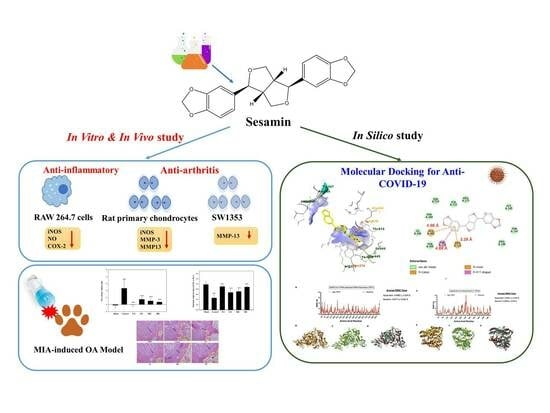
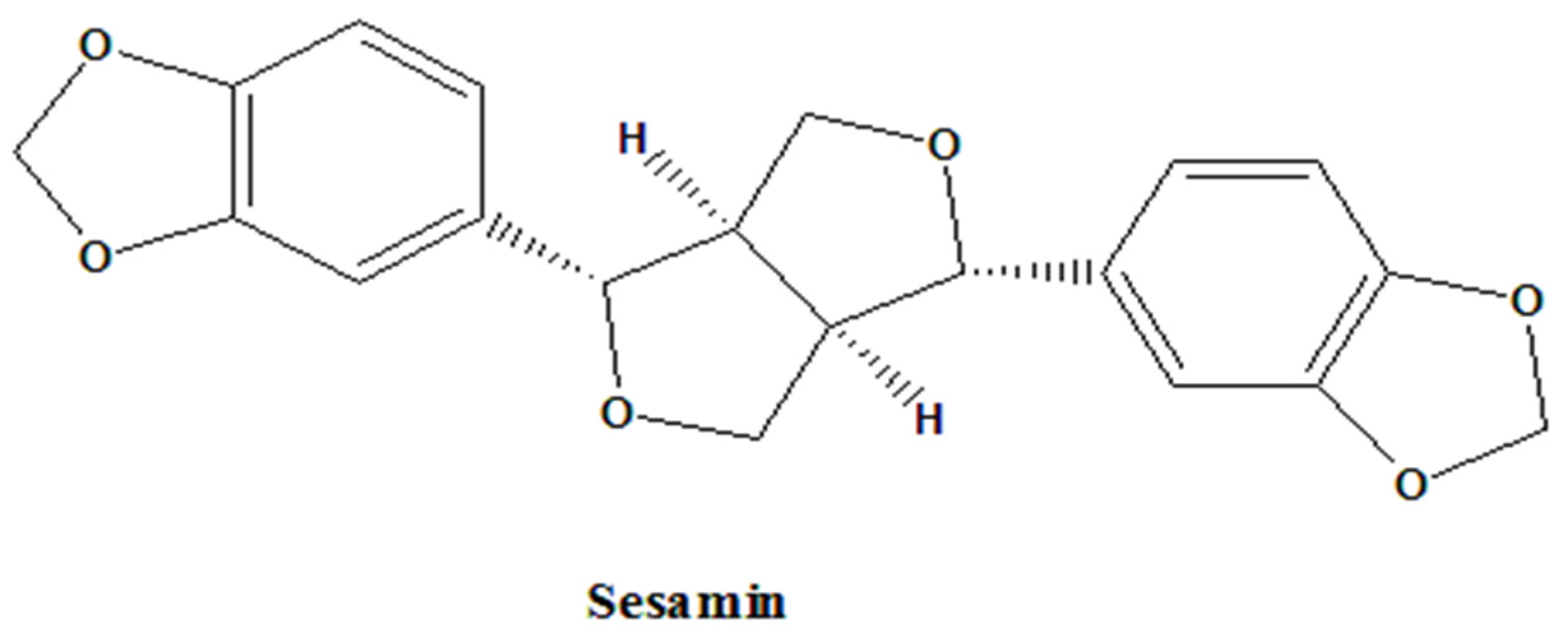
Anti-COVID-19, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anti-Osteoarthritis Activities of Sesamin from Sesamum indicum L.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagent
2.2. Anti-Inflammatory Assay
2.2.1. Rat Chondrocyte Primary Culture
2.2.2. Cell Cultures
2.2.3. 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-Diphenyltetrazolium Bromide (MTT) Assay
2.3. Animals
2.3.1. MIA-Induced OA Model
2.3.2. Histology of Cartilage and Immunohistochemistry
2.4. In Silico Analysis (for Sesamin–RdRp and ACE2)
2.4.1. Ligand Preparation
2.4.2. Protein Preparation and Validation
2.4.3. Molecular Docking Analysis
2.4.4. Molecular Dynamics Analysis
2.4.5. Pharmacophore, Drug-Likeness, and ADMET Screening
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Cell Toxicity
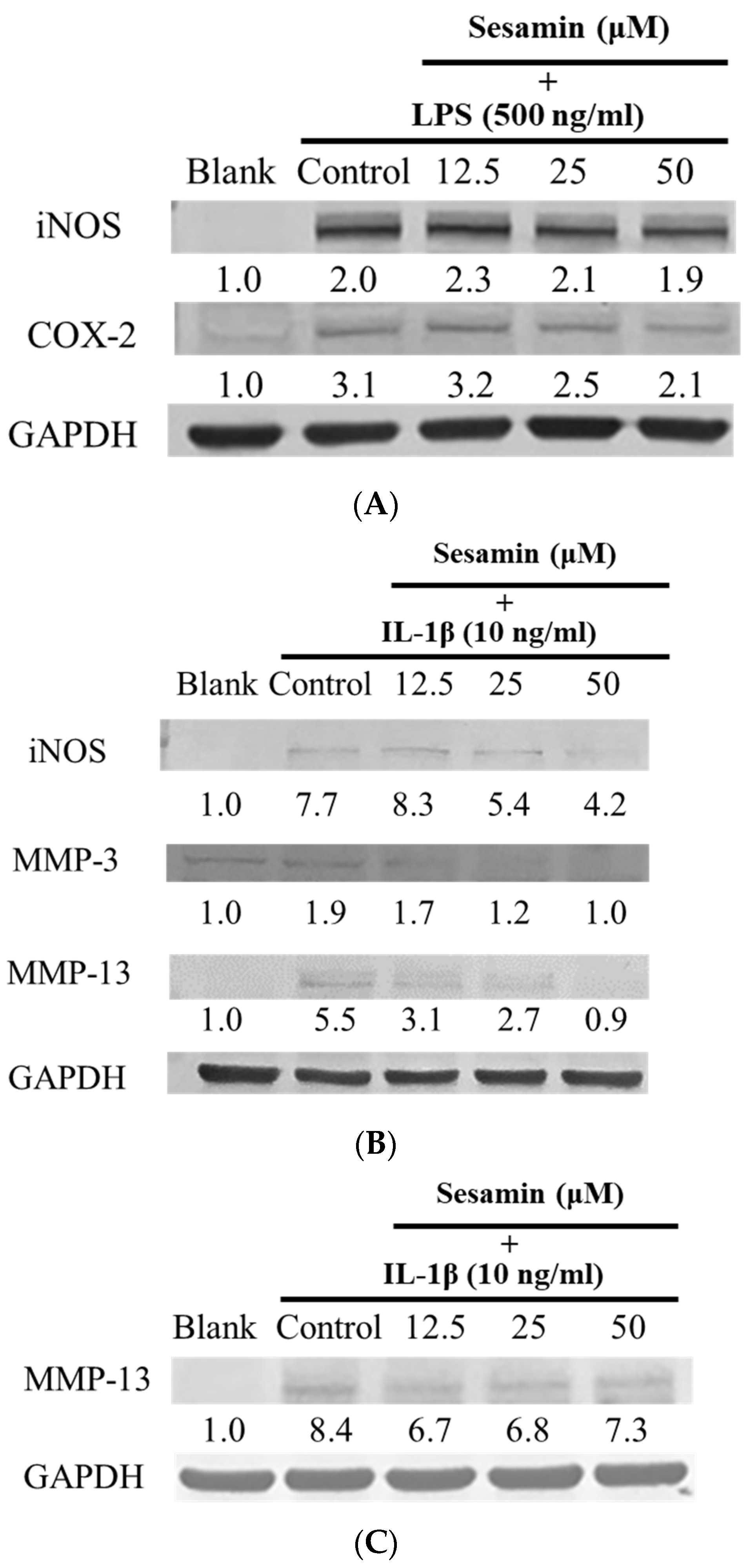
3.2. Sesamin’s Anti-Inflammatory Effects
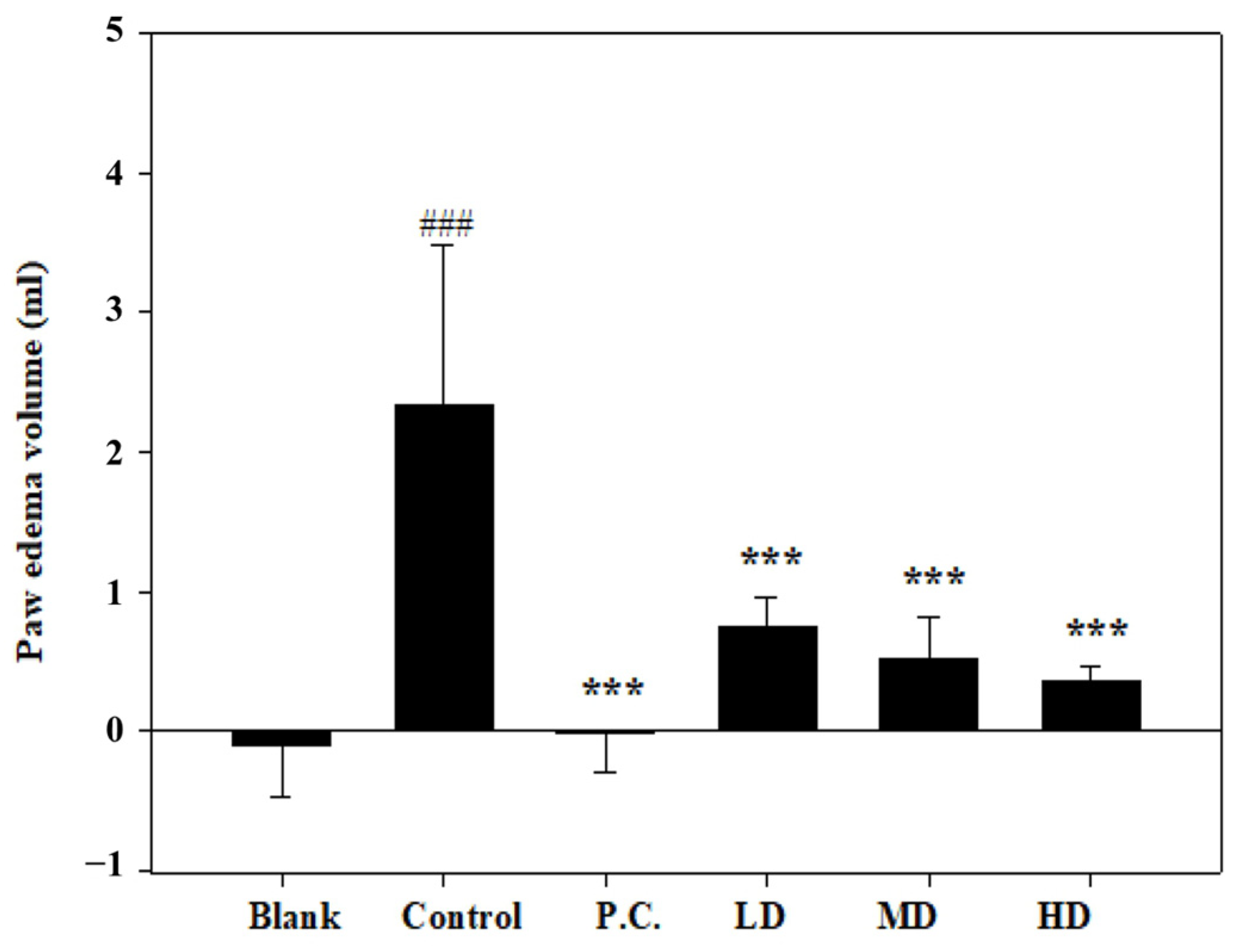
3.3. Effects of Sesamin on Paw Edema Volume
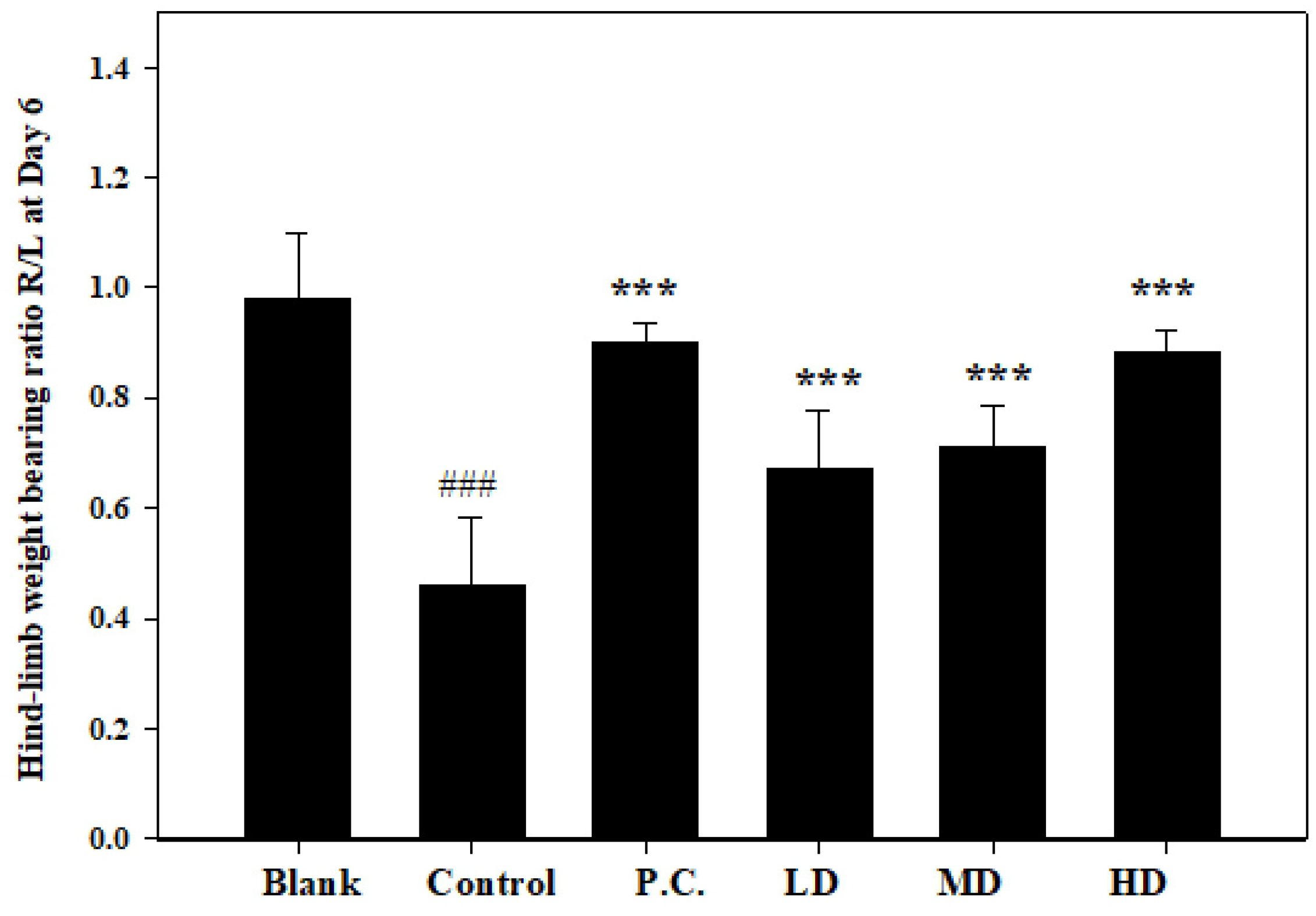
3.4. Effects of Sesamin on Hind-Limb Weight-Bearing Ratio
3.5. H&E Stain Assay
3.6. Anti-Viral Activity Screening
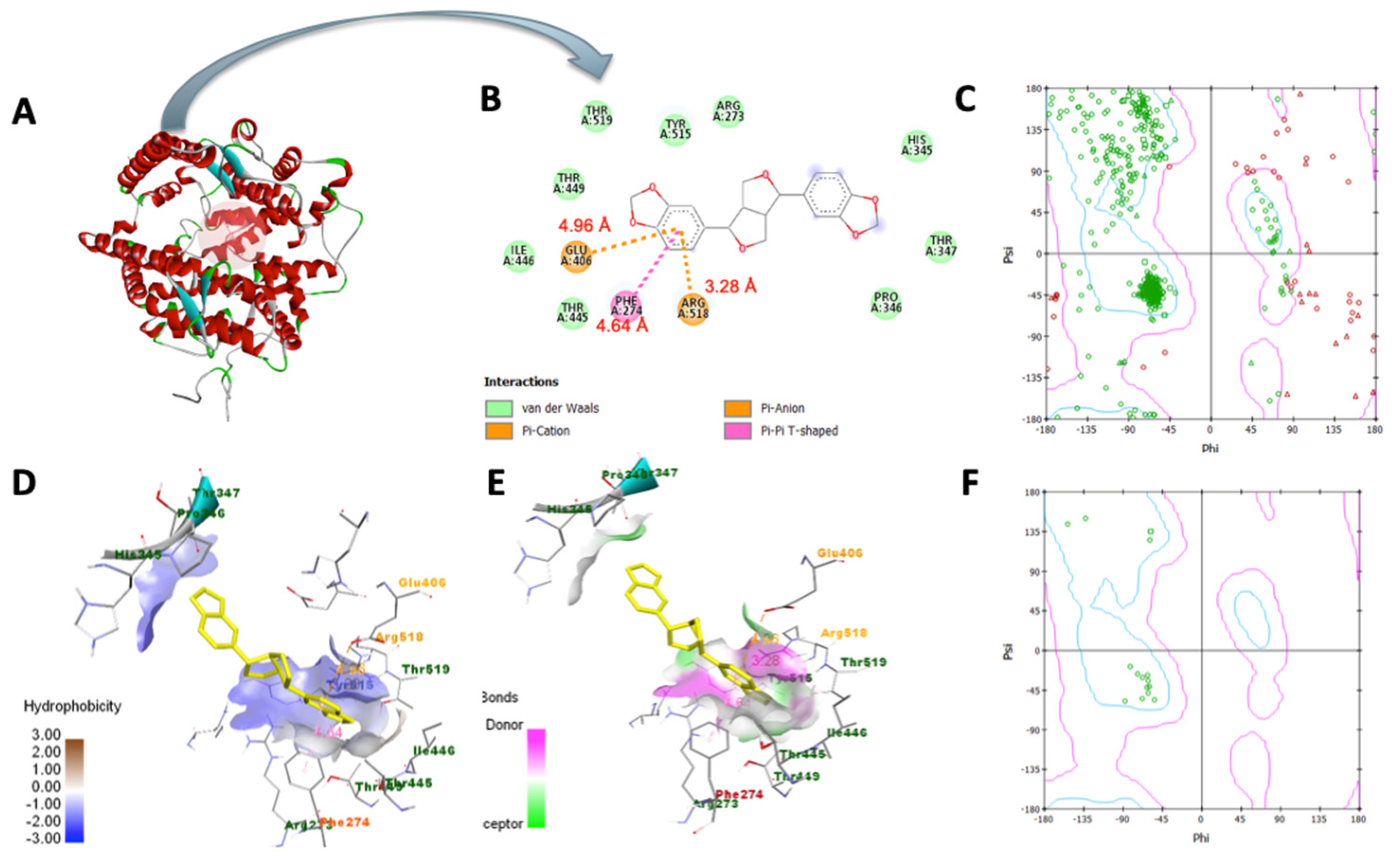
3.7. Molecular Docking Analysis
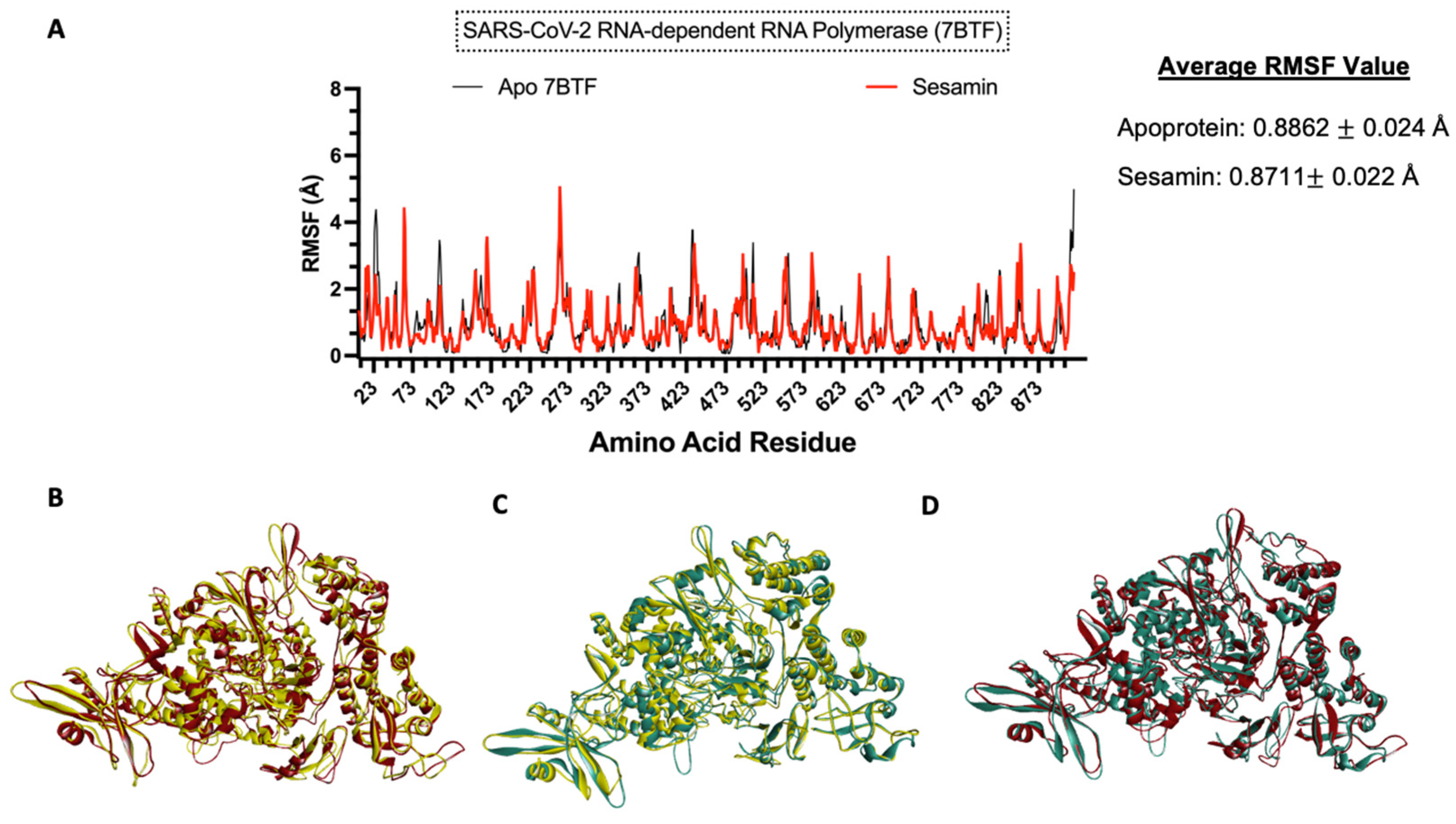
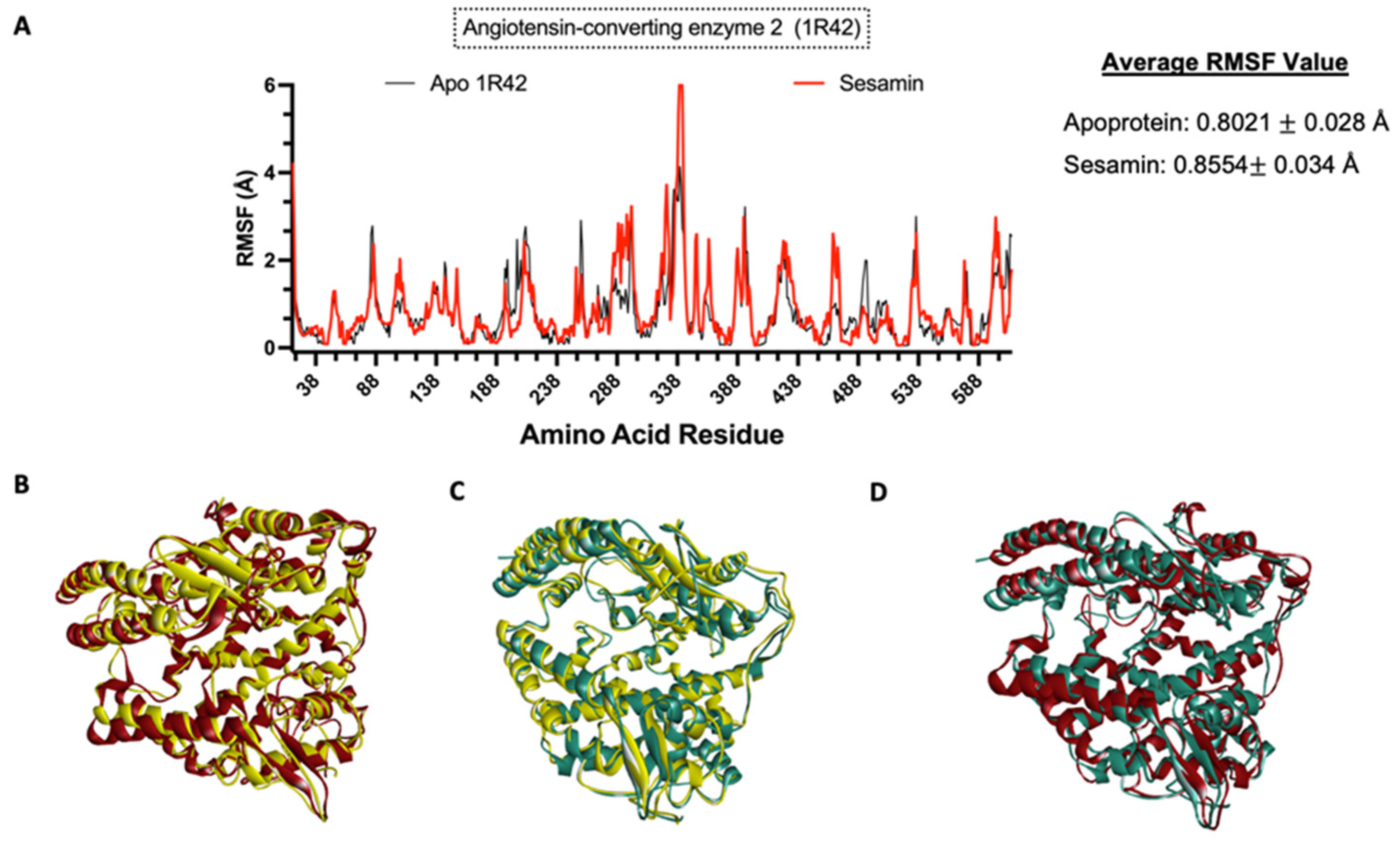
3.8. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
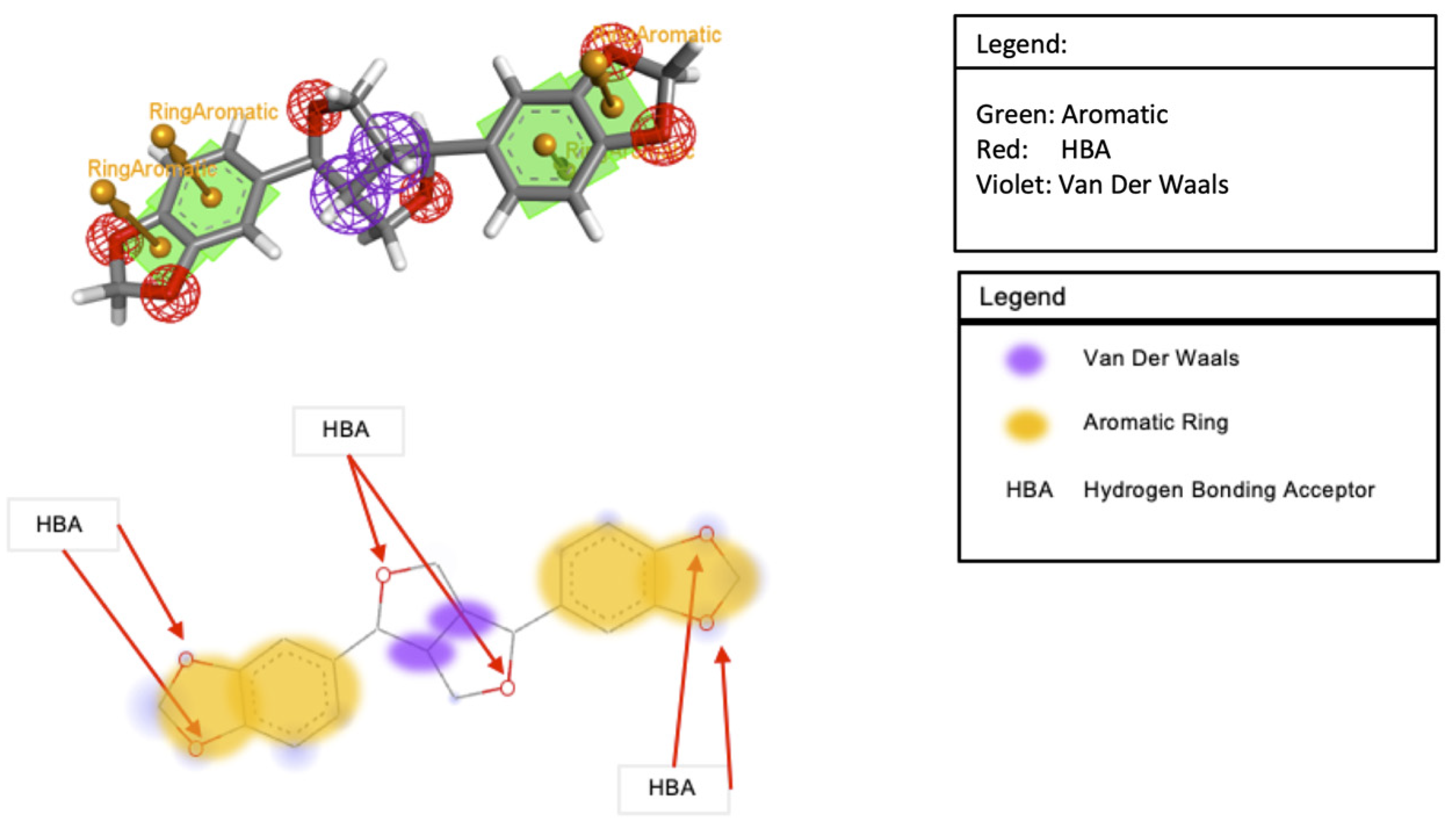
3.9. Drug-Likeness and ADMET Screening
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Docherty, A.B.; Harrison, E.M.; Green, C.A.; Hardwick, H.E.; Pius, R.; Norman, L.; Holden, K.A.; Read, J.M.; Dondelinger, F.; Carson, G. Features of 20 133 UK Patients in Hospital with Covid-19 Using the ISARIC WHO Clinical Characterisation Protocol: Prospective Observational Cohort Study. bmj 2020, 2020, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raveendran, A.V.; Jayadevan, R.; Sashidharan, S. Long COVID: An Overview. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2021, 15, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauwers, M.; Au, M.; Yuan, S.; Wen, C. COVID-19 in Joint Ageing and Osteoarthritis: Current Status and Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, A.Y.S.; MacKenna, B.; Morton, C.E.; Schultze, A.; Walker, A.J.; Bhaskaran, K.; Brown, J.P.; Rentsch, C.T.; Williamson, E.; Drysdale, H. Use of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and Risk of Death from COVID-19: An OpenSAFELY Cohort Analysis Based on Two Cohorts. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewanjee, S.; Kandimalla, R.; Kalra, R.S.; Valupadas, C.; Vallamkondu, J.; Kolli, V.; Dey Ray, S.; Reddy, A.P.; Reddy, P.H. COVID-19 and Rheumatoid Arthritis Crosstalk: Emerging Association, Therapeutic Options and Challenges. Cells 2021, 10, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quicke, J.G.; Conaghan, P.G.; Corp, N.; Peat, G. Osteoarthritis Year in Review 2021: Epidemiology & Therapy. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2021, 30, 196–206. [Google Scholar]
- Castiglione, G.M.; Zhou, L.; Xu, Z.; Neiman, Z.; Hung, C.-F.; Duh, E.J. Evolutionary Pathways to SARS-CoV-2 Resistance Are Opened and Closed by Epistasis Acting on ACE2. PLoS Biol. 2021, 19, e3001510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Krüger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.-H.; Nitsche, A. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.-L.; Wang, X.-G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.-R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.-L. A Pneumonia Outbreak Associated with a New Coronavirus of Probable Bat Origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpagnano, G.E.; Di Lecce, V.; Quaranta, V.N.; Zito, A.; Buonamico, E.; Capozza, E.; Palumbo, A.; Di Gioia, G.; Valerio, V.N.; Resta, O. Vitamin D Deficiency as a Predictor of Poor Prognosis in Patients with Acute Respiratory Failure Due to COVID-19. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2021, 44, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadizadeh, F. Supplementation with Vitamin D in the COVID-19 Pandemic? Nutr. Rev. 2021, 79, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Rathi, H.; Haq, A.; Wimalawansa, S.J.; Sharma, A. Putative Roles of Vitamin D in Modulating Immune Response and Immunopathology Associated with COVID-19. Virus Res. 2021, 292, 198235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffith, J.F. Musculoskeletal Complications of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome. Semin. Musculoskelet. Radiol. 2011, 15, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuzun, S.; Keles, A.; Okutan, D.; Yildiran, T.; Palamar, D. Assessment of musculoskeletal pain, fatigue and grip strength in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2021, 57, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-de-Las-Peñas, C.; Rodríguez-Jiménez, J.; Fuensalida-Novo, S.; Palacios-Ceña, M.; Gómez-Mayordomo, V.; Florencio, L.L.; Hernández-Barrera, V.; Arendt-Nielsen, L. Myalgia as a Symptom at Hospital Admission by Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection Is Associated with Persistent Musculoskeletal Pain as Long-Term Post-COVID Sequelae: A Case-Control Study. Pain 2021, 162, 2832–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosato, M.; Carfì, A.; Martis, I.; Pais, C.; Ciciarello, F.; Rota, E.; Tritto, M.; Salerno, A.; Zazzara, M.B.; Martone, A.M. Prevalence and Predictors of Persistence of COVID-19 Symptoms in Older Adults: A Single-Center Study. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2021, 22, 1840–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiyegbusi, O.L.; Hughes, S.E.; Turner, G.; Rivera, S.C.; McMullan, C.; Chandan, J.S.; Haroon, S.; Price, G.; Davies, E.H.; Nirantharakumar, K. Symptoms, Complications and Management of Long COVID: A Review. J. R. Soc. Med. 2021, 114, 428–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vehar, S.; Boushra, M.; Ntiamoah, P.; Biehl, M. Post-Acute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Caring for the ‘Long-Haulers. ’ Cleve Clin. J. Med. 2021, 88, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, J.H.; Rai, V.; Dilisio, M.F.; Agrawal, D.K. Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns in the Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis: Potentially Novel Therapeutic Targets. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2017, 434, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolove, J.; Lepus, C.M. Role of Inflammation in the Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis: Latest Findings and Interpretations. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2013, 5, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayami, T.; Pickarski, M.; Zhuo, Y.; Wesolowski, G.A.; Rodan, G.A.; Duong, L.E.T. Characterization of Articular Cartilage and Subchondral Bone Changes in the Rat Anterior Cruciate Ligament Transection and Meniscectomized Models of Osteoarthritis. Bone 2006, 38, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearle, A.D.; Warren, R.F.; Rodeo, S.A. Basic Science of Articular Cartilage and Osteoarthritis. Clin. Sports Med. 2005, 24, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldring, M.B. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage: The Role of Cytokines. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2000, 2, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rietschel, E.T.; Kirikae, T.; Schade, F.U.; Mamat, U.; Schmidt, G.; Loppnow, H.; Ulmer, A.J.; Zähringer, U.; Seydel, U.; di Padova, F. Bacterial Endotoxin: Molecular Relationships of Structure to Activity and Function. FASEB J. 1994, 8, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, A.W.M.; Stabler, T.V.; Bolognesi, M.; Kraus, V.B. Selenomethionine Inhibits IL-1β Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase (INOS) and Cyclooxygenase 2 (COX2) Expression in Primary Human Chondrocytes. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2011, 19, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daheshia, M.; Yao, J.Q. The Interleukin 1β Pathway in the Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2008, 35, 2306–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Struglics, A.; Larsson, S.; Pratta, M.A.; Kumar, S.; Lark, M.W.; Lohmander, L.S. Human Osteoarthritis Synovial Fluid and Joint Cartilage Contain Both Aggrecanase-and Matrix Metalloproteinase-Generated Aggrecan Fragments. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2006, 14, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, P.G.; Magna, H.A.; Reeves, L.M.; Lopresti-Morrow, L.L.; Yocum, S.A.; Rosner, P.J.; Geoghegan, K.F.; Hambor, J.E. Cloning, Expression, and Type II Collagenolytic Activity of Matrix Metalloproteinase-13 from Human Osteoarthritic Cartilage. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 97, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grougnet, R.; Magiatis, P.; Laborie, H.; Lazarou, D.; Papadopoulos, A.; Skaltsounis, A.-L. Sesamolinol Glucoside, Disaminyl Ether, and Other Lignans from Sesame Seeds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, N.; Sanjay, K.R.; Prasad, D.S.; Vijay, N.; Kothari, R. Nutrition & Food. J. Nutr. 2012, 2, 1000127. [Google Scholar]
- Anilakumar, K.R.; Pal, A.; Khanum, F.; Bawa, A.S. Nutritional, Medicinal and Industrial Uses of Sesame (Sesamum Indicum L.) Seeds-an Overview. Agric. Conspec. Sci. 2010, 75, 159–168. [Google Scholar]
- Mukta, N.; Neeta, P.M. A Review on Sesame-an Ethno Medicinally Significant Oil Crop. Int. J. Life Sci. Pharma Res. 2017, 7, L58–L63. [Google Scholar]
- Bedigian, D. History and Lore of Sesame in Southwest Asia. Econ. Bot. 2004, 58, 329–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedigian, D.; Harlan, J.R. Evidence for Cultivation of Sesame in the Ancient World. Econ. Bot. 1986, 40, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Raj, S.K.; Snehi, S.K. first report of’candidatus phytoplasma asteris’affecting sesame cultivation in india. J. Plant Pathol. 2007, 89, 301. [Google Scholar]
- Saydut, A.; Duz, M.Z.; Kaya, C.; Kafadar, A.B.; Hamamci, C. Transesterified Sesame (Sesamum Indicum L.) Seed Oil as a Biodiesel Fuel. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 6656–6660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moazzami, A.A. Sesame Seed Lignans Diversity, Human Metabolism and Bioactivities; Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences: Uppsala, Sweden, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Pathak, N.; Rai, A.K.; Kumari, R.; Bhat, K. v Value Addition in Sesame: A Perspective on Bioactive Components for Enhancing Utility and Profitability. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2014, 8, 147. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schwertner, H.A.; Rios, D.C. Analysis of Sesamin, Asarinin, and Sesamolin by HPLC with Photodiode and Fluorescent Detection and by GC/MS: Application to Sesame Oil and Serum Samples. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2012, 89, 1943–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, T.S.M.; Basha, S.D.; Mahesh, G.; Rani, P.V.S.; Kumar, N.S.; Chetty, C.M. Analgesic, Anti-Pyretic and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Dietary Sesame Oil in Experimental Animal Models. Pharmacologia 2011, 2, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periasamy, S.; Chien, S.-P.; Chang, P.-C.; Hsu, D.-Z.; Liu, M.-Y. Sesame Oil Mitigates Nutritional Steatohepatitis via Attenuation of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation: A Tale of Two-Hit Hypothesis. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 25, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-T.; Liu, M.-Y. Daily Sesame Oil Supplementation Attenuates Local Renin-Angiotensin System via Inhibiting MAPK Activation and Oxidative Stress in Cardiac Hypertrophy. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 42, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, J.; Ge, J.; Yu, J.; Shan, S.; Zhou, H.; Fan, S.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; et al. Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor-Binding Domain Bound to the ACE2 Receptor. Nature 2020, 581, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Boyle, N.M.; Banck, M.; James, C.A.; Morley, C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Hutchison, G.R. Open Babel: An Open Chemical Toolbox. J. Cheminform. 2011, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizvi, S.M.D.; Shakil, S.; Haneef, M. A Simple Click by Click Protocol to Perform Docking: AutoDock 4.2 Made Easy for Non-Bioinformaticians. EXCLI J. 2013, 12, 831. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, R.J.; Weng, Z.; Campbell, R.K.; Jiang, X. Main-chain Conformational Tendencies of Amino Acids. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2005, 60, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doharey, P.K.; Singh, V.; Gedda, M.R.; Sahoo, A.K.; Varadwaj, P.K.; Sharma, B. In Silico Study Indicates Antimalarials as Direct Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2-RNA Dependent RNA Polymerase. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 5588–5605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eweas, A.F.; Alhossary, A.A.; Abdel-Moneim, A.S. Molecular Docking Reveals Ivermectin and Remdesivir as Potential Repurposed Drugs against SARS-CoV-2. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 2021, 3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the Speed and Accuracy of Docking with a New Scoring Function, Efficient Optimization, and Multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriata, A.; Gierut, A.M.; Oleniecki, T.; Ciemny, M.P.; Kolinski, A.; Kurcinski, M.; Kmiecik, S. CABS-Flex 2.0: A Web Server for Fast Simulations of Flexibility of Protein Structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W338–W343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneidman-Duhovny, D.; Dror, O.; Inbar, Y.; Nussinov, R.; Wolfson, H.J. PharmaGist: A Webserver for Ligand-Based Pharmacophore Detection. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, W223–W228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barratt, E.; Bingham, R.J.; Warner, D.J.; Laughton, C.A.; Phillips, S.E.V.; Homans, S.W. Van Der Waals Interactions Dominate Ligand− Protein Association in a Protein Binding Site Occluded from Solvent Water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 11827–11834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, E.A.; Castellano, R.K.; Diederich, F. Interactions with Aromatic Rings in Chemical and Biological Recognition. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 1210–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.-F.; Wang, M.-Y.; Wang, D.; Li, J.-Y.; Hao, G.-F.; Li, Q.X.; Yang, G.-F. A Comprehensive Analysis of Protein Data Bank Reveals Low Desolvation Penalty in π-Cation System. Chem. Biol. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard, R.E.; Haider, M.K. Hydrogen Bonds in Proteins: Role and Strength. eLS 2010, 2010, 112. [Google Scholar]
- Raschka, S.; Wolf, A.J.; Bemister-Buffington, J.; Kuhn, L.A. Protein–Ligand Interfaces Are Polarized: Discovery of a Strong Trend for Intermolecular Hydrogen Bonds to Favor Donors on the Protein Side with Implications for Predicting and Designing Ligand Complexes. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2018, 32, 511–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, J.P.K.; Dangerfield, T.L.; Taylor, D.W.; Johnson, K.A. Remdesivir Is a Delayed Translocation Inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 Replication. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 1548–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez, B.G.; Santos, M.S.; Ferrarini, M.; Fernandes, J.P.S. Evaluation of Blockbuster Drugs under the Rule-of-Five. Pharm. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 65, 148–152. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Li, C.; Liu, G.; Liu, R.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Cao, Z.; Zhao, B.; Lu, C.; Liu, Y. Drug-Metabolizing Cytochrome P450 Enzymes Have Multifarious Influences on Treatment Outcomes. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2021, 60, 585–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, M.M.; Pang, K.S. First-Pass Effect: Significance of the Intestine for Absorption and Metabolism. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 1997, 20, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackman, R.L. Phosphoramidate Prodrugs Continue to Deliver, The Journey of Remdesivir (GS-5734) from RSV to SARS-CoV-2. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi-Boroujeni, A.; Mahmoudian-Sani, M.; Bahadoram, M.; Alghasi, A. COVID-19: A Case for Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome, Suppression of Inflammation with Curcumin? Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2021, 128, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fara, A.; Mitrev, Z.; Rosalia, R.A.; Assas, B.M. Cytokine Storm and COVID-19: A Chronicle of pro-Inflammatory Cytokines. Open Biol. 2020, 10, 200160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomão, R.; Assis, V.; de Sousa Neto, I.V.; Petriz, B.; Babault, N.; Durigan, J.L.Q.; de Cássia Marqueti, R. Involvement of Matrix Metalloproteinases in COVID-19: Molecular Targets, Mechanisms, and Insights for Therapeutic Interventions. Biology 2023, 12, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelzo, M.; Cacciapuoti, S.; Pinchera, B.; De Rosa, A.; Cernera, G.; Scialò, F.; Comegna, M.; Mormile, M.; Fabbrocini, G.; Parrella, R.; et al. Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMP) 3 and 9 as Biomarkers of Severity in COVID-19 Patients. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phitak, T.; Pothacharoen, P.; Settakorn, J.; Poompimol, W.; Caterson, B.; Kongtawelert, P. Chondroprotective and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Sesamin. Phytochemistry 2012, 80, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, P.; Chen, G.; Jiang, A.; Wang, Y.; Song, C.; Zhuang, J.; Xi, C.; Wang, G.; Ji, Y.; Yan, J. Sesamin Inhibits IL-1β-Stimulated Inflammatory Response in Human Osteoarthritis Chondrocytes by Activating Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 83720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Towler, P.; Staker, B.; Prasad, S.G.; Menon, S.; Tang, J.; Parsons, T.; Ryan, D.; Fisher, M.; Williams, D.; Dales, N.A. ACE2 X-Ray Structures Reveal a Large Hinge-Bending Motion Important for Inhibitor Binding and Catalysis. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 17996–18007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vangeel, L.; Chiu, W.; De Jonghe, S.; Maes, P.; Slechten, B.; Raymenants, J.; André, E.; Leyssen, P.; Neyts, J.; Jochmans, D. Remdesivir, Molnupiravir and Nirmatrelvir Remain Active against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron and Other Variants of Concern. Antivir. Res. 2022, 198, 105252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takashita, E.; Yamayoshi, S.; Simon, V.; van Bakel, H.; Sordillo, E.M.; Pekosz, A.; Fukushi, S.; Suzuki, T.; Maeda, K.; Halfmann, P.; et al. Efficacy of Antibodies and Anti-viral Drugs against Omicron BA.2.12.1, BA.4, and BA.5 Subvariants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 468–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, I.; Pawara, R.; Surana, S.; Patel, H. The Repurposed ACE2 Inhibitors: SARS-CoV-2 Entry Blockers of COVID-19. Top. Curr. Chem. 2021, 379, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Target | PDB Code | Grid Parameters of the Binding Site | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coordinates | Size | |||
| Viral RdRp | 7BTF | x = 127.0598 | x = 14 | [47] |
| y = 124.6167 | y = 14 | |||
| z = 128.7631 | z =14 | |||
| ACE2 | 1R42 | x = 52.292033 | x = 10 | [48] |
| y = 62.932978 | y = 10 | |||
| z = 29.089189 | z = 10 | |||
| Target Protein | Verify3D ≥ 80% | ERRAT ≥ 50% | Ramachandran Plot (Amino Acid in the Preferred Region) ≥ 95% |
|---|---|---|---|
| SARS-CoV-2 Viral RdRp | 82.44 | 89.264 | 99.551 |
| Human ACE2 | 92.13 | 95.068 | 98.881 |
| Ligand | Sesamin | Remdesivir | MLN-4760 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binding Energy (kcal/mol) | SARS-CoV-2 RdRp | −6.6 | −6.1 | n.a. |
| Human ACE2 | −5.1 | n.a. | −4.8 |
| Compound | Sesamin | Remdesivir | MLN-4760 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C20H18O6 | C27H35N6O8P | C19H23Cl2N3O4 |
| Molecular Weight (Da) ≤ 500 | 354.11 | 602.60 | 428.30 |
| Log p ≤ 5 | 4.051 | 1.761 | 0.836 |
| HBA p ≤ 5 | 0 | 5 | 3 |
| HBD p ≤ 10 | 6 | 14 | 7 |
| TPSA (Å2) ≤ 140 Å2 | 55.38 | 204.28 | 104.45 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, S.-M.; Hsieh, C.-Y.; Ting, J.U.; De Castro-Cruz, K.A.; Wang, C.-C.; Lee, C.-J.; Tsai, P.-W. Anti-COVID-19, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anti-Osteoarthritis Activities of Sesamin from Sesamum indicum L. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10111263
Huang S-M, Hsieh C-Y, Ting JU, De Castro-Cruz KA, Wang C-C, Lee C-J, Tsai P-W. Anti-COVID-19, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anti-Osteoarthritis Activities of Sesamin from Sesamum indicum L. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(11):1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10111263
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Shu-Ming, Cheng-Yang Hsieh, Jasmine U. Ting, Kathlia A. De Castro-Cruz, Ching-Chiung Wang, Chia-Jung Lee, and Po-Wei Tsai. 2023. "Anti-COVID-19, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anti-Osteoarthritis Activities of Sesamin from Sesamum indicum L." Bioengineering 10, no. 11: 1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10111263
APA StyleHuang, S.-M., Hsieh, C.-Y., Ting, J. U., De Castro-Cruz, K. A., Wang, C.-C., Lee, C.-J., & Tsai, P.-W. (2023). Anti-COVID-19, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anti-Osteoarthritis Activities of Sesamin from Sesamum indicum L. Bioengineering, 10(11), 1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10111263