Effect of Pulmonary Inflammation by Surface Functionalization of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of ZnO NPs
2.2. Animals and ZnO NPs Exposure
2.3. Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Analysis and Cytokine Expression
2.4. Histopathology
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Properties of ZnO NPs
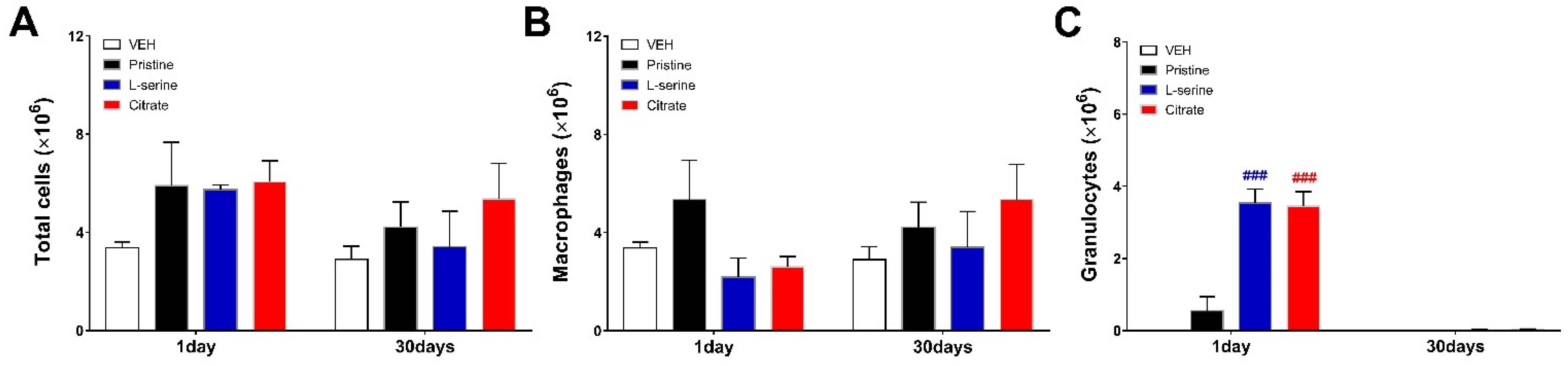
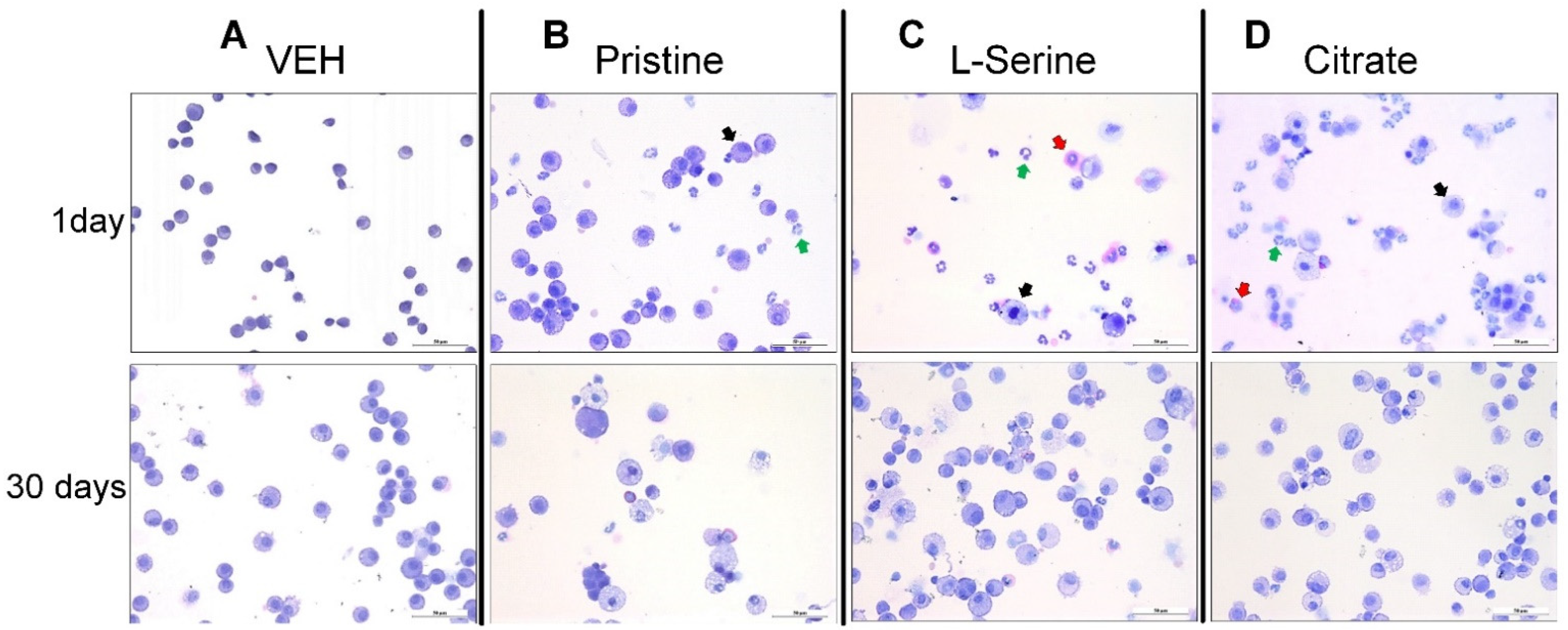
3.2. Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Analysis
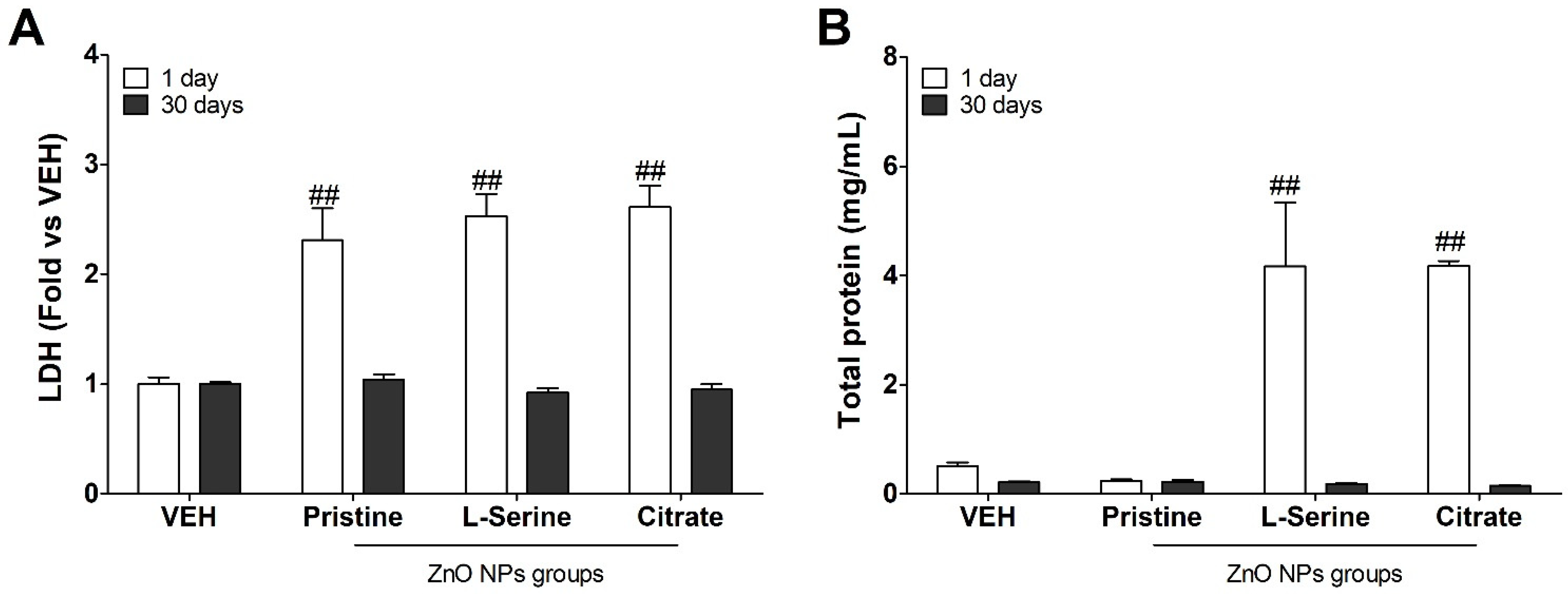
3.3. Changes in Biochemical Indicators following Instillation with ZnO NPs
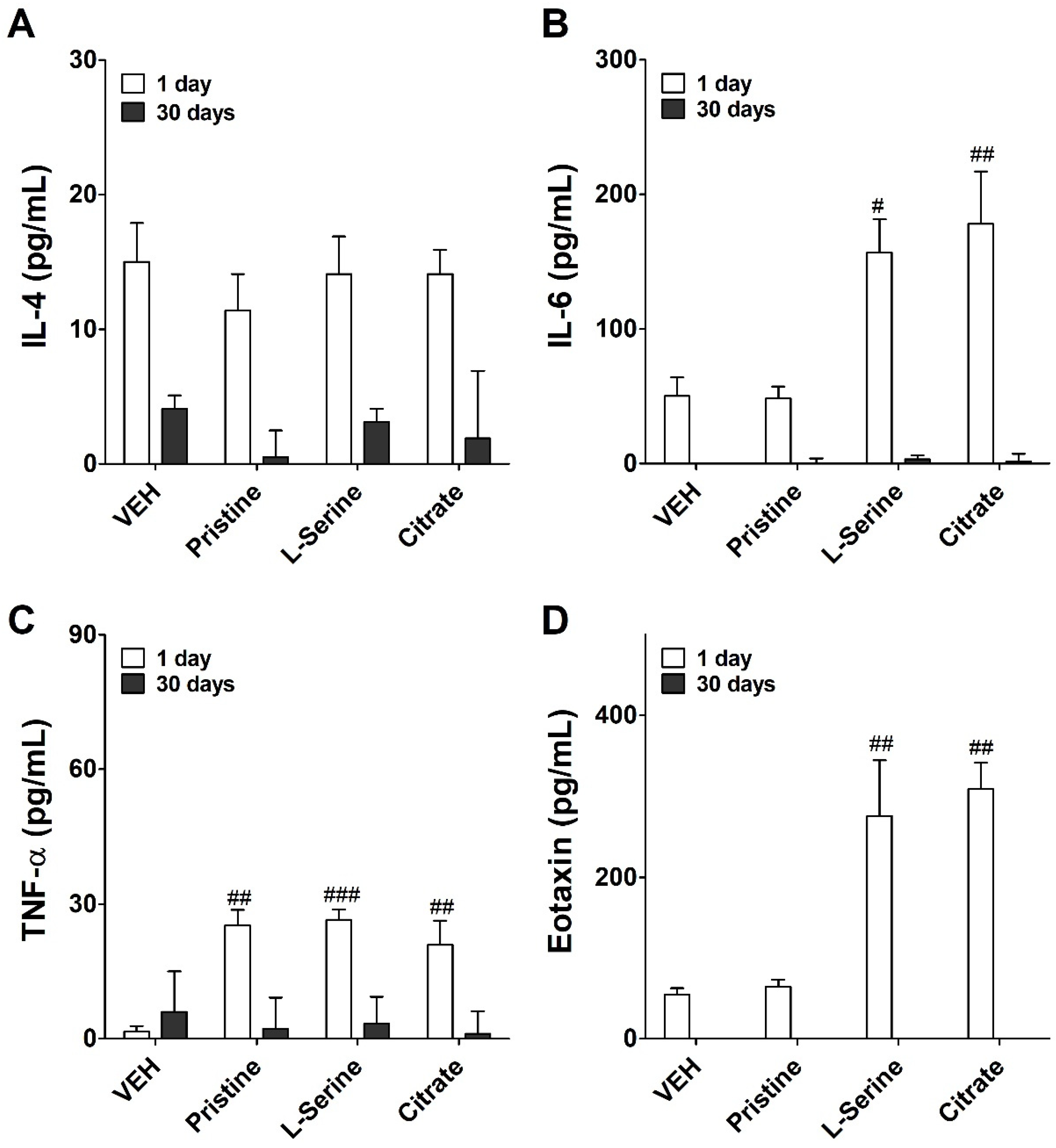
3.4. Inflammatory Cytokine Expression following Instilled with ZnO NPs
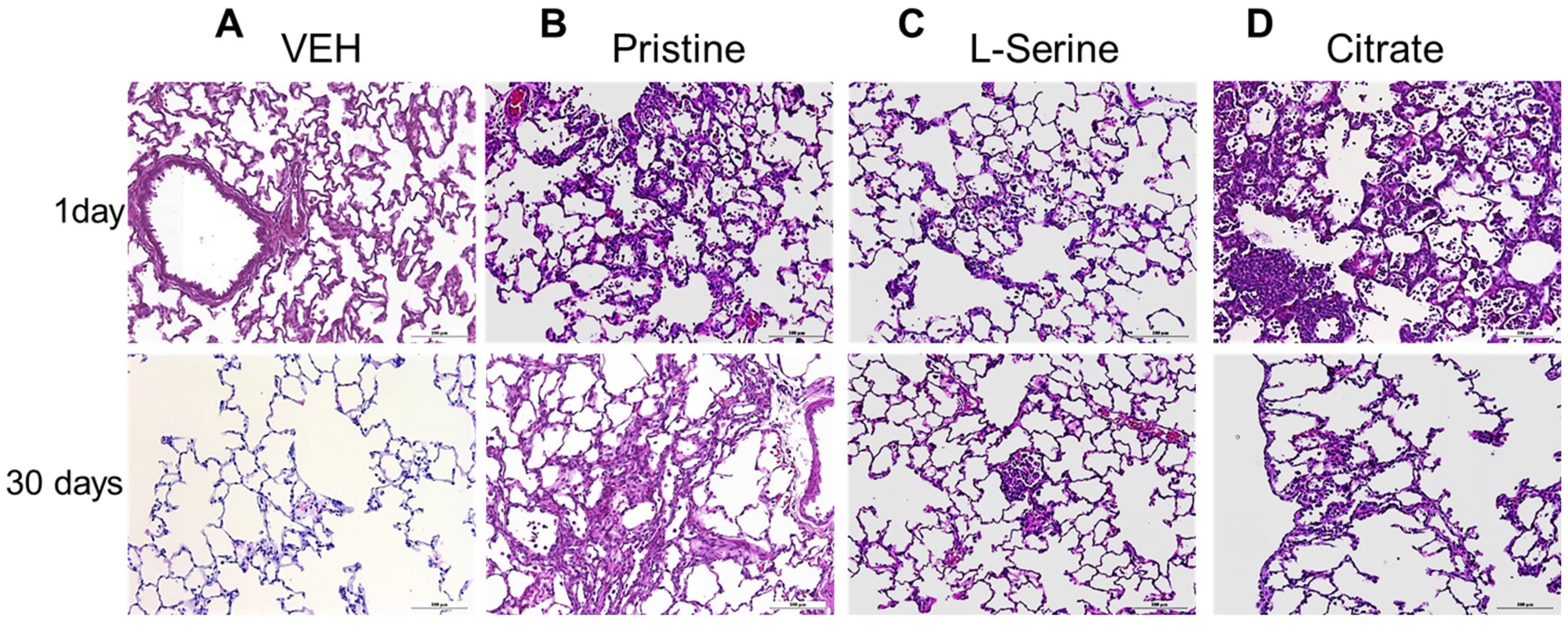
3.5. Histopathology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, W. Nanoparticles and their biological and environmental applications. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2006, 102, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju-Nam, Y.; Lead, J.R. Manufactured nanoparticles: An overview of their chemistry, interactions and potential environmental implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 400, 396–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Xia, T.; Nel, A.E. The role of oxidative stress in ambient particulate matter-induced lung diseases and its implications in the toxicity of engineered nanoparticles. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 44, 1689–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, L.; Yang, S.; Li, S.; Meng, Y.; Wang, H.; Lei, H. Acute toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles to the rat olfactory system after intranasal instillation. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2013, 33, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasupuleti, S.; Alapati, S.; Ganapathy, S.; Anumolu, G.; Pully, N.R.; Prakhya, B.M. Toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles through oral route. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2012, 28, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surekha, P.; Kishore, A.S.; Srinivas, A.; Selvam, G.; Goparaju, A.; Reddy, P.N.; Murthy, P.B. Repeated dose dermal toxicity study of nano zinc oxide with Sprague-Dawley rats. Cutan. Ocul. Toxicol. 2012, 31, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Feng, W.; Wang, T.; Jia, G.; Wang, M.; Shi, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Chai, Z. Acute toxicity of nano-and micro-scale zinc powder in healthy adult mice. Toxicol. Lett. 2006, 161, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Feng, W.; Wang, M.; Wang, T.; Gu, Y.; Zhu, M.; Ouyang, H.; Shi, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, Y. Acute toxicological impact of nano-and submicro-scaled zinc oxide powder on healthy adult mice. J. Nanopart. Res. 2008, 10, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, M.; Kim, M.; Cho, H.; Lee, J.; Yu, J.; Chung, H.; Choi, S. Factors influencing the cytotoxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles: Particle size and surface charge. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2011, 304, 012044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Kovochich, M.; Liong, M.; Madler, L.; Gilbert, B.; Shi, H.; Yeh, J.I.; Zink, J.I.; Nel, A.E. Comparison of the mechanism of toxicity of zinc oxide and cerium oxide nanoparticles based on dissolution and oxidative stress properties. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 2121–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Liu, C.; Yang, D.; Zhang, H.; Xi, Z. Comparative study of cytotoxicity, oxidative stress and genotoxicity induced by four typical nanomaterials: The role of particle size, shape and composition. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2009, 29, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayes, C.M.; Reed, K.L.; Warheit, D.B. Assessing toxicity of fine and nanoparticles: Comparing in vitro measurements to in vivo pulmonary toxicity profiles. Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 97, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Berardis, B.; Civitelli, G.; Condello, M.; Lista, P.; Pozzi, R.; Arancia, G.; Meschini, S. Exposure to ZnO nanoparticles induces oxidative stress and cytotoxicity in human colon carcinoma cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2010, 246, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, H.; Chen, L.; Ainsworth, D.; Peoples, S.; Amdur, M. Pulmonary function of guinea pigs exposed to freshly generated ultrafine zinc oxide with and without spike concentrations. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 1988, 49, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fine, J.M.; Gordon, T.; Chen, L.C.; Kinney, P.; Falcone, G.; Beckett, W.S. Metal fume fever: Characterization of clinical and plasma IL-6 responses in controlled human exposures to zinc oxide fume at and below the threshold limit value. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 1997, 39, 722–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Kim, T.; Kim, H.; Kim, H.; Gwak, G.; Paek, S.; Oh, J. Colloidal behaviors of ZnO nanoparticles in various aqueous media. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 2012, 4, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, B.C.; Zhao, X.; Xiong, S.; Ng, K.W.; Boey, F.Y.; Loo, J.S. Toxicity of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles on human bronchial epithelial cells (BEAS-2B) is accentuated by oxidative stress. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 1762–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Aronstam, R.S.; Chen, D.; Huang, Y. Oxidative stress, calcium homeostasis, and altered gene expression in human lung epithelial cells exposed to ZnO nanoparticles. Toxicol. Vitr. 2010, 24, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senapati, V.A.; Kumar, A.; Gupta, G.S.; Pandey, A.K.; Dhawan, A. ZnO nanoparticles induced inflammatory response and genotoxicity in human blood cells: A mechanistic approach. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 85, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Bae, J.; Jung, A.; Park, S.; Chung, S.; Seok, J.; Roh, H.; Han, Y.; Oh, J.; Sohn, S. Surface functionalization-specific binding of coagulation factors by zinc oxide nanoparticles delays coagulation time and reduces thrombin generation potential in vitro. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Duffin, R.; Poland, C.; Daly, P.; Murphy, F.; Drost, E.; Macnee, W.; Stone, V.; Donaldson, K. Efficacy of simple short-term in vitro assays for predicting the potential of metal oxide nanoparticles to cause pulmonary inflammation. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, W.S.; Duffin, R.; Poland, C.A.; Howie, S.E.; MacNee, W.; Bradley, M.; Megson, I.L.; Donaldson, K. Metal oxide nanoparticles induce unique inflammatory footprints in the lung: Important implications for nanoparticle testing. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1699–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pryhuber, G.S.; Huyck, H.L.; Baggs, R.; Oberdörster, G.; Finkelstein, J.N. Induction of chemokines by low-dose intratracheal silica is reduced in TNFR I (p55) null mice. Toxicol. Sci. 2003, 72, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oberdorster, G.; Oberdorster, E.; Oberdorster, J. Nanotoxicology: An emerging discipline evolving from studies of ultrafine particles. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 823–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, C.; Santos-Martinez, M.; Radomski, A.; Corrigan, O.; Radomski, M. Nanoparticles: Pharmacological and toxicological significance. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 150, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baggs, R.; Ferin, J.; Oberdörster, G. Regression of pulmonary lesions produced by inhaled titanium dioxide in rats. Vet. Pathol. 1997, 34, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Geiser, M.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Kapp, N.; Schurch, S.; Kreyling, W.; Schulz, H.; Semmler, M.; Im Hof, V.; Heyder, J.; Gehr, P. Ultrafine particles cross cellular membranes by nonphagocytic mechanisms in lungs and in cultured cells. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 1555–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, W.; Choi, M.; Han, B.S.; Cho, M.; Oh, J.; Park, K.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, S.H.; Jeong, J. Inflammatory mediators induced by intratracheal instillation of ultrafine amorphous silica particles. Toxicol. Lett. 2007, 175, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, N.; Cheong, T.; Min, J.H.; Wu, J.H.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, D.; Yang, J.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y.K.; Seong, S. A multifunctional core–shell nanoparticle for dendritic cell-based cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, R.; Kumar, D.; Sharma, A.; Gupta, P.; Chaudhari, B.P.; Tripathi, A.; Das, M.; Dwivedi, P.D. ZnO nanoparticles induced adjuvant effect via toll-like receptors and Src signaling in Balb/c mice. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 230, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Håkansson, H.F.; Smailagic, A.; Brunmark, C.; Miller-Larsson, A.; Lal, H. Altered lung function relates to inflammation in an acute LPS mouse model. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 25, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, D.; Jeon, S.; Kim, S.; Jeong, J.; Kim, J.S.; Cho, J.H.; Park, H.; Cho, W. Combination effect of nanoparticles on the acute pulmonary inflammogenic potential: Additive effect and antagonistic effect. Nanotoxicology 2021, 15, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papanicolaou, D.A.; Wilder, R.L.; Manolagas, S.C.; Chrousos, G.P. The pathophysiologic roles of interleukin-6 in human disease. Ann. Intern. Med. 1998, 128, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croft, M. The role of TNF superfamily members in T-cell function and diseases. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tripathi, S.S.; Mishra, V.; Shukla, M.; Verma, M.; Chaudhury, B.P.; Kumar, P.; Chhabra, J.K.; Pandey, H.P.; Paul, B. IL-6 receptor-mediated lung Th2 cytokine networking in silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Arch. Toxicol. 2010, 84, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, S.; Pandey, H.; Paul, B. Overview of cytokines and receptors in Silicosis. J. App. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Z.; Fujimura, M.; Kurashima, K.; Nakao, S.; Mukaida, N. Enhanced airway inflammation and decreased subepithelial fibrosis in interleukin 6-deficient mice following chronic exposure to aerosolized antigen. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2004, 34, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.J.; Rosenberg, H.F. (Eds.) Eosinophils in Health and Disease. In Eosinophil Trafficking; Elsevier: Boston, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 121–166. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.K.; Kim, T.S.; Bae, J.Y.; Jung, A.Y.; Lee, S.M.; Seok, J.H.; Roh, H.S.; Song, C.W.; Choi, M.J.; Jeong, J. Organ-specific distribution of gold nanoparticles by their surface functionalization. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2015, 35, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, S.; Clavadetscher, J.; Lee, D.; Chankeshwara, S.V.; Bradley, M.; Cho, W. Surface charge-dependent cellular uptake of polystyrene nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
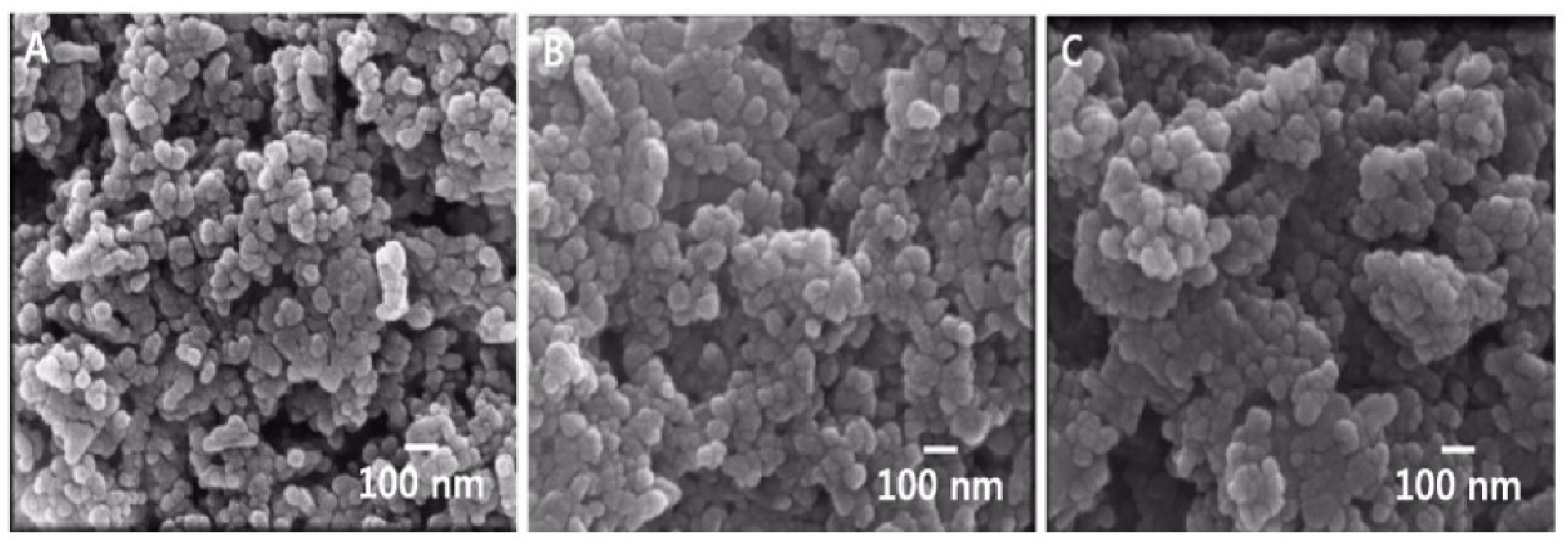
| Modification | 20 nm ZnO NPs | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Measurements | Pristine | L-Serine | Citrate |
| Primary size (nm) a | 26.8 ± 4.5 | 27.1 ± 7.5 | 26.9 ± 4.3 |
| Hydrodynamic size (nm) b | 399 ± 16 | 219 ± 3 | 341 ± 61 |
| Polydispersity (PDI) b | 0.50 ± 0.02 | 0.62 ± 0.07 | 0.63 ± 0.06 |
| Zeta potential (mV) b | 21.4 ± 4.6 | 30.0 ± 3.4 | −36.0 ± 2.6 |
| Endotoxin (Unit/mL) | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, A.; Kim, S.-H.; Yang, J.-Y.; Jeong, J.; Lee, J.K.; Oh, J.-H.; Lee, J.H. Effect of Pulmonary Inflammation by Surface Functionalization of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. Toxics 2021, 9, 336. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9120336
Jung A, Kim S-H, Yang J-Y, Jeong J, Lee JK, Oh J-H, Lee JH. Effect of Pulmonary Inflammation by Surface Functionalization of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. Toxics. 2021; 9(12):336. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9120336
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Ayoung, Sung-Hyun Kim, Jun-Young Yang, Jayoung Jeong, Jong Kwon Lee, Jae-Ho Oh, and Jin Hee Lee. 2021. "Effect of Pulmonary Inflammation by Surface Functionalization of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles" Toxics 9, no. 12: 336. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9120336
APA StyleJung, A., Kim, S.-H., Yang, J.-Y., Jeong, J., Lee, J. K., Oh, J.-H., & Lee, J. H. (2021). Effect of Pulmonary Inflammation by Surface Functionalization of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. Toxics, 9(12), 336. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9120336






