-
 Very High Molecular Weight Hyaluronic Acid as an Enhanced Vehicle in Therapeutic Eye Drops: Application in a Novel Latanoprost Formulation for Glaucoma
Very High Molecular Weight Hyaluronic Acid as an Enhanced Vehicle in Therapeutic Eye Drops: Application in a Novel Latanoprost Formulation for Glaucoma -
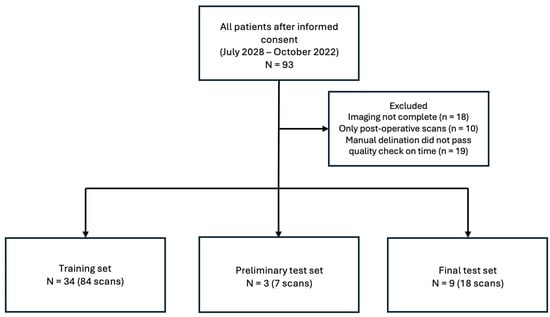
 Toward Sensor-to-Text Generation: Leveraging LLM-Based Video Annotations for Stroke Therapy Monitoring
Toward Sensor-to-Text Generation: Leveraging LLM-Based Video Annotations for Stroke Therapy Monitoring -
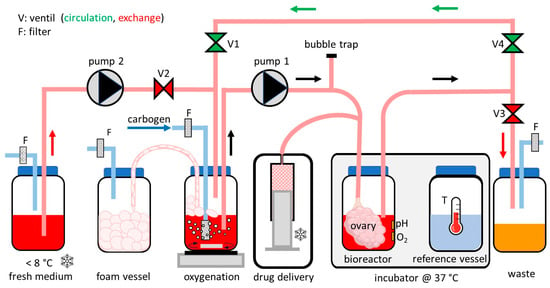
 Therapeutic Potential of Local Application of Fibroblast Growth Factor-2 to Periodontal Defects in a Preclinical Osteoporosis Model
Therapeutic Potential of Local Application of Fibroblast Growth Factor-2 to Periodontal Defects in a Preclinical Osteoporosis Model -
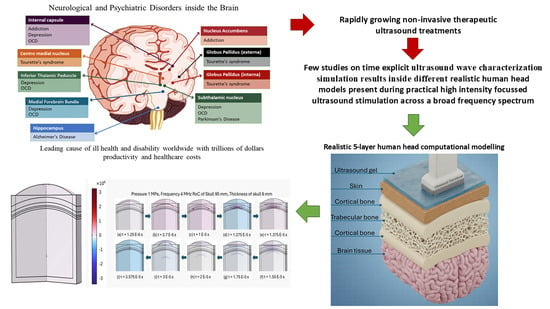
 Peripheral Nerve Regeneration Reimagined: Cutting-Edge Biomaterials and Biotechnological Innovations
Peripheral Nerve Regeneration Reimagined: Cutting-Edge Biomaterials and Biotechnological Innovations
Journal Description
Bioengineering
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, CAPlus / SciFinder, Inspec, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Engineering, Biomedical)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 19.2 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.3 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Latest Articles
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Deadline: 20 December 2025
Deadline: 31 December 2025
Deadline: 31 March 2026
Deadline: 31 May 2026
Conferences
Special Issues
Deadline: 31 October 2025
Deadline: 31 October 2025
Deadline: 31 October 2025
Deadline: 31 October 2025