Abstract
The serious global microplastic pollution has attracted public concern in recent years. Microplastics are widely distributed in various environments and their pollution is already ubiquitous in the ocean system, which contributes to exponential concern in the past decade and different research areas. Due to their tiny size coupled with the various microbial communities in aquatic habitats capable of accumulating organic pollutants, abundant literature is available for assessing the negative impact of MPs on the physiology of marine organisms and eventually on the human health. This study summarizes the current literature on MPs in the marine environment to obtain a better knowledge about MP contamination. This review contains three sections: (1) sources and fates of MPs in the marine environment, (2) impacts of MPs on marine organisms, and (3) bacteria for the degradation of marine MPs. Some measures and efforts must be taken to solve the environmental problems caused by microplastics. The knowledge in this review will provide background information for marine microplastics studies and management strategies in future.
1. Introduction
Plastics have brought a lot of benefits to modern life, driving the tremendous growth in plastic demand, because of their low cost, light weight, and durable character [1,2]. It was reported that 3 billion tons of plastic were manufactured in 2016, and every year, some 8 million tons of plastics will eventually enter the marine environment [3,4]. One of the consequences of this accumulation in the marine environment is the low percentage of recycled plastics [5,6] as just 9.4 million tonnes of plastic postconsumer waste were collected in Europe to be recycled in 2018 (both inside and outside the Europe) [7]. Plastic pollution is already ubiquitous in the ocean environment. Most worrying of all, it was estimated that the weight of plastics in the ocean will be more than that of the fish by 2050 [8].
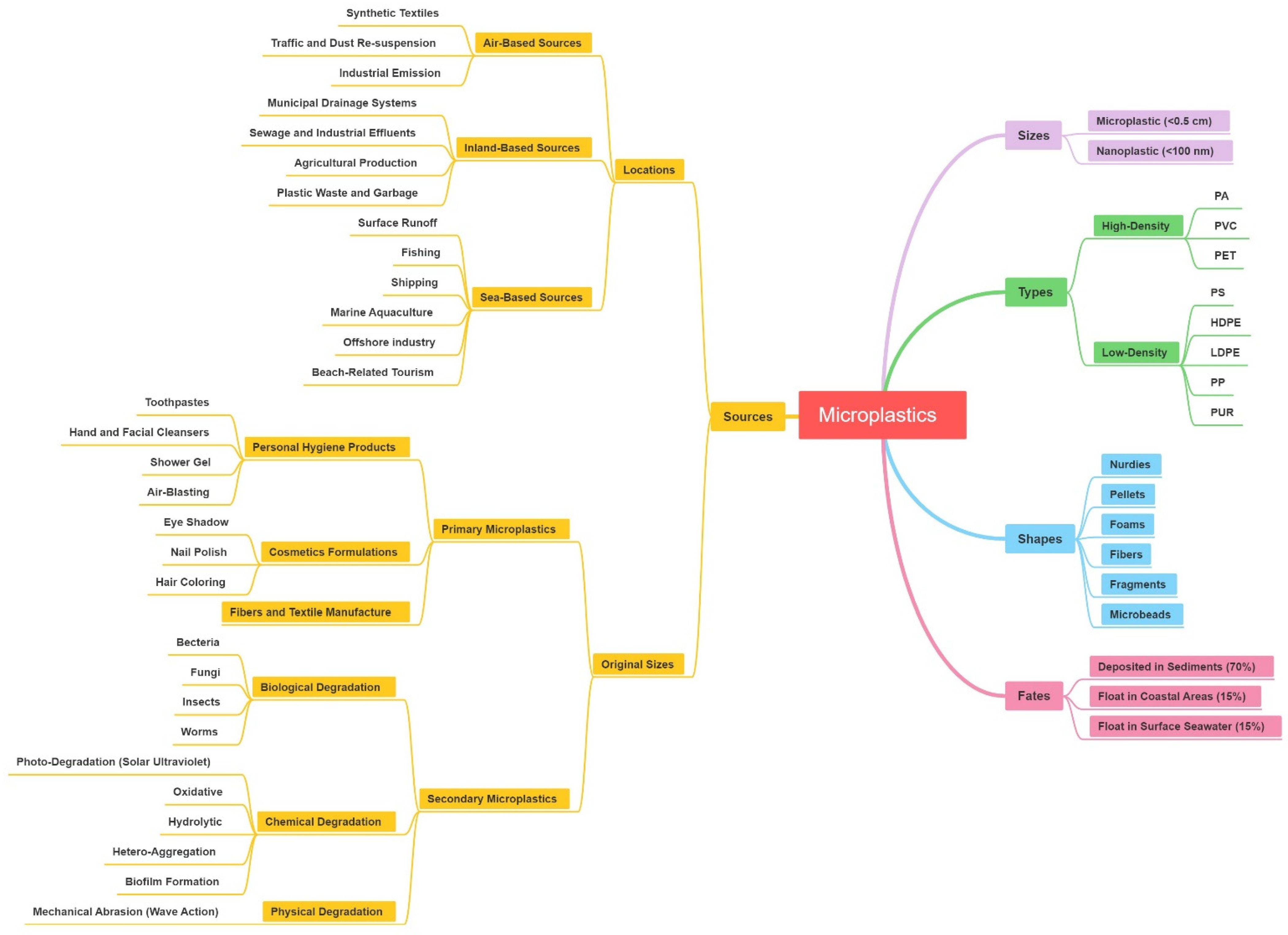
Microplastics (MPs) are plastic fragments or particles with a diameter of less than 5 mm formed by fragmentation of larger plastics [9,10,11,12,13,14]. Plastics can fragment into smaller particles in the marine environment [15,16]. Microplastics appear in various shapes, such as foils, foams, fibers, pellets, fragments and microbeads [17,18]. Generally, plastics are chemically diverse. The density of polyamide (PA), polyvinylchloride (PVC), and polyethylene terephthalate (PET) are higher than that of seawater, increasing the settlement rates in sediments, while polystyrene (PS), high-density polyethylene (HDPE), low-density polyethylene (LDPE), polypropylene (PP) and polyurethane (PUR) with lower densities might float mainly on seawater [19,20,21,22] (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
The basic characteristics of microplastic about size, type, shape, source and fate.
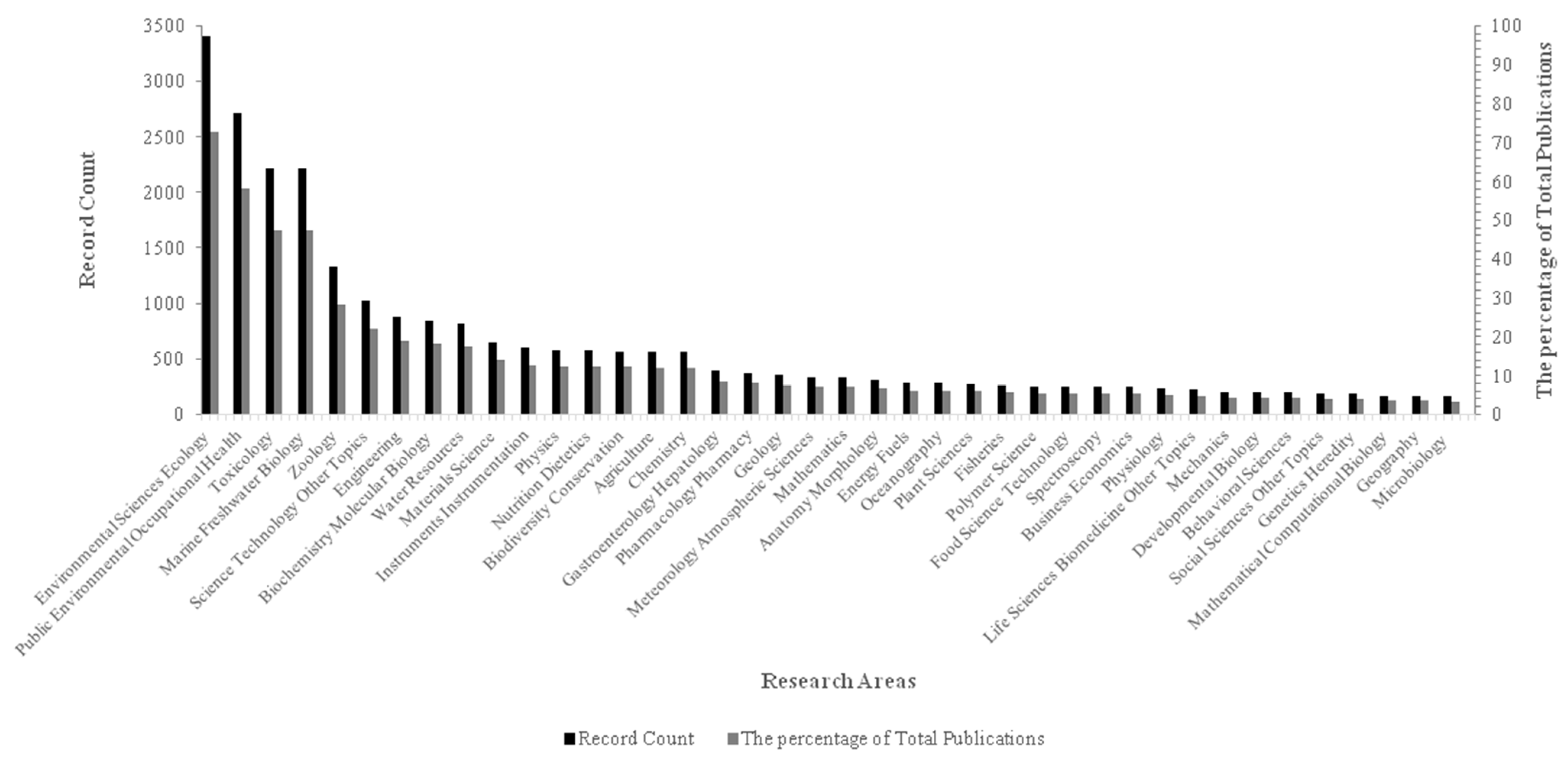
Microplastics are prevalent in the environment, especially the marine environment, due to hydrodynamic processes, transportation by wind and ocean currents, ranging from the large ocean gyres such as the Pacific Ocean [9,23], the Atlantic Ocean [24], Indian Ocean [25], polar regions [26,27,28], and the equator [29], and from coasts [30,31] to open seas [32,33]. It was estimated that more than 15 trillion microplastics were present in the global ocean in 2014, weighing more than 93 thousand metric tons [34]. MPs are abundant in the Great Pacific Garbage Patch, with about 1.69 trillion (94%) floating pieces [10] that are microplastics. Generally, microplastics pollution is already a ubiquitous presence in the ocean environment, which contributes to exponential public and scientific concern in last decade and different research areas (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
The record count and the percentage of total publications in the top 40 research areas related to the assessment of the microplastic effects on organisms and bacterial degradation over time. Source: Web of Science; Period: 1944–2020; Total Publications: 4685; h-index: 162; Average citations per item: 29.31; Sum of Times Cited: 137,315 (without self-citations: 53,749); Citing articles: 32,830 (without self-citations: 29,560). TS = (microplastic * OR micro-plastic * OR plastic particle * OR plastic particulate OR plastic debris OR plastisphere * OR microplastic pollution *) AND (source * OR fate * OR occurrence * OR distribute * OR influence * OR impact * OR affect OR risk * OR effect * OR exposure * OR exposed OR colonize OR colonization OR bacteria * OR germ * OR microbiological OR microorganisms OR microbial OR microbiota OR macrobiotic OR biotechnological OR degrade * OR degradation * OR biodegradation * OR biodegrade * OR organisms * OR creature * OR biota * OR habitat *) AND (marine * OR ocean * OR sea * OR seawater * OR beach * OR shore * OR coast * OR seacoast * OR seaboard *).
Due to their tiny size, MPs can be ingested accidentally by marine species [35,36], such as fish [37], mussels [38,39,40], zooplankton [41], seabirds [42], sand hoppers [43] and worms [44].
The ecological threat of MPs to the oceanic environment and their health risk to organisms have not been fully clarified, but given the sharply increasing amount of evidence about the presence and effects of MPs in the marine environment, MP pollution has become a great environmental concern [45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55]. Some measures and efforts must be taken to solve the problems caused by microplastics and improve plastic waste management.
The present review will summarize existing research on MPs in the marine environment to provide a better understanding about MPs contamination in marine environment. This review contains three sections: (1) sources and fates of MPs in marine environment, (2) impacts of MPs on marine organisms, and (3) bacteria for the degradation of marine MPs.
2. Sources and Fates of MPs in Marine Environment
2.1. Sources of marine MPs
Marine microplastic pollution originates from a variety of sources and can generally be divided into inland-based, sea-based and air-based sources [19,56,57,58] (Figure 1). Rivers are considered to be the most important pathways for microplastics to be transported from inland areas to the ocean [59]. About 80% of the plastic pieces in the ocean originated from the terrestrial environment [12,56,60]. Plastic debris in municipal drainage systems and sewage effluents, or improper management of inland areas is blown into the sea through rivers, and plastic waste from beach-related tourism is discarded directly into the environment [18,56,57,61]. Sea-based sources originate from fishing, shipping and offshore industries [62,63]. The emissions and leaks of large shipping are considered as an important source of microplastics [64]. Loss and damage of fishing and aquaculture equipment can easily introduce plastic particles into the ocean [9,65,66]. Followed by marine aquaculture, the main offshore source is the world’s fishing fleet [67], garbage illegally discarded from ships or offshore platforms [68], and a large proportion of items comes from lost containers [56,69]. In addition, airborne MPs are also important sources [70].
According to their original sizes, microplastics can be divided into two groups. Originally designed plastic microbeads, industrially produced particles and powders (<5 mm in diameter) could enter the ocean directly through sewage effluent, which is called primary microplastics [57,71]. When subjected to the combined effects of physical, biological and chemical processes, large plastic fragments are broken down and degraded into tiny fragments, which are secondary microplastics and can be transported to the marine environment [72,73,74]. Primary microplastics are widely used in personal hygiene products containing abrasives and scrubs (like toothpastes, hand and facial cleansers; shower gels and air-blasting aids, etc.) [28,75,76,77,78], cosmetics formulations (such as eye shadow, nail polish, hair coloring, etc.) [79,80], and also fiber and textile manufacture [81].
Generally, secondary microplastics imply the breakdown of large plastic debris due to biological, chemical and physical degradation, which are representative of microbial species biodegradation, photodegradation (solar ultraviolet radiation) and mechanical abrasion (wave action), respectively. Plastic debris in the ocean are subject to mechanical damage and photodegradation well as oxidative degradation, which break down fragile plastics into microplastics [82,83]. Besides, microplastics can further degrade to nano-scale plastic pieces [40]. These microplastics and nanoplastics are more easily ingested and will have long-term adverse impacts on the marine environment, making them become a public concern in the future [40,83,84,85] (Figure 1).
2.2. Fates of Marine MPs
Generally, debris in any water body will ultimately enter the ocean. Transported by water power and wind power, microplastics gradually migrate and diffuse through the ocean, eventually becoming as ubiquitous as they are today, ranging from the large ocean gyres (e.g., the Pacific Ocean [9,23]; the Atlantic Ocean [24]; Indian Ocean [25]) to the polar regions and equator, from densely populated areas to remote islands, and from beaches down to the abysses of the sea [26,27,29,30,33]. They come in various shapes, with fibers being the most common form, followed by fragments. Marine circulation, estuaries and other coastal areas where humans are active are the ecosystems most seriously polluted by microplastics [86,87,88]. Approximately 70% of marine plastic debris is deposited in sediments, 15% floats in coastal areas and the remainder float on the surface seawater (Figure 1). Microplastics will be accumulated in the global ocean circulation, since some of them are less dense than seawater and float on the sea surface, and the converging sea currents concentrate and retain debris for a long time [23,35,89,90]. According to the surveys, there are only at least 7000 tonnes of plastic debris on the surface of the high seas [89], but at least 4.8 million tonnes of plastic debris enter the marine environment each year [91], which is inconsistent with data on surface plastics, suggesting that a significant number of plastics sinks to unknown depths. Microplastics have even been found on the seafloor at 2200–10,000 m depth, containing both high [92] and low [93] density (relative to seawater) microplastics. This indicates that the migration of microplastics is a dynamic process, which may not only be carried to every part of the marine through physical effects such as crushing and coastal deposition, but also through chemical processes such as oxidation or hydrolysis [62,94], and may also be carried to every part of the ocean through biological absorption, digestion and excretion [95].
Weathering processes, biodegradation processes, oxidative and hydrolytic degradation [62,93] and hetero-aggregation and biofilm formation [96,97] could significantly affect the fate of microplastic pieces in the oceanic environment (Figure 1). Biological pollution and subsequent chemical deposition of plastics, could dominate migration in seawater environments [98,99,100]. Therefore, according to biofilm growth, sedimentation and marine depth distribution of various physical factors such as light, salinity, water density, temperature, and viscosity, a theoretical predicted model was established to simulate the impact of biological pollution on the migration of microplastics, and forecast the size-dependent vertical migration of sea microplastics [101].
In addition to the origin and fate of MPs, many papers have also focused on the particle size, shape, type, color and mesh size of MPS and how to sample it to fully understand the characteristics of MPS in marine ecosystems (Table 1). This information will be helpful for further evaluation of plastic production plans and for more scientific and effective control of plastic products [102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117].

Table 1.
The characterization of MPs in marine ecosystem.
3. Impacts on Marine Organisms of MPs
Recently, abundant literature has assessed the accumulation of microplastics in marine organisms through direct contact [36] or food chain exposure [37] to MPs. MPs are ingested by organisms and have negative effects on their development, metabolism, reproduction and cellular response, and so on [118,119,120,121,122,123,124,125,126,127,128,129,130,131,132,133,134].
3.1. Exposure
Basically, there are two primary modes of MP exposure for marine organisms: bathing contact and ingestion. Bathing, of course, is the most common contact method in MP bioassays of natural marine environments, making it possible to study the various adverse effects caused by microplastics on the aquatic organisms through contact [36]. For example, microplastics could attach to the surface of skin, crust and ectoderm of Artemia franciscana [55]. Besides, microplastics could be ingested by low-nutrient organisms (like zooplankton such as artemia [55,118,135] and larvae of various marine animals such as shellfish and sea squirts [118,135,136], which are more readily available and easily exposed to suspended microplastics, since microplastics are similar than planktonic organisms and sediments in size and density [38,55,137,138,139].
3.2. Translocation
Microplastics are found in the circulatory system and tissues of some marine organisms because they could pass through epithelial tissues and even cell membranes. This phenomenon was called “translocation” [36,140]. For example, after a 3 h exposure, HDPE was detected in mussels’ stomachs and accumulated in the lysosomal system [39]. Since microplastics cannot be digested or absorbed, they can pass through cell membranes, transport through the inner layer of intestinal epithelium into the circulatory system and enter tissues after ingestion [38,56]. Therefore, MPs could be translocated and accumulated in cells and specialized tissues, such as gills and guts [141], liver [142], lysosomal system and hemolymph in blood cells [39].
Translocation efficiency depends mainly on the size of the MPs, but is also biologically affected by other factors, such as shape, concentration and the related organisms [143,144]. MP < 10 μm may be compatible with the use of membrane surface recognition elements through the epithelium [145]. As the size of microplastics decreases, the ability for microplastics to accumulate in marine organisms may increase, because the smaller the microplastics, the easier their transport. Currently, one of the main techniques for studying translocation is to expose organisms to fluorescently labeled plastic particles and then use a microscope (e.g., fluorescence and confocal microscopy) to observe MPs in the tissue, as well as do the quantitative analysis through flow cytometry [146,147].
3.3. Bioaccumulation and Bioavailability
The two important indexes to access the impacts of MPs to organisms are bioaccumulation and bioavailability [36]. There are interactions between MPs and organisms in the marine environment [148]. Microplastics can be ingested directly by marine organisms or transferred and accumulated in the food web from lower trophic organisms to higher trophic organisms, and the higher the trophic level, the more microplastics may be enriched in the organism [149]. In addition, toxic pollutants could be transported and accumulated in organisms along with microplastics through the ingestion, which has been demonstrated during experimental exposure tests. It has been speculated that POPs could be significantly bioaccumulated in the food web via microplastics [137,150,151].
The bioaccumulation of MPs has been identified in the digestive tract such as the oral area [33], gastrointestinal tract [37,116,142,152] and liver [153] of marine organisms, and followed by translocation to the circulatory system, other specific tissues and cells [39,141,142]. According to Bottari et al., fibrous microplastics are found in the digestive systems of Zeus faber and Lepidopus caudatus [152]. Microplastics have been reported to be found in fish populations at the bottom of the Mediterranean, with PE accounting for the largest proportion [153]. Furthermore, it has been reported that when Dicentrarchus labrax ingest microplastics, the particles accumulate in the liver, accompanied by oxidative stress [154]. Even some endangered species, such as bluefin tuna, have been found to have microplastics in their bodies, which raises concerns about the extent of microplastics pollution in marine species [142].
Bioavailability strongly relies on the physiochemical properties of microplastics, like their size, shape, and density [11,138]. The conclusion is that the size of microplastics is the most important factor. As the size decreases, the potential of bioaccumulation and bioavailability increase [9,138], because microplastics with smaller size are similar to planktonic organisms, and could be easily mistakenly ingested by zooplankton [36]. The irregular shape of plastic particles or fibers results in different bioavailability [155].
Additionally, biological factors could increase the microplastic bioavailability. MPs egested within fecal matter might be ingested by subsequent detritivores and suspension feeders [156], then be cast up on the benthos, attracted to the sediment, and MPs could be available for infauna, sediment-dwelling organisms capable of bioturbation [30,57,137]. Furthermore, their bioavailability in the water column is also influenced by biological fouling and aggregation, and after decontamination, they float at the sea-air interface [56] or sink below the marine surface, due to reduced buoyancy [96].
Microplastics could enhance the bioavailability of adsorbed pollutants, which has attracted more interest from scientists [135,136]. Unfortunately, due to the very high number of possible interaction factors, including physical (e.g., salinity, pH, and temperature), chemical (e.g., hydrolysis, oxidation, reduction and enrichment) and biological factors (e.g., organisms variables), it is difficult to assess how the bioavailability of pollutants enhanced by microplastics [136].
3.4. Toxic Effects
Microplastics have toxic effects on marine organisms. Different types and sizes of microplastics have different toxic effects on marine species, which are ultimately reflected in the physiological response of organisms and the damage they are subjected to [118,119,120,121,122,123,124,125,126,127,128,129,130,131,132,133,134] (Table 2). In addition, different microplastics also adsorb different pollutants, which combine to further damage the health of living marine organisms [150,157,158,159,160,161,162] (Table 2).

Table 2.
Effects of microplastics and nanoplastics on marine organisms
3.4.1. Physiological Impacts
Some morphological changes were detected in the marine phytoplankton when they ingested microplastics. For example, some thylakoids were deformed and cell walls were thickened [118], algae homo-aggregation and algae-microplastics hetero-aggregation [118], as well as expression of certain chloroplast genes was reduced [119].
As for the development, studies examining the impact of MPs have reported significant effects on the development of marine zooplankton and other invertebrates, such as dry weight loss in lugworms [120], intergenerational developmental responses in copepods [121], anomalous growth delays in juvenile [122] and larval [123] development in sea urchins and ascidians, development parameter alteration in shellfish [124], malformations or dead embryos [105], embryonic development abnormalities [125] in a dose- [120,124,126], time- [127], and size- [128] dependent manner in larvae and adults of different invertebrates. Particularly, the microplastics in the larvae of marine organisms will seriously affect the normal growth of the organism and sometimes microplastics might even cause death, due to their limited abilities to control their internal environment [127]. It was reported that the molting times of the larvae increased significantly in a short period of time after ingesting microparticles [55] and that microparticles had a restrictive effect on their feeding, that is, the microparticles had a sublethal effect on the larvae [55]. Studies have shown that after worms’ ingestion of microplastics, their energy reserves are significantly reduced and particles accumulate in the intestines where they induce inflammation [36].
The effects of microplastics on oxidative stress, inflammatory reactions and metabolic disorders of marine animals were studied. For example, the accumulation of MPs may result in inflammation, lipid accumulation and energy metabolism in fish [128], while oxidative stress and enzyme activity reductions occur in crabs [129].
The adverse impact of microplastic on the reproduction in marine animals, such as egg production [130], fecundity [121], fertilization rates [125], oocyte number [127], population size [130,131] and population growth rate [131] were assessed with significant dose-dependent [130] and distinct size-dependent effects [98,107] being observed in marine invertebrates studies.
At the cellular level, exposure marine animals to MPs induced comprehensive cellular responses. Microplastics could significantly down-regulate histone 3 gene expression [130], and up-regulate Abcb1, cas-8 [132], sod, gpx, idp, pk [133] gene expression. Besides, the activity of phagocytes and mitochondria is significantly increased, and the proportion of oxy radical and immune cells is also up-regulated [134].
3.4.2. Joint Toxicity
Due to the high adsorption capacity of microplastics, many hydrophobic pollutants could adsorb and accumulate on microplastics and accompanied by biomagnification (e.g., PAHs, PCBs, nonylphenols, pesticides, dioxins) [150,157]. Studies have shown that millimeter-sized microplastics have no obvious adsorption toxicity, while micron-sized or even nanosized microplastics have a relatively strong ability to absorb pollutants [131]. For heavy metal pollutants, 32–40 μm plastic particles exposed to heavy metals induce oxidative stress in fish and stimulate their innate immunity [158]. As for organic pollutants, there are studies that have shown that 50 nm plastic particles exposed to PAHs are obviously toxic to aquatic zooplankton and cause significant chemical damage [159]. The biological amplification of organic pollutants becomes higher because plastics reduce the metabolism of pollutants, and the combined toxicity presents an additive effect [160].
In addition to the original monomer, many microplastic products also contain a variety of additives, such as flame retardants, plasticizers, dyes and antioxidants, which make microplastics display joint toxicity with the additives [157,161].
The accumulation and biomagnification of microplastics and their surface-adsorbed pollutants need to be further studied. The joint toxicity may pose a persistent threat to marine ecosystems, due to the durability of microplastics and toxic chemicals [17,162]. Because the toxicity mechanism of microplastics is not fully clear, understanding toxic effects caused by microplastics is important to assess their environmental impacts.
4. Bacteria for Degradation of Marine MPs
4.1. Bacteria Colonizing Microplastics
Some studies highlight the differences between the bacteria living on organic particles with seawater [166], on microplastics and in a free state [167]. The bacterial community that settles on the surfaces of marine microplastic is significantly different from that in surrounding middle and upper waters or other particle types [166]. If these bacteria have been established enzymatic mechanism for degrading plastic, they would be of particular interest for bioremediation and bioengineering.
Studies show that some bacterial groups such as the phyla Bacteroidetes, Proteobacteria, Cyanobacteria and Firmicutes appear to colonize microplastics more often than others, indicating that the specific taxonomic bacteria consider microplastics as a beneficially ecological niche and a potential metabolic adaptation to the material (e.g., attachment, additive resistance, chemotaxis, and degradation). Similar taxa belonging to Bacteroidetes and Proteobacteria seem to be shared by the core bacteria of the seafloor and subsurface plastisphere share, and some photoautotrophic bacteria dominated the sub-surface communities [168,169].
4.2. Plastisphere Served as a New Niche for Marine Environment
Recently, the first study using the modern technology of large-scale DNA sequencing gave a detailed image of the microbial communities that inhabit microplastics [128]. Debris is usually described by the term “plastisphere” in marine biology research [169], they serve as various habitats for microbial colonies in aquatic environments besides accumulating organic pollutants [168,169,170,171].
Based on morphological data and DNA sequencing technology, the factors that drive the composition of plastisphere are complex and comprehensive. In addition to the main factors, season and surrounding environment, polymer type, surface feature, and size also affected the diversity and abundance of the colonizing bacterial groups [168,172]. For example, studies highlighted significant differences in microbiota communities on microplastics from the two different oceans, and the diversity of bacteria living in water columns and bacteria attached to microplastic debris [173]. Studies show that plastic surfaces could be rapidly colonized by heterotrophic bacteria, which can survive longer than in the surrounding aquatic environments [174].
4.3. Biodegradation of Bacteria in Marine Environment
Microbial biodegradation is a process in which microbial communities (bacteria, actinomycetes and fungi) use organic matter as a carbon source to metabolize, resulting in a transformation from organic carbon to biogas and biomass [175,176]. Generally, the biodegradation process of MPs is proposed to consist of four main basic stages and continuous successive steps: biodeterioration, biofragmentation, assimilation and mineralization [168].
Interest in plastic biodegradation is also growing, and bacteria are considered to be one of the most important ways to solve marine plastic pollution, because of their potential capacity for biodegradation of plastic wastes. Corynebacterium, Arthrobacter, Pseudomonas, Micrococcus, Streptomyces and Rhodococcus are the main bacterial groups in this context, and they can use plastics as sole carbon source under lab conditions [176]. Interestingly, it was discovered that significant differences exist in the diversity, abundance and activity of bacterial and physiochemical characters of plastics between biodegradable and non-biodegradable plastics, indicating the presence of plastic-degrading microbes [177]. Nowadays, there is an increasing number of anecdotal evidence that bacteria can show the capability to degrade ocean plastic pieces [169,172,174] (Table 3).

Table 3.
Outstanding plastic-degrading bacteria in existing research.
The factors involved in plastic biodegradability depend not only on the ability of microorganisms but also on the characteristics and surface structure of the material, such as the roughness, electrostatic interactions, topography, hydrophobicity, and free energy [106]. In addition, various environmental factors, such as oxygen level, temperature, humidity, salinity, and limitation of light have an important impact on the biodegradation of plastics [186]. The additives in the polymer could increase the rate of biodegradability. These additives will affect their chemical and thermal sensitivity as well as their ability to absorb ultraviolet light and lead to the loss of stable properties that are more suitable for microbial attachment [187].
The current test standards for assessing plastic biodegradability of marine plastics tend to use to use optical, atomic force and scanning electron microscopy to confirm the results of major tests based on respirometers, since each of them has limitations, and none of these techniques are sufficient by itself [188]. To date, standard guidelines and methods for conducting these experiments have not been established.
Our understanding of metabolic mechanisms of biodegradable marine bacteria and their enzymes is very limited. Furthermore, the biodegradation mechanics of marine plastic debris and its potential impact processes need further research to make full use of its impact.
5. Conclusions
The accumulation of microplastics in the marine environment is a serious threat to the health of marine organisms, which may eventually affect the survival of human beings. Therefore, it has attracted extensive attention from society and researchers. Many studies have shown that different bacterial communities colonize microplastics in the marine environment, which has inspired us to investigate the bacterial degradation of marine microplastics. However, until now, we don’t know much about how these bacteria work. The rich diversity and activity of these bacteria indicate their potential in the biogeochemical cycling of plastics, but further research is needed. Contact experiments must be carefully designed to test the ability of these bacteria to react with plastics and adapt to changing marine environments, so it is important to integrate research approaches from multiple disciplines. In order to take full advantage of the influence of bacterial communities on MPs, more controlled experiments are needed to simulate real marine ecosystems. Further studies of bacteria associated with plastic degradation will help develop situ biodegradable methods and materials. According to the current technology and methods, it is impossible to completely remove all the microplastics in the ocean, but we can still try to partially reduce marine microplastic pollution. Bacterial degradation is an appropriate choice for this. While developing methods for degrading plastics, relevant stakeholders such as governments, the public, manufacturers and scientists should pay high attention to the problem of marine microplastics pollution. We should take responsibility and working together to reduce unnecessary plastic production and reduce plastic waste by recycling plastic to tackle increasing MP issues.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.W. and H.Y.; formal analysis, G.C.; investigation, G.C.; data curation, H.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, H.Y.; writing—review and editing, J.W. and G.C.; visualization, J.W.; supervision, J.W. and H.Y.; project administration, J.W. and H.Y.; funding acquisition, J.W. and H.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFD0900604), Guangdong Forestry Science and Technology Innovation Project, Provincial Projects with Special Funds for Promoting Economic Development of Marine and Fisheries Department of Guangdong (SDYY-2018-05), Project of Guangzhou Association for Science & Technology (K20200102008); Guangdong Province Universities and Colleges Pearl River Scholar Funded Scheme (2018), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42077364), and Key Research Projects of Universities in Guangdong Province (2019KZDXM003 and 2020KZDZX1040).
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the provision of SCAU Wushan Campus Teaching & Research Base.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The authors themselves are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
References
- Andrady, A.L.; Neal, M.A. Applications and societal benefits of plastics. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1977–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.C.; Swan, S.H.; Moore, C.J.; vom Saal, F.S. Our plastic age. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2009, 364, 1973–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Das, K.R.; Naik, M.M. Co-selection of multi-antibiotic resistance in bacterial pathogens in metal and microplastic contaminated environments: An emerging health threat. Chemosphere 2019, 215, 846–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, K.L. Plastics in the Marine Environment. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2017, 9, 205–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dris, R.; Imhof, H.; Sanchez, W.; Gasperi, J.; Galgani, F.; Tassin, B.; Laforsch, C. Beyond the ocean: Contamination of freshwater ecosystems with (micro-)plastic particles. Environ. Chem. 2015, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahladakis, J.N.; Velis, C.A.; Weber, R.; Iacovidou, E.; Purnell, P. An overview of chemical additives present in plastics: Migration, release, fate and environmental impact during their use, disposal and recycling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 179–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plastics Europe. Plastics—The Facts 2020 An Analysis of European Plastics Production, Demand and Waste Data. Plastics Europe. 2020. Available online: https://www.plasticseurope.org/en/resources/publications/4312-plastics-facts-2020 (accessed on 22 January 2021).
- Rocha-Santos, T.A.P. Editorial overview: Micro and nano-plastics. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 1, 52–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, K.L.; Thompson, R.C. Microplastics in the seas. Oceans 2014, 345, 144–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebreton, L.; Slat, B.; Ferrari, F.; Sainte-Rose, B.; Aitken, J.; Marthouse, R.; Hajbane, S.; Cunsolo, S.; Schwarz, A.; Levivier, A.; et al. Evidence that the Great Pacific Garbage Patch is rapidly accumulating plastic. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, S.L.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S. The physical impacts of microplastics on marine organisms: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GESAMP. Sources, Fate and Effects of Microplastics in the Marine Environment: Part 2 of A Global Assessment. 2016. Available online: http://www.gesamp.org/publications/microplastics-in-the-marine-environment-part-2 (accessed on 21 February 2021).
- Galgani, F.; Hanke, G.; Werner, S.; De Vrees, L. Marine litter within the European Marine Strategy Framework Directive. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2013, 70, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellini, G.; Gomiero, A.; Fortibuoni, T.; Ferra, C.; Grati, F.; Tassetti, A.N.; Polidori, P.; Fabi, G.; Scarcella, G. Characterization of microplastic litter in the gastrointestinal tract of Solea solea from the Adriatic Sea. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 943–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, T.S.; Cole, M.; Lewis, C. Interactions of microplastic debris throughout the marine ecosystem. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigault, J.; ter Halle, A.; Baudrimont, M.; Pascal, P.Y.; Gauffre, F.; Phi, T.L.; El Hadri, H.; Grassl, B.; Reynaud, S. Current opinion: What is a nanoplastic? Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 1030–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Ruz, V.; Gutow, L.; Thompson, R.C.; Thiel, M. Microplastics in the marine environment: A review of the methods used for identification and quantification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3060–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.; Worch, E.; Knepper, T.P. Occurrence and Spatial Distribution of Microplastics in River Shore Sediments of the Rhine-Main Area in Germany. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6070–6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auta, H.S.; Emenike, C.U.; Fauziah, S.H. Distribution and importance of microplastics in the marine environment: A review of the sources, fate, effects, and potential solutions. Environ. Int. 2017, 102, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duis, K.; Coors, A. Microplastics in the aquatic and terrestrial environment: Sources (with a specific focus on personal care products), fate and effects. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2016, 28, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revel, M.; Chatel, A.; Mouneyrac, C. Micro (nano) plastics: A threat to human health? Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 1, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauscher, H.; Sokull-Kluttgen, B.; Stamm, H. The European Commission’s recommendation on the definition of nanomaterial makes an impact. Nanotoxicology 2013, 7, 1195–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksen, M.; Mason, S.; Wilson, S.; Box, C.; Zellers, A.; Edwards, W.; Farley, H.; Amato, S. Microplastic pollution in the surface waters of the Laurentian Great Lakes. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 77, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozar, A.; Marti, E.; Duarte, C.M.; Garcia-de-Lomas, J.; van Sebille, E.; Ballatore, T.J.; Eguiluz, V.M.; Gonzalez-Gordillo, J.I.; Pedrotti, M.L.; Echevarria, F.; et al. The Arctic Ocean as a dead end for floating plastics in the North Atlantic branch of the Thermohaline Circulation. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, M.S.; Basha, S.; Adimurthy, S.; Ramachandraiah, G. Description of the small plastics fragments in marine sediments along the Alang-Sosiya ship-breaking yard, India. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 68, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, M.; Sandhop, N.; Schewe, I.; D’Hert, D. Observations of floating anthropogenic litter in the Barents Sea and Fram Strait, Arctic. Polar Biol. 2016, 39, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeken, I.; Primpke, S.; Beyer, B.; Gutermann, J.; Katlein, C.; Krumpen, T.; Bergmann, M.; Hehemann, L.; Gerdts, G. Arctic sea ice is an important temporal sink and means of transport for microplastic. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waller, C.L.; Griffiths, H.J.; Waluda, C.M.; Thorpe, S.E.; Loaiza, I.; Moreno, B.; Pacherres, C.O.; Hughes, K.A. Microplastics in the Antarctic marine system: An emerging area of research. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Sul, J.A.I.; Spengler, A.; Costa, M.F. Here, there and everywhere. Small plastic fragments and pellets on beaches of Fernando de Noronha (Equatorial Western Atlantic). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1236–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claessens, M.; De Meester, S.; Van Landuyt, L.; De Clerck, K.; Janssen, C.R. Occurrence and distribution of microplastics in marine sediments along the Belgian coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2199–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.; Lusher, A.; Thompson, R.C.; Morley, A. The Deposition and Accumulation of Microplastics in Marine Sediments and Bottom Water from the Irish Continental Shelf. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, M.L.; Gwinnett, C.; Robinson, L.F.; Woodall, L.C. Plastic microfibre ingestion by deep-sea organisms. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Cauwenberghe, L.; Vanreusel, A.; Mees, J.; Janssen, C.R. Microplastic pollution in deep-sea sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 182, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Sebille, E.; Wilcox, C.; Lebreton, L.; Maximenko, N.; Hardesty, B.D.; van Franeker, J.A.; Eriksen, M.; Siegel, D.; Galgani, F.; Law, K.L. A global inventory of small floating plastic debris. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, M.C.; Titmus, A.J.; Ford, M. Scales of spatial heterogeneity of plastic marine debris in the northeast pacific ocean. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.L.; Rowe, D.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S. Microplastic ingestion decreases energy reserves in marine worms. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, R1031–R1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lusher, A.L.; McHugh, M.; Thompson, R.C. Occurrence of microplastics in the gastrointestinal tract of pelagic and demersal fish from the English Channel. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 67, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, M.A.; Dissanayake, A.; Galloway, T.S.; Lowe, D.M.; Thompson, R.C. Ingested microscopic plastic translocates to the circulatory system of the mussel, Mytilus edulis (L). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5026–5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Moos, N.; Burkhardt-Holm, P.; Kohler, A. Uptake and effects of microplastics on cells and tissue of the blue mussel Mytilus edulis L. after an experimental exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11327–11335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, A.; Besseling, E.; Foekema, E.M.; Kamermans, P.; Koelmans, A.A. Effects of nanopolystyrene on the feeding behavior of the blue mussel (Mytilus edulis L.). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 2490–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Fileman, E.; Halsband, C.; Goodhead, R.; Moger, J.; Galloway, T.S. Microplastic ingestion by zooplankton. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6646–6655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.; Rodriguez, B.; Nazaret Carrasco, M. High prevalence of parental delivery of plastic debris in Cory’s shearwaters (Calonectris diomedea). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 2219–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugolini, A.; Ungherese, G.; Ciofini, M.; Lapucci, A.; Camaiti, M. Microplastic debris in sandhoppers. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 129, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.A.; Niven, S.J.; Galloway, T.S.; Rowland, S.J.; Thompson, R.C. Microplastic moves pollutants and additives to worms, reducing functions linked to health and biodiversity. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 2388–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandts, I.; Teles, M.; Goncalves, A.P.; Barreto, A.; Franco-Martinez, L.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; Martins, M.A.; Soares, A.; Tort, L.; Oliveira, M. Effects of nanoplastics on Mytilus galloprovincialis after individual and combined exposure with carbamazepine. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avio, C.G.; Gorbi, S.; Milan, M.; Benedetti, M.; Fattorini, D.; d’Errico, G.; Pauletto, M.; Bargelloni, L.; Regoli, F. Pollutants bioavailability and toxicological risk from microplastics to marine mussels. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 198, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, M.; Coppock, R.; Lindeque, P.K.; Altin, D.; Reed, S.; Pond, D.W.; Sorensen, L.; Galloway, T.S.; Booth, A.M. Effects of Nylon Microplastic on Feeding, Lipid Accumulation, and Moulting in a Coldwater Copepod. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 7075–7082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tallec, K.; Huvet, A.; Di Poi, C.; Gonzalez-Fernandez, C.; Lambert, C.; Petton, B.; Le Goic, N.; Berchel, M.; Soudant, P.; Paul-Pont, I. Nanoplastics impaired oyster free living stages, gametes and embryos. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 1226–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enfrin, M.; Lee, J.; Gibert, Y.; Basheer, F.; Kong, L.; Dumee, L.F. Release of hazardous nanoplastic contaminants due to microplastics fragmentation under shear stress forces. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.S.; Cho, H.J.; Kim, E.; Huh, Y.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, B.; Kang, T.; Lee, J.S.; Jeong, J. Bioaccumulation of polystyrene nanoplastics and their effect on the toxicity of Au ions in zebrafish embryos. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 3173–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trevisan, R.; Voy, C.; Chen, S.; Di Giulio, R.T. Nanoplastics Decrease the Toxicity of a Complex PAH Mixture but Impair Mitochondrial Energy Production in Developing Zebrafish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 8405–8415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, N.R.; van Hage, P.; Hunting, E.R.; Haramis, A.G.; Vink, S.C.; Vijver, M.G.; Schaaf, M.J.M.; Tudorache, C. Polystyrene nanoplastics disrupt glucose metabolism and cortisol levels with a possible link to behavioural changes in larval zebrafish. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, N.R.; Koch, B.E.V.; Varela, M.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Spaink, H.P.; Vijver, M.G. Nanoparticles induce dermal and intestinal innate immune system responses in zebrafish embryos. Environ. Sci. Nano 2018, 5, 904–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yin, D.; Jia, Y.; Schiwy, S.; Legradi, J.; Yang, S.; Hollert, H. Enhanced uptake of BPA in the presence of nanoplastics can lead to neurotoxic effects in adult zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 1312–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergami, E.; Bocci, E.; Vannuccini, M.L.; Monopoli, M.; Salvati, A.; Dawson, K.A.; Corsi, I. Nano-sized polystyrene affects feeding, behavior and physiology of brine shrimp Artemia franciscana larvae. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 123, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrady, A.L. Microplastics in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, M.A.; Crump, P.; Niven, S.J.; Teuten, E.; Tonkin, A.; Galloway, T.; Thompson, R. Accumulation of microplastic on shorelines woldwide: Sources and sinks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9175–9179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saal, F.S.; Parmigiani, S.; Palanza, P.L.; Everett, L.G.; Ragaini, R. The plastic world: Sources, amounts, ecological impacts and effects on development, reproduction, brain and behavior in aquatic and terrestrial animals and humans Introduction. Environ. Res. 2008, 108, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebreton, L.C.M.; van der Zwet, J.; Damsteeg, J.W.; Slat, B.; Andrady, A.; Reisser, J. River plastic emissions to the world’s oceans. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, T.; Hauk, A.; Walter, U.; Burkhardt-Holm, P. Microplastics profile along the Rhine River. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, D.K.; Galgani, F.; Thompson, R.C.; Barlaz, M. Accumulation and fragmentation of plastic debris in global environments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.D.; Watson, R.A.; Ye, Y. Global fishing capacity and fishing effort from 1950–2012 (vol 18, pg 489, 2017). Fish Fish. 2017, 18, 792–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, R.A.; Cheung, W.W.L.; Anticamara, J.A.; Sumaila, R.U.; Zeller, D.; Pauly, D. Global marine yield halved as fishing intensity redoubles. Fish Fish. 2013, 14, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.C.; Olsen, Y.; Mitchell, R.P.; Davis, A.; Rowland, S.J.; John, A.W.G.; McGonigle, D.; Russell, A.E. Lost at sea: Where is all the plastic? Science 2004, 304, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Oufi, H.; McLean, E.; Kumar, A.S.; Claereboudt, M.; Al-Habsi, M. The effects of solar radiation upon breaking strength and elongation of fishing nets. Fish. Res. 2004, 66, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.N.; Hridayanathan, C. The effect of natural sunlight on the strength of polyamide 6 multifilament and monofilament fishing net materials. Fish. Res. 2006, 81, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinojosa, I.A.; Thiel, M. Floating marine debris in fjords, gulfs and channels of southern Chile. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheavly, S.B.; Register, K.M. Marine debris & plastics: Environmental concerns, sources, impacts and solutions. J. Polym. Environ. 2007, 15, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derraik, J.G. The pollution of the marine environment by plastic debris: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2002, 44, 842–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Wang, J.; Peng, J.; Tan, Z.; Zhan, Z.; Tan, X.; Chen, Q. Characteristic of microplastics in the atmospheric fallout from Dongguan city, China: Preliminary research and first evidence. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 24928–24935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Halsband, C.; Galloway, T.S. Microplastics as contaminants in the marine environment: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2588–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Villamizar, C.A.; Vazquez-Morillas, A. Degradation of Conventional and Oxodegradable High Density Polyethylene in Tropical Aqueous and Outdoor Environments. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 2018, 34, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, D.A.; Corcoran, P.L. Effects of mechanical and chemical processes on the degradation of plastic beach debris on the island of Kauai, Hawaii. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, J.M.; Fleet, D.; Kinsey, S.; Nilsson, P.; Vlachogianni, T.; Werner, S.; Galgani, F.; Thompson, R.C.; Dagevos, J.; Gago, J.; et al. Identifying Sources of Marine Litter. MSFD GES TG Marine Litter Thematic Report; JRC Technical Reports. 2016. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/81685372.pdf (accessed on 21 February 2021).
- Chang, M. Reducing microplastics from facial exfoliating cleansers in wastewater through treatment versus consumer product decisions. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fendall, L.S.; Sewell, M.A. Contributing to marine pollution by washing your face: Microplastics in facial cleansers. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1225–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, M.R. Environmental implications of plastic debris in marine settings--entanglement, ingestion, smothering, hangers-on, hitch-hiking and alien invasions. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2013–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, K.; Qiao, F.; Liu, Q.; Wei, Z.; Qi, H.; Cui, S.; Yue, X.; Deng, Y.; An, L. Microplastics releasing from personal care and cosmetic products in China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 123, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaneda, R.A.; Avlijas, S.; Simard, M.A.; Ricciardi, A. Microplastic pollution in St. Lawrence River sediments. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2014, 71, 1767–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napper, I.E.; Bakir, A.; Rowland, S.J.; Thompson, R.C. Characterisation, quantity and sorptive properties of microplastics extracted from cosmetics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 99, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesa, F.S.; Turra, A.; Baruque-Ramos, J. Synthetic fibers as microplastics in the marine environment: A review from textile perspective with a focus on domestic washings. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 1116–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, D. Polymer weathering: Photo-oxidation. J. Polym. Environ. 2002, 10, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.; Scherer, C.; Alvarez-Munoz, D.; Brennholt, N.; Bourrain, X.; Buchinger, S.; Fries, E.; Grosbois, C.; Klasmeier, J.; Marti, T.; et al. Microplastics in freshwater ecosystems: What we know and what we need to know. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2014, 26, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkranz, P.; Chaudhry, Q.; Stone, V.; Fernandes, T.F. A comparison of nanoparticle and fine particle uptake by Daphnia magna. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2009, 28, 2142–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velzeboer, I.; Kwadijk, C.J.; Koelmans, A.A. Strong sorption of PCBs to nanoplastics, microplastics, carbon nanotubes, and fullerenes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4869–4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, M.; Lebreton, L.C.; Carson, H.S.; Thiel, M.; Moore, C.J.; Borerro, J.C.; Galgani, F.; Ryan, P.G.; Reisser, J. Plastic Pollution in the World’s Oceans: More than 5 Trillion Plastic Pieces Weighing over 250,000 Tons Afloat at Sea. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galgani, F.; Hanke, G.; Maes, T. Global Distribution, Composition and Abundance of Marine Litter. In Marine Anthropogenic Litter; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 29–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, C.A.; Bratton, S.P. Urbanization is a major influence on microplastic ingestion by sunfish in the Brazos River Basin, Central Texas, USA. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 210, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozar, A.; Echevarria, F.; Gonzalez-Gordillo, J.I.; Irigoien, X.; Ubeda, B.; Hernandez-Leon, S.; Palma, A.T.; Navarro, S.; Garcia-de-Lomas, J.; Ruiz, A.; et al. Plastic debris in the open ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 10239–10244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisser, J.; Slat, B.; Noble, K.; du Plessis, K.; Epp, M.; Proietti, M.; de Sonneville, J.; Becker, T.; Pattiaratchi, C. The vertical distribution of buoyant plastics at sea: An observational study in the North Atlantic Gyre. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambeck, J.R.; Geyer, R.; Wilcox, C.; Siegler, T.R.; Perryman, M.; Andrady, A.; Narayan, R.; Law, K.L. Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science 2015, 347, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtene-Jones, W.; Quinn, B.; Gary, S.F.; Mogg, A.O.M.; Narayanaswamy, B.E. Microplastic pollution identified in deep-sea water and ingested by benthic invertebrates in the rockall trough, north atlantic ocean. Environ. Pollut. 2017. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Chen, M.; Chen, S.; Dasgupta, S.; Xu, H.; Ta, K.; Du, M.; Li, J.; Guo, Z.; Bai, S. Microplastics contaminate the deepest part of the world’s ocean. Geochem. Perspect. Lett. 2018, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, S.; Wagner, M. Environmental performance of bio-based and biodegradable plastics: The road ahead. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 6855–6871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, K.L.; Moret-Ferguson, S.; Maximenko, N.A.; Proskurowski, G.; Peacock, E.E.; Hafner, J.; Reddy, C.M. Plastic accumulation in the North Atlantic subtropical gyre. Science 2010, 329, 1185–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rummel, C.D.; Jahnke, A.; Gorokhova, E.; Kuhnel, D.; Schmitt-Jansen, M. Impacts of Biofilm Formation on the Fate and Potential Effects of Microplastic in the Aquatic Environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 4, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodall, L.C.; Sanchez-Vidal, A.; Canals, M.; Paterson, G.L.J.; Coppock, R.; Sleight, V.; Calafat, A.; Rogers, A.D.; Narayanaswamy, B.E.; Thompson, R.C. The deep sea is a major sink for microplastic debris. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2014, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besseling, E.; Foekema, E.M.; van den Heuvel-Greve, M.J.; Koelmans, A.A. The Effect of Microplastic on the Uptake of Chemicals by the Lugworm Arenicola marina (L.) under Environmentally Relevant Exposure Conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 8795–8804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.; Paul-Pont, I.; Hegaret, H.; Moriceau, B.; Lambert, C.; Huvet, A.; Soudant, P. Interactions between polystyrene microplastics and marine phytoplankton lead to species-specific hetero-aggregation. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 228, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.W.; Zhang, S.F.; Wang, J.Y.; Wang, Y.; Mu, J.L.; Wang, P.; Lin, X.Z.; Ma, D.Y. Microplastic pollution in the surface waters of the Bohai Sea, China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooi, M.; van Nes, E.H.; Scheffer, M.; Koelmans, A.A. Ups and Downs in the Ocean: Effects of Biofouling on Vertical Transport of Microplastics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 7963–7971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tata, T.; Belabed, B.E.; Bououdina, M.; Bellucci, S. Occurrence and characterization of surface sediment microplastics and litter from North African coasts of Mediterranean Sea: Preliminary research and first evidence. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J. Greenland Sea Gyre increases microplastic pollution in the surface waters of the Nordic Seas. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 136484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfriso, A.A.; Tomio, Y.; Rosso, B.; Gambaro, A.; Sfriso, A.; Corami, F.; Rastelli, E.; Corinaldesi, C.; Mistri, M.; Munari, C. Microplastic accumulation in benthic invertebrates in Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea, Antarctica). Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdinia, A.; Dehbandi, R.; Hamzehpour, A.; Rahnama, R. Identification of microplastics in the sediments of southern coasts of the Caspian Sea, north of Iran. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falahudin, D.; Cordova, M.R.; Sun, X.; Yogaswara, D.; Wulandari, I.; Hindarti, D.; Arifin, Z. The first occurrence, spatial distribution and characteristics of microplastic particles in sediments from Banten Bay, Indonesia. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mataji, A.; Taleshi, M.S.; Balimoghaddas, E. Distribution and Characterization of Microplastics in Surface Waters and the Southern Caspian Sea Coasts Sediments. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 78, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomiero, A.; Oysaed, K.B.; Agustsson, T.; van Hoytema, N.; van Thiel, T.; Grati, F. First record of characterization, concentration and distribution of microplastics in coastal sediments of an urban fjord in south west Norway using a thermal degradation method. Chemosphere 2019, 227, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, D.; Webber, M. Characterization of microplastics in the surface waters of Kingston Harbour. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Guo, H.G.; Chen, H.Z.; Wang, S.M.; Sun, X.W.; Zou, Q.P.; Zhang, Y.B.; Lin, H.; Cai, S.Z.; Huang, J. Microplastics in the Northwestern Pacific: Abundance, distribution, and characteristics. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 1913–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, K.N.; Yang, R.J.; Li, R.Z.; Li, Y.F. Characterization, source, and retention of microplastic in sandy beaches and mangrove wetlands of the Qinzhou Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 136, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusher, A.L.; Tirelli, V.; O’Connor, I.; Officer, R. Microplastics in Arctic polar waters: The first reported values of particles in surface and sub-surface samples. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desforges, J.P.W.; Galbraith, M.; Dangerfield, N.; Ross, P.S. Widespread distribution of microplastics in subsurface seawater in the NE Pacific Ocean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 79, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimba, C.G.; Faggio, C. Microplastics in the marine environment: Current trends in environmental pollution and mechanisms of toxicological profile. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 68, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzzetti, E.; Sureda, A.; Tejada, S.; Faggio, C. Microplastic in marine organism: Environmental and toxicological effects. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 64, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savoca, S.; Capillo, G.; Mancuso, M.; Bottari, T.; Crupi, R.; Branca, C.; Romano, V.; Faggio, C.; D’Angelo, G.; Spano, N. Microplastics occurrence in the Tyrrhenian waters and in the gastrointestinal tract of two congener species of seabreams. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 67, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savoca, S.; Capillo, G.; Mancuso, M.; Faggio, C.; Panarello, G.; Crupi, R.; Bonsignore, M.; D’Urso, L.; Compagnini, G.; Neri, F.; et al. Detection of artificial cellulose microfibers in Boops boops from the northern coasts of Sicily (Central Mediterranean). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 691, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.; Ai, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zeng, P.; Kang, L.; Li, W.; Gu, W.; He, Q.; Li, H. Phytoplankton response to polystyrene microplastics: Perspective from an entire growth period. Chemosphere 2018, 208, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjollema, S.B.; Redondo-Hasselerharm, P.; Leslie, H.A.; Kraak, M.H.S.; Vethaak, A.D. Do plastic particles affect microalgal photosynthesis and growth? Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 170, 259–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besseling, E.; Wegner, A.; Foekema, E.M.; van den Heuvel-Greve, M.J.; Koelmans, A.A. Effects of Microplastic on Fitness and PCB Bioaccumulation by the Lugworm Arenicola marina (L.). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.W.; Shim, W.J.; Kwon, O.Y.; Kang, J.H. Size-dependent effects of micro polystyrene particles in the marine copepod Tigriopus japonicus. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11278–11283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messinetti, S.; Mercurio, S.; Parolini, M.; Sugni, M.; Pennati, R. Effects of polystyrene microplastics on early stages of two marine invertebrates with different feeding strategies. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 1080–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobre, C.R.; Santana, M.F.M.; Maluf, A.; Cortez, F.S.; Cesar, A.; Pereira, C.D.S.; Turra, A. Assessment of microplastic toxicity to embryonic development of the sea urchin Lytechinus variegatus (Echinodermata: Echinoidea). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 92, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbi, T.; Camisassi, G.; Montagna, M.; Fabbri, R.; Franzellitti, S.; Carbone, C.; Dawson, K.; Canesi, L. Impact of cationic polystyrene nanoparticles (PS-NH(2)) on early embryo development of Mytilus galloprovincialis: Effects on shell formation. Chemosphere 2017, 186, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Gomez, C.; Leon, V.M.; Calles, S.; Gomariz-Olcina, M.; Vethaak, A.D. The adverse effects of virgin microplastics on the fertilization and larval development of sea urchins. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 130, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandara, E.S.P.P.; Nobre, C.R.; Resaffe, P.; Pereira, C.D.S.; Gusmao, F. Leachate from microplastics impairs larval development in brown mussels. Water Res. 2016, 106, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sussarellu, R.; Suquet, M.; Thomas, Y.; Lambert, C.; Fabioux, C.; Pernet, M.E.J.; Le Goic, N.; Quillien, V.; Mingant, C.; Epelboin, Y.; et al. Oyster reproduction is affected by exposure to polystyrene microplastics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 2430–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Jiang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Geng, J.; Ding, L.; Ren, H. Uptake and Accumulation of Polystyrene Microplastics in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) and Toxic Effects in Liver. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4054–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Liu, Z.; Wu, D.; Chen, M.; Lv, W.; Zhao, Y. Accumulation of polystyrene microplastics in juvenile Eriocheir sinensis and oxidative stress effects in the liver. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 200, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heindler, F.M.; Alajmi, F.; Huerlimann, R.; Zeng, C.; Newman, S.J.; Vamvounis, G.; van Herwerden, L. Toxic effects of polyethylene terephthalate microparticles and Di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate on the calanoid copepod, Parvocalanus crassirostris. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 141, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snell, T.W.; Hicks, D.G. Assessing Toxicity of Nanoparticles Using Brachionus manjavacas (Rotifera). Environ. Toxicol. 2011, 26, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Torre, C.; Bergami, E.; Salvati, A.; Faleri, C.; Cirino, P.; Dawson, K.A.; Corsi, I. Accumulation and Embryotoxicity of Polystyrene Nanoparticles at Early Stage of Development of Sea Urchin Embryos Paracentrotus lividus. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 12302–12311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul-Pont, I.; Lacroix, C.; Gonzalez Fernandez, C.; Hegaret, H.; Lambert, C.; Le Goic, N.; Frere, L.; Cassone, A.L.; Sussarellu, R.; Fabioux, C.; et al. Exposure of marine mussels Mytilus spp. to polystyrene microplastics: Toxicity and influence on fluoranthene bioaccumulation. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 724–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomiero, A.; Strafella, P.; Pellini, G.; Salvalaggio, V.; Fabi, G. Comparative Effects of Ingested PVC Micro Particles With and Without Adsorbed Benzo(a)pyrene vs. Spiked Sediments on the Cellular and Sub Cellular Processes of the Benthic Organism Hediste diversicolor. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleight, V.A.; Bakir, A.; Thompson, R.C.; Henry, T.B. Assessment of microplastic-sorbed contaminant bioavailability through analysis of biomarker gene expression in larval zebrafish. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 116, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.; Ribeiro, A.; Hylland, K.; Guilhermino, L. Single and combined effects of microplastics and pyrene on juveniles (0+group) of the common goby Pomatoschistus microps (Teleostei, Gobiidae). Ecol. Indic. 2013, 34, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, F.; Cowie, P.R. Plastic contamination in the decapod crustacean Nephrops norvegicus (Linnaeus, 1758). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1207–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, C.; Brennholt, N.; Reifferscheid, G.; Wagner, M. Feeding type and development drive the ingestion of microplastics by freshwater invertebrates. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setala, O.; Norkko, J.; Lehtiniemi, M. Feeding type affects microplastic ingestion in a coastal invertebrate community. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 102, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setala, O.; Fleming-Lehtinen, V.; Lehtiniemi, M. Ingestion and transfer of microplastics in the planktonic food web. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 185, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, A.J.R.; Lewis, C.; Goodhead, R.M.; Beckett, S.J.; Moger, J.; Tyler, C.R.; Galloway, T.S. Uptake and Retention of Microplastics by the Shore Crab Carcinus maenas. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 8823–8830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, T.; Pietro, B.; Peda, C.; Consoli, P.; Andaloro, F.; Fossi, M.C. First evidence of presence of plastic debris in stomach of large pelagic fish in the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 95, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunov, O.; Syrovets, T.; Loos, C.; Beil, J.; Delacher, M.; Tron, K.; Nienhaus, G.U.; Musyanovych, A.; Mailander, V.; Landfester, K.; et al. Differential uptake of functionalized polystyrene nanoparticles by human macrophages and a monocytic cell line. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 1657–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurais, D.; Ernande, B.; Quazuguel, P.; Severe, A.; Huelvan, C.; Madec, L.; Mouchel, O.; Soudant, P.; Robbens, J.; Huvet, A.; et al. Evaluation of the impact of polyethylene microbeads ingestion in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) larvae. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 112, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolton, A.; Vignier, J.; Volety, A.K.; Pierce, R.H.; Henry, M.; Shumway, S.E.; Bricelj, V.M.; Hegaret, H.; Soudant, P. Effects of field and laboratory exposure to the toxic dinoflagellate Karenia brevis on the reproduction of the eastern oyster, Crassostrea virginica, and subsequent development of offspring. Harmful Algae 2016, 57, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collard, F.; Gilbert, B.; Compere, P.; Eppe, G.; Das, K.; Jauniaux, T.; Parmentier, E. Microplastics in livers of European anchovies (Engraulis encrasicolus, L.). Environ. Pollut. 2017, 229, 1000–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolandhasamy, P.; Su, L.; Li, J.; Qu, X.; Jabeen, K.; Shi, H. Adherence of microplastics to soft tissue of mussels: A novel way to uptake microplastics beyond ingestion. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collignon, A.; Hecq, J.H.; Glagani, F.; Voisin, P.; Collard, F.; Goffart, A. Neustonic microplastic and zooplankton in the North Western Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 861–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welden, N.A.; Abylkhani, B.; Howarth, L.M. The effects of trophic transfer and environmental factors on microplastic uptake by plaice, Pleuronectes plastessa, and spider crab, Maja squinado. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 239, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardrop, P.; Shimeta, J.; Nugegoda, D.; Morrison, P.D.; Miranda, A.; Tang, M.; Clarke, B.O. Chemical Pollutants Sorbed to Ingested Microbeads from Personal Care Products Accumulate in Fish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4037–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottari, T.; Savoca, S.; Mancuso, M.; Capillo, G.; GiuseppePanarello, G.; MartinaBonsignore, M.; Crupi, R.; Sanfilippo, M.; D’Urso, L.; Compagnini, G.; et al. Plastics occurrence in the gastrointestinal tract of Zeus faber and Lepidopus caudatus from the Tyrrhenian Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capillo, G.; Savoca, S.; Panarello, G.; Mancuso, M.; Branca, C.; Romano, V.; D’Angelo, G.; Bottari, T.; Spano, N. Quali-quantitative analysis of plastics and synthetic microfibers found in demersal species from Southern Tyrrhenian Sea (Central Mediterranean). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 150, 110596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barboza, L.G.A.; Vieira, L.R.; Branco, V.; Carvalho, C.; Guilhermino, L. Microplastics increase mercury bioconcentration in gills and bioaccumulation in the liver, and cause oxidative stress and damage in Dicentrarchus labrax juveniles. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogonowski, M.; Schur, C.; Jarsen, A.; Gorokhova, E. The Effects of Natural and Anthropogenic Microparticles on Individual Fitness in Daphnia magna. PLoS ONE 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.E.; Kach, D.J. Marine aggregates facilitate ingestion of nanoparticles by suspension-feeding bivalves. Mar. Environ. Res 2009, 68, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochman, C.M.; Hoh, E.; Kurobe, T.; Teh, S.J. Ingested plastic transfers hazardous chemicals to fish and induces hepatic stress. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teuten, E.L.; Saquing, J.M.; Knappe, D.R.; Barlaz, M.A.; Jonsson, S.; Bjorn, A.; Rowland, S.J.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S.; Yamashita, R.; et al. Transport and release of chemicals from plastics to the environment and to wildlife. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2027–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Jin, S.R.; Chen, Z.Z.; Gao, J.Z.; Liu, Y.N.; Liu, J.H.; Feng, X.S. Single and combined effects of microplastics and cadmium on the cadmium accumulation, antioxidant defence and innate immunity of the discus fish (Symphysodon aequifasciatus). Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Huang, A.; Cao, S.; Sun, F.; Wang, L.; Guo, H.; Ji, R. Effects of nanoplastics and microplastics on toxicity, bioaccumulation, and environmental fate of phenanthrene in fresh water. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diepens, N.J.; Koelmans, A.A. Accumulation of Plastic Debris and Associated Contaminants in Aquatic Food Webs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 8510–8520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eerkes-Medrano, D.; Thompson, R.C.; Aldridge, D.C. Microplastics in freshwater systems: A review of the emerging threats, identification of knowledge gaps and prioritisation of research needs. Water Res. 2015, 75, 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusher, A.L.; Burke, A.; O’Connor, I.; Officer, R. Microplastic pollution in the Northeast Atlantic Ocean: Validated and opportunistic sampling. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 88, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Fernandez, C.; Toullec, J.; Lambert, C.; Le Goic, N.; Seoane, M.; Moriceau, B.; Huvet, A.; Berchel, M.; Vincent, D.; Courcot, L.; et al. Do transparent exopolymeric particles (TEP) affect the toxicity of nanoplastics on Chaetoceros neogracile? Environ. Pollut. 2019, 250, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, C.B.; Kang, H.M.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, J.S.; Seo, J.S.; Wang, M.; Lee, J.S. Nanoplastic Ingestion Enhances Toxicity of Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) in the Monogonont Rotifer Brachionus koreanus via Multixenobiotic Resistance (MXR) Disruption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 11411–11418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.; Martins, M.A.; Soares, A.M.V.; Cuesta, A.; Oliveira, M. Polystyrene nanoplastics alter the cytotoxicity of human pharmaceuticals on marine fish cell lines. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 69, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberbeckmann, S.; Kreikemeyer, B.; Labrenz, M. Environmental Factors Support the Formation of Specific Bacterial Assemblages on Microplastics. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debroas, D.; Mone, A.; Ter Halle, A. Plastics in the North Atlantic garbage patch: A boat-microbe for hitchhikers and plastic degraders. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599, 1222–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dussud, C.; Hudec, C.; George, M.; Fabre, P.; Higgs, P.; Bruzaud, S.; Delort, A.M.; Eyheraguibel, B.; Meistertzheim, A.L.; Jacquin, J.; et al. Colonization of Non-biodegradable and Biodegradable Plastics by Marine Microorganisms. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zettler, E.R.; Mincer, T.J.; Amaral-Zettler, L.A. Life in the “Plastisphere”: Microbial Communities on Plastic Marine Debris. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7137–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, A.; Hoellein, T.J.; Mason, S.A.; Schluep, J.; Kelly, J.J. Microplastic is an Abundant and Distinct Microbial Habitat in an Urban River. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 11863–11871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberbeckmann, S.; Loeder, M.G.J.; Gerdts, G.; Osborn, A.M. Spatial and seasonal variation in diversity and structure of microbial biofilms on marine plastics in Northern European waters. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 90, 478–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisser, J.; Shaw, J.; Hallegraeff, G.; Proietti, M.; Barnes, D.K.A.; Thums, M.; Wilcox, C.; Hardesty, B.D.; Pattiaratchi, C. Millimeter-Sized Marine Plastics: A New Pelagic Habitat for Microorganisms and Invertebrates. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral-Zettler, L.A.; Zettler, E.R.; Slikas, B.; Boyd, G.D.; Melvin, D.W.; Morrall, C.E.; Proskurowski, G.; Mincer, T.J. The biogeography of the Plastisphere: Implications for policy. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2015, 13, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, H.K.; Crawford, R.J.; Sawabe, T.; Ivanova, E.P. Poly(ethylene terephthalate) Polymer Surfaces as a Substrate for Bacterial Attachment and Biofilm Formation. Microbes Environ. 2009, 24, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukumar, T.; Aravinthan, A.; Lakshmi, K.; Venkatesan, R.; Vedaprakash, L.; Doble, M. Fouling and stability of polymers and composites in marine environment. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 2011, 65, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.A.; Hasan, F.; Hameed, A.; Ahmed, S. Biological degradation of plastics: A comprehensive review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2008, 26, 246–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negoro, S. Biodegradation of nylon oligomers. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2000, 54, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, J.; Wu, W.-M.; Zhao, J.; Song, Y.; Gao, L.; Yang, R.; Jiang, L. Biodegradation and Mineralization of Polystyrene by Plastic-Eating Mealworms: Part 1. Chemical and Physical Characterization and Isotopic Tests. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12080–12086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, J.; Wu, W.M.; Zhao, J.; Song, Y.; Gao, L.; Yang, R.; Jiang, L. Biodegradation and Mineralization of Polystyrene by Plastic-Eating Mealworms: Part 2. Role of Gut Microorganisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12087–12093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Yang, Y.; Wu, W.M.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, L. Evidence of polyethylene biodegradation by bacterial strains from the guts of plastic-eating waxworms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 13776–13784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, V.; Natarajan, K.; Hemambika, B.; Ramesh, N.; Sumathi, C.S.; Kottaimuthu, R.; Rajesh Kannan, V. High-density polyethylene (HDPE)-degrading potential bacteria from marine ecosystem of Gulf of Mannar, India. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 51, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima-Kambe, T.; Onuma, F.; Kimpara, N.; Nakahara, T. Isolation and characterization of a bacterium which utilizes polyester polyurethane as a sole carbon and nitrogen source. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1995, 129, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima-Kambe, T.; Onuma, F.; Kimpara, N.; Nakahara, T. Determination of the polyester polyurethane breakdown products and distribution of the polyurethane degrading enzyme of Comamonas acidovorans, strain TB-35. J. Food Sci. Technol. 1997, 83, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.H.; Shih, Y.H.; Lai, Y.C.; Liu, Y.Z.; Liu, Y.T.; Lin, N.C. Degradation of polyurethane by bacterium isolated from soil and assessment of polyurethanolytic activity of a Pseudomonas putida strain. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2014, 21, 9529–9537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, R.T.; Qin, L.F.; Yang, Y. Biodegradation of polyurethane by the spacecraft-inhabiting bacterium [C]. China Soc. Biotechnol. Young Sci. F 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Tender, C.A.; Devriese, L.I.; Haegeman, A.; Maes, S.; Ruttink, T.; Dawyndt, P. Bacterial Community Profiling of Plastic Litter in the Belgian Part of the North Sea. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 9629–9638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaeger, F.; Tagg, A.S.; Otto, S.; Biemuller, M.; Sartorius, I.; Labrenz, M. Residual Monomer Content Affects the Interpretation of Plastic Degradation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, J.P.; Boardman, C.; O’Callaghan, K.; Delort, A.M.; Song, J. Biodegradability standards for carrier bags and plastic films in aquatic environments: A critical review. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 171792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).