Fast and Environment-Friendly GC-MS Method for Eleven Organophosphorus Flame Retardants in Indoor Air, Dust, and Skin Wipes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Standards and Chemicals
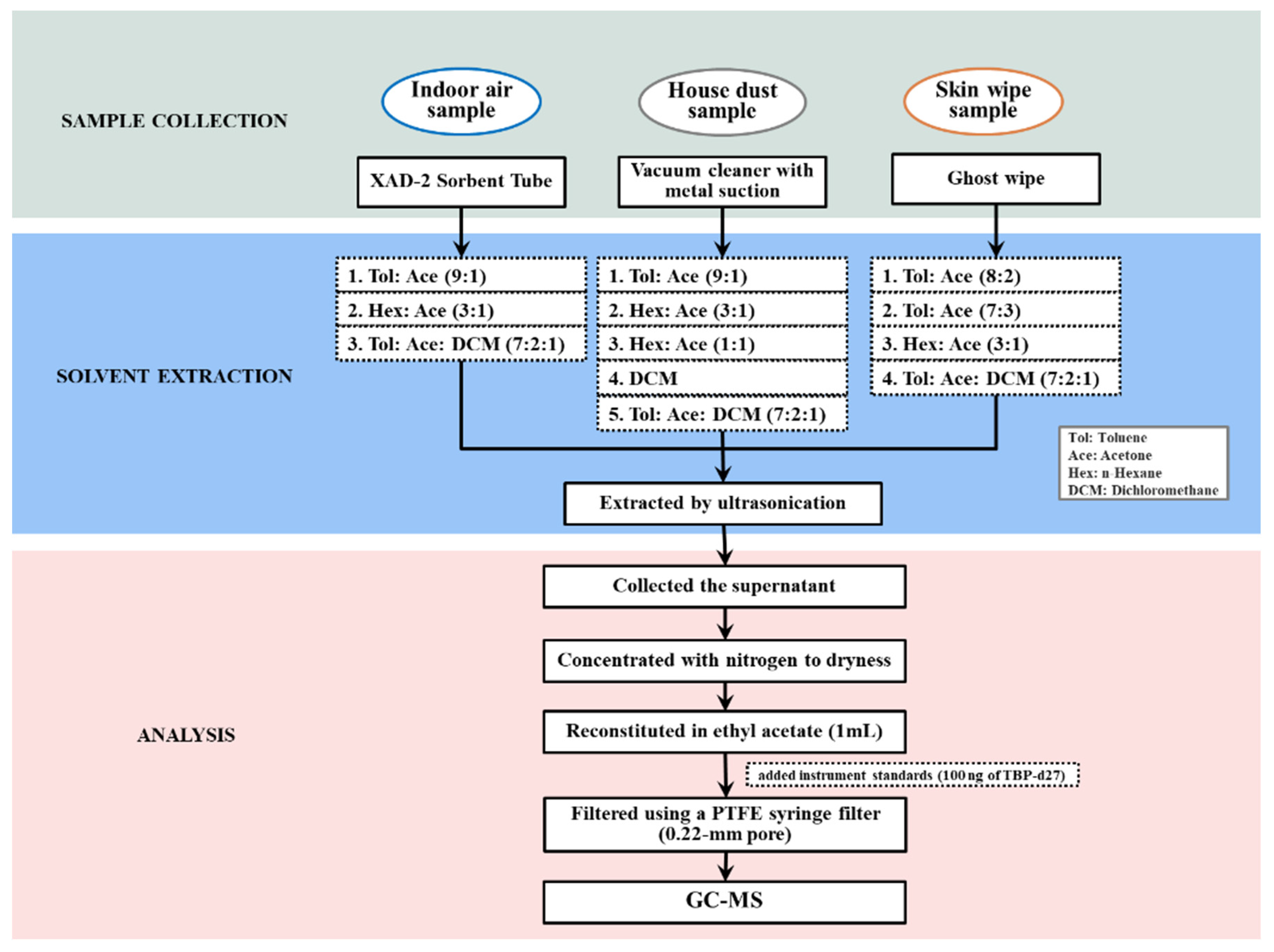
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Optimization of the Sample Preparation
2.4. Instrumental Method
2.5. QA/QC and Validation Procedure
2.6. Index of Green Analytical Chemistry
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization
3.1.1. Instrument Optimization in the GC-MS System
3.1.2. Sample Preparation
3.2. Method Performance
3.2.1. Linearity
3.2.2. Sensitivity
3.2.3. Recoveries, Precision and Accuracy
3.3. Main Achievements
3.4. Application of the Proposed Methods to Real Samples
3.4.1. Dust SRM 2585
3.4.2. Taiwanese Indoor Air, House Dust and Skin Wipe Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EU) 2017/227 of 9 February 2017. Off. J. Eur. Union 2017, 35, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Regulation of Persistent, Bioaccumulative, and Toxic Chemicals under TSCA Section 6(h); EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Stockholm Convention. Available online: http://chm.pops.int/ (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- Van der Veen, I.; de Boer, J. Phosphorus flame retardants: Properties, production, environmental occurrence, toxicity and analysis. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 1119–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantelaki, I.; Voutsa, D. Organophosphate flame retardants (OPFRs): A review on analytical methods and occurrence in wastewater and aquatic environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Li, M.; Du, M.; Li, X.; Li, Y. A review of a class of emerging contaminants: The classification, distribution, intensity of consumption, synthesis routes, environmental effects and expectation of pollution abatement to organophosphate flame retardants (OPFRs). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Ma, J.; Fang, D.; Shi, T.; Gong, Y. Organophosphate flame retardants in soils of Zhejiang Province, China: Levels, distribution, sources, and exposure risks. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 78, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stapleton, H.M.; Klosterhaus, S.; Eagle, S.; Fuh, J.; Meeker, J.D.; Blum, A.; Webster, T.F. Detection of organophosphate flame retardants in furniture foam and US house dust. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 7490–7495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Hou, M.M.; Zhang, Q.N.; Wu, X.W.; Zhao, H.X.; Xie, Q.; Chen, J.W. Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in building and decoration materials and their potential burdens in newly decorated houses in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 10991–10999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Saborit, J.M. Indoor air as a contributor to air pollution exposure. In Indoor Air Pollution; Harrison, R.M., Hester, R.E., Eds.; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Liu, X.; Allen, M.R. Measurements of parameters controlling the emissions of organophosphate flame retardants in indoor environments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 5821–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Liu, X.; Allen, M.R. The influence of temperature on the emissions of organophosphate ester flame retardants from polyisocyanurate foam: Measurement and modeling. Chemosphere 2019, 233, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, U.J.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.H.; Kannan, K. Occurrence of and human exposure to organophosphate flame retardants/plasticizers in indoor air and dust from various microenvironments in the United States. Environ. Int. 2019, 125, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Hiltscher, M.; Puttmann, W. Occurrence and human exposure assessment of organophosphate flame retardants in indoor dust from various microenvironments of the Rhine/Main region, Germany. Indoor Air 2017, 27, 1113–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Li, H.; Xu, S.; Zhou, Q.; Jin, M.; Tang, J. A review of organophosphorus flame retardants (OPFRs): Occurrence, bioaccumulation, toxicity, and organism exposure. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 22126–22136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, R.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z. Review of OPFRs in animals and humans: Absorption, bioaccumulation, metabolism, and internal exposure research. Chemosphere 2016, 153, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugeng, E.J.; de Cock, M.; Leonards, P.E.G.; van de Bor, M. Toddler behavior, the home environment, and flame retardant exposure. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Zartarian, V.; Moya, J.; Freeman, N.; Beamer, P.; Black, K.; Tulve, N.; Shalat, S. A meta-analysis of children’s hand-to-mouth frequency data for estimating nondietary ingestion exposure. Risk Anal. 2007, 27, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ATSDR. Toxicology Profile for Phosphate Ester Flame Retardants; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): Atlanta, GA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Meeker, J.D.; Stapleton, H.M. House dust concentrations of organophosphate flame retardants in relation to hormone levels and semen quality parameters. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, C.; Wang, X.; Thai, P.; Mueller, J.F.; Gallen, C.; Li, Y.; Baduel, C. Development and validation of a multi-residue method for the analysis of brominated and organophosphate flame retardants in indoor dust. Talanta 2017, 164, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, L.; Tao, Y.; Luo, D.; Feng, J.; Wang, L.; Yu, M.; Li, Y.; Covaci, A.; Mei, S. Simultaneous biomonitoring of 15 organophosphate flame retardants metabolites in urine samples by solvent induced phase transition extraction coupled with ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 2019, 233, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosarac, I.; Kubwabo, C.; Foster, W.G. Quantitative determination of nine urinary metabolites of organophosphate flame retardants using solid phase extraction and ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS). J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2016, 1014, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vykoukalova, M.; Venier, M.; Vojta, S.; Melymuk, L.; Becanova, J.; Romanak, K.; Prokes, R.; Okeme, J.O.; Saini, A.; Diamond, M.L.; et al. Organophosphate esters flame retardants in the indoor environment. Environ. Int. 2017, 106, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergh, C.; Torgrip, R.; Emenius, G.; Ostman, C. Organophosphate and phthalate esters in air and settled dust—A multi-location indoor study. Indoor Air 2011, 21, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marklund, A.; Andersson, B.; Haglund, P. Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in air from various indoor environments. J. Environ. Monit. 2005, 7, 814–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, R.; Li, Y.; Xiang, P.; Li, C.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, S.; Cui, X.; Ma, L.Q. Organophosphorus flame retardants and phthalate esters in indoor dust from different microenvironments: Bioaccessibility and risk assessment. Chemosphere 2016, 150, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luongo, G.; Ostman, C. Organophosphate and phthalate esters in settled dust from apartment buildings in Stockholm. Indoor Air 2016, 26, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugeng, E.J.; Leonards, P.E.G.; van de Bor, M. Brominated and organophosphorus flame retardants in body wipes and house dust, and an estimation of house dust hand-loadings in Dutch toddlers. Environ. Res. 2017, 158, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kademoglou, K.; Xu, F.; Padilla-Sanchez, J.A.; Haug, L.S.; Covaci, A.; Collins, C.D. Legacy and alternative flame retardants in Norwegian and UK indoor environment: Implications of human exposure via dust ingestion. Environ. Int. 2017, 102, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khairy, M.A.; Lohmann, R. Selected organohalogenated flame retardants in Egyptian indoor and outdoor environments: Levels, sources and implications for human exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1536–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hammel, S.C.; Hoffman, K.; Phillips, A.L.; Levasseur, J.L.; Lorenzo, A.M.; Webster, T.F.; Stapleton, H.M. Comparing the use of silicone wristbands, hand wipes, and dust to evaluate children’s exposure to flame retardants and plasticizers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 4484–4494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galuszka, A.; Konieczka, P.; Migaszewski, Z.M.; Namiesnik, J. Analytical Eco-Scale for assessing the greenness of analytical procedures. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 37, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena-Pereira, F.; Wojnowski, W.; Tobiszewski, M. AGREE—Analytical GREEnness metric approach and software. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 10076–10082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobiszewski, M.; Namiesnik, J.; Pena-Pereira, F. Environmental risk-based ranking of solvents using the combination of a multimedia model and multi-criteria decision analysis. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agnieszka, G.; Zdzisław, M.; Namieśnik, J. The 12 principles of green analytical chemistry and the SIGNIFICANCE mnemonic of green analytical practices. TrAC Trends Analyt. Chem. 2013, 50, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, J.; Wang, T.; Hagberg, J. Organophosphate flame retardants and plasticizers in indoor dust, air and window wipes in newly built low-energy preschools. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628–629, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokumura, M.; Hatayama, R.; Tatsu, K.; Naito, T.; Takeda, T.; Raknuzzaman, M.; Al-Mamun, M.H.; Masunaga, S. Organophosphate flame retardants in the indoor air and dust in cars in Japan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Hites, R.A. Electron impact, electron capture negative ionization and positive chemical ionization mass spectra of organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers. J. Mass Spectrom. 2013, 48, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Eede, N.; Dirtu, A.C.; Neels, H.; Covaci, A. Analytical developments and preliminary assessment of human exposure to organophosphate flame retardants from indoor dust. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokumura, M.; Miyake, Y.; Wang, Q.; Nakayama, H.; Amagai, T.; Ogo, S.; Kume, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Takasu, S.; Ogawa, K. Methods for the analysis of organophosphorus flame retardants—Comparison of GC-EI-MS, GC-NCI-MS, LC-ESI-MS/MS, and LC-APCI-MS/MS. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 2018, 53, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; He, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Wu, N.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, Z. Assessing the threats of organophosphate esters (flame retardants and plasticizers) to drinking water safety based on USEPA oral reference dose (RfD) and oral cancer slope factor (SFO). Water Res. 2019, 154, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.R.; Steiniche, T.; Romanak, K.A.; Johnson, E.; Quiros, R.; Mutegeki, R.; Wasserman, M.D.; Venier, M. Atmospheric occurrence of legacy pesticides, current use pesticides, and flame retardants in and around protected areas in Costa Rica and Uganda. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 6171–6181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, T.; Matsunaga, I.; Oda, H. Simultaneous determination of semivolatile organic compounds in indoor air by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry after solid-phase extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1023, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cequier, E.; Ionas, A.C.; Covaci, A.; Marce, R.M.; Becher, G.; Thomsen, C. Occurrence of a broad range of legacy and emerging flame retardants in indoor environments in Norway. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 6827–6835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, K.; de Wit, C.A.; Sellstrom, U.; Sahlstrom, L.; Lindh, C.H.; Berglund, M. Brominated flame retardants and organophosphate esters in preschool dust and children’s hand wipes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 4878–4888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yu, G.; Cao, Z.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Deng, S.; Wang, Y. Occurrence of organophosphorus flame retardants on skin wipes: Insight into human exposure from dermal absorption. Environ. Int. 2017, 98, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Giovanoulis, G.; van Waes, S.; Padilla-Sanchez, J.A.; Papadopoulou, E.; Magner, J.; Haug, L.S.; Neels, H.; Covaci, A. Comprehensive study of human external exposure to organophosphate flame retardants via air, dust, and hand wipes: The Importance of sampling and assessment strategy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 7752–7760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, E.M.; Covaci, A.; van Nuijs, A.L.; Webster, T.F.; Stapleton, H.M. Analysis of the flame retardant metabolites bis(1,3-dichloro-2-propyl) phosphate (BDCPP) and diphenyl phosphate (DPP) in urine using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 2123–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brommer, S.; Harrad, S.; Van den Eede, N.; Covaci, A. Concentrations of organophosphate esters and brominated flame retardants in German indoor dust samples. J. Environ. Monit. 2012, 14, 2482–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otake, T.; Yoshinaga, J.; Yanagisawa, Y. Analysis of organic esters of plasticizer in indoor air by GC-MS and GC-FPD. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 3099–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristale, J.; Lacorte, S. Development and validation of a multiresidue method for the analysis of polybrominated diphenyl ethers, new brominated and organophosphorus flame retardants in sediment, sludge and dust. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1305, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Eede, N.; Dirtu, A.C.; Ali, N.; Neels, H.; Covaci, A. Multi-residue method for the determination of brominated and organophosphate flame retardants in indoor dust. Talanta 2012, 89, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.T.; Zheng, J.; Qiao, L.; Chen, S.J.; Yang, J.Z.; Yuan, J.G.; Yang, Z.Y.; Mai, B.X. Occurrence of organophosphorus flame retardants in indoor dust in multiple microenvironments of southern China and implications for human exposure. Chemosphere 2015, 133, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, I.C.; Devi, N.L.; Zhong, G.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Covaci, A. Occurrence and fate of organophosphate ester flame retardants and plasticizers in indoor air and dust of Nepal: Implication for human exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 229, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, K.; Garantziotis, S.; Birnbaum, L.S.; Stapleton, H.M. Monitoring indoor exposure to organophosphate flame retardants: Hand wipes and house dust. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Samples/Compounds | Quantifier-Qualifier Ions | Calibration | Detection Limits (n = 7) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear Range | RSD (%) | R2 | IDL (μg/mL) | MDL a | ||
| Indoor air (μg/m3) | ||||||
| TEP | 99, 155 | 0.034–6.87 | 5.87% | 0.999 | 0.016 | 0.006 |
| TIBP | 99, 57 | 0.034–6.87 | 4.91% | 0.998 | 0.015 | 0.005 |
| TNBP | 99, 151 | 0.034–6.87 | 2.69% | 0.999 | 0.016 | 0.009 |
| TCEP | 63, 249 | 0.034–6.87 | 4.03% | 0.999 | 0.019 | 0.007 |
| TCIPP | 99, 125 | 0.034–6.87 | 4.16% | 0.999 | 0.030 | 0.010 |
| TDCIPP | 75, 77 | 0.034–6.87 | 4.24% | 0.999 | 0.027 | 0.009 |
| TPHP | 99, 113 | 0.034–6.87 | 5.38% | 0.998 | 0.023 | 0.008 |
| TBOEP | 57, 125 | 0.034–6.87 | 9.90% | 0.998 | 0.028 | 0.010 |
| EHDPP | 251, 250 | 0.034–6.87 | 9.54% | 0.999 | 0.019 | 0.007 |
| TEHP | 326, 77 | 0.034–6.87 | 9.66% | 0.999 | 0.023 | 0.008 |
| TCP | 368, 367 | 0.034–6.87 | 8.50% | 0.998 | 0.025 | 0.010 |
| House dust (μg/g) | ||||||
| TEP | 99, 155 | 2.00–400 | 5.87% | 0.999 | 0.016 | 0.325 |
| TIBP | 99, 57 | 2.00–400 | 4.91% | 0.998 | 0.015 | 0.301 |
| TNBP | 99, 151 | 2.00–400 | 2.69% | 0.999 | 0.016 | 0.313 |
| TCEP | 63, 249 | 2.00–400 | 4.03% | 0.999 | 0.019 | 0.269 |
| TCIPP | 99, 125 | 2.00–400 | 4.16% | 0.999 | 0.030 | 0.539 |
| TDCIPP | 75, 77 | 2.00–400 | 4.24% | 0.999 | 0.027 | 0.540 |
| TPHP | 99, 113 | 2.00–400 | 5.38% | 0.998 | 0.023 | 0.34 |
| TBOEP | 57, 125 | 2.00–400 | 9.90% | 0.998 | 0.028 | 0.502 |
| EHDPP | 251, 250 | 2.00–400 | 9.54% | 0.999 | 0.019 | 0.342 |
| TEHP | 326, 77 | 2.00–400 | 9.66% | 0.999 | 0.023 | 0.310 |
| TCP | 368, 367 | 2.00–400 | 8.50% | 0.998 | 0.025 | 0.508 |
| Skin wipe (μg/m2) | ||||||
| TEP | 99, 155 | 2.22–444 | 4.64% | 0.999 | 0.016 | 0.111 |
| TIBP | 99, 57 | 2.22–444 | 11.0% | 0.999 | 0.015 | 0.076 |
| TNBP | 99, 151 | 2.22–444 | 13.1% | 0.998 | 0.016 | 0.093 |
| TCEP | 63, 249 | 2.22–444 | 13.3% | 0.998 | 0.019 | 0.351 |
| TCIPP | 99, 125 | 2.22–444 | 12.3% | 0.998 | 0.030 | 0.351 |
| TDCIPP | 75, 77 | 2.22–444 | 13.0% | 0.999 | 0.027 | 0.351 |
| TPHP | 99, 113 | 2.22–444 | 14.4% | 0.999 | 0.023 | 0.133 |
| TBOEP | 57, 125 | 2.22–444 | 13.8% | 0.999 | 0.028 | 0.498 |
| EHDPP | 251, 250 | 2.22–444 | 14.2% | 0.999 | 0.019 | 0.098 |
| TEHP | 326, 77 | 2.22–444 | 13.4% | 0.999 | 0.023 | 0.413 |
| TCP | 368, 367 | 2.22–444 | 11.8% | 0.998 | 0.025 | 0.316 |
| Selected OPFRs | Rec (%) (n = 18) | Intra-Day (n = 9) | Inter-Day (n = 9) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 ppm | 5 ppm | 10 ppm | 0.1 ppm | 5 ppm | 10 ppm | ||||||||
| RSD (%) | Accu (%) | RSD (%) | Accu (%) | RSD (%) | Accu (%) | RSD (%) | Accu (%) | RSD (%) | Accu (%) | RSD (%) | Accu (%) | ||
| Indoor air (μg/m3) | |||||||||||||
| TEP | 105 | 1.80 | 1.98 | 5.30 | 4.28 | 7.90 | 4.69 | 2.20 | 3.95 | 1.10 | 6.03 | 3.80 | −10.9 |
| TIBP | 113 | 7.90 | 6.96 | 9.20 | 5.19 | 10.2 | 7.95 | 6.00 | 6.91 | 2.70 | 5.50 | 3.30 | 4.85 |
| TNBP | 110 | 3.40 | 3.91 | 1.10 | 2.79 | 4.50 | 4.90 | 4.40 | 6.62 | 2.50 | 3.51 | 0.700 | 2.99 |
| TCEP | 100 | 4.10 | −5.11 | 6.70 | 5.96 | 8.40 | 5.20 | 6.10 | 13.2 | 3.70 | 5.65 | 3.10 | 5.88 |
| TCIPP | 104 | 9.30 | 6.39 | 6.30 | 7.58 | 2.00 | −4.00 | 3.50 | 9.52 | 4.40 | 7.89 | 3.80 | −6.74 |
| TDCIPP | 110 | 3.70 | 2.54 | 1.90 | −3.51 | 5.90 | 4.88 | 1.40 | 4.74 | 2.50 | 8.67 | 3.60 | 4.70 |
| TPHP | 94.2 | 3.10 | 4.02 | 6.40 | −7.53 | 9.10 | −8.13 | 8.20 | 6.93 | 1.10 | 18.9 | 3.30 | −11.9 |
| TBOEP | 98.3 | 2.90 | 2.79 | 3.70 | −8.39 | 9.60 | −7.18 | 5.10 | 11.3 | 14.4 | 12.6 | 2.20 | −19.5 |
| EHDPP | 95.9 | 2.40 | 5.61 | 5.70 | 5.52 | 5.00 | −7.31 | 8.90 | 7.95 | 3.20 | 8.42 | 5.00 | 9.82 |
| TEHP | 98.1 | 1.30 | −5.60 | 9.60 | 5.58 | 7.70 | 4.79 | 4.30 | 10.1 | 7.20 | 9.66 | 3.70 | 10.0 |
| TCP | 95.0 | 2.30 | −4.01 | 2.20 | −5.83 | 2.90 | −4.25 | 5.70 | 4.15 | 3.90 | 6.68 | 2.40 | −4.81 |
| House dust (μg/g) | |||||||||||||
| TEP | 79.4 | 6.70 | −2.25 | 4.10 | −5.06 | 3.20 | −2.69 | 11.8 | −9.65 | 6.00 | −9.01 | 2.20 | −2.90 |
| TIBP | 94.6 | 7.30 | 6.97 | 4.30 | 3.89 | 9.10 | 5.79 | 6.60 | −7.38 | 3.40 | −4.04 | 2.40 | −10.9 |
| TNBP | 94.6 | 10.1 | −3.36 | 4.50 | 3.34 | 11.6 | −11.5 | 10.0 | −8.22 | 2.10 | 1.78 | 11.5 | 10.2 |
| TCEP | 77.1 | 6.90 | −6.94 | 3.50 | −5.82 | 9.80 | −8.70 | 7.00 | −6.14 | 8.10 | −6.53 | 7.60 | −4.80 |
| TCIPP | 109 | 4.70 | 7.30 | 6.00 | 3.15 | 12.4 | 10.8 | 9.90 | 7.64 | 0.30 | 6.15 | 9.20 | 9.80 |
| TDCIPP | 94.8 | 5.00 | 6.45 | 3.70 | −4.28 | 7.10 | −8.90 | 7.90 | 7.44 | 4.90 | 11.6 | 10.7 | 13.4 |
| TPHP | 106 | 11.6 | 4.58 | 9.10 | 1.72 | 10.0 | 11.2 | 13.5 | 6.58 | 2.80 | 7.63 | 10.0 | 3.25 |
| TBOEP | 88.0 | 0.700 | −3.94 | 1.10 | −4.45 | 8.60 | −9.79 | 8.40 | 4.67 | 2.40 | −4.86 | 13.9 | 3.82 |
| EHDPP | 103 | 9.60 | 7.75 | 3.40 | 5.94 | 2.20 | −9.98 | 11.4 | 7.69 | 1.50 | 11.7 | 12.1 | 9.20 |
| TEHP | 102 | 9.20 | 7.10 | 7.40 | 2.43 | 7.90 | 7.16 | 13.3 | 9.07 | 1.50 | −2.74 | 11.7 | 14.4 |
| TCP | 105 | 7.80 | 8.04 | 7.40 | 4.32 | 10.6 | 7.40 | 8.30 | 7.51 | 1.30 | 10.1 | 4.20 | 7.67 |
| Skin wipe (μg/m2) | |||||||||||||
| TEP | 74.8 | 8.50 | −4.55 | 2.30 | −1.82 | 8.20 | −4.91 | 8.20 | −3.82 | 1.90 | −2.58 | 1.70 | −1.59 |
| TIBP | 106 | 13.0 | −6.84 | 1.70 | −1.67 | 6.60 | 5.54 | 9.40 | 3.90 | 5.50 | 2.90 | 7.10 | 11.8 |
| TNBP | 104 | 6.20 | −7.41 | 6.50 | −1.06 | 6.00 | 5.64 | 5.10 | 12.1 | 1.50 | 3.74 | 8.80 | 12.8 |
| TCEP | 73.4 | 6.80 | −2.89 | 3.40 | −2.66 | 3.90 | −3.99 | 1.10 | −2.75 | 1.90 | −2.64 | 1.80 | −5.58 |
| TCIPP | 113 | 14.0 | −3.29 | 17.3 | −9.33 | 1.30 | 8.40 | 7.00 | 5.73 | 3.10 | 10.7 | 5.30 | 8.33 |
| TDCIPP | 104 | 5.60 | −5.17 | 3.80 | −2.49 | 0.600 | −4.43 | 3.30 | 5.88 | 1.20 | 14.7 | 5.20 | 16.1 |
| TPHP | 113 | 2.70 | −6.15 | 3.70 | −2.26 | 3.20 | 2.85 | 3.00 | −11.1 | 0.800 | 2.15 | 5.10 | 3.59 |
| TBOEP | 90.2 | 10.5 | 12.4 | 7.10 | 1.65 | 4.10 | 5.67 | 5.90 | 0.62 | 1.10 | 14.5 | 12.4 | 12.6 |
| EHDPP | 98.8 | 4.00 | −1.93 | 3.20 | −4.58 | 1.90 | −1.08 | 1.00 | −6.68 | 6.00 | −5.35 | 1.90 | 1.43 |
| TEHP | 87.0 | 9.30 | −8.08 | 0.10 | −1.30 | 2.90 | −7.91 | 6.60 | −9.14 | 2.50 | 4.14 | 8.10 | 9.50 |
| TCP | 99.0 | 2.30 | −8.07 | 8.80 | −5.58 | 10.3 | 2.70 | 3.10 | −15.1 | 6.20 | 10.8 | 5.80 | 7.29 |
| Homes | TEP | TIBP | TNBP | TCEP | TCIPP | TDCIPP | TBOEP | TEHP | TPHP | EHDPP | TCP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indoor air (μg/m3) | H 1 | <0.006 | 0.27 | <0.009 | <0.007 | 0.360 | <0.009 | <0.01 | <0.004 | <0.004 | <0.004 | <0.004 |
| H 2 | 0.300 | 0.10 | <0.009 | <0.007 | 0.370 | <0.009 | <0.01 | <0.004 | <0.004 | <0.004 | 0.010 | |
| H 3 | 0.170 | <0.005 | <0.009 | <0.007 | <0.01 | <0.009 | <0.01 | <0.004 | <0.004 | <0.004 | <0.004 | |
| H 4 | <0.006 | <0.005 | <0.009 | <0.007 | 0.530 | 0.070 | 0.22 | <0.004 | <0.004 | <0.004 | <0.004 | |
| H 5 | <0.006 | <0.005 | <0.009 | 0.04 | 0.300 | 0.070 | 0.25 | <0.004 | <0.004 | <0.004 | <0.004 | |
| H 6 | <0.006 | <0.005 | <0.009 | 0.03 | 0.460 | 0.260 | 0.78 | <0.004 | 0.25 | <0.004 | <0.004 | |
| H 7 | 0.060 | <0.005 | 0.040 | 0.08 | 1.10 | 2.81 | 0.74 | <0.004 | 1.03 | <0.004 | <0.004 | |
| H 8 | 0.040 | <0.005 | <0.009 | <0.007 | 1.04 | <0.009 | 0.08 | <0.004 | <0.004 | <0.004 | <0.004 | |
| H 9 | <0.006 | <0.005 | <0.009 | <0.007 | 0.450 | <0.009 | 0.05 | <0.004 | <0.004 | <0.004 | <0.004 | |
| H 10 | 0.110 | <0.005 | 0.060 | <0.007 | 1.32 | <0.009 | 0.08 | <0.004 | <0.004 | <0.004 | <0.004 | |
| House dust (μg/g) | H 1 | 2.04 | <0.300 | <0.310 | <0.270 | 2.45 | <0.54 | 11.7 | <0.310 | <0.340 | <0.340 | <0.510 |
| H 2 | 2.20 | <0.300 | <0.310 | <0.270 | 2.37 | 3.58 | 39.1 | <0.310 | 2.80 | <0.340 | <0.510 | |
| H 3 | 3.17 | <0.300 | <0.310 | <0.270 | <0.54 | 59.7 | 62.1 | <0.310 | <0.340 | <0.340 | <0.510 | |
| H 4 | 3.20 | <0.300 | <0.310 | <0.270 | 9.81 | 2.71 | 78.2 | <0.310 | <0.340 | <0.340 | <0.510 | |
| H 5 | 2.50 | <0.300 | <0.310 | <0.270 | 3.28 | 2.83 | 33.5 | <0.310 | <0.340 | <0.340 | <0.510 | |
| H 6 | <0.330 | <0.300 | <0.310 | <0.270 | <0.54 | <0.54 | 12.8 | <0.310 | <0.340 | <0.340 | <0.510 | |
| H 7 | <0.330 | <0.300 | <0.310 | <0.270 | <0.54 | 9.87 | 14.5 | <0.310 | <0.340 | <0.340 | <0.510 | |
| H 8 | 2.15 | <0.300 | <0.310 | <0.270 | 2.25 | <0.54 | 31.7 | <0.310 | <0.340 | <0.340 | <0.510 | |
| H 9 | <0.330 | <0.300 | <0.310 | <0.270 | <0.54 | <0.54 | 18.4 | <0.310 | <0.340 | <0.340 | <0.510 | |
| H 10 | 4.33 | <0.300 | <0.310 | <0.270 | 9.38 | <0.54 | 13.4 | <0.310 | <0.340 | <0.340 | <0.510 | |
| Skin wipe (μg/m2) | H 1 | 4.90 | <0.080 | <0.090 | <0.350 | <0.35 | <0.35 | <0.500 | <0.410 | <0.130 | <0.100 | <0.320 |
| H 2 | 3.68 | <0.080 | <0.090 | <0.350 | <0.35 | <0.35 | <0.500 | <0.410 | <0.130 | <0.100 | <0.320 | |
| H 3 | <0.110 | <0.080 | <0.090 | <0.350 | 4.39 | <0.35 | 2297 | 22.2 | <0.130 | <0.100 | <0.320 | |
| H 4 | <0.110 | <0.080 | <0.090 | <0.350 | 25.0 | 31.8 | 82.2 | <0.410 | <0.130 | <0.100 | <0.320 | |
| H 5 | <0.110 | <0.080 | <0.090 | <0.350 | 8.89 | <0.35 | 10.2 | <0.410 | <0.130 | <0.100 | <0.320 | |
| H 6 | <0.110 | <0.080 | <0.090 | <0.350 | 44.9 | <0.35 | 304 | <0.410 | 3.56 | <0.100 | <0.320 | |
| H 7 | <0.110 | <0.080 | <0.090 | <0.350 | 25.8 | 13.4 | 128 | <0.410 | <0.130 | <0.100 | <0.320 | |
| H 8 | <0.110 | <0.080 | <0.090 | <0.350 | 18.7 | 2.46 | 231 | <0.410 | <0.130 | <0.100 | <0.320 | |
| H 9 | <0.110 | <0.080 | <0.090 | <0.350 | 16.4 | 32.0 | 165 | <0.410 | 3.11 | <0.100 | <0.320 | |
| H 10 | <0.110 | <0.080 | <0.090 | 8.02 | 18.2 | 3.64 | 217 | <0.410 | 6.22 | 8.89 | <0.320 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, C.-Y.; Liu, Y.-H.; Chieh, C.-H.; Chang, W.-H. Fast and Environment-Friendly GC-MS Method for Eleven Organophosphorus Flame Retardants in Indoor Air, Dust, and Skin Wipes. Toxics 2021, 9, 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9120350
Chen C-Y, Liu Y-H, Chieh C-H, Chang W-H. Fast and Environment-Friendly GC-MS Method for Eleven Organophosphorus Flame Retardants in Indoor Air, Dust, and Skin Wipes. Toxics. 2021; 9(12):350. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9120350
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Chung-Yu, Yu-Hsuan Liu, Chia-Hui Chieh, and Wei-Hsiang Chang. 2021. "Fast and Environment-Friendly GC-MS Method for Eleven Organophosphorus Flame Retardants in Indoor Air, Dust, and Skin Wipes" Toxics 9, no. 12: 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9120350
APA StyleChen, C.-Y., Liu, Y.-H., Chieh, C.-H., & Chang, W.-H. (2021). Fast and Environment-Friendly GC-MS Method for Eleven Organophosphorus Flame Retardants in Indoor Air, Dust, and Skin Wipes. Toxics, 9(12), 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9120350







