Multi-Modal Data Correspondence for the 4D Analysis of the Spine with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
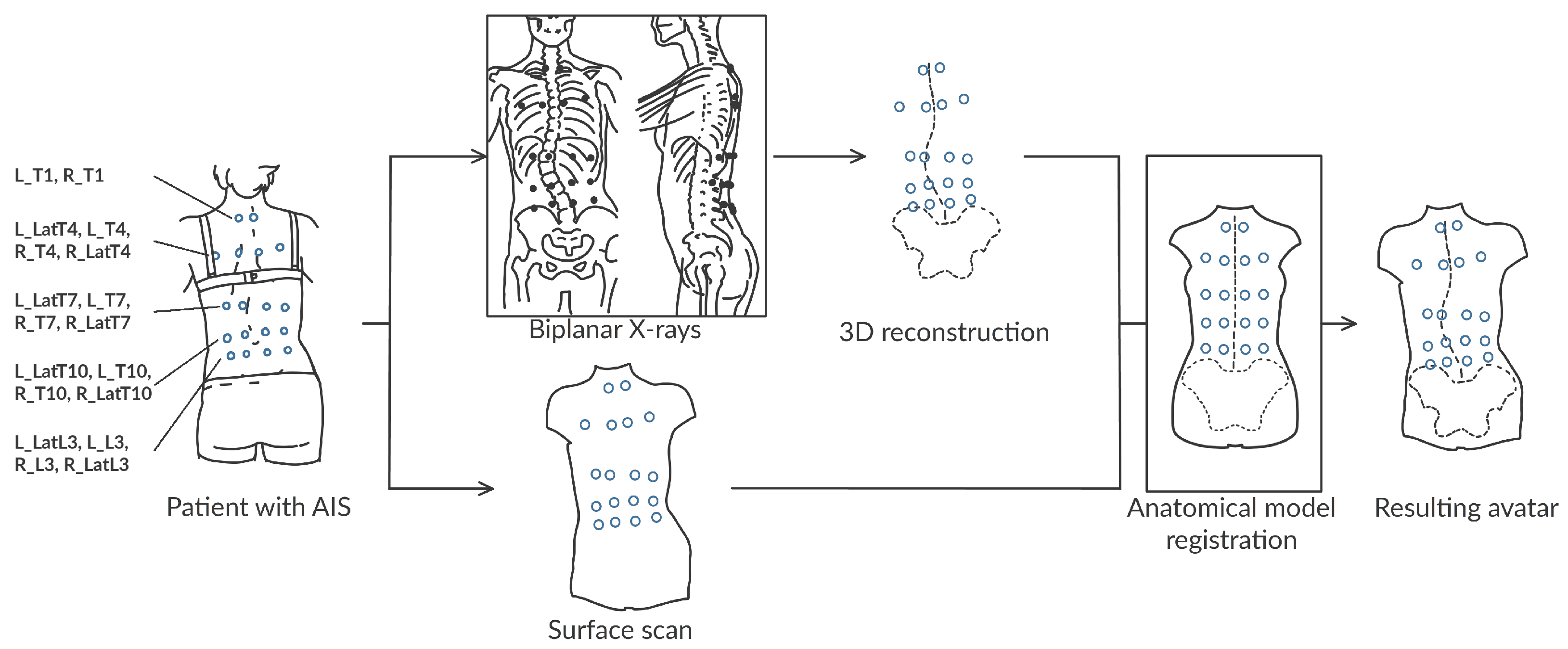
2.1. Collected Data
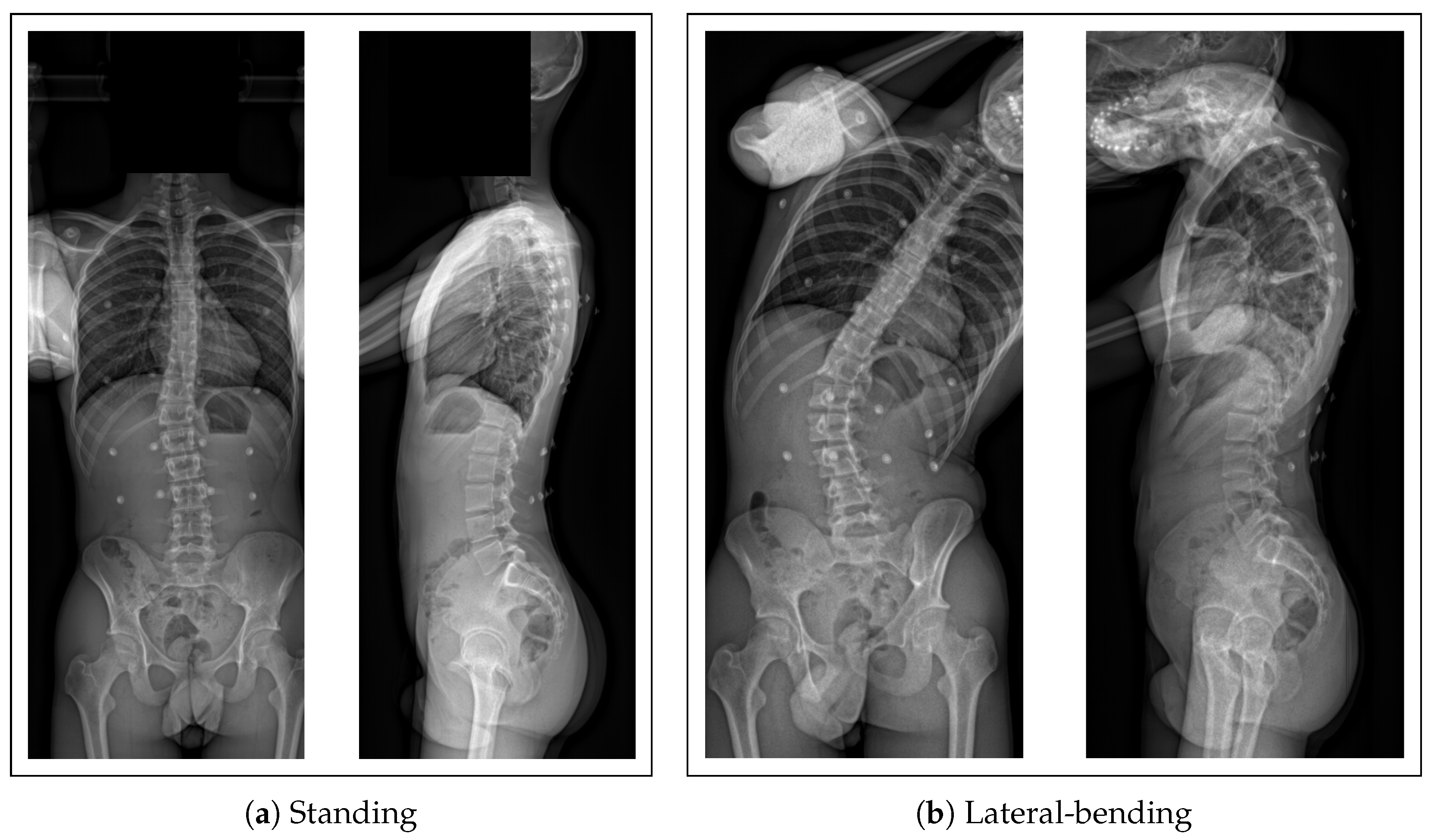
- A biplanar X-ray of their trunk made with an EOS imaging system
- A surface scan of the back using an Occipital Structure Sensor Mark II (XRPro, LLC, Saratov)
2.2. Data Processing
2.3. The Subject-Specific Kinematic Model
2.4. Accuracy of the Anatomical Model
2.5. Validation of the Kinematic Predictions
3. Results
3.1. Accuracy of the Subject-Specific Model in Standing
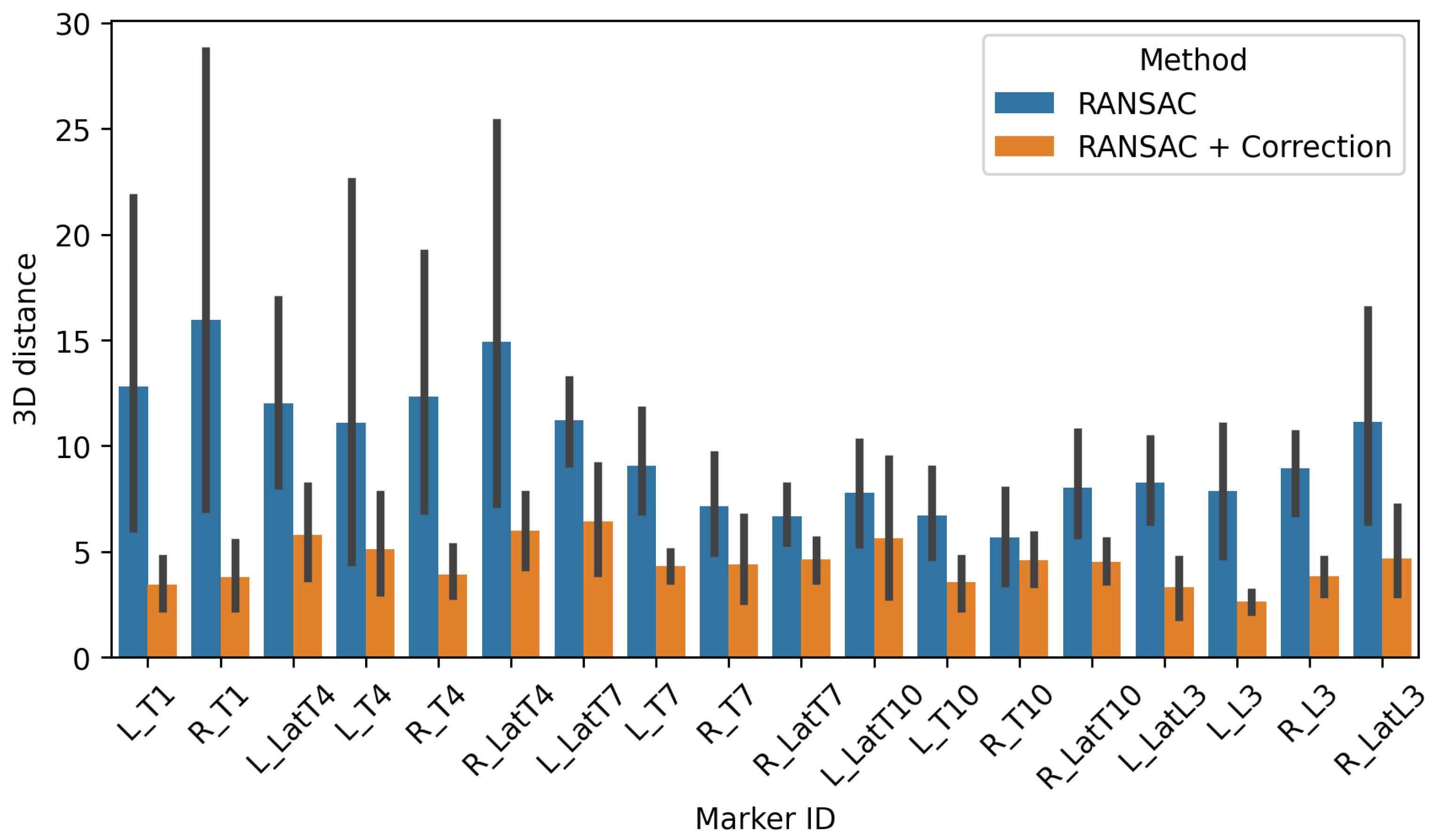
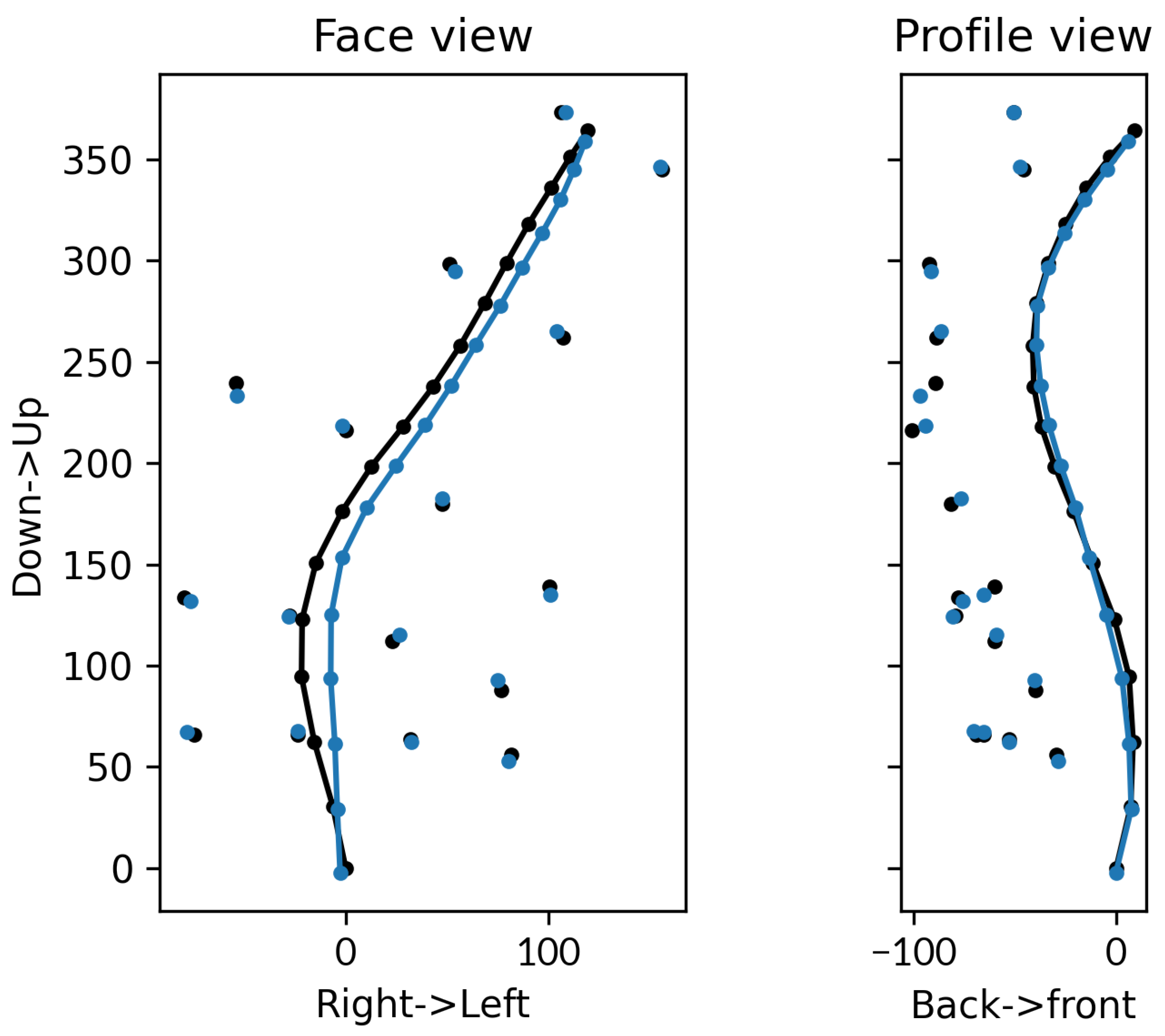
3.1.1. External Accuracy
3.1.2. Internal Accuracy
3.2. Accuracy of the Subject-Specific Model in Bending
3.2.1. External Accuracy
3.2.2. Internal Accuracy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AIS | Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis |
| DOF | Degrees-of-freedom |
| MAE | Mean absolute error |
| ISB | International Society of Biomechanics |
| RANSAC | RANdom SAmple Consensus |
References
- Weinstein, S.L.; Dolan, L.A.; Cheng, J.C.; Danielsson, A.; Morcuende, J.A. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Lancet 2008, 371, 1527–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Addai, D.; Zarkos, J.; Bowey, A.J. Current concepts in the diagnosis and management of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2020, 36, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Kim, H.S.; Moon, E.S.; Yoon, C.S.; Chung, T.S.; Song, H.T.; Suh, J.S.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, S. Scoliosis imaging: What Radiologists should know. Radiographics 2010, 30, 1823–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skalli, W.; Vergari, C.; Ebermeyer, E.; Courtois, I.; Drevelle, X.; Kohler, R.; Abelin-Genevois, K.; Dubousset, J. Early Detection of Progressive Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Severity Index. Spine 2017, 42, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, S.; Studer, D.; Hasler, C.C.; Romkes, J.; Taylor, W.R.; Lorenzetti, S.; Brunner, R. Quantifying spinal gait kinematics using an enhanced optical motion capture approach in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Gait Posture 2016, 44, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severijns, P.; Overbergh, T.; Thauvoye, A.; Baudewijns, J.; Monari, D.; Moke, L.; Desloovere, K.; Scheys, L. A subject-specific method to measure dynamic spinal alignment in adult spinal deformity. Spine J. 2020, 20, 934–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overbergh, T.; Severijns, P.; Beaucage-Gauvreau, E.; Jonkers, I.; Moke, L.; Scheys, L. Development and validation of a modeling workflow for the generation of image-based, subject-specific thoracolumbar models of spinal deformity. J. Biomech. 2020, 110, 109946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, S.; Studer, D.; Hasler, C.C.; Romkes, J.; Taylor, W.R.; Brunner, R.; Lorenzetti, S. Using Skin Markers for Spinal Curvature Quantification in Main Thoracic Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: An Explorative Radiographic Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Desroches, G.; Aubin, C.E.; Sucato, D.J.; Rivard, C.H. Simulation of an anterior spine instrumentation in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis using a flexible multi-body model. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2007, 45, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courvoisier, A.; Nesme, M.; Gerbelot, J.; Moreau-Gaudry, A.; Faure, F. Prediction of brace effect in scoliotic patients: Blinded evaluation of a novel brace simulator—An observational cross-sectional study. Eur. Spine J. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasser, M.R.; Gerber, G.; Passaplan, C.; Cornaz, F.; Snedeker, J.G.; Farshad, M.; Widmer, J. Computational model predicts risk of spinal screw loosening in patients. Eur. Spine J. 2022, 31, 2639–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humbert, L.; Guise, J.D.; Aubert, B.; Godbout, B.; Skalli, W. 3D reconstruction of the spine from biplanar X-rays using parametric models based on transversal and longitudinal inferences. Med. Eng. Phys. 2009, 31, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groisser, B. Geometry of the EOS(R) Radiographic Scanner. arXiv 2019, arXiv:eess.IV/1904.06711. [Google Scholar]
- Fischler, M.A.; Bolles, R.C. Random Sample Consensus: A Paradigm for Model Fitting with Applications to Image Analysis and Automated Cartography. Commun. ACM 1981, 24, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicko, A.H.; Liu, T.; Gilles, B.; Kavan, L.; Faure, F.; Palombi, O.; Cani, M.P. Anatomy Transfer. ACM Trans. Graph. 2013, 32, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasegawa, K.; Amabile, C.; Nesme, M.; Dubousset, J. Gravity center estimation for evaluation of standing whole body compensation using virtual barycentremetry based on biplanar slot-scanning stereoradiography-validation by simultaneous force plate measurement. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignasiak, D.; Dendorfer, S.; Ferguson, S.J. Thoracolumbar spine model with articulated ribcage for the prediction of dynamic spinal loading. J. Biomech. 2016, 49, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutras, C.; Perez, J.; Kardash, K.; Otaduy, M.A. A Study of the Sensitivity of Biomechanical Models of the Spine for Scoliosis Brace Design. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Siegler, S.; Allard, P.; Kirtley, C.; Leardini, A.; Rosenbaum, D.; Whittle, M.; D’Lima, D.D.; Cristofolini, L.; Witte, H.; et al. ISB recommendation on definitions of joint coordinate system of various joints for the reporting of human joint motion—Part I: Ankle, hip, and spine. J. Biomech. 2002, 35, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groisser, B.; Kimmel, R.; Feldman, G.; Rozen, N.; Wolf, A. 3D Reconstruction of Scoliotic Spines from Stereoradiography and Depth Imaging. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 46, 1206–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Joint Region | Shear | Compr. | Flex.-Ext. | Ax.-Rotation | Lat. Bending |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thoracic | 262 | 1720 | 286 | 177 | 223 |
| Lumbar | 245 | 1720 | 143 | 498 | 149 |
| ID | Positions (mm) | Orientations (deg) | Shape (mm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D Distance | Anteropos. | Mediolat. | Inferosup. | Coronal | Sagittal | Axial | P.-t.-S. Distance | |
| T01 | 1.32 (3.28) | 1.05 (2.78) | 0.7 (1.78) | 0.11 (0.18) | 1.67 (2.92) | 1.98 (2.6) | 3.58 (5.33) | 0.31 (0.33) |
| T02 | 0.33 (0.7) | 0.15 (0.26) | 0.27 (0.66) | 0.06 (0.08) | 1.25 (1.23) | 3.19 (2.34) | 1.55 (1.09) | 0.28 (0.27) |
| T03 | 0.17 (0.18) | 0.14 (0.19) | 0.06 (0.04) | 0.05 (0.06) | 1.33 (0.77) | 7.22 (4.66) | 1.87 (1.38) | 0.28 (0.25) |
| T04 | 0.27 (0.28) | 0.23 (0.26) | 0.06 (0.06) | 0.1 (0.12) | 2.16 (1.44) | 3.4 (3.69) | 1.28 (0.86) | 0.31 (0.28) |
| T05 | 0.18 (0.23) | 0.14 (0.23) | 0.04 (0.02) | 0.07 (0.09) | 2.77 (2.98) | 1.52 (1.0) | 1.67 (0.53) | 0.29 (0.28) |
| T06 | 0.07 (0.06) | 0.06 (0.06) | 0.03 (0.02) | 0.02 (0.01) | 1.48 (1.55) | 2.14 (1.47) | 2.47 (2.23) | 0.26 (0.24) |
| T07 | 0.24 (0.25) | 0.15 (0.2) | 0.09 (0.08) | 0.15 (0.14) | 1.04 (1.52) | 2.23 (1.56) | 1.17 (1.13) | 0.31 (0.28) |
| T08 | 0.13 (0.06) | 0.1 (0.06) | 0.03 (0.02) | 0.06 (0.04) | 0.92 (0.79) | 5.14 (2.36) | 3.07 (3.09) | 0.29 (0.31) |
| T09 | 0.15 (0.07) | 0.12 (0.08) | 0.06 (0.04) | 0.03 (0.04) | 1.17 (0.58) | 4.35 (2.29) | 2.29 (3.84) | 0.28 (0.25) |
| T10 | 0.14 (0.06) | 0.11 (0.08) | 0.04 (0.03) | 0.04 (0.02) | 1.79 (0.96) | 7.8 (3.5) | 4.21 (3.44) | 0.31 (0.3) |
| T11 | 0.21 (0.23) | 0.16 (0.16) | 0.05 (0.06) | 0.12 (0.17) | 1.4 (0.87) | 8.11 (2.24) | 2.63 (2.21) | 0.3 (0.28) |
| T12 | 0.12 (0.15) | 0.09 (0.14) | 0.05 (0.07) | 0.04 (0.04) | 1.34 (0.63) | 1.63 (1.56) | 2.27 (2.02) | 0.29 (0.27) |
| L01 | 0.19 (0.28) | 0.14 (0.28) | 0.07 (0.04) | 0.06 (0.09) | 1.78 (1.83) | 3.84 (3.28) | 1.79 (1.17) | 0.31 (0.3) |
| L02 | 0.29 (0.27) | 0.24 (0.27) | 0.07 (0.06) | 0.1 (0.12) | 1.57 (1.61) | 5.43 (4.81) | 4.66 (8.08) | 0.28 (0.26) |
| L03 | 0.31 (0.27) | 0.28 (0.24) | 0.05 (0.06) | 0.1 (0.14) | 2.62 (3.85) | 4.74 (1.3) | 2.79 (2.64) | 0.28 (0.26) |
| L04 | 0.44 (0.23) | 0.43 (0.22) | 0.05 (0.06) | 0.06 (0.06) | 1.16 (1.22) | 5.74 (2.15) | 3.04 (5.16) | 0.31 (0.29) |
| L05 | 0.61 (0.29) | 0.58 (0.26) | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.15 (0.09) | 1.65 (1.4) | 2.37 (2.25) | 3.7 (5.79) | 0.3 (0.28) |
| All | 0.31 (0.83) | 0.25 (0.70) | 0.11 (0.46) | 0.08 (0.10) | 1.59 (1.73) | 4.17 (3.32) | 2.59 (3.49) | 0.29 (0.28) |
| ID | Positions (mm) | Orientations (deg) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anteropos. | Mediolat. | Inferosup. | Coronal | Sagittal | Axial | |
| T01 | 4.53 (1.32) | 2.38 (1.21) | 3.62 (2.56) | 6.17 (6.03) | 2.3 (2.47) | 2.2 (1.63) |
| T02 | 3.84 (1.9) | 3.35 (3.84) | 3.71 (2.47) | 7.73 (6.57) | 1.7 (1.36) | 5.27 (4.24) |
| T03 | 3.47 (2.64) | 4.98 (4.97) | 2.6 (2.99) | 6.39 (4.48) | 1.17 (1.05) | 3.41 (3.92) |
| T04 | 3.78 (3.13) | 6.31 (5.98) | 2.6 (1.71) | 4.56 (4.52) | 1.53 (0.98) | 2.04 (1.04) |
| T05 | 4.21 (3.57) | 7.13 (6.23) | 1.86 (0.9) | 4.87 (2.11) | 1.69 (1.2) | 2.96 (0.63) |
| T06 | 4.94 (4.25) | 7.45 (6.25) | 1.38 (1.17) | 2.53 (1.45) | 2.47 (1.99) | 4.32 (2.0) |
| T07 | 5.55 (3.54) | 7.12 (6.92) | 0.92 (1.45) | 2.03 (1.14) | 2.35 (0.8) | 4.4 (4.34) |
| T08 | 5.24 (2.64) | 7.57 (6.86) | 1.29 (1.03) | 2.14 (2.15) | 2.83 (1.35) | 2.94 (1.33) |
| T09 | 4.39 (2.73) | 9.0 (6.03) | 1.49 (1.43) | 3.65 (3.58) | 1.8 (1.77) | 2.99 (0.43) |
| T10 | 4.22 (3.44) | 10.66 (2.45) | 1.05 (0.95) | 4.59 (6.29) | 1.31 (1.07) | 5.48 (4.8) |
| T11 | 3.32 (4.42) | 12.01 (0.78) | 1.53 (0.82) | 4.19 (4.46) | 1.55 (1.81) | 7.28 (4.04) |
| T12 | 3.26 (2.65) | 12.93 (1.76) | 2.15 (0.37) | 4.39 (4.06) | 3.54 (1.08) | 7.14 (4.02) |
| L01 | 5.42 (5.78) | 14.42 (3.96) | 1.36 (0.76) | 7.69 (11.85) | 8.1 (9.25) | 8.01 (6.84) |
| L02 | 5.19 (5.13) | 13.79 (4.57) | 1.82 (1.19) | 2.98 (2.99) | 4.0 (1.19) | 9.54 (6.36) |
| L03 | 5.39 (5.58) | 11.09 (2.7) | 0.94 (0.33) | 2.9 (3.03) | 1.23 (0.92) | 7.1 (0.32) |
| L04 | 4.04 (3.97) | 6.75 (3.64) | 1.43 (0.19) | 6.05 (7.55) | 3.12 (2.57) | 6.13 (5.55) |
| L05 | 3.78 (3.2) | 7.38 (4.52) | 1.59 (0.92) | 4.76 (3.16) | 2.95 (3.06) | 13.98 (5.02) |
| All | 4.39 (3.13) | 8.49 (5.13) | 1.84 (1.45) | 4.57 (4.53) | 2.57 (2.77) | 5.60 (4.38) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Comte, N.; Pujades, S.; Courvoisier, A.; Daniel, O.; Franco, J.-S.; Faure, F.; Boyer, E. Multi-Modal Data Correspondence for the 4D Analysis of the Spine with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10070874
Comte N, Pujades S, Courvoisier A, Daniel O, Franco J-S, Faure F, Boyer E. Multi-Modal Data Correspondence for the 4D Analysis of the Spine with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(7):874. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10070874
Chicago/Turabian StyleComte, Nicolas, Sergi Pujades, Aurélien Courvoisier, Olivier Daniel, Jean-Sébastien Franco, François Faure, and Edmond Boyer. 2023. "Multi-Modal Data Correspondence for the 4D Analysis of the Spine with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis" Bioengineering 10, no. 7: 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10070874
APA StyleComte, N., Pujades, S., Courvoisier, A., Daniel, O., Franco, J.-S., Faure, F., & Boyer, E. (2023). Multi-Modal Data Correspondence for the 4D Analysis of the Spine with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Bioengineering, 10(7), 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10070874








