Runoff Variations and Quantitative Analysis in the Qinghai Lake Basin Under Changing Environments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Mann–Kendall Non-Parametric Trend and Change Point Tests
2.4. Runoff Attribution Analysis Method Based on the Budyko Hypothesis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Watershed Runoff Changes
3.2. Analysis of the Impact of Climate Change on Runoff
3.3. Analysis of the Impact of Land Surface Changes on Runoff
3.4. Quantitative Analysis of the Impact of Climate and Land Surface Changes on Runoff
3.4.1. Quantitative Analysis of the Impact of Climate Change and Land Surface Characteristics on Surface Runoff
3.4.2. Quantitative Analysis of the Impact of Climate Change and Land Surface Characteristics on Subsurface Runoff
3.4.3. Quantitative Analysis of the Impact of Climate Change and Land Surface Characteristics on Lake Water Levels
4. Discussion
4.1. Driving Factors of Runoff Changes in the Qinghai Lake Basin
4.2. Response Mechanisms of Runoff Evolution in the Qinghai Lake Basin Under a Changing Environment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| T | Average Temperature |
| P | Precipitation |
| U | Average Wind Speed (10 m height) |
| U2 | Wind Speed at 2 m Height |
| SSD | Sunshine Duration |
| RHU | Relative Humidity |
| ET0 | Potential Evapotranspiration |
| Rn | Net Radiation |
| h | Water Level |
| Δh | Water Level Difference |
| Q | Runoff |
| E | Actual Evapotranspiration |
| Δs | Water Storage Change |
| ω | Surface Characteristic Parameter |
| Pl | Lake Precipitation |
| Rls | Inflow Runoff Depth |
| El | Lake Evaporation |
| Rlg | Inflow Groundwater Runoff |
| ε | Error |
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Lake Water Balance Model and Climate Elasticity Coefficient Theory
References
- Fu, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Feng, X.; Liu, S.; Miao, C.; Wang, X.; He, C.; Li, C.; Ye, A.; et al. Optimization for Qinghai-Xizang Plateau ecological security barrier system. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2024, 39, 1882–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Cao, S.; Lei, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, W.; Kang, L. Spatial and Temporal Characteristics and Driving Analysis of Ecosystem Water Use Efficiency in the Qinghai Lake Basin. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2024, 32, 3554–3566. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, F. Characteristics Analysis of Temperature and Precipitation in Qinghai Lake Basin. J. China Hydrol. 2022, 42, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, G.; Yin, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, C. Hydrological Frequency Analysis in Changing Environments Based on Empirical Mode Decomposition and Metropolis-Hastings Sampling Bayesian Models. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2023, 28, 04023027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhan, C.; Liu, C. Review for impacts of climate change and human activities on water cycle. Shuili Xuebao 2013, 44, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Li, Y. Study on runoff trends of the six larger basins in China over the past 50 years. Adv. Water Sci. 2007, 18, 230–234. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, D.; Yang, H.; Lei, H. Analysis of the dominant causes for runoff reduction in five major basins over China during 1960–2010. Adv. Water Sci. 2015, 26, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S. Variation trends of runoffs seasonal distribution of the six larger basins in China over the past 50 years. Adv. Water Sci. 2008, 19, 656–661. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Hu, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, C.; Yin, X.; Xie, M. Analysis on runoff and sediment regimes and its causes of the Yellow River in recent 70 years. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 112–119. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, F.; Li, L.; Liang, H.; Yuan, J.; Lu, S. Climate change characteristics and its impacts on water resources in the Liaohe river basin from 1961 to 2009. J. Meteorol. Environ. 2012, 28, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Huang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Peng, S.; Li, J.; Zhou, L.; Liu, H.; Ma, Y.; Ding, Y.; et al. The Impacts of Climate Change on Water Resources and Agriculture in China. Nature 2010, 467, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Gao, X.; Giorgi, F. Upgrades to the REA Method for Producing Probabilistic Climate Change Predictions. Clim. Res. 2010, 41, 61–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Wu, W.; Zhou, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, J. Investigation of the Dramatic Changes in Lake Level of the Bosten Lake in Northwestern China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 119, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Feng, Z.; Ma, M. Climate Changes and Hydrological Processes. Water 2022, 14, 3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Gao, W.; Duan, C.; Zhu, Y.; Pan, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, W.; Yang, G. Water level variation and its driving factors in Lake Dianchi, Fuxian and Yangzong during 1988–2015. J. Lake Sci. 2019, 31, 1379–1390. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, B.; Chen, D.; Lei, L. Long-Term Changes of Lake Level and Water Budget in the Nam Co Lake Basin, Central Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 1312–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J. Responses of Hydrological Extreme Events and Water Budget under Changing Environment. Ph.D. Thesis, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X. Advances in Separating Effects of Climate Variability and Human Activity on Stream Discharge: An Overview. Adv. Water Resour. 2014, 71, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zou, X.; Gao, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, C.; Tang, D.; Wang, T.; Wu, X. Quantifying the Anthropogenic and Climatic Contributions to Changes in Water Discharge and Sediment Load into the Sea: A Case Study of the Yangtze River, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 536, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wei, X.; Sun, P.; Liu, S. The Effect of Forest Harvesting and Climatic Variability on Runoff in a Large Watershed: The Case Study in the Upper Minjiang River of Yangtze River Basin. J. Hydrol. 2012, 464–465, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. Evolution of watershed ecological hydrology in Haihe basin mountainous area. Ph.D. Thesis, Beijing Foresty University, Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Schaake, J.C. From climate to flow. In Climate Change and US Water Resources; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Milly, P.C.D.; Dunne, K.A. Macroscale Water Fluxes 2. Water and Energy Supply Control of Their Interannual Variability. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 24-1–24-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Shi, S. Study on the Relation between Groundwater Dynamics and Vegetation Degeneration in Erjina Oasis. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2002, 24, 421–425. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.; Gu, X. Quantitative evaluations of human- and climate-induced impacts on hydrological processes of China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2016, 71, 1875–1885. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Li, L.; Qin, Y.; Liang, L.; Li, J.; Liu, Y. Impacts of Climate Variability on Streamflow in the Upper and Middle Reaches of the Taoer River Based on the Budyko Hypothesis. Resour. Sci. 2011, 33, 70–76. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, B.; Shi, Y. The Hydrological Characteristics and The Cause of The Declining of Water Level in Qinghai Lake. Acta Geogr. Sin. 1992, 47, 267–273. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Liu, F. Effect of Climatic Change of Water Balance of Qinghai Lake Basin for Recent Thirty Years and Possible Tendency. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 1995, 15, 128–135, 199. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, A. Analysis on the Influence of Climate Change and the Human Activities on Inland Lake. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2007, 21, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Fu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Yan, L.; Xiao, J. Climate Change and Its Environmental Effects in the Surrounding Area of Qinghai Lake. Resour. Sci. 2008, 30, 348–353. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Li, X.; Tang, J.; Xu, H. Climate Change and Hydrological Response in the Watershed of Qinghai Lake. Resour. Sci. 2008, 30, 354–362. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhao, H.; Wang, G.; Yao, K.; Xin, Q.; He, Z.; Li, L. Influence of watershed hydrothermal conditions and vegetation status on lake level of Qinghai Lake. Arid Land Geogr. 2019, 42, 499–508. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, B.; Huang, Q. Evaluation of the Climatic Change Impacts on the Inland Lake—A Case Study of Lake Qinghai, China. Clim. Change 1998, 39, 695–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, L.; Wang, G.; Yao, K.; He, Z.; Xiao, J. Water Level and Agriculture and Husbandry Characteristics in Qinghai Lake Basin: The Response to Climate Warming and Wetting. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2018, 34, 119–127. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. Study on Mechanism of Microbial-Driven NitrogenMigration and Transformation Based on WatershedWater Cycle-Taking Qinghai Lake Basin as an Example. Ph.D. Thesis, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Cong, Z.; Gao, B.; Li, G.; Wang, X. The Water Level Change and Its Attribution of the Qinghai Lake from 1960 to 2020. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 52, 101688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y. Water Balance an Forecasting of Water Level Change in Qinghai Lake. J. Lake Sci. 1994, 6, 298–307. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Tian, F. Abrupt Change of Runoff and Its Major Driving Factors in Haihe River Catchment, China. J. Hydrol. 2009, 374, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Gemmer, M.; Jiang, T. Spatial and Temporal Variation of Extreme Precipitation over the Yangtze River Basin. Larg. Asian Rivers Their Interact. Estuaries Coasts 2008, 186, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric Tests Against Trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Zhang, J.; Lin, Y.; Bu, T.; Wang, X.; Xue, Z.; Li, Y.; Ma, X.; Yu, Z.; Bai, P. Variation of streamflow and its drivers in Xin’an River Basin. J. Nat. Resour. 2019, 34, 1771–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, G.; Mu, X.; Gao, P.; Sun, W. Attribution of runoff variation in the Wei River basin based on the Budyko hypothesis. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 7607–7617. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, T. The Spatiotemporal Variability of Catchment Evapotranspiration and Its Attribution Analysis in the Loess Plateau under the Budyko Framework. Ph.D. Thesis, Research Center of Soil and Water Conservation and Ecological Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Ministry of Education, Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, B. On the Calculation of the Evaporation from Land Surface. Sci. Atmos. Sin. 1981, 5, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Yang, D.; Lei, Z.; Sun, F. New Analytical Derivation of the Mean Annual Water-Energy Balance Equation. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W03410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yang, D.; Yang, H.; Lei, H. Attribution Analysis Based on the Budyko Hypothesis for Detecting the Dominant Cause of Runoff Decline in Haihe Basin. J. Hydrol. 2014, 510, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y. Time instability of hydrological model parameters under changing environment. Ph.D. Thesis, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Wei, X.; Li, Y. Groundwater Dynamic Evolution Under Climatic Change and Human Activites in Shiyang River Basin. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2009, 16, 183–187. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.; Liu, C.; Liu, K.; Wu, J.; Fan, C.; Xue, B.; Ma, R.; Song, C. Potential impact of the dramatical expansion of Lake Qinghai on the habitat facilities and grassland since 2004. J. Lake Sci. 2021, 33, 922–934. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Li, R.; Gan, Y.; Wu, Y. Attribution analysis of runoff change in Buha River basin based on Budyko hypothesis. South--North Water Transf. Water Sci. Technol. 2023, 21, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Ren, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Ma, X.; Li, P.; Shen, Z. Evolution of the Precipitation–Stream Runoff Relationship in Different Precipitation Scenarios in the Yellow River Basin. Urban Clim. 2023, 51, 101609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q. Investigation of Runoff Evolution at the Headwaters of Yangtze River and Its Driving Forces. J. Yangtze River Sci. Res. Inst. 2018, 35, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Tang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Chiew, F.H.S.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, H. Different Precipitation Elasticity of Runoff for Precipitation Increase and Decrease at Watershed Scale. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 11932–11943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Shen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S. Analysis of Changing Pan Evaporation in the Arid Region of Northwest China. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 2205–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Fan, Y.; Wang, H.; Fang, G. Research progress on the impact of climate change on water resources in the arid region of Northwest China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2014, 69, 1295–1304. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Tan, K.; Zhao, S.; Fang, J. Changing Climate Affects Vegetation Growth in the Arid Region of the Northwestern China. J. Arid Environ. 2011, 75, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Guo, Y. Vegetation Dynamics and Their Response to Hydroclimatic Factors in the Tarim River Basin, China. Ecohydrology 2013, 6, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yuan, G. Biophysical effects of the different underlying factors on land the surface temperature in the Qinghai Lake Basin. Arid Zone Res. 2024, 41, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Hu, G.; Zou, D.; Wu, X.; Ma, L.; Sun, Z.; Yuan, L.; Zhou, H.; Liu, S. Permafrost Changes and Its Effects on Hydrological Processes on Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2019, 34, 1233–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Huo, S.; Li, S.; Du, Y. Application of SWAT model to analysis of runoff variation of Buha River Basin of Qinghai Lake. J. Hohai Univ. 2007, 35, 159–163. [Google Scholar]
- Andréassian, V. Waters and Forests: From Historical Controversy to Scientific Debate. J. Hydrol. 2004, 291, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhou, G.; Liu, S.; Sun, G. Forests and Streamflow—Consistence and Complexity. J. Nat. Resour. 2005, 20, 761–770. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Zhong, J. The Influence of Forest Cover Upon Annual Runoff in the Loess Plateau of China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 1978, 33, 112–127. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Forest and Slope-runoff. World For. Res. 2005, 18, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Mo, X.; Hu, S.; Chen, X. Responses of vegetation greenness to temperature and precipitation in the Three-North Shelter Forest Program. Geogr. Res. 2020, 39, 152–165. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, E.; Xue, B. A review of influences of land use and land cover change on ecosystems. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2020, 44, 543–552. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B. Spatial and temporal variation characteristics of grassland and lake in Qinghai Lake basin under climate change. Ph.D. Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H. Long Sequence Runoff in the Source of the Yangtze River: Variation Law and Its Relationship with Meteorological Elements. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2019, 35, 123–129. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, H.; Xu, B.; Huang, F.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lu, Z.; Qi, S.; Song, F.; Chen, Y.; Qu, L. Impact causes of runoff in mountainous areas of the Ili River basin. Chin. J. Nat. 2024, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Han, Y.; Song, L. The Summarize of Development of Global Climate Change and It’s Effect Factors. Adv. Earth Sci. 2005, 20, 990. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Y.; Cao, S.; Cao, G.; Yang, Y.; Lan, Y.; Ji, Y.; Li, H. Study on surface water and groundwater interaction of Shaliu River Basin in Qinghai Lake in different periods. J. Nat. Resour. 2020, 35, 2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Mu, X.; Sun, W.; Gao, P.; Zhao, G. Comparative Analysis of the Responses of Rainstorm Flood and Sediment Yield to Vegetation Rehabilitation in the Yanhe River Basin. J. Nat. Resour. 2017, 32, 1755–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Liu, F. Estimating on Water Balance Elements in the Drainage Basin of Qinghai Lake. Arid Land Geogr. 1993, 16, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yang, D. Derivation of Climate Elasticity of Runoff to Assess the Effects of Climate Change on Annual Runoff. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W07526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




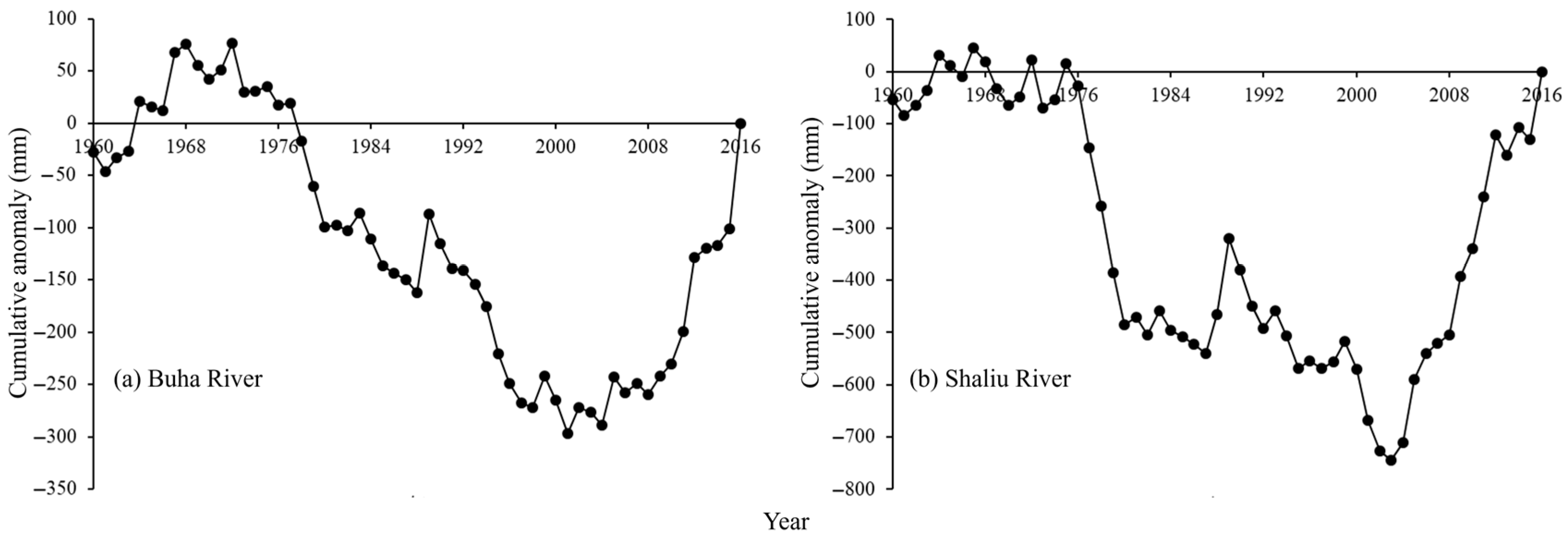

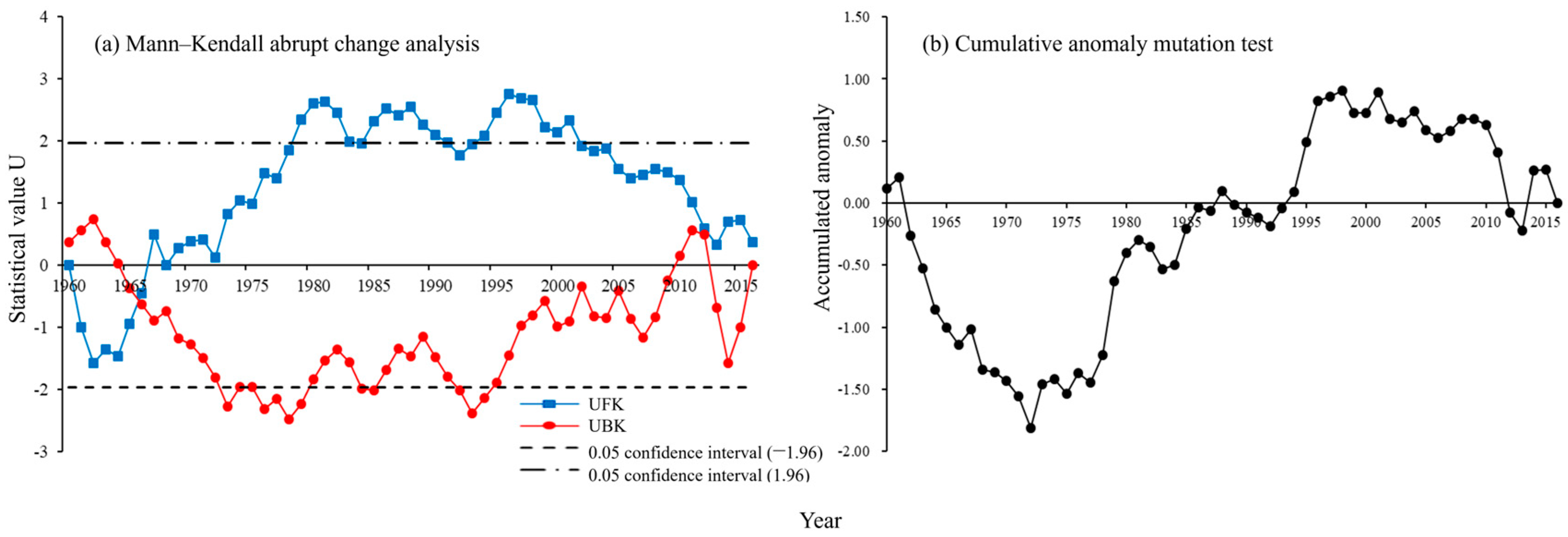
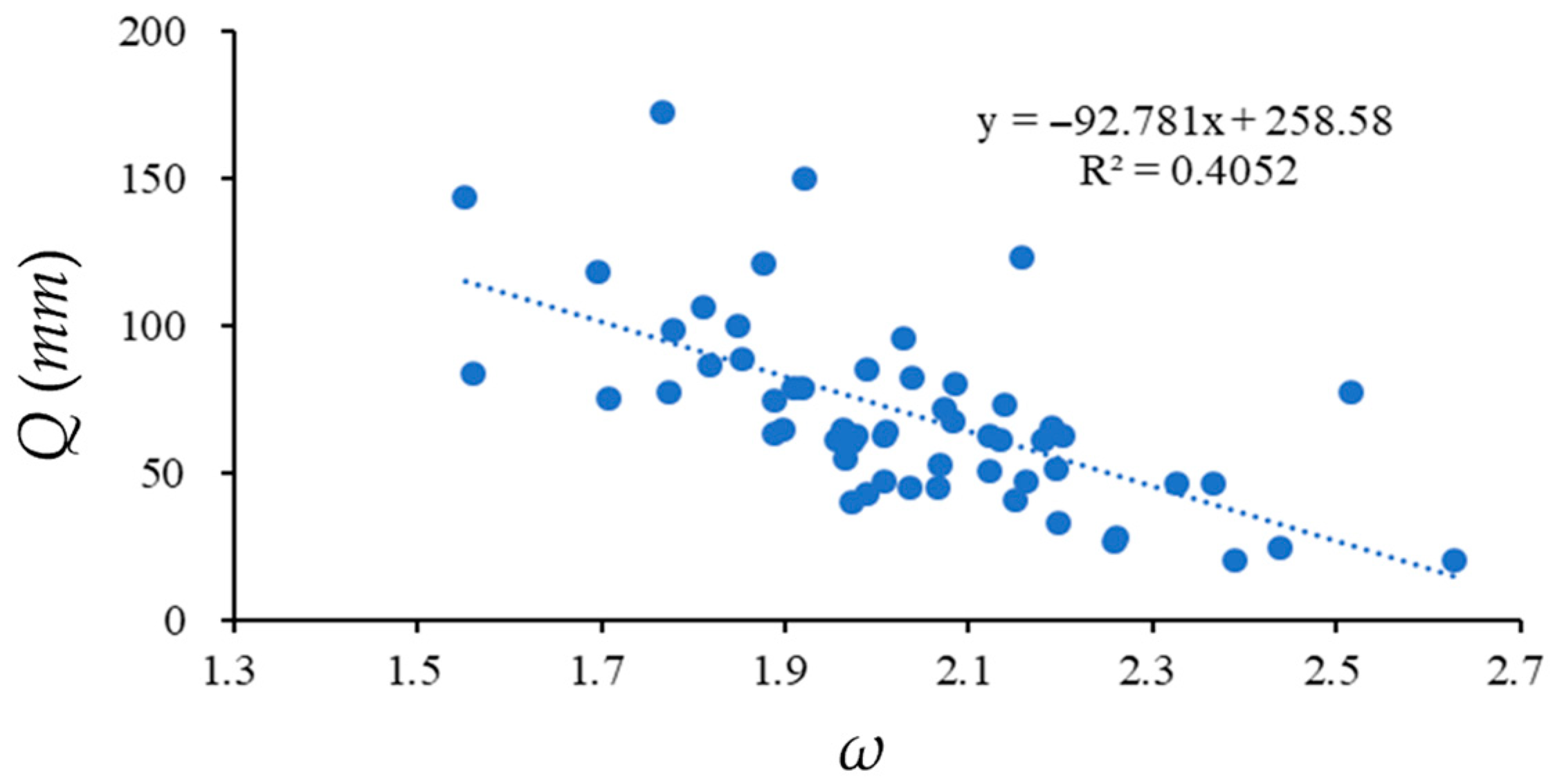
| Hydrological Station Name | River Name | Catchment Area (km2) | Flow (m³/s) | Annual Runoff (108 m3) | Runoff Depth (mm) | Runoff Coefficient [10−3 m3/(s·km2)] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buha River Estuary | Buhua River | 14,337 | 25.6 | 7.83 | 56.3 | 1.79 |
| Gang Cha | Shaliu River | 1442 | 7.2 | 2.51 | 157.5 | 4.99 |
| Total | 15,779 | 10.34 |
| Station Code | Station Name | Latitude (°N) | Longitude (°E) | Elevation (m) | Data Time Span |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 52645 | Ye Niugou | 38.43 | 99.60 | 3315 | 1960–2016 |
| 52842 | Cha Ka | 36.78 | 99.08 | 3088 | 1960–2016 |
| 52633 | Tuo Le | 38.82 | 98.42 | 3368 | 1960–2016 |
| 52833 | Wu Lan | 36.93 | 98.48 | 2951 | 1960–2016 |
| 52836 | Du Lan | 36.30 | 98.10 | 3190 | 1960–2016 |
| 52737 | De Lingha | 37.37 | 97.38 | 2982 | 1960–2016 |
| 52868 | Gui De | 36.02 | 101.37 | 2274 | 1960–2016 |
| 52657 | Qi Lian | 38.18 | 100.25 | 2788 | 1960–2016 |
| 52754 | Gang Cha | 37.33 | 100.13 | 3302 | 1960–2016 |
| 52856 | Gong He | 36.27 | 100.62 | 2836 | 1960–2016 |
| 52943 | Xing Hai | 35.58 | 99.98 | 3324 | 1960–2016 |
| 52765 | Men Yuan | 37.38 | 101.62 | 2851 | 1960–2016 |
| 52866 | Xi Ning | 36.73 | 101.75 | 2296 | 1960–2016 |
| 52955 | Gui Nan | 35.58 | 100.73 | 3121 | 1960–2016 |
| 52745 | Tian Jun | 37.30 | 99.02 | 3417 | 1961–2010 |
| 52855 | Huang Yuan | 36.68 | 101.25 | 2675 | 1961–2010 |
| 52853 | Hai Yan | 36.90 | 100.98 | 3010 | 1961–2010 |
| 1329500 | Bu Hua | 37.03 | 99.73 | 3191 | 1962–2016 |
| No. | Abbreviation | Name | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | T | Average Temperature | °C |
| 2 | P | Precipitation | mm |
| 3 | U | Average Wind Speed (10 m height) | m/s |
| 4 | U2 | Wind Speed at 2 m Height | m/s |
| 5 | SSD | Sunshine Duration | h |
| 6 | RHU | Relative Humidity | % |
| 7 | ET0 | Potential Evapotranspiration | mm |
| 8 | Rn | Net Radiation | MJ/m2 |
| 9 | h | Water Level | m |
| 10 | Δh | Water Level Difference | mm |
| 11 | Q | Runoff | mm |
| 12 | E | Actual Evapotranspiration | mm |
| 13 | Δs | Water Storage Change | mm |
| 14 | ω | Surface Characteristic Parameter | |
| 15 | Pl | Lake Precipitation | mm |
| 16 | Rls | Inflow Runoff Depth | mm |
| 17 | El | Lake Evaporation | mm |
| 18 | Rlg | Inflow Groundwater Runoff | mm |
| 19 | ε | Error |
| Time | T | P | U | SSD | RHU | ET0 | Rn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1960–2016 year | 0.17 | 0.72 ** | −0.42 ** | −0.19 | 0.47 ** | −0.50 ** | −0.45 ** |
| 1960–2003 year | −0.19 | 0.72 ** | −0.39 ** | −0.03 | 0.71 ** | −0.73 ** | −0.44 ** |
| 2004–2016 year | 0.39 | −0.10 | −0.08 | 0.55 | −0.44 | 0.37 | 0.36 |
| 1960–1993 year | −0.34 * | 0.74 ** | −0.53 ** | −0.09 | 0.76 ** | −0.78 ** | −0.36 * |
| 1994–2016 year | 0.49 * | 0.70 ** | −0.15 | −0.32 | 0.00 | −0.13 | −0.46 * |
| Climatic Variables | Multi-Year Average | Linear Tendency Rate | Unit | Significance (P) | Rate of Change | Z Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ET0 | 887.40 | 1.51 | mm/a/10a | >0.05 | 0.02% | 0.10 |
| P | 325.81 | 17.45 | mm/a/10a | 0.01 | 0.54% | 3.72 |
| Rn | 2906.93 | −7.39 | MJ/(m2·a)/10a | 0.05 | −0.03% | −2.07 |
| T | 0.81 | 0.36 | °C/a/10a | 0.01 | 4.47% | 6.90 |
| U2 | 2.70 | −0.08 | m/s/a/10a | 0.01 | −0.28% | −4.44 |
| RHU | 47.20 | 0.03 | %/a/10a | >0.05 | 0.01% | 0.72 |
| Q | 60.72 | 4.12 | mm/a/10a | >0.05 | 2.87% | 1.36 |
| Factor | Elastic Coefficient | Value |
|---|---|---|
| P | ɛ1 | 1.98 |
| ET0 | ɛ2 | −0.98 |
| Rn | ɛ3 | 0.66 |
| T | ɛ4 | 0.02 |
| U2 | ɛ5 | 0.16 |
| RHU | ɛ6 | −0.56 |
| Category | ΔQ | ΔQclimate | ΔQcatchment | Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Influence quantity (mm) | 33.85 | 25.42 | 6.44 | −1.99 |
| Contribution rate (%) | 100 | 79.79% | 20.21% | −5.89% |
| Variable | x1 | x2 | x3 | x4 | x5 | x6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x1 | 1 | 0.36 ** | 0.51 ** | −0.71 ** | 0.63 ** | −0.23 |
| x2 | 1 | 0.61 ** | −0.56 ** | 0.73 ** | −0.24 | |
| x3 | 1 | −0.56 ** | 0.61 ** | −0.56 ** | ||
| x4 | 1 | −0.63 ** | 0.27 * | |||
| x5 | 1 | −0.045 | ||||
| x6 | 1 |
| Matrix | γ1 | γ2 | γ3 | γ4 | γ5 | γ6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y | 0.82 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.83 | 0.79 | 0.84 |
| Principal Component | Eigenvalue | Contribution Rate% | Cumulative Contribution Rate% |
|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 3.61 | 60.09 | 60.09 |
| F2 | 0.93 | 15.45 | 75.54 |
| F3 | 0.89 | 14.78 | 90.32 |
| F4 | 0.31 | 5.09 | 95.41 |
| F5 | 0.25 | 4.15 | 99.56 |
| F6 | 0.03 | 0.44 | 100 |
| Principal Component | x1 | x2 | x3 | x4 | x5 | x6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 0.36 | −0.57 | 0.38 | 0.25 | 0.57 | 0.06 |
| F2 | 0.45 | 0.52 | 0.13 | −0.09 | 0.12 | 0.70 |
| F3 | 0.44 | −0.08 | −0.29 | 0.70 | −0.47 | −0.01 |
| Contribution Rate% | Pl | Rls | El | Rlg ± ε | Δh |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate change | 100 | 79.79 | 100 | 88.43 | 93.02 |
| Changes in underlying surface characteristics | 0 | 20.21 | 0 | 11.57 | 6.98 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mo, L.; Yu, X.; Feng, Y.; Jiang, T. Runoff Variations and Quantitative Analysis in the Qinghai Lake Basin Under Changing Environments. Hydrology 2025, 12, 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12040094
Mo L, Yu X, Feng Y, Jiang T. Runoff Variations and Quantitative Analysis in the Qinghai Lake Basin Under Changing Environments. Hydrology. 2025; 12(4):94. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12040094
Chicago/Turabian StyleMo, Li, Xinxiao Yu, Yonghan Feng, and Tao Jiang. 2025. "Runoff Variations and Quantitative Analysis in the Qinghai Lake Basin Under Changing Environments" Hydrology 12, no. 4: 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12040094
APA StyleMo, L., Yu, X., Feng, Y., & Jiang, T. (2025). Runoff Variations and Quantitative Analysis in the Qinghai Lake Basin Under Changing Environments. Hydrology, 12(4), 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12040094





