Med-cDiff: Conditional Medical Image Generation with Diffusion Models
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Methods
3.1. Background
3.2. Training and Sampling
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets
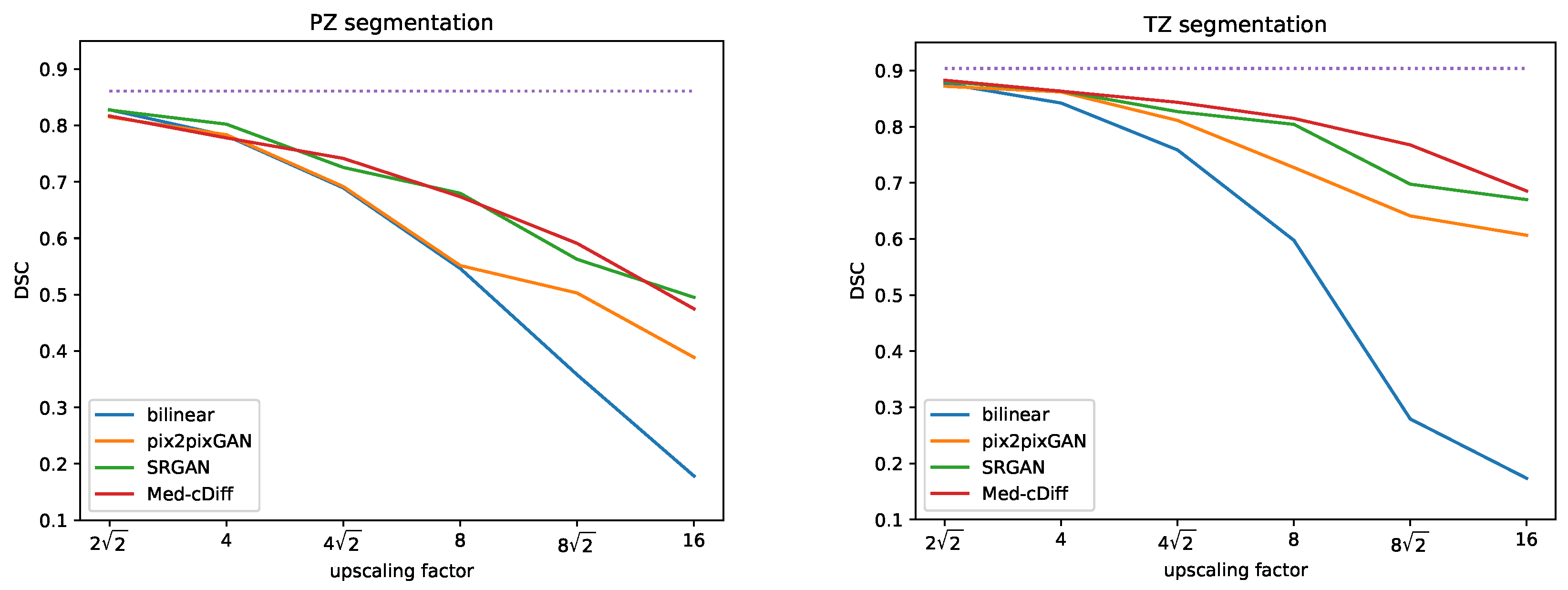
- MRI Super Resolution: The dataset consists of 296 patients who underwent pre-operative prostate MRI prior to robotic-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy. T2-weighted imaging was used for the experiment, acquired by the Turbo Spin Echo (TSE) MRI sequence following the standardized imaging protocol of the European Society of Urogenital Radiology (ESUR) PI-RADS guidelines [56]. Additionally, the dataset includes annotation of the transition zone (TZ) and peripheral zone (PZ) of the prostate. Overall, 238, 29, and 29 patients were used for training, validation, and testing, respectively. To perform super-resolution, we downsampled the images by a factor of , 4, , 8, , and 16.
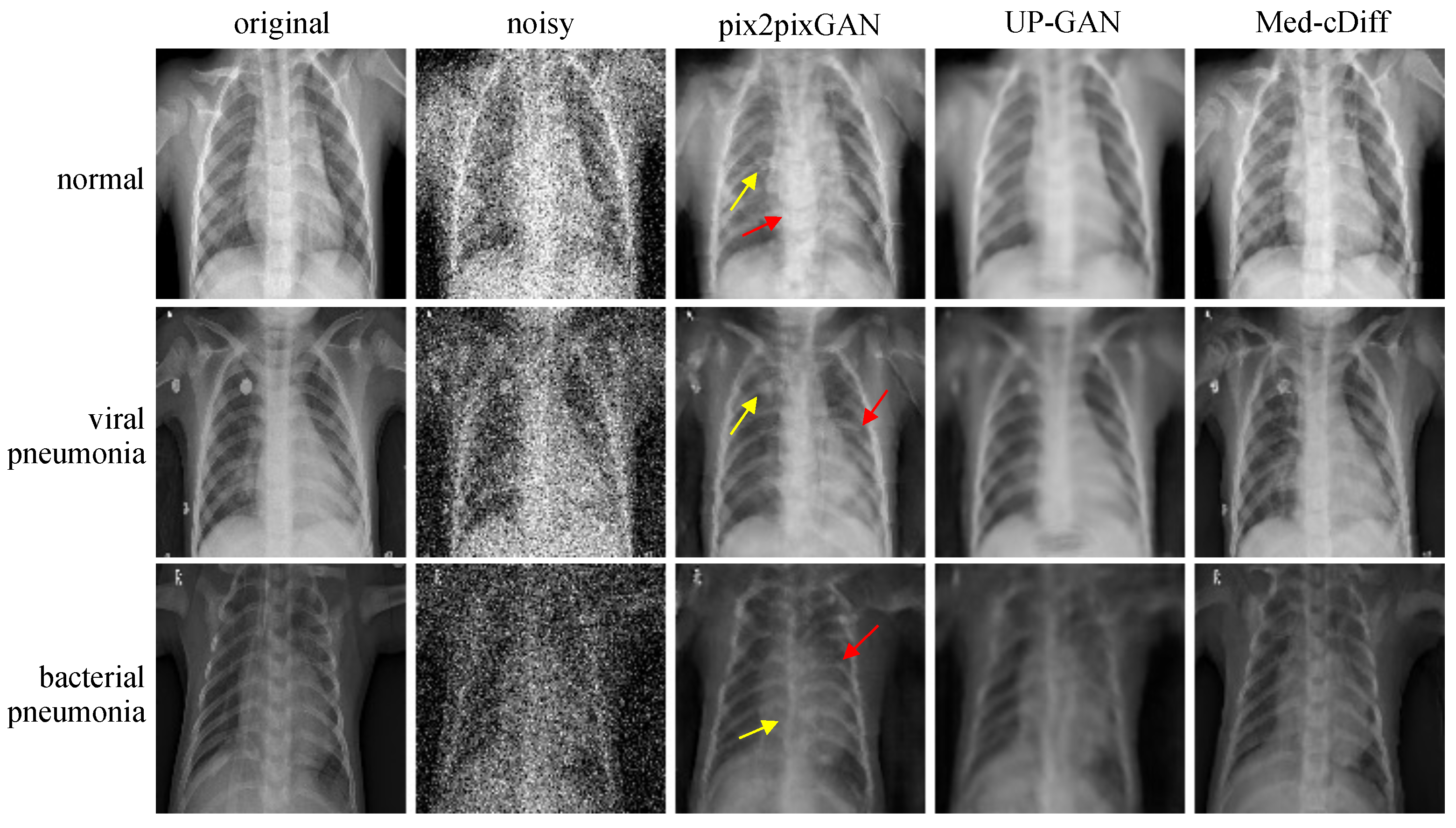
- X-ray Denoising: The public chest X-ray dataset [57] contains 5863 X-ray images with pneumonia and normal patients. Overall, 624 images were used for testing. Pneumonia patients were further categorized as virus- or bacteria-infected patients. We randomly added Gaussian noise as well as salt and pepper noise to the images and used the original images as the ground truth.
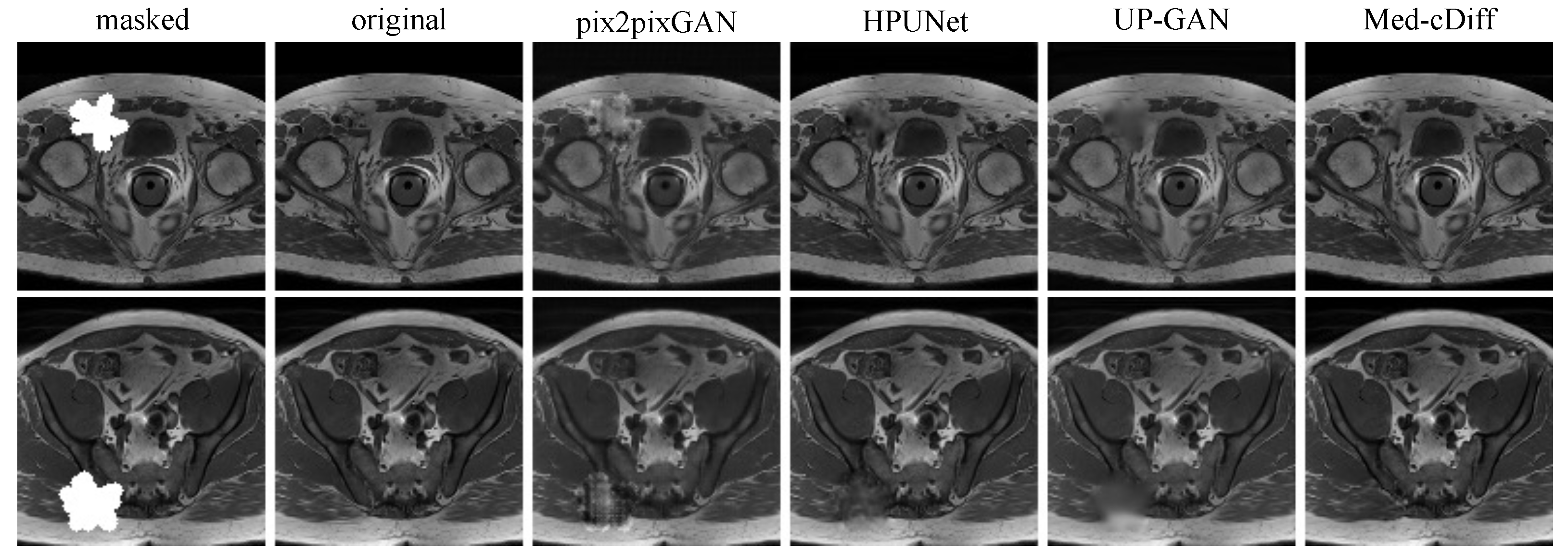
- MRI Inpainting: The dataset consists of 18,813 T1-weighted prostate MRI images that were acquired by the Spoiled Gradient Echo (SPGR) sequence. We used 6271 of them for testing. The masks were randomly generated during training, and they were fixed among different tests for testing.
4.2. Implementation and Evaluation Details
4.3. MRI Super-Resolution
4.4. X-ray Denoising
4.5. MRI Inpainting
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Havaei, M.; Mao, X.; Wang, Y.; Lao, Q. Conditional generation of medical images via disentangled adversarial inference. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 72, 102106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, A.L.Y.; Sun, Z.; Chen, W.; Galeotti, J. Hierarchical probabilistic ultrasound image inpainting via variational inference. In Proceedings of the First MICCAI Workshop on Deep Generative Models, and Data Augmentation, Labelling, and Imperfections, Strasbourg, France, 1 October 2021; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 83–92. [Google Scholar]
- Mahapatra, D.; Bozorgtabar, B.; Garnavi, R. Image super-resolution using progressive generative adversarial networks for medical image analysis. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2019, 71, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Dewey, B.E.; Pham, D.L.; Calabresi, P.A.; Reich, D.S.; Prince, J.L. SMORE: A self-supervised anti-aliasing and super-resolution algorithm for MRI using deep learning. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 40, 805–817. [Google Scholar]
- Armanious, K.; Jiang, C.; Fischer, M.; Küstner, T.; Hepp, T.; Nikolaou, K.; Gatidis, S.; Yang, B. MedGAN: Medical image translation using GANs. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2020, 79, 101684. [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyay, U.; Chen, Y.; Hepp, T.; Gatidis, S.; Akata, Z. Uncertainty-guided progressive GANs for medical image translation. In Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, Strasbourg, France, 27 September–1 October 2021; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 614–624. [Google Scholar]
- Cetin, I.; Stephens, M.; Camara, O.; Ballester, M.A.G. Attri-VAE: Attribute-based interpretable representations of medical images with variational autoencoders. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2023, 104, 102158. [Google Scholar]
- Ehrhardt, J.; Wilms, M. Autoencoders and variational autoencoders in medical image analysis. In Biomedical Image Synthesis and Simulation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 129–162. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.; Marinescu, R.; Dalca, A.V.; Bonkhoff, A.K.; Bretzner, M.; Rost, N.S.; Golland, P. 3D-StyleGAN: A style-based generative adversarial network for generative modeling of three-dimensional medical images. In Proceedings of the First MICCAI Workshop on Deep Generative Models, and Data Augmentation, Labelling, and Imperfections, Strasbourg, France, 1 October 2021; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 24–34. [Google Scholar]
- AlAmir, M.; AlGhamdi, M. The Role of generative adversarial network in medical image analysis: An in-depth survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 55, 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- van de Schaft, V.; van Sloun, R.J. Ultrasound speckle suppression and denoising using MRI-derived normalizing flow priors. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.13110. [Google Scholar]
- Hajij, M.; Zamzmi, G.; Paul, R.; Thukar, L. Normalizing flow for synthetic medical images generation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Healthcare Innovations and Point of Care Technologies, Houston, TX, USA, 10–11 March 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 46–49. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, J.; Jain, A.; Abbeel, P. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 6840–6851. [Google Scholar]
- Dhariwal, P.; Nichol, A. Diffusion models beat GANS on image synthesis. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 8780–8794. [Google Scholar]
- Saharia, C.; Chan, W.; Chang, H.; Lee, C.; Ho, J.; Salimans, T.; Fleet, D.; Norouzi, M. Palette: Image-to-image diffusion models. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH 2022 Conference, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–11 August 2022; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Saharia, C.; Ho, J.; Chan, W.; Salimans, T.; Fleet, D.J.; Norouzi, M. Image super-resolution via iterative refinement. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 4713–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinaya, W.H.; Tudosiu, P.D.; Dafflon, J.; Da Costa, P.F.; Fernandez, V.; Nachev, P.; Ourselin, S.; Cardoso, M.J. Brain imaging generation with latent diffusion models. In Proceedings of the Second MICCAI Workshop on Deep Generative Models, Singapore, 22 September 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 117–126. [Google Scholar]
- Özbey, M.; Dalmaz, O.; Dar, S.U.; Bedel, H.A.; Özturk, Ş.; Güngör, A.; Çukur, T. Unsupervised medical image translation with adversarial diffusion models. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging, 2023; early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolleb, J.; Sandkühler, R.; Bieder, F.; Valmaggia, P.; Cattin, P.C. Diffusion models for implicit image segmentation ensembles. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Imaging with Deep Learning, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–8 July 2022; pp. 1336–1348. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, H.; Ye, J.C. Score-based diffusion models for accelerated MRI. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 80, 102479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.; Lee, E.S.; Ye, J.C. MR Image Denoising and Super-Resolution Using Regularized Reverse Diffusion. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2022, 42, 922–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 2672–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1125–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.B.; Oh, S.; Tang, Y.X.; Xiao, J.; Summers, R.M. CT-realistic data augmentation using generative adversarial network for robust lymph node segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2019: Computer-Aided Diagnosis, San Diego, CA, USA, 17–20 February 2019; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2019; Volume 10950, pp. 976–981. [Google Scholar]
- Popescu, D.; Deaconu, M.; Ichim, L.; Stamatescu, G. Retinal blood vessel segmentation using Pix2Pix GAN. In Proceedings of the 29th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation, Puglia, Italy, 22–25 June 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1173–1178. [Google Scholar]
- Aljohani, A.; Alharbe, N. Generating synthetic images for healthcare with novel deep Pix2Pix GAN. Electronics 2022, 11, 3470. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Du, Y.; Li, C.; Wu, T.H.; Yang, B.; Mok, G.S. Pix2Pix generative adversarial network for low dose myocardial perfusion SPECT denoising. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2022, 12, 3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2223–2232. [Google Scholar]
- Du, M.; Liang, K.; Xing, Y. Reduction of metal artefacts in CT with Cycle-GAN. In Proceedings of the IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 10–17 November 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Sun, J.; Carass, A.; Zhao, C.; Lee, J.; Xu, Z.; Prince, J. Unpaired brain MR-to-CT synthesis using a structure-constrained CycleGAN. In Proceedings of the International Workshops on Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support, Granada, Spain, 20 September 2018; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 174–182. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, A.; Shi, H.; Huang, S.; Zheng, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, X. CT synthesis from MRI using multi-cycle GAN for head-and-neck radiation therapy. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2021, 91, 101953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, J.; Lei, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, J.; Tang, X.; Curran, W.J.; Liu, T.; Yang, X. Paired cycle-GAN-based image correction for quantitative cone-beam computed tomography. Med. Phys. 2019, 46, 3998–4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karras, T.; Laine, S.; Aila, T. A style-based generator architecture for generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 4401–4410. [Google Scholar]
- Fetty, L.; Bylund, M.; Kuess, P.; Heilemann, G.; Nyholm, T.; Georg, D.; Löfstedt, T. Latent space manipulation for high-resolution medical image synthesis via the StyleGAN. Z. Med. Phys. 2020, 30, 305–314. [Google Scholar]
- Su, K.; Zhou, E.; Sun, X.; Wang, C.; Yu, D.; Luo, X. Pre-trained StyleGAN based data augmentation for small sample brain CT motion artifacts detection. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Data Mining and Applications, Foshan, China, 12–14 November 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 339–346. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Welling, M. Auto-encoding variational Bayes. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1312.6114. [Google Scholar]
- Vahdat, A.; Kautz, J. NVAE: A deep hierarchical variational autoencoder. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 19667–19679. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, J.; Xie, Y.; Gong, K.; Kim, K.; Yang, J.; Larson, P.; Hope, T.; Behr, S.; Seo, Y.; Liu, H.; et al. PET denoising and uncertainty estimation based on NVAE model. In Proceedings of the IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference, virtual, 16–23 October 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Grover, A.; Chute, C.; Shu, R.; Cao, Z.; Ermon, S. AlignFlow: Cycle consistent learning from multiple domains via normalizing flows. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 4028–4035. [Google Scholar]
- Bui, T.D.; Nguyen, M.; Le, N.; Luu, K. Flow-based deformation guidance for unpaired multi-contrast MRI image-to-image translation. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, Lima, Peru, 4–8 October 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 728–737. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Chaudhari, P.; Davatzikos, C. Harmonization with flow-based causal inference. In Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, Strasbourg, France, 27 September–1 October 2021; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 181–190. [Google Scholar]
- Beizaee, F.; Desrosiers, C.; Lodygensky, G.A.; Dolz, J. Harmonizing Flows: Unsupervised MR harmonization based on normalizing flows. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Processing in Medical Imaging, San Carlos de Bariloche, Argentina, 18–23 June 2023; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 347–359. [Google Scholar]
- Kadkhodaie, Z.; Simoncelli, E.P. Solving linear inverse problems using the prior implicit in a denoiser. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.13640. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, C.; He, Y.; Song, Y.; Song, J.; Wu, J.; Zhu, J.Y.; Ermon, S. SDEdit: Guided image synthesis and editing with stochastic differential equations. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.01073. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, A.; Song, J.; Meng, C.; Ermon, S. D2C: Diffusion-decoding models for few-shot conditional generation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 12533–12548. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, H.; Willcocks, C.G.; Breckon, T.P. UNIT-DDPM: Unpaired image translation with denoising diffusion probabilistic models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.05358. [Google Scholar]
- Wolleb, J.; Bieder, F.; Sandkühler, R.; Cattin, P.C. Diffusion models for medical anomaly detection. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, Singapore, 18–22 September 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 35–45. [Google Scholar]
- Behrendt, F.; Bhattacharya, D.; Krüger, J.; Opfer, R.; Schlaefer, A. Patched diffusion models for unsupervised anomaly detection in brain MRI. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.03758. [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt, J.; Leach, A.; Schmon, S.M.; Willcocks, C.G. AnoDDPM: Anomaly detection with denoising diffusion probabilistic models using simplex noise. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 650–656. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, A.; Valanarasu, J.M.J.; Hacihaliloglu, I.; Patel, V.M. Ambiguous medical image segmentation using diffusion models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 11536–11546. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Fang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Y. MedSegDiff: Medical image segmentation with diffusion probabilistic model. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.00611. [Google Scholar]
- Zbinden, L.; Doorenbos, L.; Pissas, T.; Sznitman, R.; Márquez-Neila, P. Stochastic segmentation with conditional categorical diffusion models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.08888. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Wang, C.; Shan, H. BerDiff: Conditional Bernoulli diffusion model for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.04429. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, C.; Cui, Z.X.; Liu, S.; Liang, D.; Zhu, Y. High-frequency space diffusion models for accelerated MRI. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.05481. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, G.; Blumenthal, M.; Heide, M.; Uecker, M. Bayesian MRI reconstruction with joint uncertainty estimation using diffusion models. Magn. Reson. Med. 2023, 90, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkbey, B.; Rosenkrantz, A.B.; Haider, M.A.; Padhani, A.R.; Villeirs, G.; Macura, K.J.; Tempany, C.M.; Choyke, P.L.; Cornud, F.; Margolis, D.J.; et al. Prostate imaging reporting and data system version 2.1: 2019 update of prostate imaging reporting and data system version 2. Eur. Urol. 2019, 76, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kermany, D.S.; Goldbaum, M.; Cai, W.; Valentim, C.C.; Liang, H.; Baxter, S.L.; McKeown, A.; Yang, G.; Wu, X.; Yan, F.; et al. Identifying medical diagnoses and treatable diseases by image-based deep learning. Cell 2018, 172, 1122–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; He, K. Group normalization. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A.; Shechtman, E.; Wang, O. The Unreasonable Effectiveness of Deep Features as a Perceptual Metric. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 586–595. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heusel, M.; Ramsauer, H.; Unterthiner, T.; Nessler, B.; Hochreiter, S. GANs trained by a two time-scale update rule converge to a local Nash equilibrium. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 6629–6640. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, G.; Jones, L. The nature and evaluation of the sharpness of photographic images. J. Soc. Motion Pict. Telev. Eng. 1952, 58, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dice, L.R. Measures of the amount of ecologic association between species. Ecology 1945, 26, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fechner, G.T. Elemente der Psychophysik; Breitkopf u. Härtel: Leipzig, Germany, 1860; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, H.; Lee, H.; Park, J.; Yoon, W.; Yoo, D. Reducing domain gap by reducing style bias. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 8690–8699. [Google Scholar]
- Romera, E.; Bergasa, L.M.; Yang, K.; Alvarez, J.M.; Barea, R. Bridging the day and night domain gap for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, Paris, France, 9–12 June 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1312–1318. [Google Scholar]
- Ledig, C.; Theis, L.; Huszár, F.; Caballero, J.; Cunningham, A.; Acosta, A.; Aitken, A.; Tejani, A.; Totz, J.; Wang, Z.; et al. Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 4681–4690. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, A.L.Y.; Zheng, H.; Miao, Q.; Raman, S.S.; Terzopoulos, D.; Sung, K. CAT-Net: A cross-slice attention transformer model for prostate zonal segmentation in MRI. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2022, 42, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]


| Factor | LPIPS ()↓ | FID↓ | acc.↑ | PZ DSC (%)↑ | TZ DSC (%)↑ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| bilinear | 2787.847 | 1.19 | 6.75 | 82.8 | 87.7 | |
| pix2pixGAN | 1.53 | 1.20 | 12.72 | 81.5 | 87.2 | |
| SRGAN | 3.30 | 1.19 | 5.60 | 82.7 | 88.0 | |
| Med-cDiff | 2.74 | 1.19 | 22.84 | 81.7 | 88.2 | |
| 4 | bilinear | 4339.392 | 1.20 | 4.51 | 78.2 | 84.2 |
| pix2pixGAN | 1.96 | 1.22 | 11.31 | 78.3 | 86.1 | |
| SRGAN | 5.03 | 1.19 | 5.11 | 80.2 | 86.2 | |
| Med-cDiff | 4.62 | 1.19 | 21.44 | 77.8 | 86.3 | |
| bilinear | 5773.238 | 1.21 | 3.28 | 68.9 | 75.9 | |
| pix2pixGAN | 2.50 | 1.22 | 12.68 | 69.2 | 81.1 | |
| SRGAN | 6.09 | 1.21 | 4.39 | 72.6 | 82.7 | |
| Med-cDiff | 5.09 | 1.20 | 21.37 | 74.2 | 84.3 |
| LPIPS ()↓ | FID↓ | Classification Accuracy (%)↑ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| original image | - | - | 70.7 |
| noisy image | 17.52 | 1.35 | 63.6 |
| pix2pixGAN | 1.77 | 1.32 | 65.1 |
| UP-GAN | 3.36 | 1.33 | 62.8 |
| Med-cDiff | 1.19 | 1.30 | 65.8 |
| LPIPS ()↓ | FID↓ | 2AFC Accuracy (%)↓ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| pix2pixGAN | 7.62 | 1.010 | 98.0 |
| HPUNet | 5.39 | 0.995 | 95.0 |
| UP-GAN | 3.17 | 0.897 | 94.5 |
| Med-cDiff | 2.96 | 0.582 | 64.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hung, A.L.Y.; Zhao, K.; Zheng, H.; Yan, R.; Raman, S.S.; Terzopoulos, D.; Sung, K. Med-cDiff: Conditional Medical Image Generation with Diffusion Models. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10111258
Hung ALY, Zhao K, Zheng H, Yan R, Raman SS, Terzopoulos D, Sung K. Med-cDiff: Conditional Medical Image Generation with Diffusion Models. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(11):1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10111258
Chicago/Turabian StyleHung, Alex Ling Yu, Kai Zhao, Haoxin Zheng, Ran Yan, Steven S. Raman, Demetri Terzopoulos, and Kyunghyun Sung. 2023. "Med-cDiff: Conditional Medical Image Generation with Diffusion Models" Bioengineering 10, no. 11: 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10111258
APA StyleHung, A. L. Y., Zhao, K., Zheng, H., Yan, R., Raman, S. S., Terzopoulos, D., & Sung, K. (2023). Med-cDiff: Conditional Medical Image Generation with Diffusion Models. Bioengineering, 10(11), 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10111258








