Predicting Respiratory Rate from Electrocardiogram and Photoplethysmogram Using a Transformer-Based Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Datasets
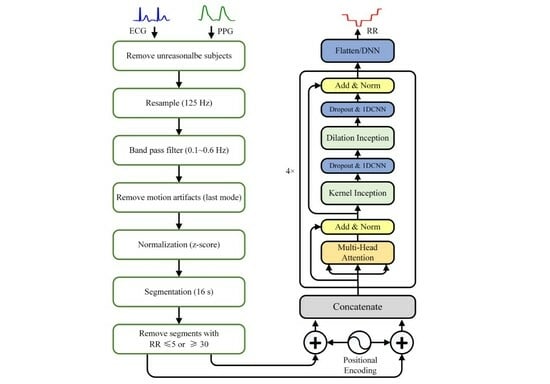
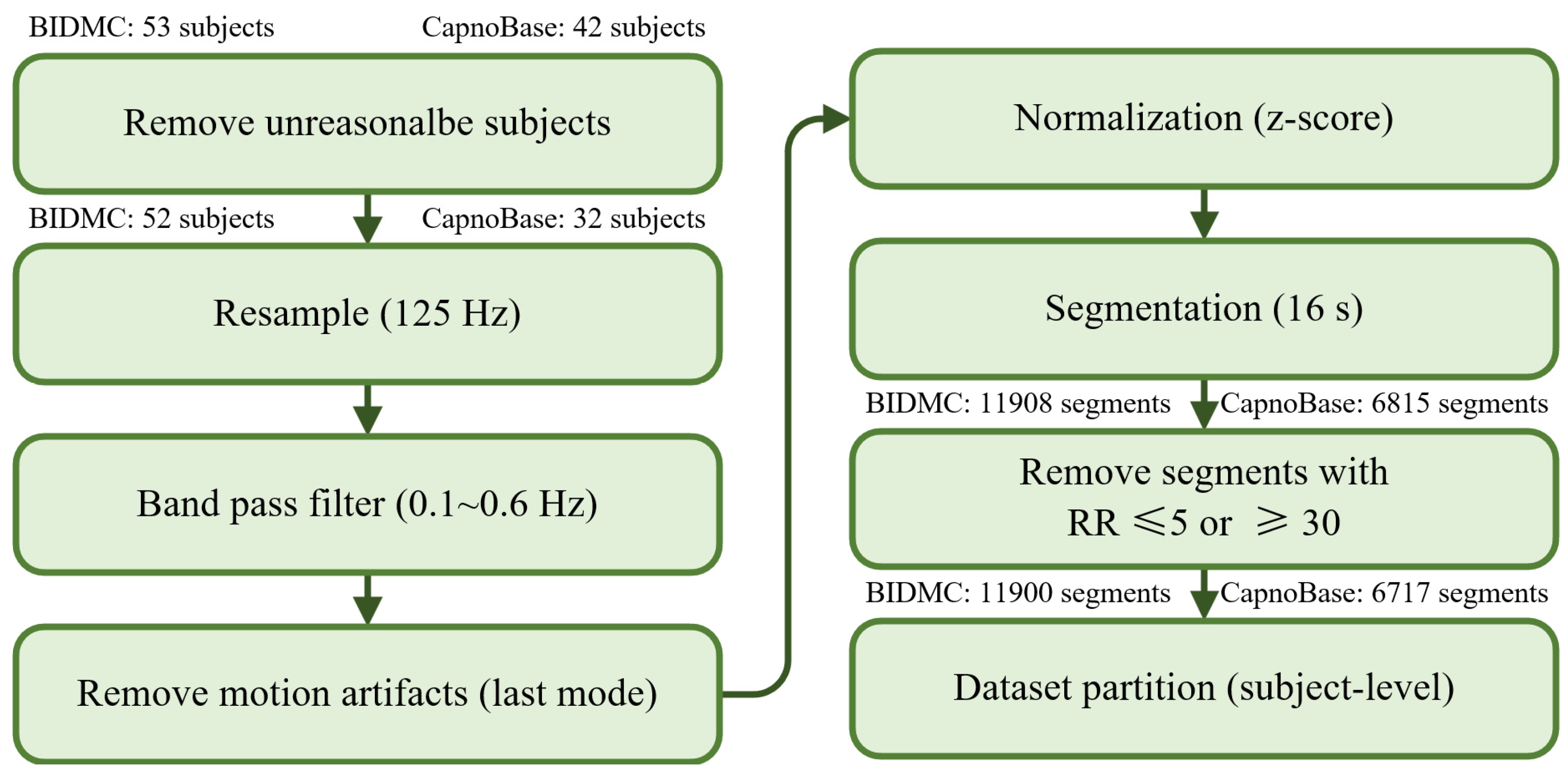
2.2. Data Preprocessing
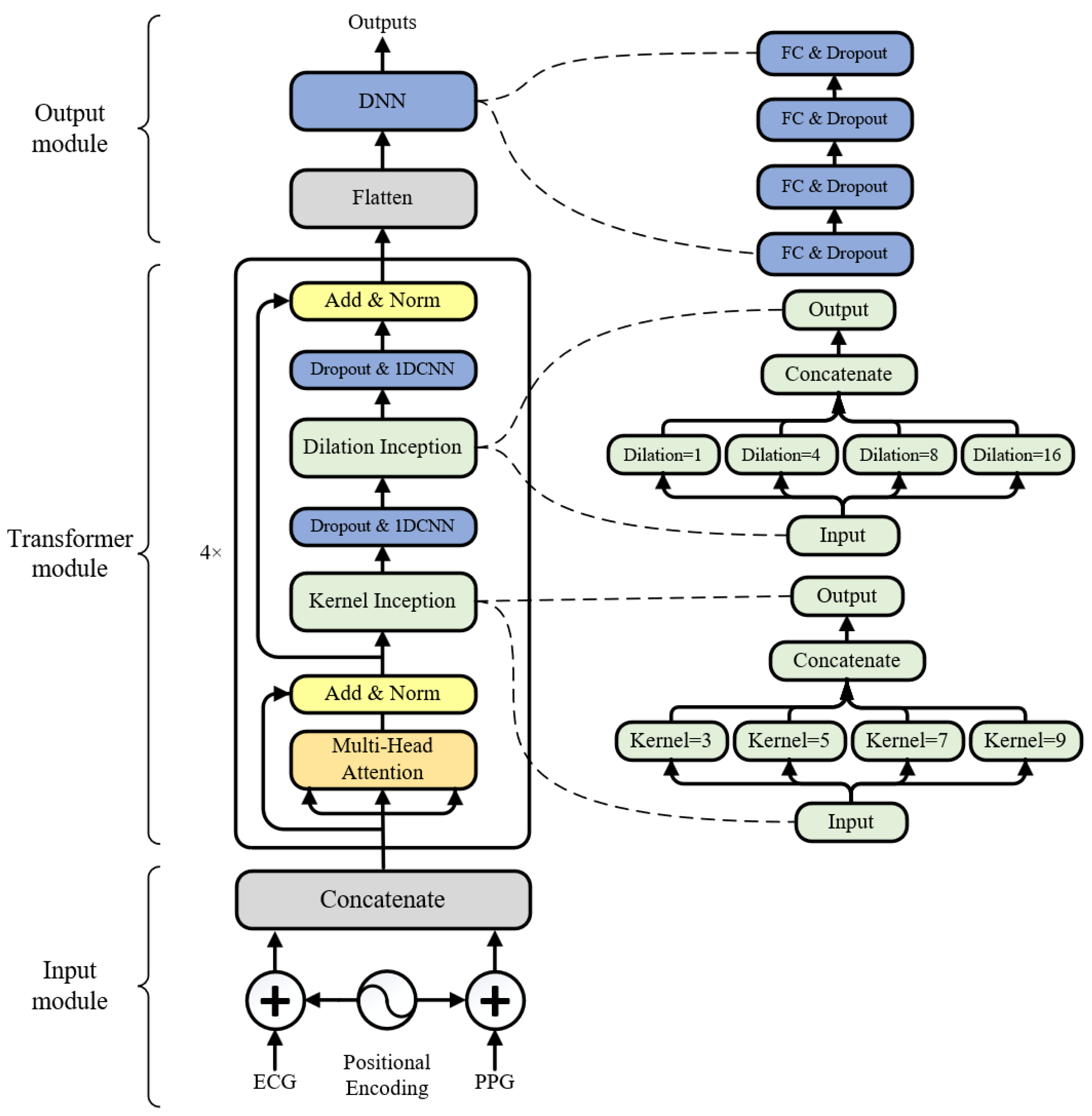
2.3. Model Architecture
2.4. Model Performance Metrics
3. Results
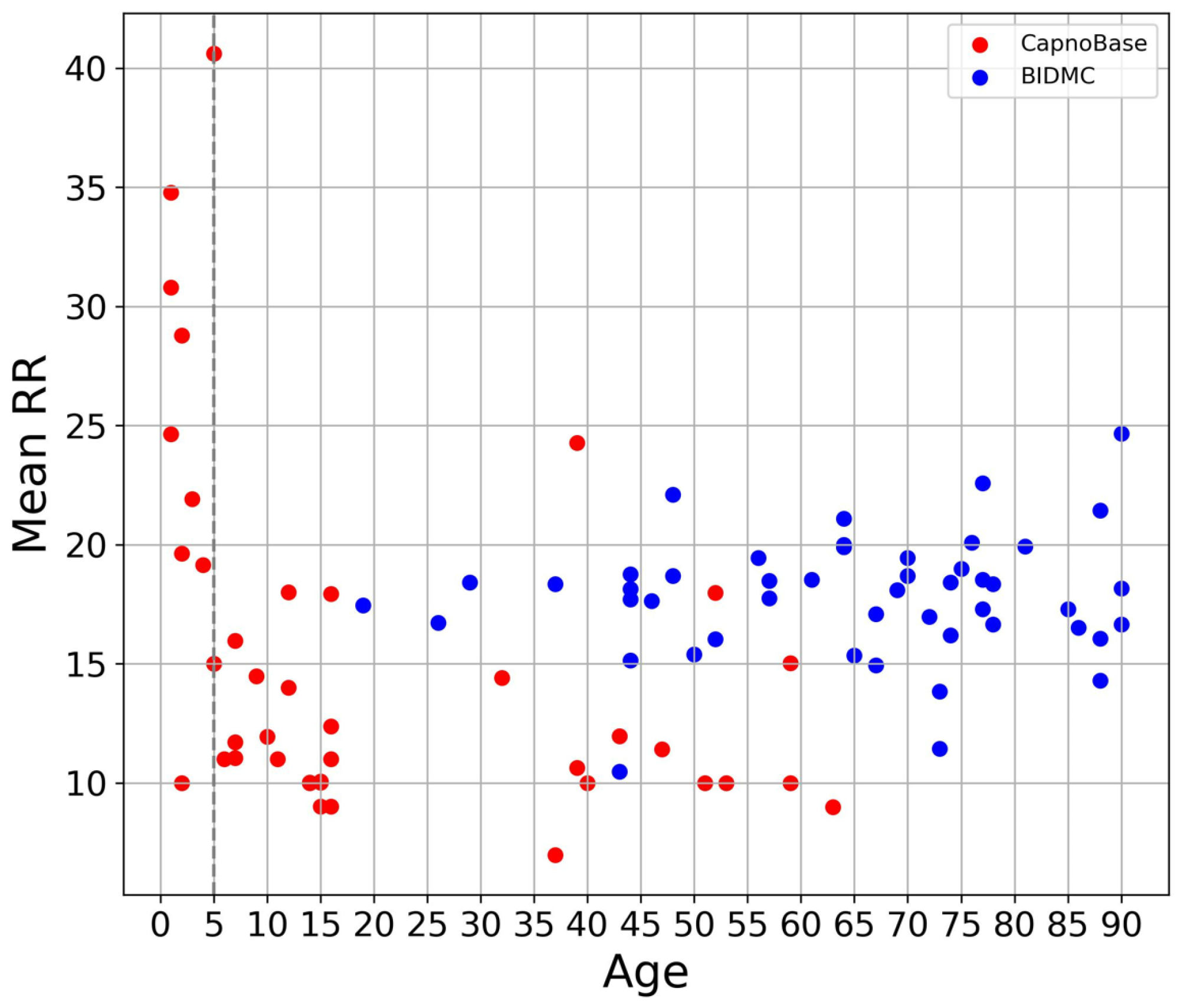
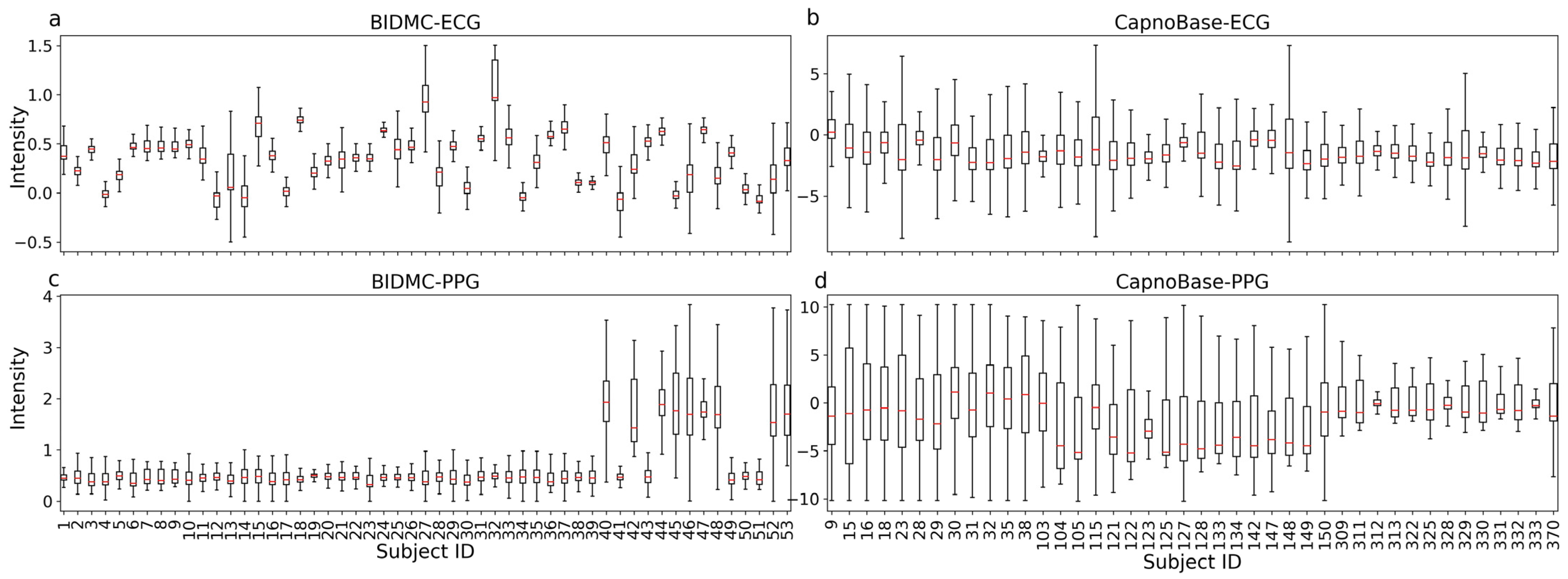
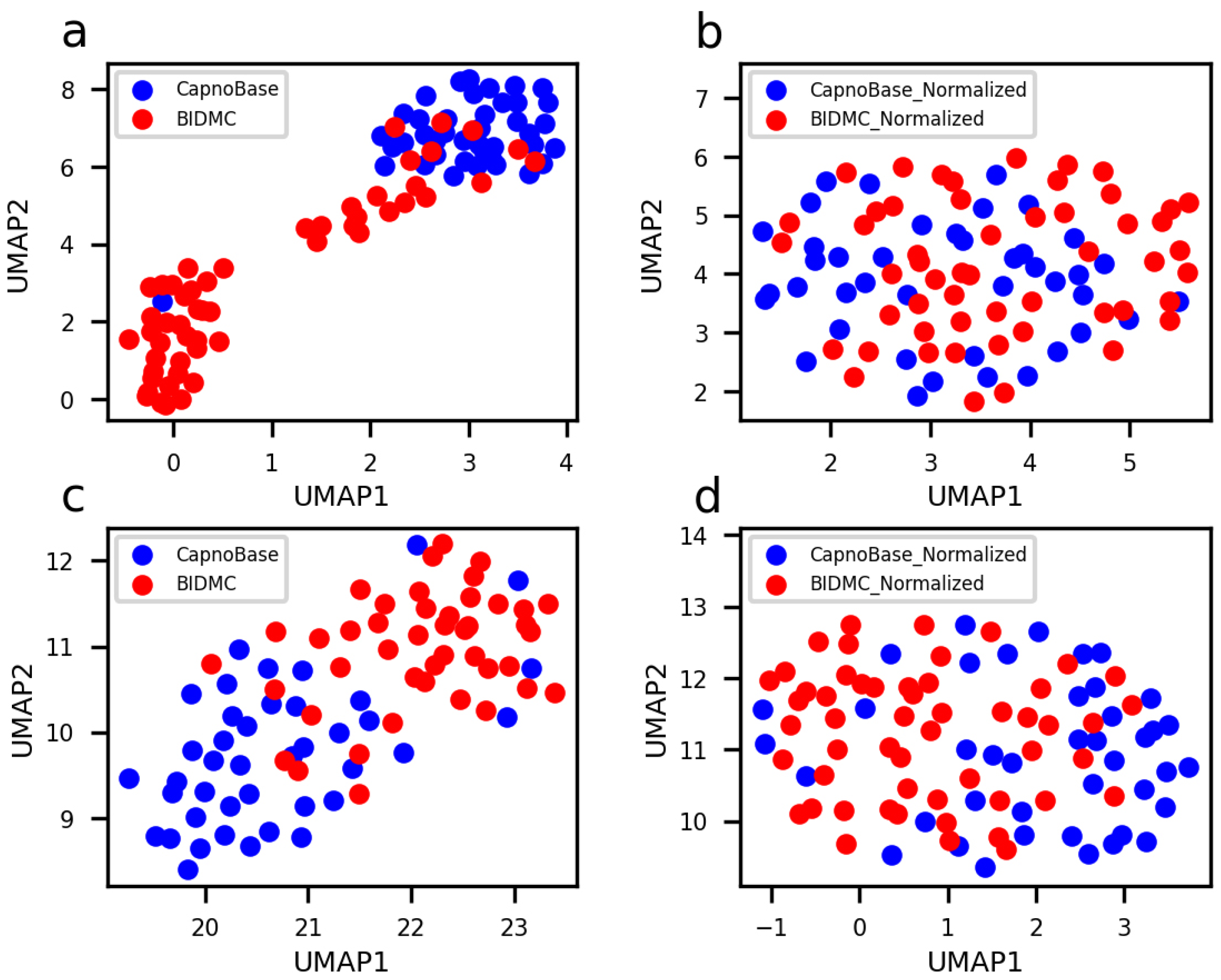
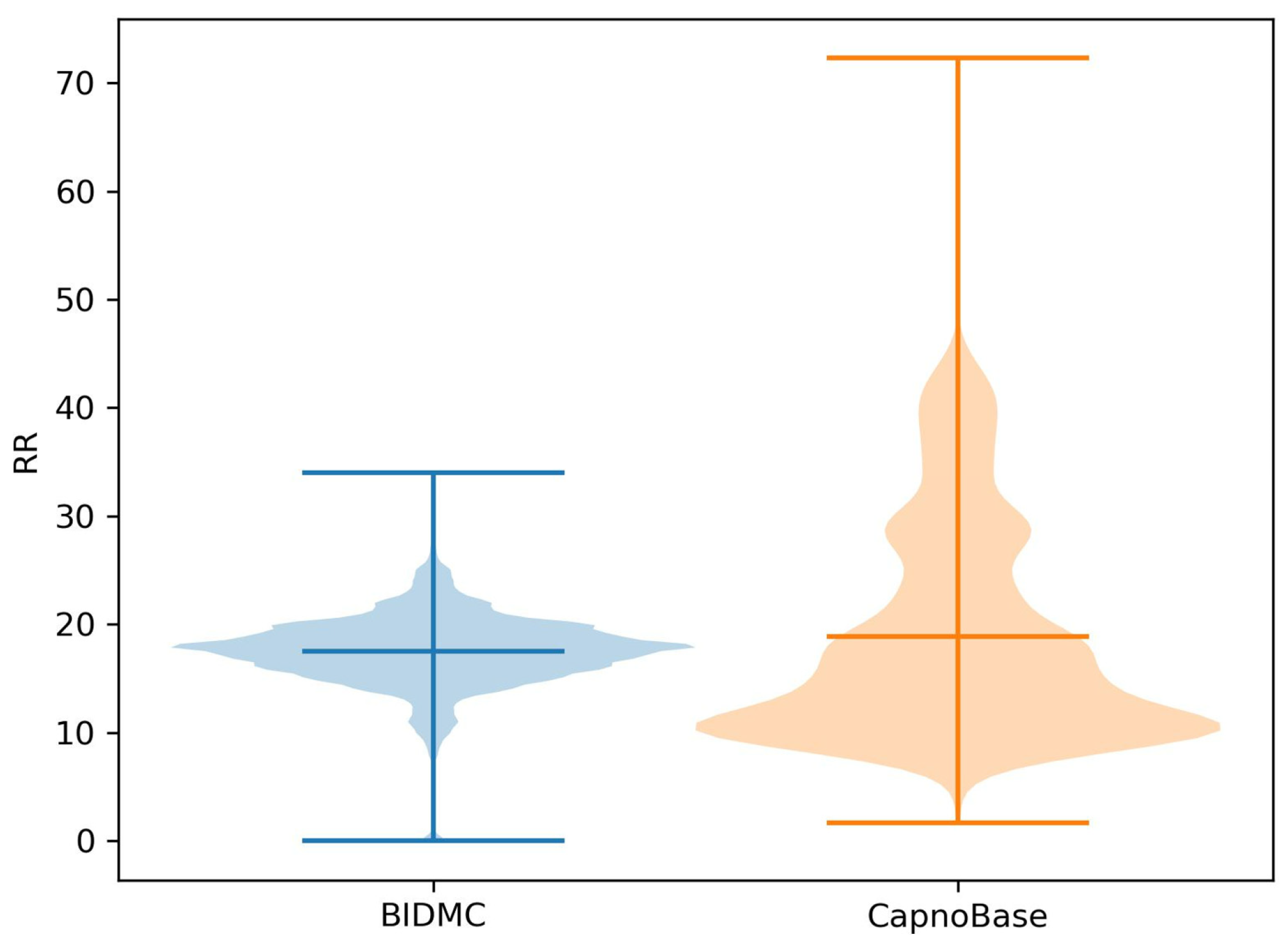
3.1. Overview of Data
3.2. Model Training
3.3. Model Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cretikos, M.A.; Bellomo, R.; Hillman, K.; Chen, J.; Finfer, S.; Flabouris, A. Respiratory Rate: The Neglected Vital Sign. Med. J. Aust. 2008, 188, 657–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fieselmann, J.F.; Hendryx, M.S.; Helms, C.M.; Wakefield, D.S. Respiratory Rate Predicts Cardiopulmonary Arrest for Internal Medicine Inpatients. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 1993, 8, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldhaber, S.Z.; Visani, L.; De Rosa, M. Acute Pulmonary Embolism: Clinical Outcomes in the International Cooperative Pulmonary Embolism Registry (ICOPER). Lancet 1999, 353, 1386–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schein, R.M.; Hazday, N.; Pena, M.; Ruben, B.H.; Sprung, C.L. Clinical Antecedents to In-Hospital Cardiopulmonary Arrest. Chest 1990, 98, 1388–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.J.; Capodilupo, J.V.; Lastella, M.; Sargent, C.; Roach, G.D.; Lee, V.H.; Capodilupo, E.R. Analyzing Changes in Respiratory Rate to Predict the Risk of COVID-19 Infection. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, T.; Foster, R.; Hao, Y. Detecting Vital Signs with Wearable Wireless Sensors. Sensors 2010, 10, 10837–10862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.W.; Jang, Y.W.; Lee, I.; Shin, S.; Kim, S. Wearable Respiratory Rate Monitoring Using Piezo-Resistive Fabric Sensor. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, Munich, Germany, 7–12 September 2009; Dössel, O., Schlegel, W.C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2009; pp. 282–284. [Google Scholar]
- Orphanidou, C.; Clifton, D.; Khan, S.; Smith, M.; Feldmar, J.; Tarassenko, L. Telemetry-Based Vital Sign Monitoring for Ambulatory Hospital Patients. In Proceedings of the 2009 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Minneapolis, Minnesota, 3–6 September 2009; pp. 4650–4653. [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe, M.B. Infrared Measurement of Carbon Dioxide in the Human Breath: “Breathe-Through” Devices from Tyndall to the Present Day. Anesth. Analg. 2008, 107, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folke, M.; Cernerud, L.; Ekström, M.; Hök, B. Critical Review of Non-Invasive Respiratory Monitoring in Medical Care. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2003, 41, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisner, A.; Clifford, G.; Mark, R. The Physiological Basis of the Electrocardiogram. In Advanced Methods and Tools for ECG Data Analysis; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2006; Volume 1, p. 1:25. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, J. Photoplethysmography and Its Application in Clinical Physiological Measurement. Physiol. Meas. 2007, 28, R1–R39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton, P.H.; Bonnici, T.; Tarassenko, L.; Alastruey, J.; Clifton, D.A.; Beale, R.; Watkinson, P.J. Extraction of Respiratory Signals from the Electrocardiogram and Photoplethysmogram: Technical and Physiological Determinants. Physiol. Meas. 2017, 38, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, D.; Douglas, J.G.; Addison, P.S.; Watson, J.N. Measurement of Respiratory Rate from the Photoplethysmogram in Chest Clinic Patients. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2007, 21, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, L.G.; Ugnell, H.; Oberg, P.A. Monitoring of Respiratory and Heart Rates Using a Fibre-Optic Sensor. Med Biol. Eng. Comput. 1992, 30, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, G.B.; Mark, R.G.; Zoccola, A.; Mantero, S. Derivation of Respiratory Signals from Multi-Lead ECGs. Comput. Cardiol. 1985, 12, 113–116. [Google Scholar]
- Charlton, P.H.; Bonnici, T.; Tarassenko, L.; Clifton, D.A.; Beale, R.; Watkinson, P.J. An Assessment of Algorithms to Estimate Respiratory Rate from the Electrocardiogram and Photoplethysmogram. Physiol. Meas. 2016, 37, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, V.; Murugesan, B.; Balakarthikeyan, V.; Ram, K.; Preejith, S.P.; Joseph, J.; Sivaprakasam, M. RespNet: A Deep Learning Model for Extraction of Respiration from Photoplethysmogram. In Proceedings of the 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; pp. 5556–5559. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 9351, pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlen, W.; Turner, M.; Cooke, E.; Dumont, G.; Ansermino, J.M. CapnoBase: Signal Database and Tools to Collect, Share and Annotate Respiratory Signals. In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Society for Technology in Anesthesia (STA), San Diego, CA, USA, 17 October 2010. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, M.H.; Shuzan, M.N.I.; Chowdhury, M.E.H.; Reaz, M.B.I.; Mahmud, S.; Al Emadi, N.; Ayari, M.A.; Ali, S.H.M.; Bakar, A.A.A.; Rahman, S.M.; et al. Lightweight End-to-End Deep Learning Solution for Estimating the Respiration Rate from Photoplethysmogram Signal. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.; Xiang, W.; Atkinson, I. Determining Respiratory Rate from Photoplethysmogram and Electrocardiogram Signals Using Respiratory Quality Indices and Neural Networks. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.K.; Ritam, M.; Han, L.; Guo, S.; Chandra, R. Deep Learning for Predicting Respiratory Rate from Biosignals. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 144, 105338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, M.A.F.; Charlton, P.H.; Clifton, D.A. Probabilistic Estimation of Respiratory Rate from Wearable Sensors. In Wearable Electronics Sensors: For Safe and Healthy Living; Mukhopadhyay, S.C., Ed.; Smart Sensors, Measurement and Instrumentation; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 241–262. ISBN 978-3-319-18191-2. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Jin, J.; Chen, X.; Sun, W.; Guo, P. Comparison of Respiratory-Induced Variations in Photoplethysmographic Signals. Physiol. Meas. 2010, 31, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberger, A.L.; Amaral, L.A.; Glass, L.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Ivanov, P.C.; Mark, R.G.; Mietus, J.E.; Moody, G.B.; Peng, C.K.; Stanley, H.E. PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: Components of a New Research Resource for Complex Physiologic Signals. Circulation 2000, 101, E215–E220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Scott, D.J.; Villarroel, M.; Clifford, G.D.; Saeed, M.; Mark, R.G. Open-Access MIMIC-II Database for Intensive Care Research. In Proceedings of the 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; Volume 2011, pp. 8315–8318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuzan, N.I.; Chowdhury, M.H.; Hossain, S.; Chowdhury, M.E.H.; Reaz, M.B.I.; Uddin, M.M.; Khandakar, A.; Mahbub, Z.B.; Ali, S.H. A Novel Non-Invasive Estimation of Respiration Rate From Motion Corrupted Photoplethysmograph Signal Using Machine Learning Model. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 96775–96790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Qiu, X. A Survey of Transformers. AI Open 2022, 3, 111–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayıroğlu, M.İ.; Altay, S. The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Coronary Artery Disease and Atrial Fibrillation. Balk. Med. J. 2023, 40, 151–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the Inception Architecture for Computer Vision. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar]
- McInnes, L.; Healy, J.; Saul, N.; Großberger, L. UMAP: Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection. J. Open Source Softw. 2018, 3, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, D.; Mehta, P.; Selvaraj, N. Respiratory Rate Estimation Using PPG: A Deep Learning Approach. In Proceedings of the 2020 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 July 2020; pp. 5948–5952. [Google Scholar]
| Dataset | BIDMC [28] | CapnoBase [20] |
|---|---|---|
| Number of subjects | 53 | 42 |
| Duration | 8 min | 8 min |
| ECG/PPG sampling rate | 125 Hz | 300 Hz |
| RR sampling rate | 1 Hz | n/a |
| The signal obtaining RR | IP | Capnometry |
| Male to female ratio | 21:32 | n/a |
| Children to adult ratio | 0:53 | 29:13 |
| Age range | 18–88 | 0.8–75.6 |
| Health condition | Critically ill | Selective surgery |
| Metric | Formula | Annotation |
|---|---|---|
| MAE | n is the number of input samples. y and are the reference RR and the predicted RR, respectively. is the mean of all reference RR. and are the standard error of reference RR and predicted RR, respectively. and are the mean and standard error of the differences between y and , respectively. | |
| E | ||
| PCC | ||
| LOA |
| Only BIDMC | Only CapnoBase | BIDMC→ CapnoBase a | CapnoBase→ BIDMC a | CapnoBase + BIDMC b | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | 1.33 | 0.96 | 3.47 | 3.98 | 1.20 |
| E | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.29 | 0.23 | 0.07 |
| PCC | 0.61 | 0.63 | 0.23 | 0.19 | 0.85 |
| LOA | [−3.46,3.71] | [−2.87, 3.11] | [−9.14, 5.99] | [−4.40, 11.13] | [−3.25, 3.97] |
| w/z-Score w/Inceptions | w/o z-Score | w/o Dilated Inception | w/o Kernel Inception | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | 1.20 | 1.49 | 1.77 | 1.91 |
| E | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.12 |
| PCC | 0.85 | 0.78 | 0.68 | 0.67 |
| LOA | [−3.25, 3.97] | [−4.57,4.80] | [−5.12,5.57] | [−6.17,5.47] |
| Model | Year | Model | Input | Output |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RespNet | 2019 | Unet | PPG | RR |
| ResNet | 2020 | ResNet | PPG | RR |
| BiLSTM | 2021 | BiLSTM | The features of PPG and ECG | RR (max-min regulated) |
| BiLSTM + Att | 2022 | BiLSTM + Att | PPG and ECG | RR |
| Convmixer | 2022 | Convmixer | PPG | RR |
| TransRR (Ours) | 2023 | TransRR | PPG and ECG | RR |
| CNN-Based Models | RNN-Based Models | Transformer-Based Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RespNet | ResNet | ConvMixer | BiLSTM | BiLSTM + Att | TransRR (Ours) | |
| MAE | 3.76 | 3.06 | 2.73 | 1.89 | 2.81 | 1.20 |
| E | 0.25 | 0.20 | 0.17 | 0.15 | 0.34 | 0.07 |
| PCC | 0.32 | 0.44 | 0.43 | 0.46 | 0.17 | 0.85 |
| LOA | [−9.61, 8.99] | [−8.32, 7.76] | [−6.92, 6.73] | [−1.85, 3.72] | [−5.04, 5.66] | [−3.25, 3.97] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Q.; Liu, F.; Song, Y.; Fan, X.; Wang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Mao, Q.; Zhao, Z. Predicting Respiratory Rate from Electrocardiogram and Photoplethysmogram Using a Transformer-Based Model. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1024. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10091024
Zhao Q, Liu F, Song Y, Fan X, Wang Y, Yao Y, Mao Q, Zhao Z. Predicting Respiratory Rate from Electrocardiogram and Photoplethysmogram Using a Transformer-Based Model. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(9):1024. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10091024
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Qi, Fang Liu, Yide Song, Xiaoya Fan, Yu Wang, Yudong Yao, Qian Mao, and Zheng Zhao. 2023. "Predicting Respiratory Rate from Electrocardiogram and Photoplethysmogram Using a Transformer-Based Model" Bioengineering 10, no. 9: 1024. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10091024
APA StyleZhao, Q., Liu, F., Song, Y., Fan, X., Wang, Y., Yao, Y., Mao, Q., & Zhao, Z. (2023). Predicting Respiratory Rate from Electrocardiogram and Photoplethysmogram Using a Transformer-Based Model. Bioengineering, 10(9), 1024. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10091024