Phthalates and Bisphenol A: Presence in Blood Serum and Follicular Fluid of Italian Women Undergoing Assisted Reproduction Techniques
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects, Samples Collection and Questionnaire
2.2. Phtalate Esters and Bisphenol a Measurement
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics
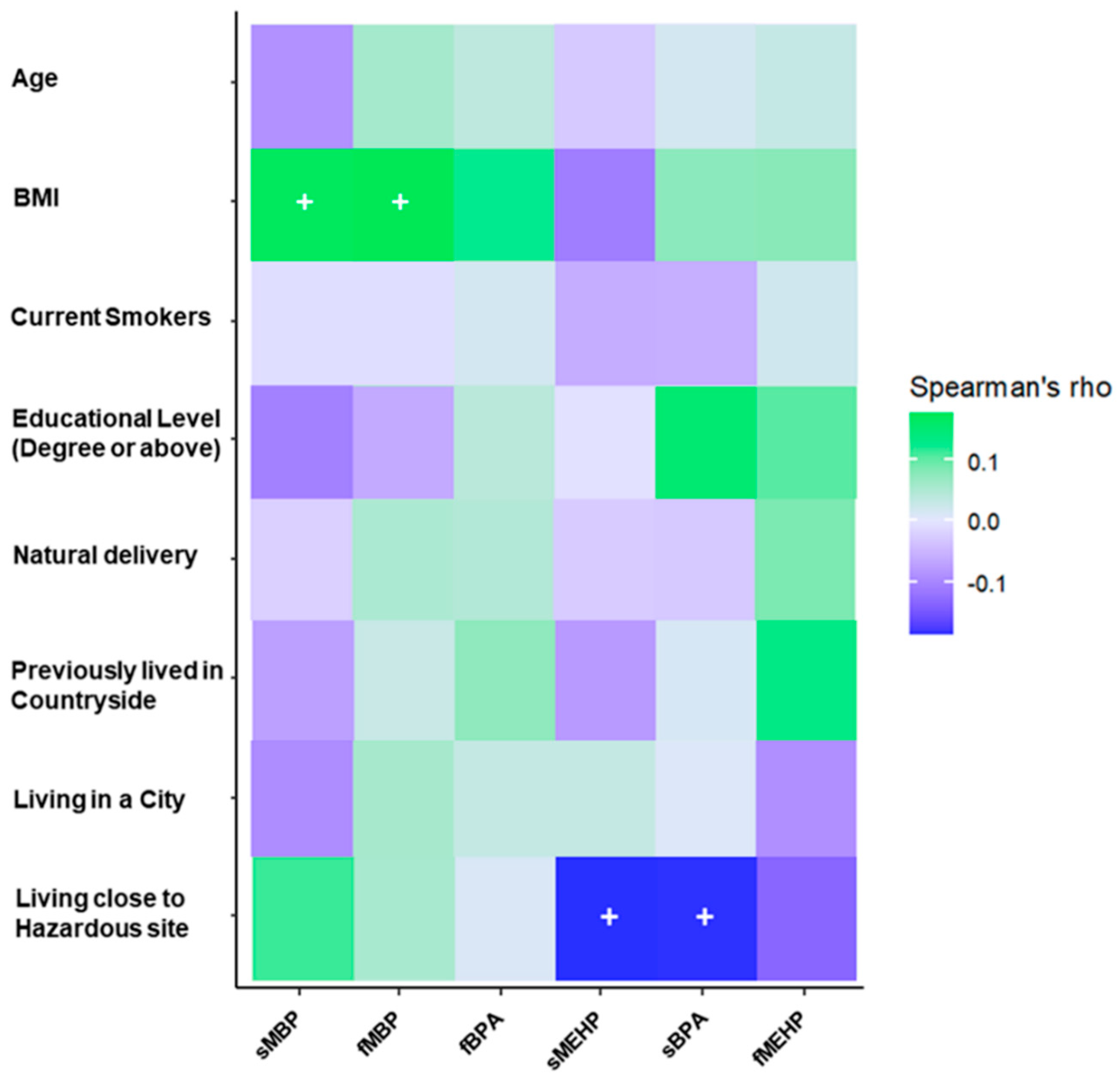
3.2. EDCs Questionnaire
3.3. Food Questionnaire
3.4. EDCs Blood and Follicular Fluid Measurement
4. Discussion
4.1. Ovarian Function and EDCs
4.2. Phthalates and BPA in Human Follicular Fluid
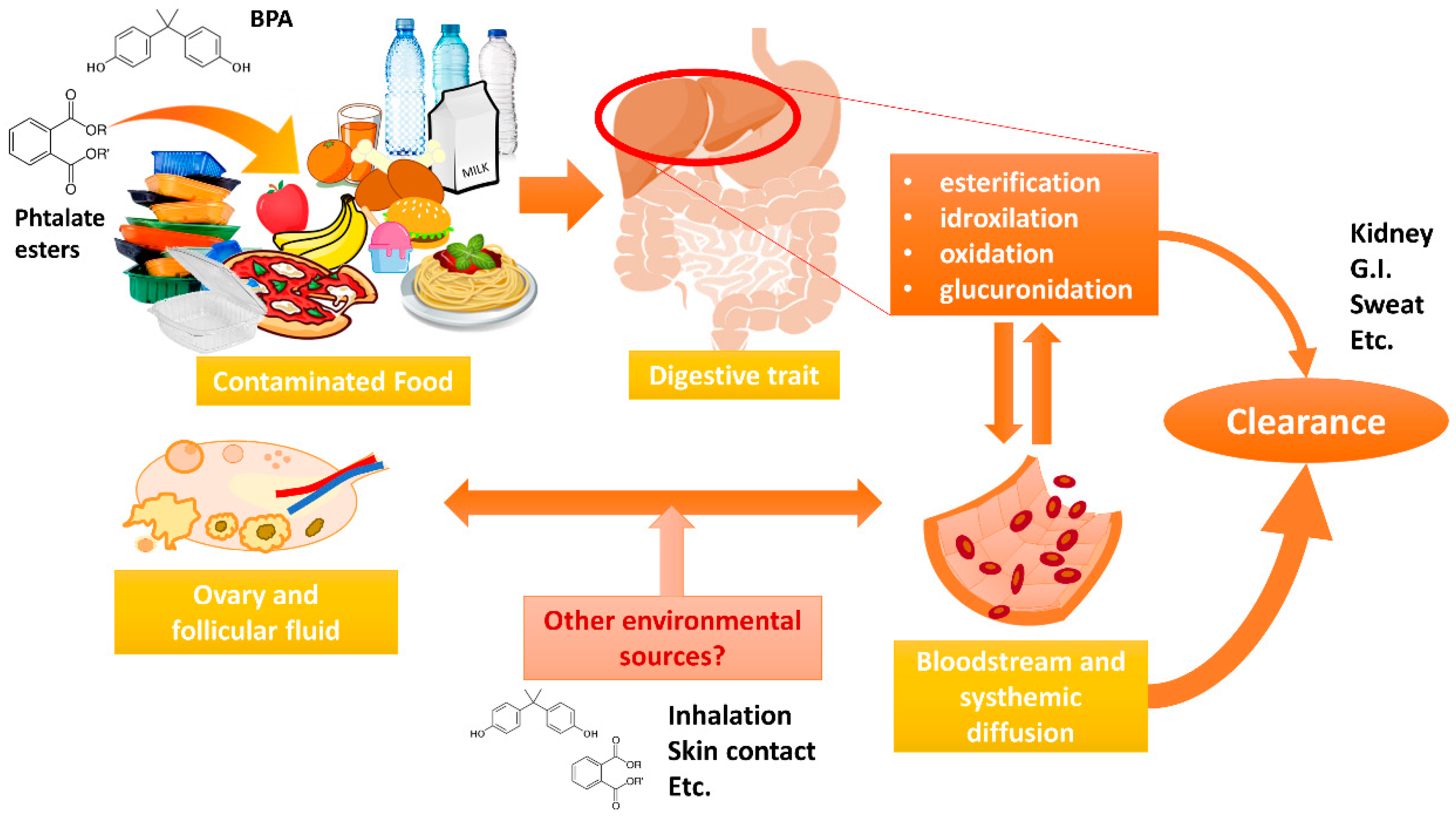
4.3. Possible Sources of Exposure to Phthalates and BPA
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sifakis, S.; Androutsopoulos, V.P.; Tsatsakis, A.M.; Spandidos, D.A. Human exposure to endocrine disrupting chemicals: Effects on the male and female reproductive systems. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 51, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, G.R.; Li, Z.; Houde, M.L.; Atkinson, C.E.; Meling, D.D.; Chiang, C.; Flaws, J.A. Ovarian Metabolism of an Environmentally Relevant Phthalate Mixture. Toxicol. Sci. 2019, 169, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventrice, P.; Ventrice, D.; Russo, E.; De Sarro, G. Phthalates: European regulation, chemistry, pharmacokinetic and related toxicity. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2013, 36, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieg, S.A.; Shahine, L.K.; Lathi, R.B. Environmental exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals and miscarriage. Fertil. Steril. 2016, 106, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heudorf, U.; Mersch-Sundermann, V.; Angerer, J. Phthalates: Toxicology and exposure. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2007, 210, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovekamp-Swan, T.; Davis, B.J. Mechanisms of phthalate ester toxicity in the female reproductive system. Environ. Health Perspect. 2003, 111, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thayer, K.A.; Doerge, D.R.; Hunt, D.; Schurman, S.H.; Twaddle, N.C.; Churchwell, M.I.; Garantziotis, S.; Kissling, G.E.; Easterling, M.R.; Bucher, J.R.; et al. Pharmacokinetics of bisphenol A in humans following a single oral administration. Environ. Int. 2015, 83, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patel, S.; Zhou, C.; Rattan, S.; Flaws, J.A. Effects of Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals on the Ovary1. Biol. Reprod. 2015, 93, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallotti, F.; Pelloni, M.; Gianfrilli, D.; Lenzi, A.; Lombardo, F.; Paoli, D. Mechanisms of Testicular Disruption from Exposure to Bisphenol A and Phtalates. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, J.-X.; Wang, F.-F.; Qu, F. The effects of di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate exposure in women with polycystic ovary syndrome undergoing In Vitro fertilization. J. Int. Med. Res. 2019, 47, 6278–6293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, T.; Du, Y.; Wang, Y.; Teng, X.; Hua, X.; Yuan, X.; Yao, Y.; Guo, N.; Li, Y.-F. The associations of urinary phthalate metabolites with the intermediate and pregnancy outcomes of women receiving IVF/ICSI treatments: A prospective single-center study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 188, 109884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, Z.R.; Wang, W.; Flaws, J.A. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals in ovarian function: Effects on steroidogenesis, metabolism and nuclear receptor signaling. Reproduction 2011, 142, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Qu, X.; Ming, Z.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, Y. The correlation between exposure to BPA and the decrease of the ovarian reserve. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2018, 11, 3375–3382. [Google Scholar]
- Radwan, P.; Wielgomas, B.; Radwan, M.; Krasiński, R.; Klimowska, A.; Kaleta, D.; Jurewicz, J. Urinary bisphenol A concentrations and in vitro fertilization outcomes among women from a fertility clinic. Reprod. Toxicol. 2020, 96, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewailly, D.; Robin, G.; Peigne, M.; Decanter, C.; Pigny, P.; Catteau-Jonard, S. Interactions between androgens, FSH, anti-Müllerian hormone and estradiol during folliculogenesis in the human normal and polycystic ovary. Hum. Reprod. Updat. 2016, 22, 709–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fowler, P.A.; Bellingham, M.; Sinclair, K.D.; Evans, N.P.; Pocar, P.; Fischer, B.; Schaedlich, K.; Schmidt, J.-S.; Amezaga, M.R.; Bhattacharya, S.; et al. Impact of endocrine-disrupting compounds (EDCs) on female reproductive health. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 355, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gore, A.C.; Chappell, V.A.; Fenton, S.E.; Flaws, J.A.; Nadal, A.; Prins, G.S.; Toppari, J.; Zoeller, R.T. EDC-2: The Endocrine Society’s Second Scientific Statement on Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals. Endocr. Rev. 2015, 36, E1–E150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannon, P.R.; Flaws, J.A. The Effects of Phthalates on the Ovary. Front. Endocrinol. 2015, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinsberg, J.; Wegener-Toper, P.; Van Der Ven, K.; Van Der Ven, H.; Klingmueller, D. Effect of mono-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate on steroid production of human granulosa cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 239, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, J.; Jann, J.-C.; Biemann, R.; Koch, H.M.; Fischer, B. Effects of the environmental contaminants DEHP and TCDD on estradiol synthesis and aryl hydrocarbon receptor and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor signalling in the human granulosa cell line KGN. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2014, 20, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernández-Ochoa, I.; Barnett-Ringgold, K.R.; Dehlinger, S.L.; Gupta, R.K.; Leslie, T.C.; Roby, K.F.; Flaws, J.A. The Ability of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor to Regulate Ovarian Follicle Growth and Estradiol Biosynthesis in Mice Depends on Stage of Sexual Maturity1. Biol. Reprod. 2010, 83, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pogrmic-Majkic, K.; Nenadov, D.S.; Fa, S.; Stanic, B.; Pjevic, A.T.; Andric, N. BPA activates EGFR and ERK1/2 through PPARγ to increase expression of steroidogenic acute regulatory protein in human cumulus granulosa cells. Chemosphere 2019, 229, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikezuki, Y.; Tsutsumi, O.; Takai, Y.; Kamei, Y.; Taketani, Y. Determination of bisphenol A concentrations in human biological fluids reveals significant early prenatal exposure. Hum. Reprod. 2002, 17, 2839–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krotz, S.P.; Carson, S.A.; Tomey, C.; Buster, J.E. Phthalates and bisphenol do not accumulate in human follicular fluid. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2012, 29, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, Y.-Y.; Fang, Y.-L.; Wang, Y.-X.; Zeng, Q.; Guo, N.; Zhao, H.; Li, Y.-F. Follicular fluid and urinary concentrations of phthalate metabolites among infertile women and associations with in vitro fertilization parameters. Reprod. Toxicol. 2016, 61, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zota, A.R.; Phillips, C.A.; Mitro, S.D. Recent Fast Food Consumption and Bisphenol A and Phthalates Exposures among the U.S. Population in NHANES, 2003–2010. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 1521–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Shi, W.; Wang, X.; Cai, J.; Zou, Z.; Lu, R.; Sun, C.; Wang, H.; et al. Associations of urinary phthalate metabolites with residential characteristics, lifestyles, and dietary habits among young children in Shanghai, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 1288–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husøy, T.; Andreassen, M.; Hjertholm, H.; Carlsen, M.; Norberg, N.; Sprong, C.; Papadopoulou, E.; Sakhi, A.; Sabaredzovic, A.; Dirven, H. The Norwegian biomonitoring study from the EU project EuroMix: Levels of phenols and phthalates in 24-h urine samples and exposure sources from food and personal care products. Environ. Int. 2019, 132, 105103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierens, T.; Vanermen, G.; Van Holderbeke, M.; De Henauw, S.; Sioen, I. Effect of cooking at home on the levels of eight phthalates in foods. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 4428–4435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunderberg, D.M.; Kristensen, K.; Liu, Y.; Misztal, P.K.; Tian, Y.; Arata, C.; Wernis, R.; Kreisberg, N.M.; Nazaroff, W.W.; Goldstein, A.H. Characterizing Airborne Phthalate Concentrations and Dynamics in a Normally Occupied Residence. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 7337–7346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frederiksen, H.; Nielsen, O.; Koch, H.M.; Skakkebaek, N.E.; Juul, A.; Jørgensen, N.; Andersson, A.-M. Changes in urinary excretion of phthalates, phthalate substitutes, bisphenols and other polychlorinated and phenolic substances in young Danish men; 2009–2017. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2020, 223, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Analyte | Calibration Linearity | LOQ (ng/mL) | Recovery (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range (ng/mL) | R² | |||
| MBP | 0.625–1000 | 0.999 | 1.25 | 85 ± 9 |
| MBzP | 0.625–1000 | 0.999 | 0.3 | 78 ± 6 |
| MEHHP | 0.625–1000 | 0.998 | 0.3 | 90 ± 4 |
| MOXP | 0.625–1000 | 0.999 | 0.3 | 89 ± 7 |
| MEHP | 0.625–1000 | 0.999 | 1.25 | 71 ± 3 |
| BPA | 0.625–1000 | 0.999 | 1.25 | 105 ± 6 |
| Study Group (122 Women) | |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 35.5 ± 3.7 23.0–40.0 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 21.8 ± 2.0 17.0–23.8 |
| Smokers | Current 30 (24.6%) Former 19 (15.6%) |
| Cigarettes/day a | 7.8 ± 5.4 5.0–20.0 |
| Years of smoking a | 12.8 ± 5.4 3.0–20.0 |
| Couples with previous children | 12 (9.8%) |
| Causes of infertility | Idiopathic 24 (20.0%) Female factor 40 (33.3%) Male factor 56 (46.7%) |
| Education Level | Lower secondary school 26 (21.3%) Upper secondary school 46 (37.7%) Graduated or higher 50 (41.0%) |
| Job | Office workers 38 (31.1%) Factory/heavy workers 17 (13.9%) Freelance professionals 10 (8.2%) Merchant/shopkeepers 7 (5.7%) Housewives 13 (10.7%) Healthcare professionals 13 (10.7%) Unemployed 9 (7.4%) Teachers 13 (10.7%) Undisclosed 2 (1.6%) |
| Housing history | Always in a city area 87 (71.3%) Previously/currently in countryside 35 (28.7%) Residential area 75 (61.5%) City outskirts 39 (32.0%) Farming area 7 (5.7%) Industrial area 1 (0.8%) |
| Hazardous sites (within 500 m) | Dump yards (solid waste) 9 (7.3%) Farms 14 (11.5%) Factories, ports, airports 16 (13.1%) None 83 (68.0%) |
| EDC | Serum Median (Q1–Q3) ng/mL | Follicular Fluid Median (Q1–Q3) ng/mL | p Value a | Detection Rate (% above LOQ) | Simultaneous Detection Rate in Both Serum and FF (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MBP | 8.96 (4.80–15.50) | 6.43 (3.37–12.68) | <0.001 | Serum: 99.2% FF: 99.2% | 97.5% |
| MBzP | 0.35 (0.30–0.56) | 0.30 (0.30–0.42) | 0.009 | Serum: 44.3% FF: 54.1% | 31.1% |
| MEOXP | 0.34 (0.30–1.02) | 0.35 (0.30–0.79) | 0.904 | Serum: 55.7% FF: 41.0% | 27.9% |
| MEHHP | 0.39 (0.30–0.96) | 0.85 (0.30–1.75) | 0.458 | Serum: 58.2% FF: 36.9% | 26.2% |
| MEHP | 9.16 (4.97–17.86) | 7.78 (4.12–14.90) | 0.375 | Serum: 95.1% FF: 79.5% | 77.0% |
| BPA | 1.89 (1.25–2.84) | 1.86 (1.25–1.90) | 0.287 | Serum: 52.4% FF: 28.7% | 25.4% |
| EDC | MBP | MBzP | MEOXP | MEHHP | MEHP | BPA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correlation Coefficient | 0.567 | 0.166 | 0.147 | 0.184 | 0.054 | 0.682 |
| p value | <0.001 | 0.680 | 0.107 | 0.043 | 0.555 | <0.001 |
| Area 1 | Area 2 | Area 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serum MBP (ng/mL) | 7.61 (0.98) | 14.40 b (0.96) | 13.56 a (1.71) |
| Follicular BPA (ng/mL) | <LOQ | 1.57 (0.05) | 1.94 c (0.12) |
| Irregular Menses | Regular Menses | |
|---|---|---|
| Follicular MBP (ng/mL) | 18.83 a (2.05) | 8.46 (0.92) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paoli, D.; Pallotti, F.; Dima, A.P.; Albani, E.; Alviggi, C.; Causio, F.; Dioguardi, C.C.; Conforti, A.; Ciriminna, R.; Fabozzi, G.; et al. Phthalates and Bisphenol A: Presence in Blood Serum and Follicular Fluid of Italian Women Undergoing Assisted Reproduction Techniques. Toxics 2020, 8, 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics8040091
Paoli D, Pallotti F, Dima AP, Albani E, Alviggi C, Causio F, Dioguardi CC, Conforti A, Ciriminna R, Fabozzi G, et al. Phthalates and Bisphenol A: Presence in Blood Serum and Follicular Fluid of Italian Women Undergoing Assisted Reproduction Techniques. Toxics. 2020; 8(4):91. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics8040091
Chicago/Turabian StylePaoli, Donatella, Francesco Pallotti, Anna Pia Dima, Elena Albani, Carlo Alviggi, Franco Causio, Carola Conca Dioguardi, Alessandro Conforti, Rosanna Ciriminna, Gemma Fabozzi, and et al. 2020. "Phthalates and Bisphenol A: Presence in Blood Serum and Follicular Fluid of Italian Women Undergoing Assisted Reproduction Techniques" Toxics 8, no. 4: 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics8040091
APA StylePaoli, D., Pallotti, F., Dima, A. P., Albani, E., Alviggi, C., Causio, F., Dioguardi, C. C., Conforti, A., Ciriminna, R., Fabozzi, G., Giuffrida, G., Gualtieri, R., Minasi, M. G., Ochetti, S., Pisaturo, V., Racca, C., Rienzi, L., Sarcina, E., Scarica, C., ... De Santis, L., on behalf of the Italian Society of Embryology Reproduction and Research (SIERR). (2020). Phthalates and Bisphenol A: Presence in Blood Serum and Follicular Fluid of Italian Women Undergoing Assisted Reproduction Techniques. Toxics, 8(4), 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics8040091









