Comparative Analysis of Plaque Removal and Wear between Electric–Mechanical and Bioelectric Toothbrushes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tested Toothbrushes and the Design of BE Toothbrush
2.2. The Brushing Simulator
2.3. Plaque Culture
2.4. Experiment
2.4.1. Plaque Removal Experiment
2.4.2. Wear Experiment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Experiment of Plaque Removal
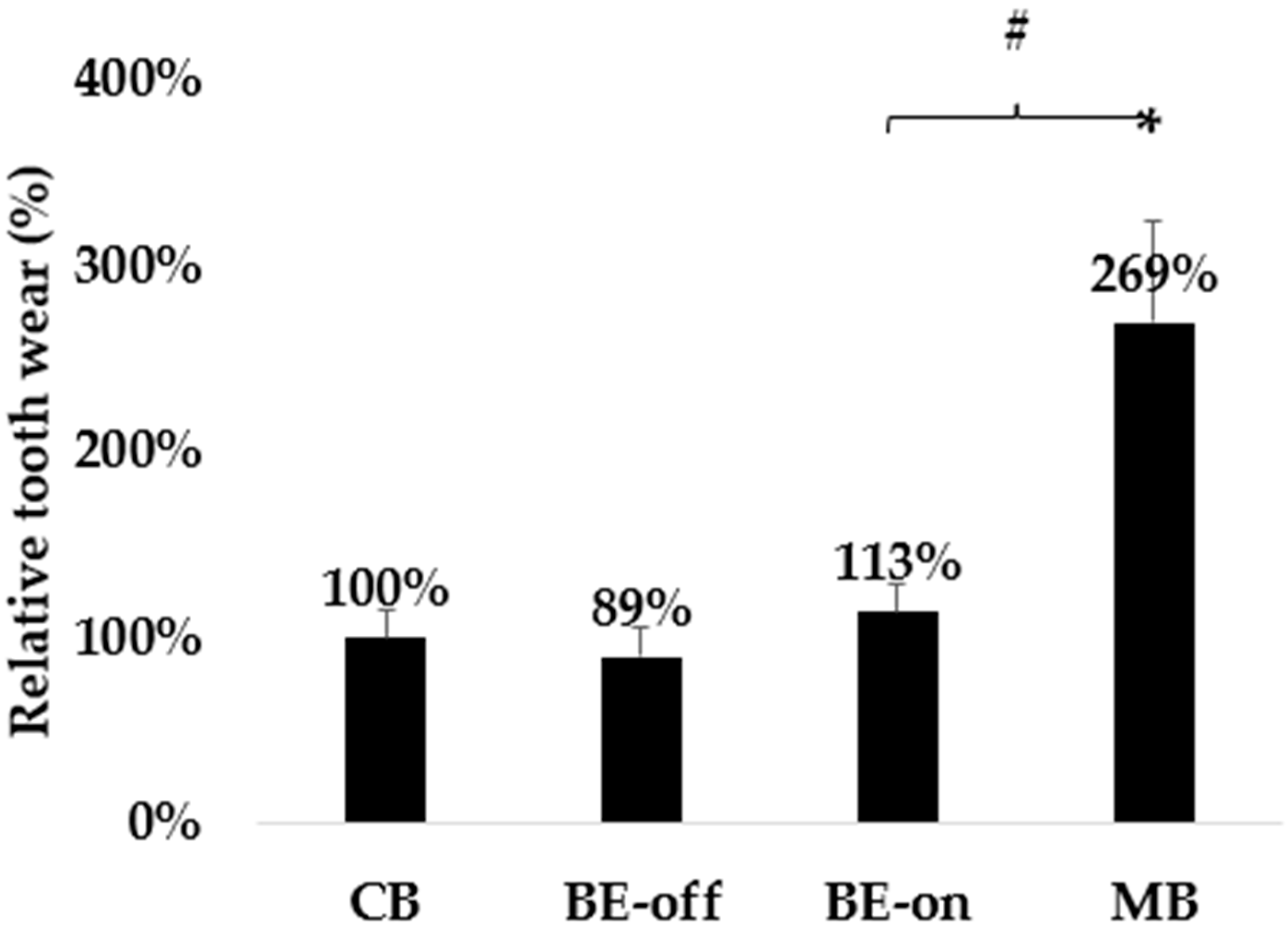
3.2. Experiment with Wear
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vargas, C.M.; Arevalo, O. How dental care can preserve and improve oral health. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 53, 399–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo-Pouso, A.I.; Pérez-Sayáns, M.; Bravo, S.B.; López-Jornet, P.; García-Vence, M.; Alonso-Sampedro, M.; Carballo, J.; García-García, A. Protein-based salivary profiles as novel biomarkers for oral diseases. Dis. Markers 2018, 2018, 6141845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/oral-health#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 8 September 2023).
- Allaker, R.P.; Douglas, C.I. Novel anti-microbial therapies for dental plaque-related diseases. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2009, 33, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, P.D. Dental plaque: Biological significance of a biofilm and community life-style. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2005, 32, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abebe, G.M. Oral biofilm and its impact on oral health, psychological and social interaction. Int. J. Oral Dent. Health 2021, 7, 127. [Google Scholar]
- Alhadainy, H.A.; Keefe, T.; Abdel-Karim, A.H.; Abdulrab, S.; Halboub, E. Association between dental diseases and history of stroke in the United States. Clin. Exp. Dent. Res. 2021, 7, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, D.A.; Ward, A.; Allweiss, P. Diabetes and oral disease: Implications for health professionals. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1255, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotronia, E.; Brown, H.; Papacosta, A.O.; Lennon, L.T.; Weyant, R.J.; Whincup, P.H.; Wannamethee, S.G.; Ramsay, S.E. Oral health and all-cause, cardiovascular disease, and respiratory mortality in older people in the UK and USA. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costerton, J.W.; Stewart, P.S.; Greenberg, E.P. Bacterial biofilms: A common cause of persistent infections. Science 1999, 284, 1318–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daubert, D.M.; Weinstein, B.F. Biofilm as a risk factor in implant treatment. Periodontology 2000 2019, 81, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.W.; Lee, J.; Lee, T.H. Bioelectric effect utilized a healthcare device for effective management of dental biofilms and gingivitis. Med. Eng. Phys. 2022, 104, 103804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hathroubi, S.; Mekni, M.A.; Domenico, P.; Nguyen, D.; Jacques, M. Biofilms: Microbial shelters against antibiotics. Microb. Drug Resist. 2017, 23, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costerton, J.W.; Ellis, B.; Lam, K.; Johnson, F.; Khoury, A.E. Mechanism of electrical enhancement of efficacy of antibiotics in killing biofilm bacteria. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1994, 38, 2803–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.W.; Subramanian, S.; Gerasopoulos, K.; Ben-Yoav, H.; Wu, H.C.; Quan, D.; Carter, K.; Meyer, M.T.; Bentley, W.E.; Ghodssi, R. Effect of electrical energy on the efficacy of biofilm treatment using the bioelectric effect. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2015, 1, 15016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.W.; Meyer, M.T.; Berkovich, A.; Subramanian, S.; Iliadis, A.A.; Bentley, W.E.; Ghodssi, R. A surface acoustic wave biofilm sensor integrated with a treatment method based on the bioelectric effect. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2016, 238, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caubet, R.; Pedarros-Caubet, F.; Chu, M.; Freye, E.; de Belém Rodrigues, M.; Moreau, J.M.; Ellison, W.J. A radio frequency electric current enhances antibiotic efficacy against bacterial biofilms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 4662–4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del Pozo, J.L.; Rouse, M.S.; Mandrekar, J.N.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Patel, R. The electricidal effect: Reduction of staphylococcus and pseudomonas biofilms by prolonged exposure to low-intensity electrical current. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoodley, P.; DeBeer, D.; Lappin-Scott, H.M. Influence of electric fields and pH on biofilm structure as related to the bioelectric effect. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1997, 41, 1876–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.W.; Lee, J.; Han, S.K.; Koo, B.-S.; Park, T.; Park, H.M.; Lee, B. A non-electrolysis bioelectric effect for gingivitis and hygiene contamination biofilm removal. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 3, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.M.; Ryu, S.; Jo, E.; Yoo, S.K.; Kim, Y.W. A study on the biofilm removal efficacy of a bioelectric toothbrush. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.; Tsoi, J.K.H.; Lo, E.C.M.; Matinlinna, J.P. Safety and design aspects of powered toothbrush—A narrative review. Dent. J. 2020, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Weijden, F.; Echeverria, J.J.; Sanz, M.; Lindhe, J. Mechanical supragingival plaque control. Clin. Periodontol. Implant Dent. 2008, 5, 724. [Google Scholar]
- Adam, R. Introducing the Oral-B iO electric toothbrush: Next generation oscillating-rotating technology. Int. Dent. J. 2020, 70, S1–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidovich, E.; Shafir, S.; Shay, B.; Zini, A. Plaque removal by a powered toothbrush versus a manual toothbrush in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatr. Dent. 2020, 4, 280–287. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, Y.; Nicolau, B. Oscillating-rotating electric toothbrushes may have a better effect on gingivitis and plaque control than sonic and manual toothbrushes in adults. J. Evid. Based Dent. Pract. 2021, 21, 101575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizhang, M.; Schmidt, I.; Chun, Y.H.P.; Arnold, W.H.; Zimmer, S. Toothbrush abrasivity in a long-term simulation on human dentin depends on brushing mode and bristle arrangement. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greuling, A.; Emke, J.M.; Eisenburger, M. Abrasion behaviour of different charcoal toothpastes when using electric toothbrushes. Dent. J. 2021, 9, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philpotts, C.J.; Weader, E.; Joiner, A. The measurement in vitro of enamel and dentine wear by toothpastes of different abrasivity. Int. J. Dent. 2005, 55, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olley, R.C.; Sehmi, H. The rise of dentine hypersensitivity and tooth wear in an ageing population. Br. Dent. J. 2017, 223, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borcic, J.; Anic, I.; Urek, M.M.; Ferreri, S. The prevalence of non-carious cervical lesions in permanent dentition. J. Oral Rehabil. 2004, 31, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.M.; Chang, K.H.; Moon, S.H.; Park, B.J.; Yoo, S.K.; Nam, K.C. In vitro delivery efficiencies of nebulizers for different breathing patterns. Biomed. Eng. Online 2021, 20, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Han, J.-S.; Yeo, I.S.L.; Yoon, H.I. Optical and surface properties of monolithic zirconia after simulated toothbrushing. Materials 2019, 12, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledder, R.G.; Latimer, J.; Forbes, S.; Penney, J.L.; Sreenivasan, P.K.; Mcbain, A.J. Visualization and quantification of the oral hygiene effects of brushing, dentifrice use, and brush wear using a tooth brushing stimulator. Front. Public Health 2019, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, K.R.; Bonfante, G.; Pegoraro, L.F.; Conti, P.C.; Oliveira, P.C.; Kaizer, O.B. In vitro wear resistance of three types of polymethyl methacrylate denture teeth. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2008, 16, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Lee, S.G.; Go, S.J.; An, S.; Kim, Y.E.; Kim, Y.I.; Hyun, K.Y.; Cho, D.S.; Choi, G.E. Anti-inflammatory effects of low-frequency stimulator using superposition of alternating microcurrent wave in the animal models. Biomed. Sci. Lett. 2021, 27, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forssten, S.D.; Björklund, M.; Ouwehand, A.C. Streptococcus mutans, caries and simulation models. Nutrients 2010, 2, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO TR 14569-1; Dental Materials-Guidance on Testing of Wear Resistance. Part 1: Wear by Tooth Brushing. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007.
- van Leeuwen, M.P.C.; van der Weijden, F.A.; Slot, D.E.; Rosema, M.A.M. Toothbrush wear in relation to toothbrushing effectiveness. Int. J. Dent. Hyg. 2019, 17, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, J.; Schidtmann, I.; Morawietz, M.; Kiesow, A.; Wehrbein, H.; Sarembe, S.; Erbe, C. In vitro surface analysis of the brushing resistance of orthodontic sealants using two different profilometric evaluation methods. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sripriya, N.; Shaik Hyder Ali, K.H. A comparative study of the efficacy of four different bristle designs of tooth brushes in plaque removal. J. Indian Soc. Pedod. Prev. Dent. 2007, 25, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addy, M.; Jenkins, S.; Newcombe, R. The effect of triclosan, stannous fluoride and chlorhexidine products on: (I) Plaque regrowth over a 4-day period. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1990, 17, 693–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binney, A.; Addy, M.; McKeown, S.; Everatt, L. The effect of a commercially available triclosan-containing toothpaste compared to a sodium-fluoride-containing toothpaste and a chlorhexidine rinse on 4-day plaque regrowth. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1995, 22, 693–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Jang, J.H. The effect of toothbrushing using microcurrent toothbrush on the fluoride concentration on the enamel surface. JTS 2020, 4, 81–91. [Google Scholar]
- Zafar, M.S. Prosthodontic applications of polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA): An Update. Polymers 2020, 12, 2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preis, V.; Hahnel, S.; Behr, M.; Rosentritt, M. Contact wear of artificial denture teeth. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2018, 62, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozdemir, A.; Mas, M.R.; Sahin, S.; Sağlamkaya, U.; Ateşkan, U. Detection of Helicobacter pylori colonization in dental plaques and tongue scrapings of patients with chronic gastritis. Quintessence Int. 2001, 32, 131–134. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Serrano, R.M.; Domínguez-Pérez, R.A.; Ayala-Herrera, J.L.; Luna-Jaramillo, A.E.; De Larrea, G.Z.-L.; Solís-Sainz, J.C.; García-Solís, P.; Loyola-Rodríguez, J.P. Dental plaque microbiota of pet owners and their dogs as a shared source and reservoir of antimicrobial resistance genes. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 21, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essalat, M.; Morrison, D.; Kak, S.; Chang, E.J.; Penso, I.R.; Kulchar, R.J.; Padilla, O.H.M.; Shetty, V. A Naturalistic study of brushing patterns using powered toothbrushes. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0263638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, L.M.; Dawes, C. The surface area of the adult human mouth and thickness of the salivary film covering the teeth and oral mucosa. J. Dent. Res. 1987, 66, 1300–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
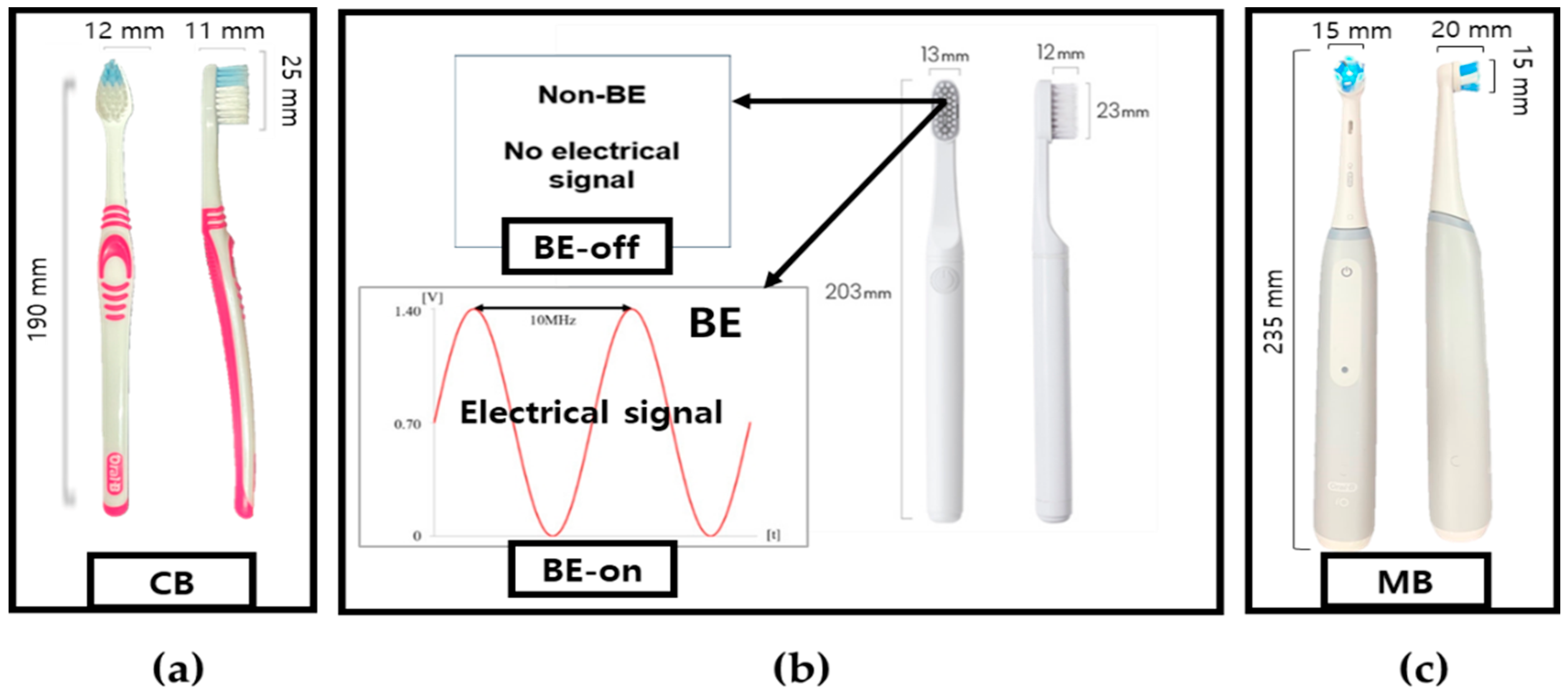





| Toothbrushes | Abbreviations | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Oral-B Ultra-fine, Oral-B Laboratories, Boston, MA, USA | CB | Typical toothbrush |
| Non-bioelectric effect | BE-off | non-BE |
| 0.7 V amplitude of 10 MHz with 0.7 V offset | BE-on | Applied BE |
| Oral-B iO3, Oral-B Laboratories, Boston, MA, USA | MB | Electric–mechanical toothbrush |
| Contents | Details | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Intensity | 0.7 V | Below-water electrolysis 0.82 V |
| Frequency | 10 MHz | Effective frequency |
| Composition (AC:DC) | 1:1 | Effective biofilm treatment |
| Conditions of the Toothbrush | Changes of the PMMA before and after the Surface Friction Wear Experiment (N = 5, Each Condition) |
|---|---|
| CB | 7.46 ± 1.12 μm |
| BE-off | 6.41 ± 1.23 μm |
| BE-on | 8.33 ± 1.18 μm |
| MB | 20.25 ± 4.02 *,# μm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.; Park, H.M.; Kim, Y.W. Comparative Analysis of Plaque Removal and Wear between Electric–Mechanical and Bioelectric Toothbrushes. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11050474
Lee J, Park HM, Kim YW. Comparative Analysis of Plaque Removal and Wear between Electric–Mechanical and Bioelectric Toothbrushes. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(5):474. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11050474
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jihyun, Hyun M. Park, and Young Wook Kim. 2024. "Comparative Analysis of Plaque Removal and Wear between Electric–Mechanical and Bioelectric Toothbrushes" Bioengineering 11, no. 5: 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11050474
APA StyleLee, J., Park, H. M., & Kim, Y. W. (2024). Comparative Analysis of Plaque Removal and Wear between Electric–Mechanical and Bioelectric Toothbrushes. Bioengineering, 11(5), 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11050474






