Thyroid effects of endocrine disrupting chemicals. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 355, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Yuan, L.; Zha, J.; Wang, Z. Developmental toxicity and thyroid hormone-disrupting effects of 2,4-dichloro-6-nitrophenol in Chinese rare minnow (Gobiocypris rarus). Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 185, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Zhou, B. Thyroid endocrine system disruption by pentachlorophenol: An in vitro and in vivo assay. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 142–143, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Liang, K.; Liu, J.; Yang, L.; Guo, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhou, B. Exposure of zebrafish embryos/larvae to TDCPP alters concentrations of thyroid hormones and transcriptions of genes involved in the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 126, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.J.; Li, H.B.; Xiang, P.; Zhang, X.; Ma, L.Q. Short-term exposure of arsenite disrupted thyroid endocrine system and altered gene transcription in the HPT axis in zebrafish. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 205, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoeller, R.T.; Tan, S.W.; Tyl, R.W. General background on the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid (HPT) axis. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2007, 37, 11–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiga-Carvalho, T.M.; Sidhaye, A.R.; Wondisford, F.E. Thyroid hormone receptors and resistance to thyroid hormone disorders. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Q.; Yu, L.; Yang, L.; Zhou, B. Bioconcentration and metabolism of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) result in thyroid endocrine disruption in zebrafish larvae. Aquat. Toxicol. 2012, 110–111, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crump, D.; Jagla, M.M.; Kehoe, A.; Kennedy, S.W. Detection of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers in Herring Gull (Larus argentatus) brains: Effects on mRNA Expression in Cultured Neuronal Cells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 7715–7721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, P.; Diez, J.J. Thyroid dysfunction and kidney disease. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2009, 160, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schairer, B.; Jungreithmayr, V.; Schuster, M.; Reiter, T.; Herkner, H.; Gessl, A.; Sengolge, G.; Winnicki, W. Effect of Thyroid Hormones on Kidney Function in Patients after Kidney Transplantation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grais, I.M.; Sowers, J.R. Thyroid and the Heart. Am. J. Med. 2014, 127, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chi, H.C.; Chen, C.Y.; Tsai, M.M.; Tsai, C.Y.; Lin, K.H. Molecular functions of thyroid hormones and their clinical significance in liver-related diseases. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 601361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sinha, R.A.; Singh, B.K.; Yen, P.M. Direct effects of thyroid hormones on hepatic lipid metabolism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, C.-T.; Hsiao, Y.-C.; Ko, F.-C.; Cheng, J.-O.; Cheng, Y.-M.; Chen, T.-H. Chronic exposure of 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether (PBDE-47) alters locomotion behavior in juvenile zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 98, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Liu, X.; Takeda, S.; Choi, K. Genotoxic potentials and related mechanisms of bisphenol A and other bisphenol compounds: A comparison study employing chicken DT40 cells. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesnage, R.; Phedonos, A.; Arno, M.; Balu, S.; Corton, J.C.; Antoniou, M.N. Transcriptome Profiling Reveals Bisphenol A Alternatives Activate Estrogen Receptor Alpha in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2017, 158, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Conc. (μg/L) | Thyroid Stimulation | TH Receptors and Transport | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| crh | tshβ | trα | trβ | ttr | |||
| 0 | 1.00 ± 0.21 | 1.00 ± 0.23 | 1.00 ± 0.34 | 1.00 ± 0.08 | 1.00 ± 0.08 | ||
| 18.2 | 0.72 ± 0.18 | 0.79 ± 0.27 | 1.43 ± 0.37 | 1.02 ± 0.24 | 1.00 ± 0.15 | ||
| 43.4 | 0.89 ± 0.16 | 0.77 ± 0.26 | 1.83 ± 0.31 | 1.21 ± 0.20 | 1.15 ± 0.26 | ||
| 105.9 | 1.13 ± 0.10 | 1.29 ± 0.20 | 1.57 ± 0.28 | 1.03 ± 0.25 | 1.16 ± 0.22 | ||
| Conc. (μg/L) | TH Synthesis | ||||||
| nkx2.1 | hhex | tshr | slc5a5 | tg a | Pax8 | tpo | |
| 0 | 1.00 ± 0.23 | 1.00 ± 0.15 | 1.00 ± 0.19 | 1.00 ± 0.17 | 1.02 (0.92–1.07) | 1.00 ± 0.26 | 1.00 ± 0.08 |
| 18.2 | 0.79 ± 0.25 | 0.83 ± 0.16 | 0.72 ± 0.25 | 0.60 ± 0.23 | 0.86 (0.35–1.01) | 0.72 ± 0.10 | 0.76 ± 0.06 |
| 43.4 | 0.86 ± 0.26 | 0.94 ± 0.13 | 0.77 ± 0.31 | 0.55 ± 0.23 | 1.03 (0.93–2.25) | 0.92 ± 0.15 | 0.98 ± 0.07 |
| 105.9 | 1.26 ± 0.26 | 1.21 ± 0.27 | 1.19 ± 0.27 | 1.04 ± 0.27 | 1.60 (1.47–2.88) | 0.78 ± 0.19 | 0.81 ± 0.11 |
| Conc. (μg/L) | TH Metabolism | ||||||
| dio1 | dio2 | dio3 a | ugt1ab | ||||
| 0 | 1.00 ± 0.19 | 1.00 ± 0.25 | 0.99 (0.89–1.12) | 1.00 ± 0.17 | |||
| 18.2 | 0.97 ± 0.03 | 0.67 ± 0.22 | 0.79 (0.45–1.16) | 0.75 ± 0.10 | |||
| 43.4 | 1.11 ± 0.13 | 0.93 ± 0.01 | 0.88 (0.71–0.88) | 0.91 ± 0.08 | |||
| 105.9 | 1.11 ± 0.03 | 1.13 ± 0.28 | 1.03 (0.87–2.29) | 1.17 ± 0.19 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.; Eghan, K.; Lee, J.; Yoo, D.; Yoon, S.; Kim, W.-K. Zebrafish Embryonic Exposure to BPAP and Its Relatively Weak Thyroid Hormone-Disrupting Effects. Toxics 2020, 8, 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics8040103
Lee S, Eghan K, Lee J, Yoo D, Yoon S, Kim W-K. Zebrafish Embryonic Exposure to BPAP and Its Relatively Weak Thyroid Hormone-Disrupting Effects. Toxics. 2020; 8(4):103. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics8040103
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Sangwoo, Kojo Eghan, Jieon Lee, Donggon Yoo, Seokjoo Yoon, and Woo-Keun Kim. 2020. "Zebrafish Embryonic Exposure to BPAP and Its Relatively Weak Thyroid Hormone-Disrupting Effects" Toxics 8, no. 4: 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics8040103
APA StyleLee, S., Eghan, K., Lee, J., Yoo, D., Yoon, S., & Kim, W.-K. (2020). Zebrafish Embryonic Exposure to BPAP and Its Relatively Weak Thyroid Hormone-Disrupting Effects. Toxics, 8(4), 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics8040103