Development of a Larval Zebrafish Model for Acute Organophosphorus Nerve Agent and Pesticide Exposure and Therapeutic Evaluation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Husbandry and Larvae Production
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Exposure and Treatment Paradigm
2.4. AChE Activity Assay
2.5. Behavioral Assay
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
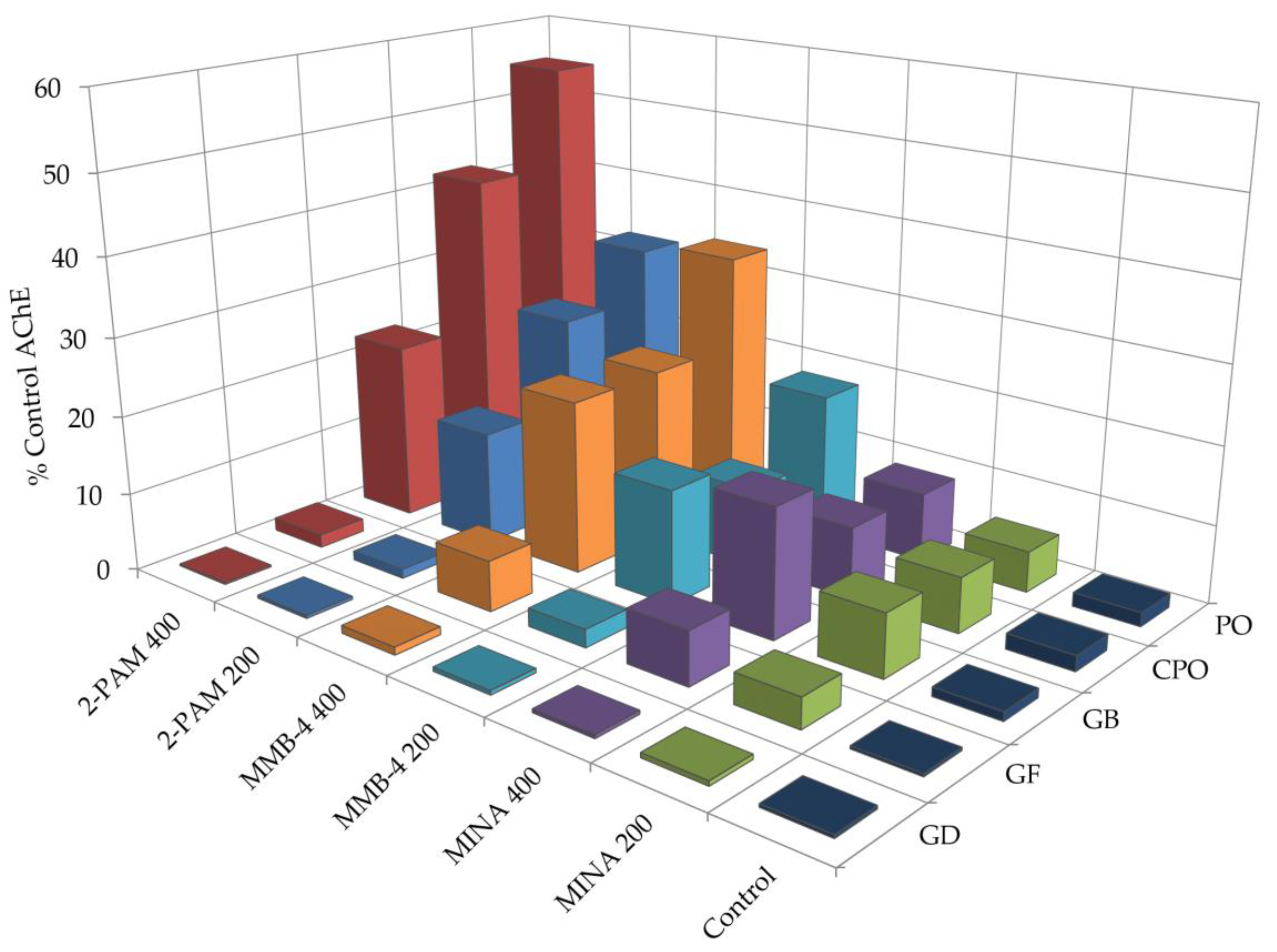
3.1. OP Lethality and AChE Inhibition
3.2. Oxime Reactivation
3.3. Behavioral Monitoring
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Disclaimer
References
- Taylor, P. Anticholinesterase agents. In Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics; Brunton, L.L., Chabner, B., Knollman, B., Eds.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 239–254. [Google Scholar]
- Wiener, S.W.; Hoffman, R.S. Nerve Agents: A Comprehensive Review. J. Intensive Care Med. 2004, 19, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrs, T.C.; Rice, P.; Vale, J.A. The role of oximes in the treatment of nerve agent poisoning in civilian casualties. Toxicol. Rev. 2006, 25, 297–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, D.H.; Clifford, C.B.; Crawford, I.T.; Cole, G.M.; Baggett, J.M. Review of Nerve Agent Inhibitors and Reactivators of Acetylcholinesterase. In Enzymes of the Cholinesterase Family; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 297–304. [Google Scholar]
- Shih, T.M.; Duniho, S.M.; McDonough, J.H. Control of nerve agent-induced seizures if critical for neuroprotection and survival. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2003, 188, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonough, J.H.; Van Shura, K.E.; Lamont, J.C.; McMonagle, J.D.; Shih, T.-M. Comparison of the intramuscular, intranasal or sublingual routes of Midazolam administration for the control of Soman-induced seizures. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2009, 104, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, G.E.; Campbell, A.J.; Olson, J.; Moorad-Doctor, D.; Morthole, V.I. Novel oximes as blood-brain barrier penetrating cholinesterase reactivators. Chem. Interactions 2010, 187, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassa, J. Review of oximes in the antidotal treatment of poisoning by organophosphorus nerve agents. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 2002, 40, 803–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, E.F.R.; Aracava, Y.; DeTolla, L.J.; Beecham, E.J.; Basinger, G.W.; Wakayama, E.J.; Albuquerque, E.X. Animal models that best reproduce the clinical manifestations of human intoxication with organophosphorus compounds. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2014, 350, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koenig, J.A.; Dao, T.L.; Kan, R.K.; Shih, T.-M. Zebrafish as a model for acetylcholinesterase-inhibiting organophosphorus agent exposure and oxime reactivation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2016, 1374, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, P.; Li, C.-Q. Zebrafish: A predictive model for assessing drug-induced toxicity. Drug Discov. Today 2008, 13, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, R.T.; Macrae, C.A. Changing the scale and efficiency of chemical warfare countermeasure discovery using the zebrafish. Drug Discov. Today: Dis. Model. 2013, 10, e37–e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zon, L.I.; Peterson, R.T. In vivo drug discovery in the zebrafish. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieschke, G.J.; Currie, P.D. Animal models of human disease: Zebrafish swim into view. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C.A.; Peterson, R.T. Zebrafish as tools for drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selderslaghs, I.W.; Hooyberghs, J.; De Coen, W.; Witters, H. Locomotor activity in zebrafish embryos: A new method to assess developmental neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicology Teratol. 2010, 32, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, C.; Chatonnet, A.; Takke, C.; Yan, Y.L.; Postlethwait, J.; Toutant, J.P.; Cousin, X. Zebrafish acetylcholinesterase is encoded by a single gene localized on linkage group 7. Gene structure and polymorphism; molecular forms and expression pattern during development. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Küster, E. Cholin- and carboxylesterase activities in developing zebrafish embryos (Danio rerio) and their potential use for insecticide hazard assessment. Aquat. Toxicol. 2005, 75, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, H.R.; Radić, Z.; Taylor, P.; Fradinger, E.A. Quaternary and tertiary aldoxime antidotes for organophosphate exposure in a zebrafish model system. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 284, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, Í.F.S.; Souza, T.M.; Vieria, L.R.; Marchi, F.C.; Nascimento, A.P.; Farias, D.F. Toxicity testing of pesticides in zebrafish-a systemic review on chemicals and associated toxicological endpoints. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 10185–10204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddleston, M.; Buckley, N.A.; Eyer, P.; Dawson, A.H. Management of acute organophosphorus pesticide poisoning. Lancet 2008, 371, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naughton, S.X.; Terry, A.V. Neurotoxicity in acute and repeated organophosphate exposure. Toxicology 2018, 408, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, T.-M.; Skovira, J.W.; O’Donnell, J.C.; McDonough, J.H. Evaluation of nine oximes on in vivo reactivation of blood, brain, and tissue cholinesterase activity inhibited by organophosphorus nerve agents at lethal dose. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2009, 19, 386–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, T.-M.; Maxwell, D.M.; Koplovitz, I.; Kan, R.K.; McDonough, J.H. Reactivation of acetylcholinesterase activity and its therapeutic benefits in nerve agent intoxication. In The Neurochemical Consequences of Organophosphate Poisoning in the CNS; Weissman, B.A., Raveh, L., Eds.; Transworld Research Network: Kerala, India, 2010; pp. 111–133. [Google Scholar]
- Skovira, J.W.; O’Donnell, J.C.; Koplovitz, I.; Kan, R.K.; McDonough, J.H.; Shih, T.-M. Reactivation of brain acetylcholinesterase by monoisonitrosoacetone increases the therapeutic efficacy against nerve agents in guinea pigs. Chem. Interact. 2010, 187, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.; Andres, V.; Featherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, M.; Garcia-Reyero, N.; Padrós, F.; Babin, P.J.; Sebastián, D.; Cachot, J.; Prats, E.; Arick, M.; Rial, E.; Knoll-Gellida, A.; et al. Zebrafish models for human acute organophosphorus poisoning. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shih, T.-M.; Kan, R.K.; McDonough, J.H. In vivo cholinesterase inhibitory specificity of organophosphorus nerve agents. Chem. Interact. 2005, 157, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worek, F.; Thiermann, H.; Szinicz, L.; Eyer, P. Kinetic analysis of interactions between human acetylcholinesterase, structurally different organophosphorus compounds and oximes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2004, 68, 2237–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.-Y.; Kwon, H.-B.; Ahn, J.-C.; Kang, D.; Kwon, S.-H.; Park, J.A.; Kim, K.-W. Functional and developmental analysis of the blood–brain barrier in zebrafish. Brain Res. Bull. 2008, 75, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.M.; Fero, K.; Arrenberg, A.B.; Bergeron, S.A.; Driever, W.; Burgess, H.A. Deep Brain Photoreceptors Control Light-Seeking Behavior in Zebrafish Larvae. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 2042–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sodhi, P.; Hartwick, A. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor-mediated stimulation of retinal ganglion cell photoreceptors. Neuropharmacology 2016, 108, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yue, W.W.S.; Jiang, Z.; Xue, T.; Kang, S.H.; Bergles, D.E.; Mikoshiba, K.; Offermanns, S.; Yau, K.-W. Synergistic signaling by light and acetylcholine in mouse iris sphincter muscle. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 1791–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gallardo, V.E.; Varshney, G.K.; Lee, M.; Bupp, S.; Xu, L.; Shinn, P.; Crawford, N.P.; Inglese, J.; Burgess, S.M. Phenotype-driven chemical screening in zebrafish for compounds that inhibit collective cell migration identifies multiple pathways potentially involved in metastatic invasion. Dis. Model. Mech. 2015, 8, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| Compound | Exposure Time (min) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 60 | 90 | 120 | sig. * | |
| GB | 229.8 (151.7–378.1) | 61.5 (45.9–83.2) | 18.9 (13.6–26.7) | 6.9 (4.7–10.0) | c |
| GD | 21.8 (13.1–38.8) | 4.0 (2.8–5.5) | 2.3 (1.1–4.2) | 1.3 (0.7–2.3) | d |
| GF | 30.6 (19.4–50.8) | 21.1 (14.0–32.8) | 15.4 (10.8–22.3) | 6.6 (3.9–12.0) | c |
| DFP | 2805.6 (2271.9–3420.8) | 257.4 (207.0–311.1) | 227.2 (171.1–307.9) | 62.7 (52.3–78.2) | b |
| CP | ND | 3206.4 (2478.0–4177.4) | 1191.8 (936.6–1508.2) | 931.0 (753.3–1144.9) | a |
| CPO | 85.4 (68.0–107.7) | 22.3 (17.5–28.5) | 7.7 (5.8–10.4) | ND | c |
| PO | 451.9 (361.9–566.2) | 165.8 (134.2–202.3) | 82.9 (63.2–109.2) | 108.7 (86.4–137.2) | b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koenig, J.A.; Acon Chen, C.; Shih, T.-M. Development of a Larval Zebrafish Model for Acute Organophosphorus Nerve Agent and Pesticide Exposure and Therapeutic Evaluation. Toxics 2020, 8, 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics8040106
Koenig JA, Acon Chen C, Shih T-M. Development of a Larval Zebrafish Model for Acute Organophosphorus Nerve Agent and Pesticide Exposure and Therapeutic Evaluation. Toxics. 2020; 8(4):106. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics8040106
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoenig, Jeffrey A., Cindy Acon Chen, and Tsung-Ming Shih. 2020. "Development of a Larval Zebrafish Model for Acute Organophosphorus Nerve Agent and Pesticide Exposure and Therapeutic Evaluation" Toxics 8, no. 4: 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics8040106
APA StyleKoenig, J. A., Acon Chen, C., & Shih, T.-M. (2020). Development of a Larval Zebrafish Model for Acute Organophosphorus Nerve Agent and Pesticide Exposure and Therapeutic Evaluation. Toxics, 8(4), 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics8040106





