- Article
Effects of River Channel Structural Modifications on High-Flow Characteristics Using 2D Rain-on-Grid HEC-RAS Modelling: A Case of Chongwe River Catchment in Zambia
- Frank Mudenda,
- Hosea M. Mwangi and
- Caroline W. Maina
- + 1 author
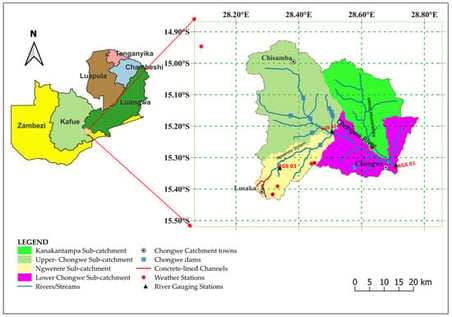
Rapid urbanization has led to increasing structural modification of river catchments through dam construction and concrete-lining of natural channels as flood management measures. These interventions can alter the natural hydrology. This necessitates assessment of their influence on hydrology at a catchment scale. However, such evaluations are particularly challenging in data-scarce regions such as the Chongwe River Catchment, where hydrometric records capturing conditions before and after structural modifications are limited. Therefore, we applied a 2D rain-on-grid approach in HEC-RAS to evaluate changes in high-flow responses to short-duration, high-intensity rainfall events in the Chongwe River Catchment in Zambia, where structural interventions have been implemented. The terrain was modified in HEC-RAS to represent 21 km of concrete drains and ten dams. Sensitivity analysis conducted on five key model parameters showed that parameters controlling surface runoff generation, particularly curve number, exerted the strongest influence on simulated peak flows, while routing-related parameters had a secondary effect. Model calibration and validation showed strong performance with R2 = 0.99, NSE = 0.75 and PBIAS = −0.68% during calibration and R2 = 0.95, NSE = 0.75, PBIAS = −2.49% during validation. Four scenarios were simulated to determine the hydrological effects of channel concrete-lining and dams. The results showed that concrete-lining of natural channels in the urban area increased high flows at the main outlet by approximately 4.6%, generated localized instantaneous maximum channel velocities of up to 20 m/s, increased flood depths by up to 11%, decreased lag times and expanded flood inundation widths by up to 15%. The existing dams reduced peak flows by about 28%, increased lag times, reduced flood depths by about 11%, and reduced flood inundation widths by up to 8% across the catchment. The findings demonstrate that enhancing stormwater conveyance through concrete-lining must be complemented by storage to manage high flows, while future work should explore nature-based solutions to reduce channel velocities and improve sustainable flood mitigation. Therefore, the study provides event-scale insights to support flood-risk management and infrastructure planning in rapidly urbanizing, data-scarce catchments.
6 February 2026